Dynamic Remodeling of Membranes and Their Lipids during Acute Hormone-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
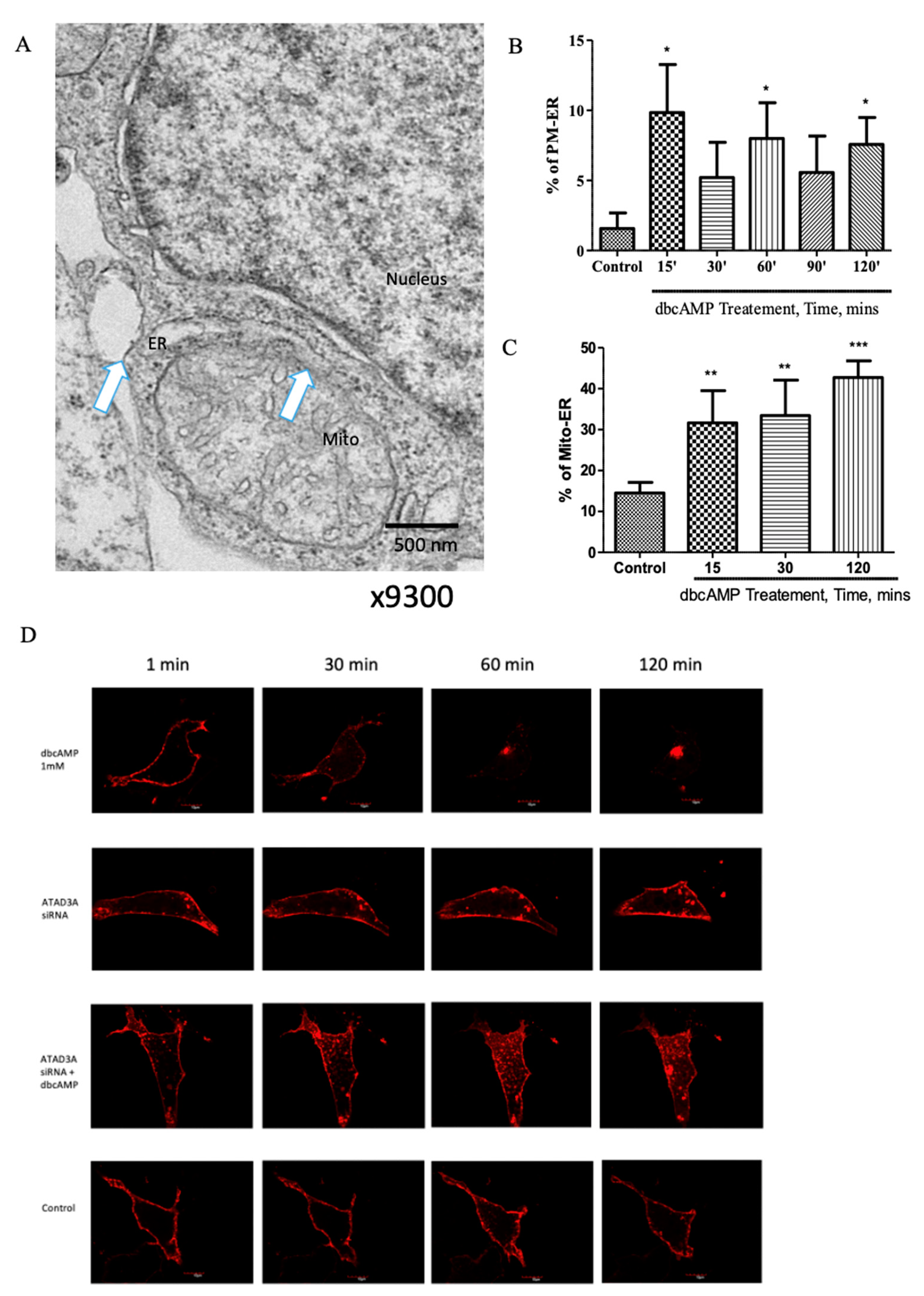
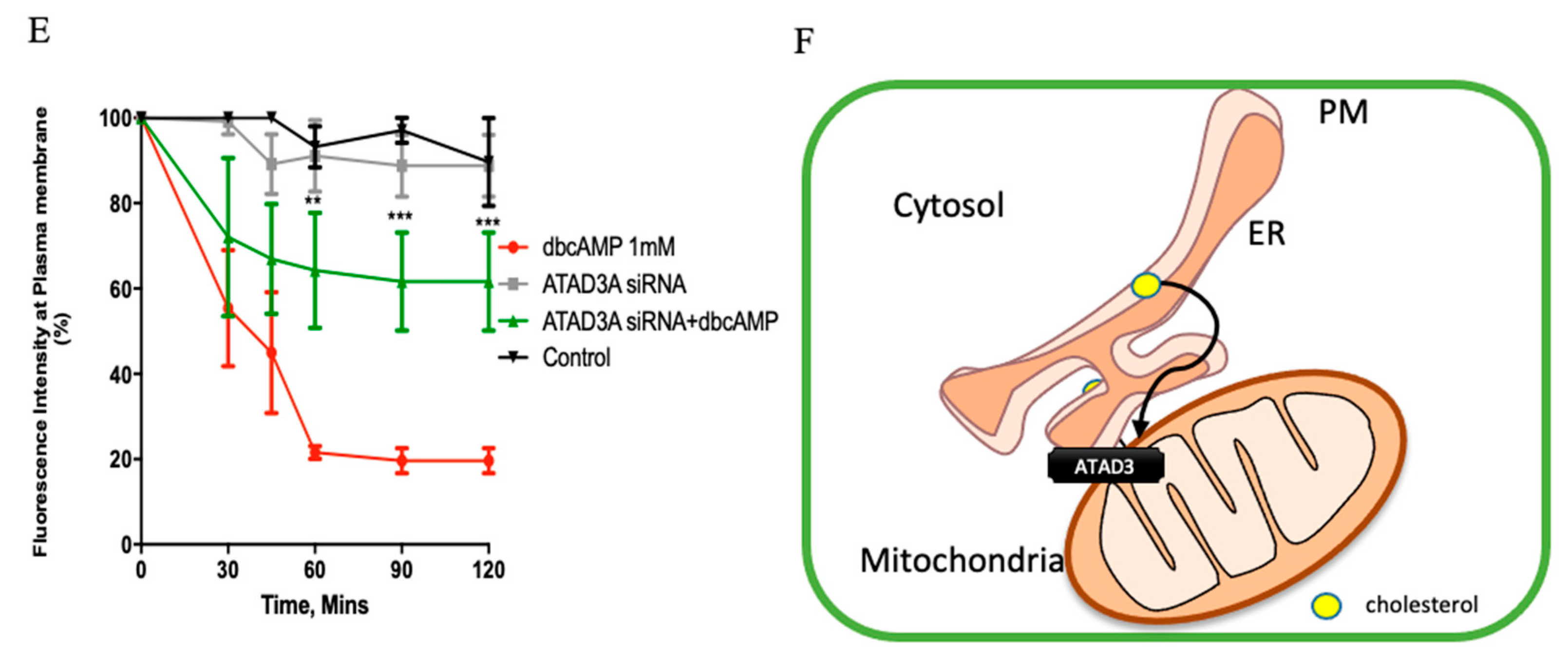
2.1. Plasma Membrane–ER–Mitochondria Communication Increases with Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP Treatment in MA-10 Cells
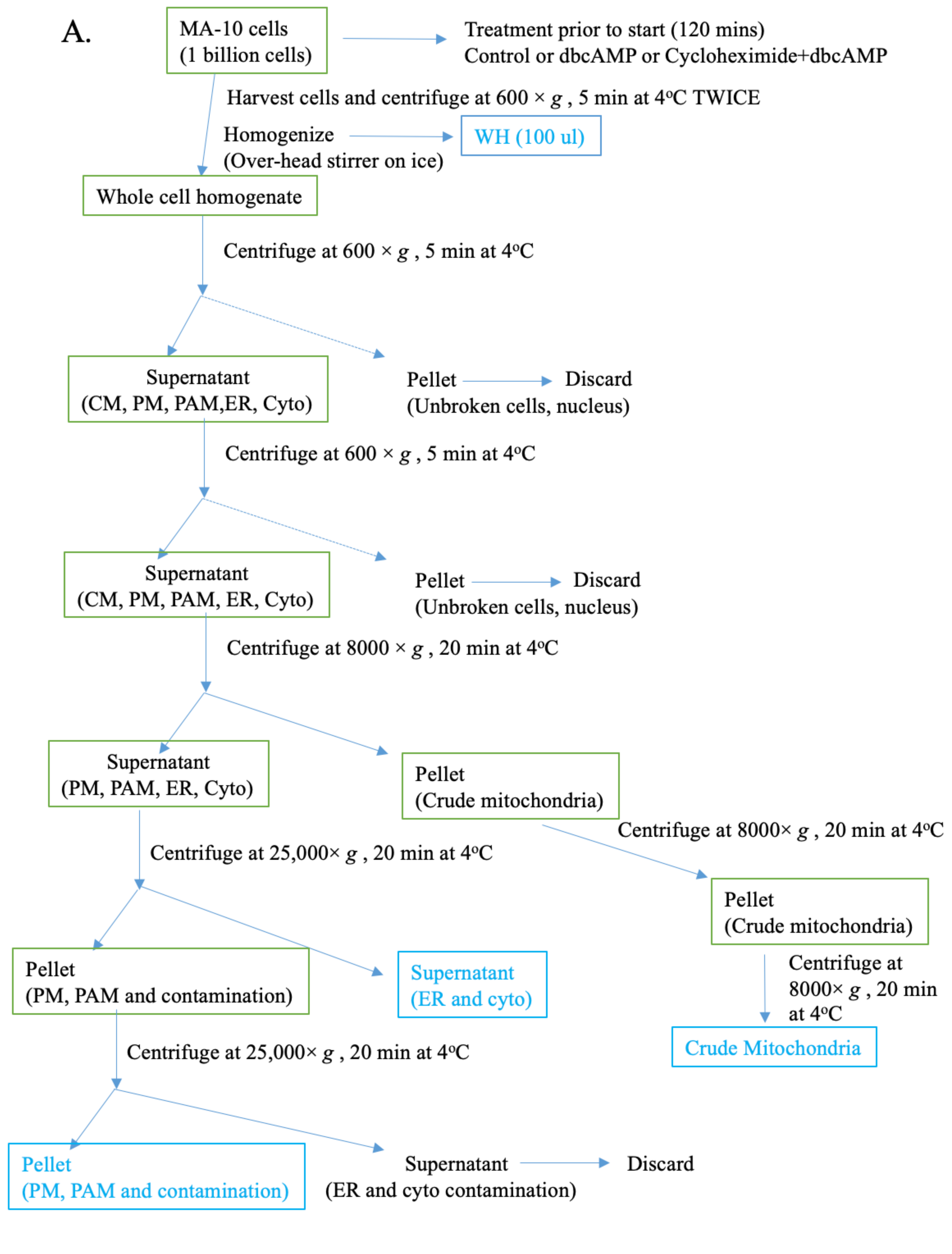
2.2. Isolation and Analysis of Subcellular Fractions in MA-10 Cells
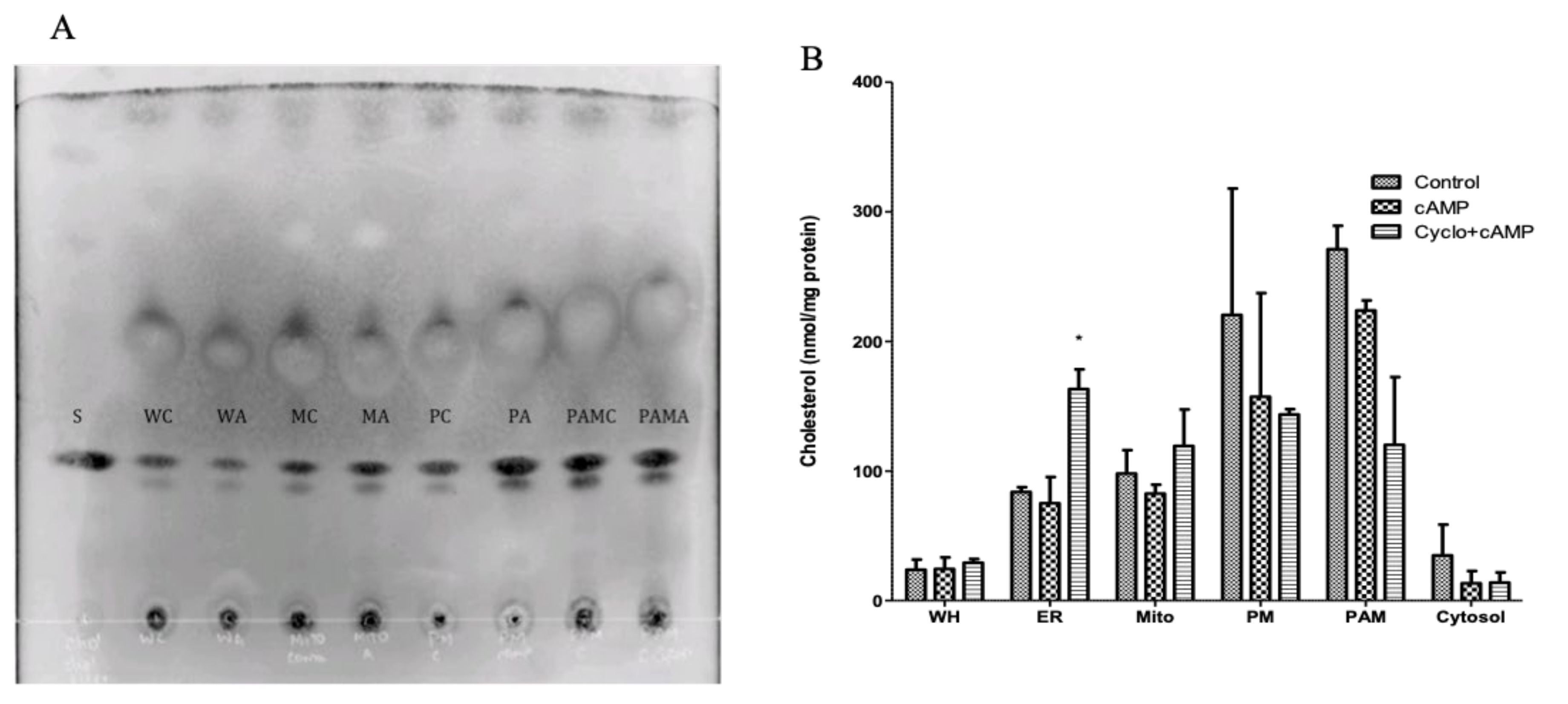
2.3. Cholesterol Composition in Isolated Subcellular Membrane Fractions
