Journal Description
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
(JTAER) is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of electronic commerce, published monthly online by MDPI (from Volume 16, Issue 3 - 2021).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SSCI (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Business) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Business, Management and Accounting )
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 10.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Hedonic Beats Utilitarian: Differential Effects of AI Chatbots and AR/VR on Consumer Engagement in E-Commerce
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020060 (registering DOI) - 7 Feb 2026
Abstract
This research investigates the impact of augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) and AI-enabled chatbots, both individually and collectively, on consumer engagement of e-commerce platforms. Moreover, this research examines the mediating effects of perceived utility, ease of use, and enjoyment and the moderating effects
[...] Read more.
This research investigates the impact of augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) and AI-enabled chatbots, both individually and collectively, on consumer engagement of e-commerce platforms. Moreover, this research examines the mediating effects of perceived utility, ease of use, and enjoyment and the moderating effects of product type and technology readiness, respectively. By applying the theories of Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Stimulus–Organism–Response (S-O-R), this research proposed this theoretical framework and adopted a mixed-method research method. This research collected its empirical findings from 486 respondents who had utilized chatbots and AR/VR technology on three of China’s most popular e-commerce platforms, including Taobao, JD.com, and Pinduoduo. Structural equation modeling was utilized for hypothesis testing, and semi-structured interviews on 30 participants were used for validation of empirical findings. Results reveal that both AI chatbot features (β = 0.35, p < 0.001) and AR/VR technologies (β = 0.42, p < 0.001) significantly enhance consumer engagement, with AR/VR demonstrating stronger effects. Perceived enjoyment emerged as the strongest mediator (AI: β = 0.14; AR/VR: β = 0.18), surpassing traditional utilitarian factors. Technology readiness significantly moderated these relationships, with high-readiness consumers showing substantially stronger responses (AI: β = 0.45; AR/VR: β = 0.52). Experience goods amplified technology effects compared to search goods. Multi-group analysis revealed platform-specific variations, while robustness checks identified diminishing returns for AI chatbots but not AR/VR technologies. This research contributes to digital marketing and information systems literature by providing empirical evidence of differential technology impacts on engagement, highlighting the dominance of hedonic over utilitarian pathways in consumer technology adoption. The findings offer practical guidance for e-commerce platforms in optimizing technology investments and designing engagement strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Data Science, AI, and e-Commerce Analytics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Explainable Turkish E-Commerce Review Classification Using a Multi-Transformer Fusion Framework and SHAP Analysis
by
Sıla Çetin and Esin Ayşe Zaimoğlu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020059 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The rapid expansion of e-commerce has significantly influenced consumer purchasing behavior, making user reviews a critical source of product-related information. However, the large volume of low-quality and superficial reviews limits the ability to obtain reliable insights. This study aims to classify Turkish e-commerce
[...] Read more.
The rapid expansion of e-commerce has significantly influenced consumer purchasing behavior, making user reviews a critical source of product-related information. However, the large volume of low-quality and superficial reviews limits the ability to obtain reliable insights. This study aims to classify Turkish e-commerce reviews as either useful or useless, thereby highlighting high-quality content to support more informed consumer decisions. A dataset of 15,170 Turkish product reviews collected from major e-commerce platforms was analyzed using traditional machine learning approaches, including Support Vector Machines and Logistic Regression, and transformer-based models such as BERT and RoBERTa. In addition, a novel Multi-Transformer Fusion Framework (MTFF) was proposed by integrating BERT and RoBERTa representations through concatenation, weighted-sum, and attention-based fusion strategies. Experimental results demonstrated that the concatenation-based fusion model achieved the highest performance with an F1-score of 91.75%, outperforming all individual models. Among standalone models, Turkish BERT achieved the best performance (F1: 89.37%), while the BERT + Logistic Regression hybrid approach yielded an F1-score of 88.47%. The findings indicate that multi-transformer architectures substantially enhance classification performance, particularly for agglutinative languages such as Turkish. To improve the interpretability of the proposed framework, SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) was employed to analyze feature contributions and provide transparent explanations for model predictions, revealing that the model primarily relies on experience-oriented and semantically meaningful linguistic cues. The proposed approach can support e-commerce platforms by automatically prioritizing high-quality and informative reviews, thereby improving user experience and decision-making processes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Explaining Inconsistent Privacy Effects: How Cognitive–Affective Inconsistency and Ambivalence Shape Online Information Disclosure
by
Jongtae Yu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020058 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines why privacy concerns do not consistently deter online information disclosure by focusing on internal evaluative dynamics underlying privacy decisions. Drawing on theories of attitudinal ambivalence and cognitive–affective inconsistency, it investigates how internal tensions shape the translation of privacy concerns into
[...] Read more.