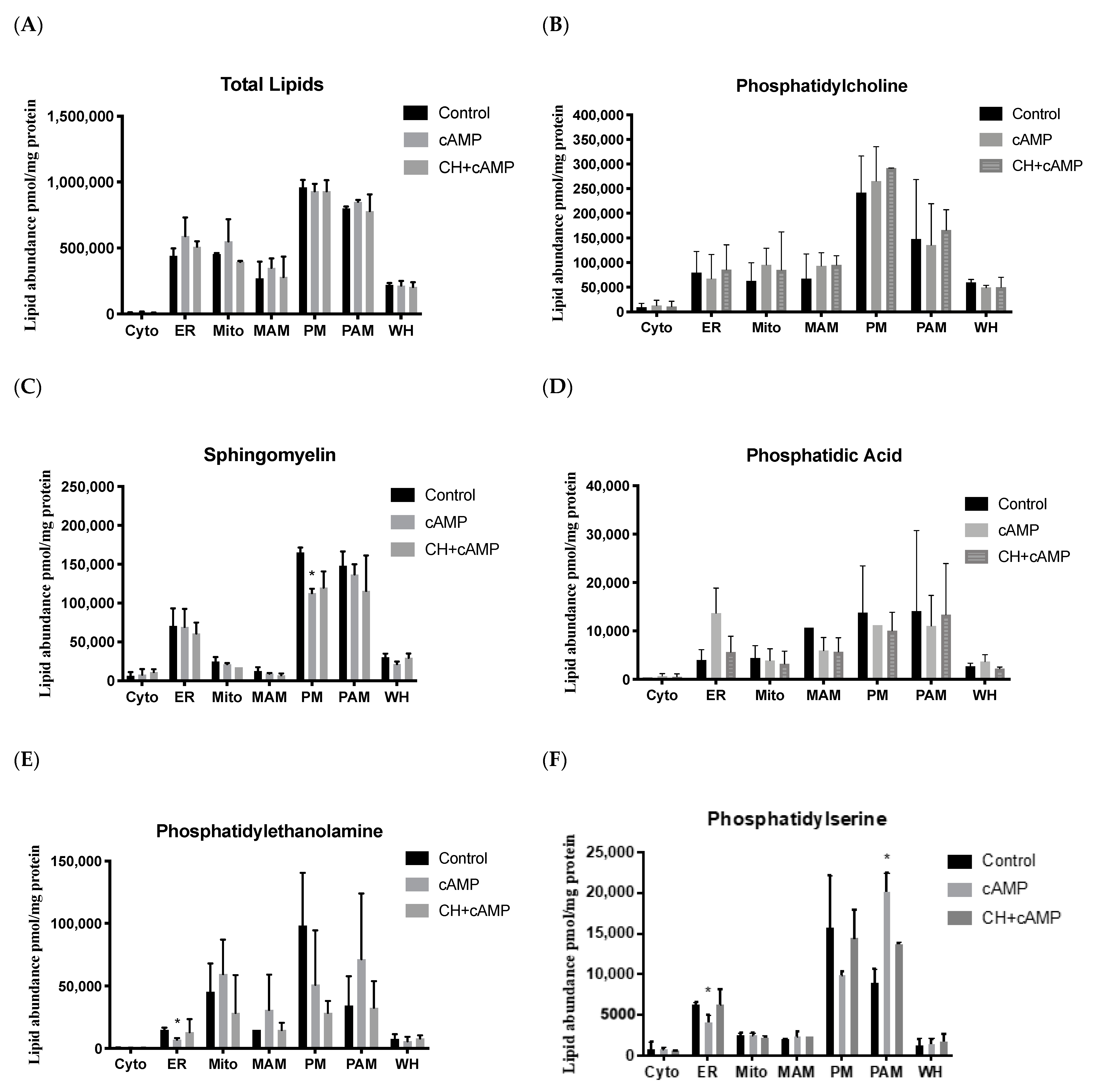
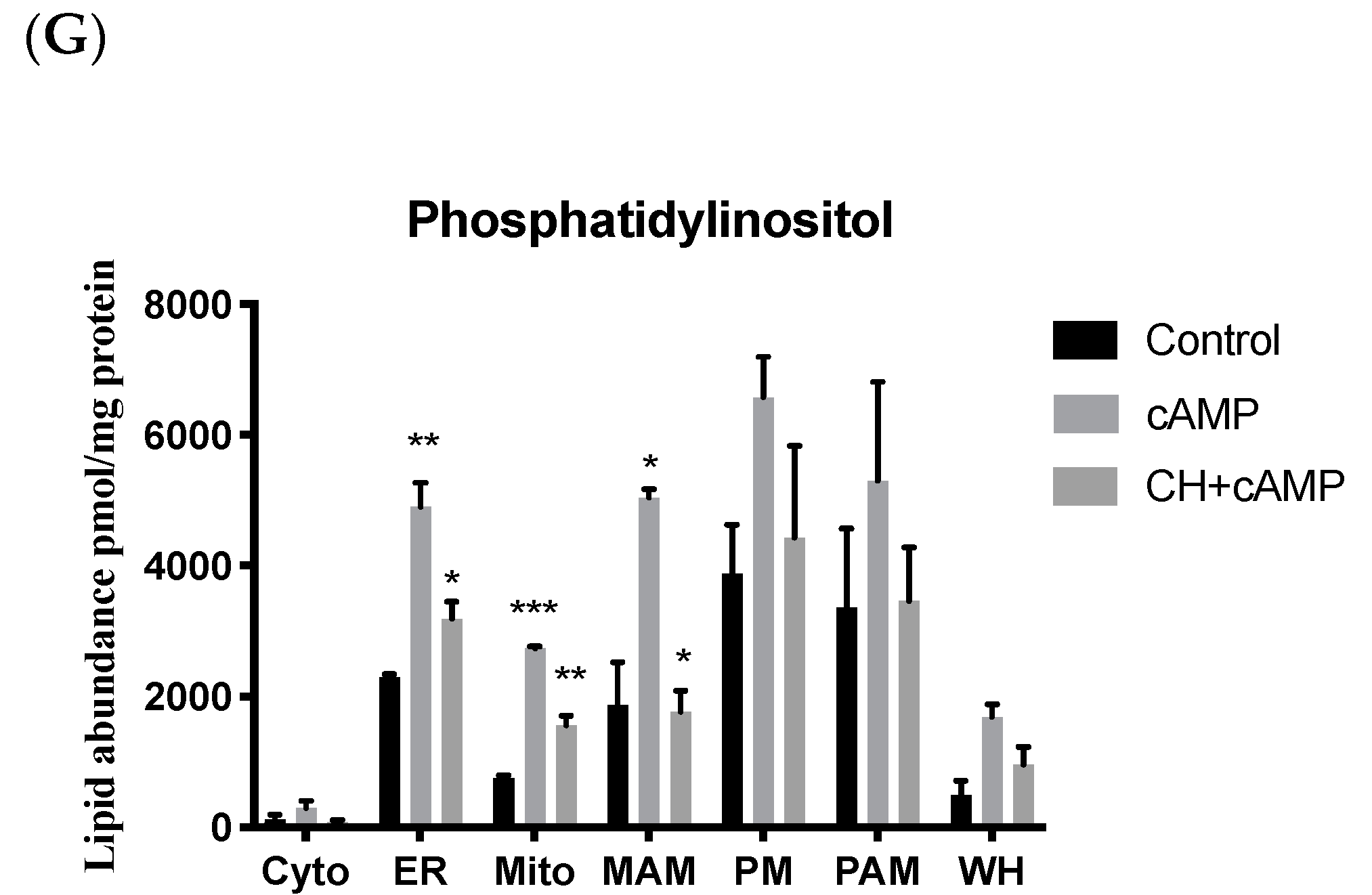
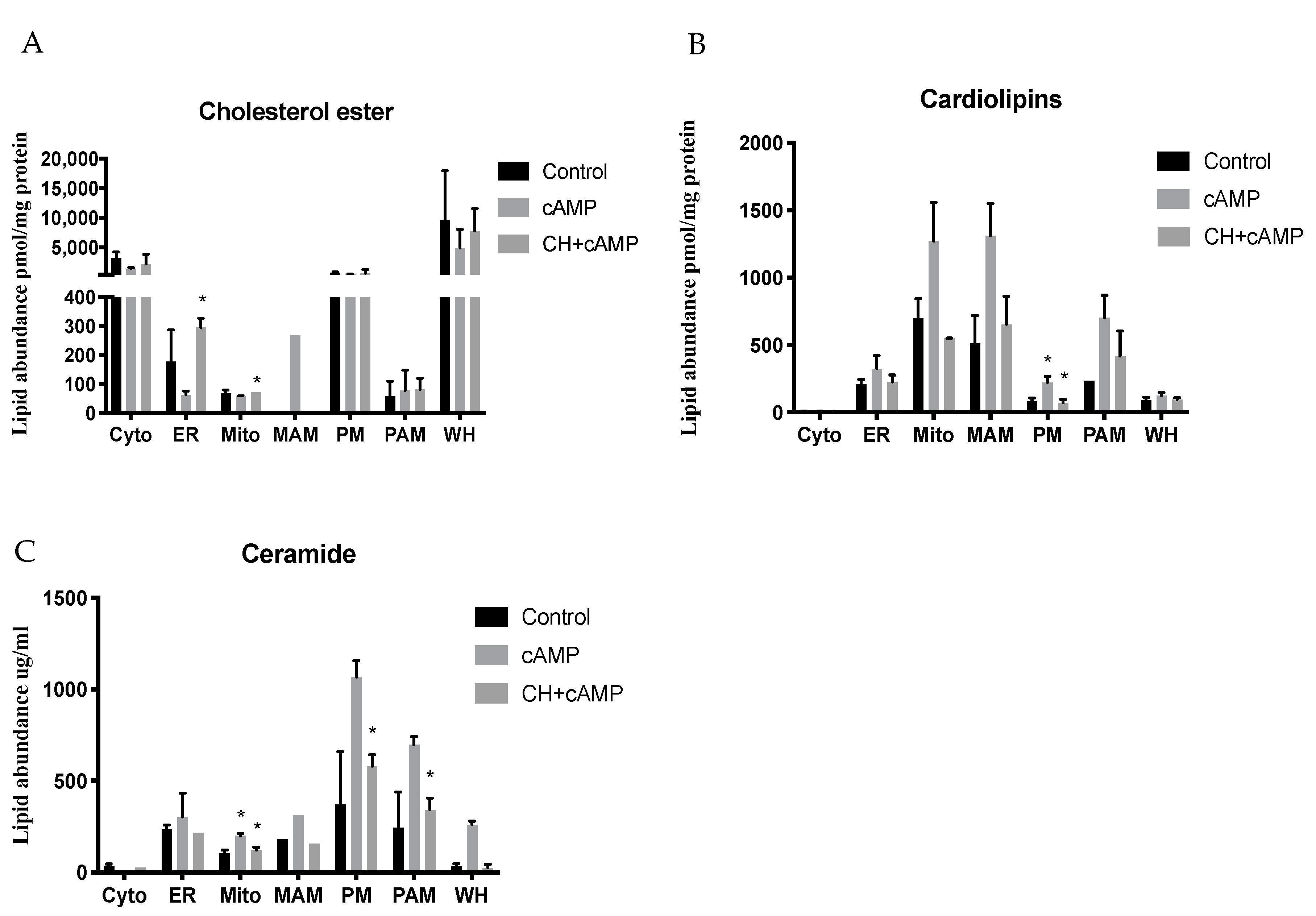
2.4. Analysis of Major Structural Lipids during Steroidogenesis
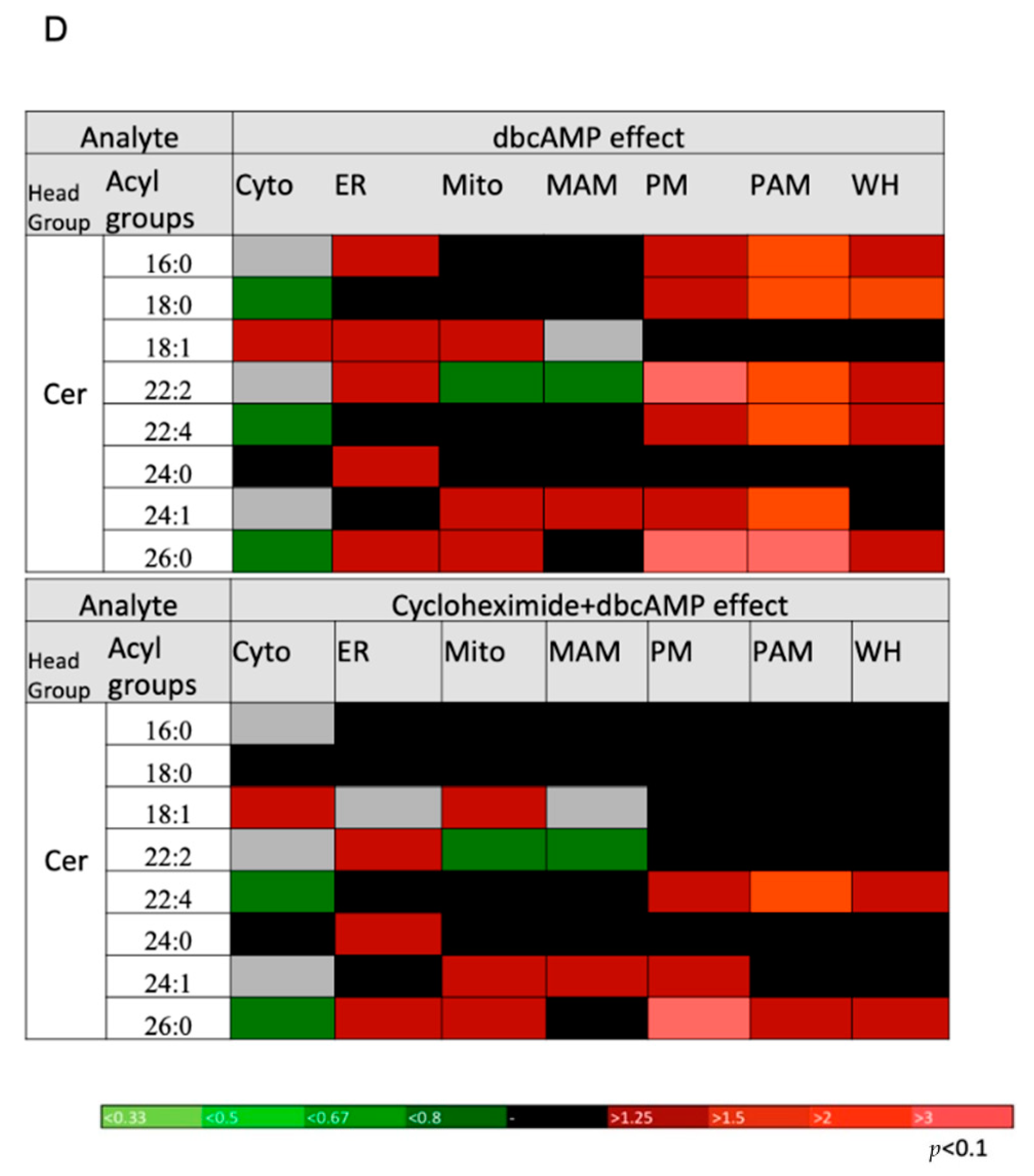