This study examines why privacy concerns do not consistently deter online information disclosure by focusing on internal evaluative dynamics underlying privacy decisions. Drawing on theories of attitudinal ambivalence and cognitive–affective inconsistency, it investigates how internal tensions shape the translation of privacy concerns into disclosure behavior. Using two-phase data comprising a survey, the research distinguishes between threat-based and coping-based evaluative conflicts by operationalizing ambivalence and cognitive–affective inconsistency across privacy risks, perceived benefits, self-efficacy, and response efficacy. Results from Phase 1, based on 540 Amazon Mechanical Turk participants, indicate that while privacy concerns generally reduce disclosure intentions, this effect is significantly weakened when individuals experience higher levels of cognitive–affective inconsistency and ambivalence. Although ambivalence significantly reduces the magnitude of inconsistency, it has a limited influence on the moderating role of inconsistency. Phase 2 findings further show that under conditions of high ambivalence, cognitive–affective inconsistency related to self-efficacy exerts a significant effect in situation-specific disclosure contexts. By elucidating the dynamic interplay of the internal tensions, this study clarifies when and why privacy concerns fail to predict disclosure behavior and highlights the importance of incorporating internal evaluative dynamics into models of digital privacy decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electronic Commerce and Information Management Towards the Digital Era)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
From Avatars to Algorithms: Virtual Streamers and AI-Enabled Consumer Behavior in Live Streaming Commerce—A Systematic Review
by
Lingyu Wang, Jasmine A. L. Yeap, Jiaqi Liu and Zongwei Li
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020057 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This review examines existing research on virtual streamers in live streaming commerce and digital marketing, identifying key factors that shape consumer responses. Based on 41 peer-reviewed studies and following PRISMA 2020 guidelines, the analysis applies the CIMCO to synthesize findings through a systematic
[...] Read more.
This review examines existing research on virtual streamers in live streaming commerce and digital marketing, identifying key factors that shape consumer responses. Based on 41 peer-reviewed studies and following PRISMA 2020 guidelines, the analysis applies the CIMCO to synthesize findings through a systematic review. Results highlight three primary mechanisms—trait-based trust, perceived social presence, and message framing—which collectively constitute an integrative model explaining how virtual streamers influence AI-enabled consumer behavior. These elements shape how consumers engage with virtual streamers across platforms and product types. However, current research is limited by geographic concentration, reliance on self-reports, and a lack of longitudinal or behavioral data, which constrains broader applicability. For retailers and platform operators, aligning avatar traits and communication styles with product categories and consumer expectations is crucial for effective digital service delivery. Transparency about whether a streamer is AI or human-operated is also important for maintaining user trust. This review proposes a triadic integration model and offers a foundation for future research on AI-driven marketing influence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Livestreaming and Influencer Marketing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Sword Effect of Electronic Informatization on Income Inequality: E-Commerce and E-Government
by
Zhuocheng Lu and Song Wang
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020056 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Market and government are the main bodies in solving the problem of income inequality, especially as both undergo electronic informatization. This study explores the effect of e-commerce and e-government on regional income inequality, along with its impact mechanisms and spatial characteristics. The results
[...] Read more.
Market and government are the main bodies in solving the problem of income inequality, especially as both undergo electronic informatization. This study explores the effect of e-commerce and e-government on regional income inequality, along with its impact mechanisms and spatial characteristics. The results show a significant “sword effect” impact: e-commerce exacerbates income inequality, while e-government suppresses it. This conclusion remains valid after endogeneity and robustness tests. Mechanistically, e-commerce widens the gap by promoting industrial agglomeration and worsening resource misallocation, while e-government narrows it by enhancing fiscal transparency and alleviating resource misallocation. Spatially, all three variables exhibit spatial correlation and β-convergence; e-commerce and income inequality show α-divergence, while e-government shows α-convergence. E-commerce presents a negative spatial spillover of “aggravating local inequality but suppressing adjacent regional inequality,” while e-government’s inhibitory effect is limited to local cities. Their impacts show significant heterogeneity across regional gradients and geographical locations, providing a basis for differentiated policy implications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digital Intelligence Empowering the Dual Carbon Strategy and E-Commerce)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcending the Paradox of Statistical and Value Rationality: A Tripartite Evolutionary Game Analysis of E-Commerce Algorithmic Involution
by
Yanni Liu, Liming Wang, Bian Chen and Dongsheng Liu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020055 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The unbridled pursuit of statistical rationality has precipitated a crisis of value rationality in e-commerce ecosystems, leading to algorithmic involution—a dilemma characterized by destructive hyper-competition. To reconcile this theoretical paradox and explore effective governance pathways, this paper constructs a tripartite evolutionary game model
[...] Read more.
The unbridled pursuit of statistical rationality has precipitated a crisis of value rationality in e-commerce ecosystems, leading to algorithmic involution—a dilemma characterized by destructive hyper-competition. To reconcile this theoretical paradox and explore effective governance pathways, this paper constructs a tripartite evolutionary game model involving e-commerce platforms, government regulators, and consumers. Simulation results indicate that high-intensity government deterrence constitutes the necessary stability foundation of hard constraints, while consumer activism acts as the decisive accelerator of the soft environment contingent on high synergistic gains and low information screening costs. Furthermore, a platform’s pivot toward “algorithm for good” is not driven by altruism, but by the rational calibration between short-term extractive gains and long-term benevolent returns. Sensitivity analysis confirms that reducing the ratio of these two factors is the effective lever to speed up system convergence. Finally, effective governance requires restructuring this payoff matrix by establishing dynamic penalty mechanisms and transparent low-cost feedback channels to render ethical algorithmic behavior a dominant strategy in terms of economic rationality. This research aims to guide the e-commerce ecosystem from a zero-sum game of involution toward a sustainable equilibrium of multi-party value co-creation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Membership Bundling in Platform Competition: To Bundle Add-Ons Together or Separately?
by
Junmin Zhou and Weijun Zeng
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020054 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Platforms are increasingly adopting membership bundling strategies to strengthen competitiveness. This paper explores how duopoly platforms bundle their membership services (the base products) with those provided by other platforms (add-ons) through a game-theoretic lens. We focus on the competing platforms’ strategic decisions to
[...] Read more.
Platforms are increasingly adopting membership bundling strategies to strengthen competitiveness. This paper explores how duopoly platforms bundle their membership services (the base products) with those provided by other platforms (add-ons) through a game-theoretic lens. We focus on the competing platforms’ strategic decisions to bundle different add-ons together or separately by examining three key determinants: the quality gap between the base products, the quality of versus consumer preference for the add-ons, and the profit-sharing ratio to partners who offer the add-ons. First, with comparable base-good qualities, symmetric bundling emerges in equilibrium. Specifically, simultaneously bundling add-ons together (or separately) dominates when the add-on quality (or the consumers’ preference) mainly drives purchase. Second, significant quality disparity in the base goods leads to asymmetric equilibria: the high-quality platform strategically selects the bundling mode, together or separately, that minimizes the profit-sharing payouts, forcing the low-quality rival to adopt a different strategy. Finally, when the base goods have similar quality, the platform competition can largely yield optimal welfare outcomes. With a significant quality disparity, however, the equilibrium strategies may deviate from social efficiency. Our study advances understanding of platform competition with membership bundling and offers regulatory insights for social planners to strategically intervene in platforms’ membership bundling decisions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of BOPS Cooperation on Advertising and Pricing Decisions in Omnichannel Retailing
by
Jiao Hu, Li Li, Xiang He and Michael Z. F. Li
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020053 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Many retailers start to implement the practice of buy online and pick up in store (BOPS) by integrating their online and offline channels. In this paper, we study the effects of BOPS cooperation (i.e., channel cooperation) in the presence of advertising competition. We
[...] Read more.
Many retailers start to implement the practice of buy online and pick up in store (BOPS) by integrating their online and offline channels. In this paper, we study the effects of BOPS cooperation (i.e., channel cooperation) in the presence of advertising competition. We first investigate how BOPS cooperation affects online and offline retailers’ advertising levels, prices, demands and profits under fixed and optimized pricing strategies and further explore the conditions under which retailers decide to implement BOPS cooperation for greater benefits. Next, we conduct a comparative study of the two pricing strategies before and after BOPS cooperation, examine the impact of different pricing strategies on advertising levels, and assess retailers’ preferences for the two pricing strategies. We also perform numerical examinations to derive insights into when BOPS cooperation is most appropriate and what advertising and pricing strategies are optimal for retailers. The numerical results show that implementing BOPS cooperation is not necessarily optimal for online and offline retailers and that the offline hassle cost, commission level and convenience coefficient in BOPS are the major determinants of retailers’ profitability. We also find that the BOPS convenience coefficient can be a partial compensation for the competitive effect of advertising in the optimized pricing strategy. In addition, we identify conditions under which retailers are better off in different cases. In particular, we find that when BOPS commission is high and offline hassle cost is low, online and offline retailers can benefit more from the optimized pricing strategy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Emerging Topics in Omni-Channel Operations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Green Two-Echelon Vehicle Routing Problem with Specialized Vehicle and Occasional Drivers Joint Delivery
by
Fuqiang Lu, Yu Zhang and Hualing Bi
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020052 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the field of logistics distribution, the two-echelon vehicle routing problem has long been a critical focus. Against the backdrop of global warming, enterprises conducting logistics operations must now prioritize not only delivery costs but also the environmental impact of carbon emissions. To
[...] Read more.
In the field of logistics distribution, the two-echelon vehicle routing problem has long been a critical focus. Against the backdrop of global warming, enterprises conducting logistics operations must now prioritize not only delivery costs but also the environmental impact of carbon emissions. To address these challenges, this study integrates occasional drivers into the two-echelon vehicle routing framework, centering on carbon emission reduction. First, Affinity Propagation (AP) clustering is applied to assign customer points to transfer centers. Subsequently, an optimization model is formulated to minimize both vehicle routing costs and carbon emission costs through a collaborative delivery system involving specialized and crowdsourced vehicles. An enhanced Sparrow–Whale Optimization Algorithm (S-WOA) is proposed to solve the model. The algorithm is tested against traditional heuristic methods on three datasets of different scales. Experimental results demonstrate that the two-echelon logistics and distribution model combining specialized vehicles and occasional drivers achieves a significant reduction in total delivery costs compared to models relying solely on specialized vehicles. Further analysis reveals that, with a fixed crowdsourced compensation coefficient, increasing the crowdsourced detour coefficient leads to a decline in total delivery costs. Conversely, when the detour coefficient remains constant, raising the compensation coefficient results in an upward trend in total costs. These insights provide actionable strategies for optimizing cost-efficiency and sustainability in logistics operations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Elaborate or Succinct? The Impact of AI Chatbots’ Language Style on Customers’ Satisfaction in Online Service
by
Yafeng Fan, Xiaohui Yue, Xiadan Zhang and Luyao Zhang
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020051 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The growing prevalence of AI-powered chatbots in digital service environments has raised user expectations from mere functional efficiency to emotionally satisfying interactions. Drawing on Language Expectancy Theory (LET), this study investigates the impact of AI chatbot language style (namely, elaborate vs. succinct language)
[...] Read more.
The growing prevalence of AI-powered chatbots in digital service environments has raised user expectations from mere functional efficiency to emotionally satisfying interactions. Drawing on Language Expectancy Theory (LET), this study investigates the impact of AI chatbot language style (namely, elaborate vs. succinct language) on customer service satisfaction. Across three studies, we demonstrate that customers exhibit higher satisfaction when interacting with chatbots employing elaborate language as opposed to succinct language. Furthermore, this effect is mediated by warmth and moderated by customer relationship norm orientation. The influence of elaborate language is more pronounced among customers with communal relationship norms, whereas those with exchange relationship norms respond more favorably to succinct language. Theoretically, this study enriches the literature on language style in human–computer interaction by introducing elaborateness as a pivotal communicative dimension. Practically, our results offer strategic guidance that can help service providers and developers to strategically tailor chatbot language styles to distinct customer segments, consequently enhancing service quality, fostering emotional engagement, and cultivating long-term customer loyalty within automated service systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Privacy Awareness Framework (CPAF): Assessing Privacy Awareness of Saudi E-Commerce Users
by
Norah D. Alotaibi, Maysoon Abulkhair and Manal Bayousef
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020050 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid expansion of the Internet, it is crucial to be aware of the different aspects of privacy, especially in light of rising global cybersecurity threats and data breaches. While previous research has identified various factors when studying privacy awareness, these studies
[...] Read more.
With the rapid expansion of the Internet, it is crucial to be aware of the different aspects of privacy, especially in light of rising global cybersecurity threats and data breaches. While previous research has identified various factors when studying privacy awareness, these studies often remain fragmented or examine key factors in isolation from one another, limiting their ability to provide a holistic view. To address this gap, this study proposes the Comprehensive Privacy Awareness Framework (CPAF), which is a theoretically grounded model that conceptualizes privacy awareness across four dimensions: individual, technological, organizational, and social. The framework is empirically validated through a case study of Saudi e-commerce users, a context chosen due to the sector’s rapid digital transformation under Vision 2030 and limited comprehensive privacy research. A CPAF-based survey was administered to 400 active e-commerce users. The quantitative results demonstrate that privacy awareness is a multidimensional construct, where each dimension is significantly associated with the others. Privacy awareness cannot be captured through a single and uniform measure. The findings further reveal notable gaps in users’ knowledge, behaviors, and perceptions of privacy risks, indicating insufficient preparedness when navigating e-commerce environments. These insights highlight the urgent need for targeted awareness initiatives and policy interventions to strengthen user protection and foster responsible digital participation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Customer Experience Regarding AI-Powered Fintech Chatbots in Terms of SOR Theory
by
Selim Çam, Murat Fatih Tuna and Talha Bayır
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020049 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines how the design and interaction features of AI-powered fintech chatbots shape the customer experience of Generation Z users by integrating the Stimulus-Organism-Response framework with dual-process perspectives. Two cross-sectional surveys were conducted in Türkiye. Study 1 (n = 166) examines the
[...] Read more.
This study examines how the design and interaction features of AI-powered fintech chatbots shape the customer experience of Generation Z users by integrating the Stimulus-Organism-Response framework with dual-process perspectives. Two cross-sectional surveys were conducted in Türkiye. Study 1 (n = 166) examines the effect of social presence, interactivity, visual appeal, design originality, and usability on perceived competence and perceived warmth, which, in turn, shape the customer experience. Social presence and design originality significantly increased perceived competence (β = 0.47, p < 0.001), while visual appeal enhanced perceived warmth (β = 0.32, p < 0.001). Together, competence and warmth explained a substantial proportion of customer experience (R2 ≈ 0.60). Usability and interactivity showed no significant effects. Study 2 (n = 195) replicated these findings with trained users and introduced task complexity as a moderator. Under high task complexity, usability and interactivity became significant predictors of competence, which emerged as the primary driver of customer experience, whereas the influence of warmth diminished. Non-normal data distributions justified the use of Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. Overall, the findings suggest a shift from heuristic to systematic processing as fintech tasks become more complex, highlighting the growing importance of competence-based evaluations in fintech chatbot interactions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Artificial Intelligence Applications in Financial Technology, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Platform Participation, Value Co-Creation, and SME Performance: Evidence from the Travel Agency Sector
by
Shenguang Miao and Feifei Yu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020048 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Digital platforms offer cost-effective, accessible tools for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, the mechanisms through which resource-constrained SMEs should participate in these platforms remain underexplored. By distinguishing participation breadth from participation depth and introducing value co-creation and external resource abundance as the
[...] Read more.
Digital platforms offer cost-effective, accessible tools for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, the mechanisms through which resource-constrained SMEs should participate in these platforms remain underexplored. By distinguishing participation breadth from participation depth and introducing value co-creation and external resource abundance as the mediating mechanism and boundary condition, respectively, this study offers an integrated account of how digital platform participation (DPP) relates to SME performance. Drawing on the theory of resource bricolage, this study conducted an online survey of 321 owners or managers, using small and medium-sized travel agencies in China as the empirical setting. This study develops an integrated mediation and moderation model and tests the hypotheses using confirmatory factor analysis, hierarchical regression, and bootstrapping analysis. The results show that both breadth and depth are positively associated with performance, with depth showing a significantly stronger association than breadth. Participation that combines transaction-oriented platforms with information-oriented platforms is associated with the largest performance gains. Value co-creation mediates the effect of depth on performance, whereas the mediation via breadth is not significant. External resource abundance weakens the performance returns to DPP. These findings inform resource-constrained SMEs’ platform strategies, particularly how to allocate scarce attention and resources between deepening and broadening participation and how to configure platform portfolios in relation to performance outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
What Is the Impact of Social Media on Consumer’s Green Response? Consider the Impact of Green Advertising, Online Interpersonal Influence, and Online Celebrity Endorsement
by
Ying Sun, Difei Wu and Haonan He
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020047 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the context of increasingly pressing environmental challenges, promoting green consumption through effective marketing of green products has become a critical focus for corporate operations. In this study, we seek to establish a theoretical framework examining the cognitive outcomes of green advertising and
[...] Read more.
In the context of increasingly pressing environmental challenges, promoting green consumption through effective marketing of green products has become a critical focus for corporate operations. In this study, we seek to establish a theoretical framework examining the cognitive outcomes of green advertising and online interpersonal influence within social media environments and to investigate the moderating roles of online celebrity endorsement and Generation Z within this framework. Based on the Stimulus–Organism–Response model, empirical data collected from 527 survey responses reveal that both green advertising and online social influence positively enhance consumers’ attitudes. These attitudes, in turn, strengthen green purchase intentions, with online celebrity endorsement serving as a significant moderator in this relationship; this moderating effect is amplified among Generation Z consumers. Additionally, purchase intentions exert a positive influence on word-of-mouth intentions. The results of this study provide important insight into the development of green consumption and social media within the Chinese context.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Retrospection on E-Commerce: An Updated Bibliometric Analysis
by
Laura-Diana Radu, Daniela Popescul and Mircea-Radu Georgescu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020046 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Companies need to allocate substantial effort and resources towards adapting to dynamic market trends and promptly meeting their customers’ evolving expectations in the online business context. Although e-commerce research has experienced significant growth over the past two decades, a comprehensive, systematic, and longitudinal
[...] Read more.
Companies need to allocate substantial effort and resources towards adapting to dynamic market trends and promptly meeting their customers’ evolving expectations in the online business context. Although e-commerce research has experienced significant growth over the past two decades, a comprehensive, systematic, and longitudinal analysis that maps the evolution of publications, academic collaboration patterns, influential actors and sources, thematic structures, and theoretical foundations of the field is still lacking. This gap limits a holistic understanding of the maturation, intellectual structure, and future research directions of e-commerce as an academic domain. Based on these premises, the primary objective of the present study is to analyse the landscape of e-commerce spanning the period from 2008 to 2024. By employing bibliometric analysis, we have identified the most prolific and influential authors and publications that have made notable contributions to the literature on e-commerce, as well as the collaborations between authors and countries within the same field. Furthermore, we have analysed the thematic map, research trends, and interconnections between research themes over the past 17 years, providing a dynamic summary of scientific topics of interest in the field of e-commerce and suggesting potential directions for future explorations. The results reveal the heterogeneity of themes associated with e-commerce. We found that research topics in this field have evolved alongside technological evolution and social changes. Some themes have persisted over the years, such as customer behaviour or trust, while others have either disappeared or transformed. For instance, research related to supporting e-commerce technologies has become more specific, focusing on topics such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, machine learning, metaverse or blockchain. From a social perspective, the impact of COVID-19 has resonated within the scientific community, becoming a significant focus of researchers around the world. This study serves as a comprehensive guide for professionals and researchers seeking to bridge current research topics with forthcoming developments in the field of e-commerce. Examining contributions and emerging trends reveals new perspectives on how technological progress interacts with the social and economic dimensions of e-commerce.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electronic Commerce and Information Management Towards the Digital Era)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Disconfirmation Dynamics in Service Recovery: Insights from Online Customer Reviews
by
Woojin Lee and Junsung Park
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020045 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
This paper analyzes the effects of service recovery and the double-deviation phenomenon on customer satisfaction using an analysis of online reviews. With the application of Word2Vec and AFINN sentiment analysis to 4793 Skytrax review comments, this paper bridges the gap between conceptual theories
[...] Read more.
This paper analyzes the effects of service recovery and the double-deviation phenomenon on customer satisfaction using an analysis of online reviews. With the application of Word2Vec and AFINN sentiment analysis to 4793 Skytrax review comments, this paper bridges the gap between conceptual theories about customer behavior and big data analysis. Findings from this research indicate that although overall types of service recovery increase customer satisfaction, explanation is the most preferable yet effective type of recovery. Most importantly, this analysis shows that service recovery disconfirmation has been found to be a highly important moderator. When service efforts involve intangible actions, such as an apology or explanation, that fail to satisfy customers, they tend to perform worse than no recovery at all, thus supporting the double-deviation phenomenon. Compensation, however, has been found to be an efficient type of recovery since its impacts are not reduced much due to service recovery disconfirmation. These insights provide service providers with critical guidance on prioritizing transparent communication and avoiding poorly executed intangible recoveries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Marketing and the Evolving Consumer Experience)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
E-Commerce Platform, Live Streaming or Combinations? Dynamic Decision Analysis of Fresh Agricultural Supply Chain
by
Linlin Zhang and Ni An
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020044 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
The growth of e-commerce live streaming has expanded sales channel options for fresh agricultural suppliers. This study investigates a two-echelon supply chain consisting of a fresh agricultural supplier and downstream retailers. Using differential game theory, we examine the supplier’s preservation technology level and
[...] Read more.
The growth of e-commerce live streaming has expanded sales channel options for fresh agricultural suppliers. This study investigates a two-echelon supply chain consisting of a fresh agricultural supplier and downstream retailers. Using differential game theory, we examine the supplier’s preservation technology level and product greenness, analyzing and comparing equilibrium strategies under three different modes: e-commerce platform sales mode (SP), head streamer sales mode (SH) and ordinary streamer sales mode (SN). The results demonstrate that SP is the dominant strategy when retailers’ marginal profits are low. Conversely, under high marginal profit conditions, the optimal selection depends on streamer cooperation costs: SH is preferred with low head streamer costs; widening cost gaps introduce temporal considerations between SH and SN; further gap expansion makes SN optimal. Furthermore, product greenness is related to supplier’s marginal profit, while the preservation technology level is jointly determined by supplier’s marginal profit and retailers’ inspection costs. Finally, combinations of these modes are also investigated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advances in Supply Chain Management in the Era of Electronic Commerce)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Psychology of BNPL: A Systematic Review of Impulsive Buying and Post-Purchase Regret (2018–2025)
by
Omar Munther Nusir, Che Aniza Che Wel, Siti Ngayesah Ab Hamid, Lamees Al-Zoubi and Ahmad Samed Al-Adwan
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020043 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There is an increasing number of academic and regulatory investigations into the behavioral and psychological implications of using Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services due to their rapid growth. There have been extensive investigations into impulse purchases using BNPL services; however, there has
[...] Read more.
There is an increasing number of academic and regulatory investigations into the behavioral and psychological implications of using Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services due to their rapid growth. There have been extensive investigations into impulse purchases using BNPL services; however, there has been relatively little focus placed upon examining post-purchase regret associated with BNPL service use. The purpose of this paper is to present a systematic review of the extant literature investigating how BNPL service use relates to both impulsive purchasing behavior and post-purchase regret. A total of ten empirical studies were identified through a comprehensive search of the Scopus database according to the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, which were all published between 2018 and 2025. The results indicated that BNPL features, including deferred payments, perceived affordability, and urgency cues, are consistent predictors of both greater impulsive purchasing and lower levels of payment salience. The results of this review, however, reveal that many existing studies have failed to directly measure post-purchase regret and instead rely on proxy indicators, including financial distress, emotional discomfort, and decreased well-being. These findings, therefore, highlight a major theoretical and methodological void in the existing literature. In addition, by providing a synthesis of the current evidence base, this review aims to provide a clearer understanding of how BNPL features influence both consumer decision-making processes and post-purchase emotional responses; additionally, this review highlights the necessity for future research to utilize valid measures of regret, longitudinal designs and ethically informed analytical frameworks when investigating the psychological impacts of adopting BNPL services.
Full article
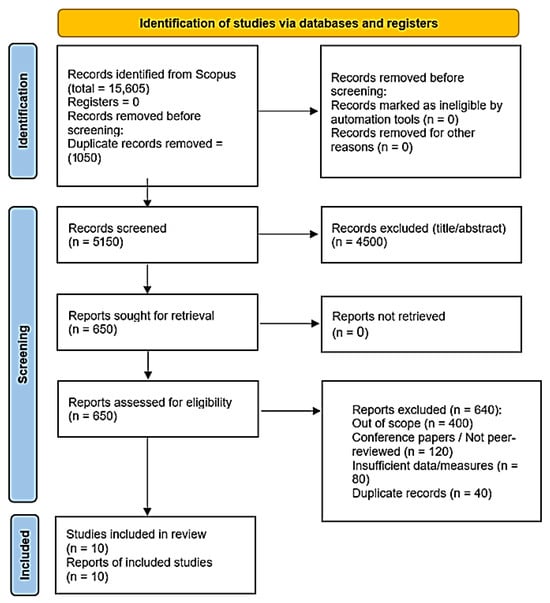
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identifying the Impact of Cross-Border E-Commerce on Urban Entrepreneurship: New Insights from China’s Cross-Border E-Commerce Comprehensive Pilot Zone
by
Xianpu Xu, Yuchen Yan and Jiarui Hu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020042 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
Cross-border e-commerce, as an emerging trade format, offers new chances for optimizing industrial chains’ layout, enhancing economic resilience, and attaining high-quality development at the city level. In this context, treating the execution of the cross-border e-commerce comprehensive pilot zone (CBEC) as a quasi-natural
[...] Read more.
Cross-border e-commerce, as an emerging trade format, offers new chances for optimizing industrial chains’ layout, enhancing economic resilience, and attaining high-quality development at the city level. In this context, treating the execution of the cross-border e-commerce comprehensive pilot zone (CBEC) as a quasi-natural experiment, this study subtly attests to how the CBEC affects urban entrepreneurship by using a difference-in-differences (DID) technique. The results exhibit that the CBEC greatly promotes urban entrepreneurship, which is supported by some robustness tests, including instrumental variable testing and placebo testing. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that in cities with more developed economies, stronger digitalization, richer cultures, sounder law rules, and better business environments, the benefit for the CBEC on entrepreneurship is more significant. Mechanism testing argues that the CBEC promotes urban entrepreneurship through talent aggregation and industrial upgrading. Precisely, the more concentrated high-quality talents are and the more advanced the industrial structure is, the higher the urban entrepreneurship. More importantly, the CBEC exhibits a spatial spillover effect on entrepreneurship, promoting local entrepreneurship while stimulating the motivation to imitate and learn in neighboring areas, thereby driving their entrepreneurship. The findings offer a viable decision-making guide for building a unified factor market and achieving regional coordinated development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Entrepreneurship, Innovation, and Digital Business Models)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Financing Schemes for E-Commerce Closed-Loop Supply Chains with Quality Uncertainty: Balancing Profitability and Environmental Impact
by
Jianhui Chen, Yan Tian, Chuan Pang and Huajun Tang
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2026, 21(2), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer21020041 - 24 Jan 2026
Abstract
The rise of the circular economy and e-commerce has led to the emergence of e-commerce closed-loop supply chains (ECLSCs). In practice, investing in process innovation (PI) is key to improving profitability and competitiveness. However, manufacturers at the downstream of ECLSCs often face financial
[...] Read more.
The rise of the circular economy and e-commerce has led to the emergence of e-commerce closed-loop supply chains (ECLSCs). In practice, investing in process innovation (PI) is key to improving profitability and competitiveness. However, manufacturers at the downstream of ECLSCs often face financial constraints and quality uncertainty of used products, while research on how to select financing strategies under these conditions remains limited. To explore the optimal financing scheme for the ECLSC, this study investigates two financing schemes: bank financing (BF) and FinTech platform financing (FPF), which offers a combination of debt financing (DF) and equity financing (EF). Some key findings are derived. For the ECLSC, the FPF scheme is more profitable when the unit manufacturing cost for new components exceeds the threshold or PI costs are relatively low. Additionally, the FPF performs better when the FPF interest rate is low and the DF ratio is high. The BF is more beneficial when consumer sensitivity to recycling prices or service is low. The FPF enables the ECLSC to achieve maximum profits and minimize environmental impact within a specific range. Furthermore, the financing models are extended to incorporate considerations of fairness, where the optimal financing scheme is primarily influenced by the manufacturing cost.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advances in Supply Chain Management in the Era of Electronic Commerce)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Businesses, Sustainability, JTAER
Digital Marketing Dynamics: From Browsing to Buying
Topic Editors: José Luís Mendes Loureiro Abrantes, Natália de Lima Figueiredo, Bruno Morgado Ferreira, Luís F. MartinezDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
AI, Applied Sciences, Systems, JTAER, Healthcare
Data Science and Intelligent Management
Topic Editors: Dongxiao Gu, Jiantong Zhang, Jia LiDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Administrative Sciences, Businesses, Informatics, JTAER
Innovations in New Media: Shaping the Future of Interactive Marketing
Topic Editors: Chenglu Wang, Hongfei Liu, Morgan Yang, Qing Ye, Yunjia ChiDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Businesses, Economies, Foods, Nutrients, Sustainability, JTAER, Platforms
Consumer Behaviour and Healthy Food Consumption, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel Escobar-Farfán, Elizabeth Emperatriz García-Salirrosas, Ivan Veas-GonzalezDeadline: 15 November 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
JTAER
Emerging Technologies and Marketing Innovation
Guest Editors: Hong Zhao, Zongshui WangDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
JTAER
AI-Based Disruption, Innovations, and New Business Models in E-Commerce: Empirical Research, Case Studies and Current Trends
Guest Editors: Stephan Böhm, Sid Suntrayuth, Müge Klein, Ela Sibel Bayrak MeydanoğluDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
JTAER
Emerging Digital Technologies and Consumer Behavior
Guest Editors: Jashim Khan, Russell Belk, Na ZuoDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
JTAER
Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC) in Electronic Commerce: Innovations, Applications and Implications
Guest Editors: Chih-Hung Wu, Yen-Chun Jim WuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
JTAER
Enhancing Consumer Experience Through Mobile Commerce: Challenges and Opportunities
Collection Editors: Dan-Cristian Dabija, Cristinel Vasiliu, Rebeka-Anna Pop
Topical Collection in
JTAER
The Connected Consumer
Collection Editors: Inma Rodríguez-Ardura, Gisela Ammetller
Topical Collection in
JTAER
Advances in Supply Chain Management in the Era of Electronic Commerce
Collection Editors: Hua Ke, Zhiguo Li, Zhang Zhao
Topical Collection in
JTAER
Utilizing Models for e-Business Decision-Making: From Data to Wisdom
Collection Editors: Mirjana Pejić-Bach, María Teresa Ballestar