2.5. DbcAMP-Induced Lipidome Remodeling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Small Interfering RNA Transfection and Live Cell Imaging
4.3. Electron Microscopy
4.4. Isolation of Organelles, PAMs, and MAMs
4.5. Lipid Extraction and Thin-Layer Chromatography
4.6. Cholesterol Analysis Using TOF-MS
4.7. Lipidomic Analysis with Hybrid Quadrupole TOF-MS
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| ACSL4 | acyl-coenzyme synthetase long-chain family member 4 |
| APCI | atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization |
| ATAD3A | ATPase family AAA-domain containing protein 3 A |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| cAMP+ CH | dbcAMP with cycloheximide-treated |
| Cer | ceramides |
| CL | cardiolipin |
| COX IV | cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV |
| CTL | control |
| D4 | domain 4 |
| dbcAMP | dibutyryl cyclic-AMP |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| Fdx | ferredoxin |
| FdxR | ferredoxin reductase |
| F12 | Ham’s F-12 Nutrient Mixture |
| HPTLC | high-performance thin-layer liquid chromatography |
| IMM | inner mitochondrial membrane |
| LC–MS | liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy |
| MA-10 | mouse Leydig tumor cells |
| MAM | mitochondria- associated membrane |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| MTBE | methyl tert-butyl ether |
| OMM | outer mitochondrial membrane |
| ORAI1 | ORAI Calcium Release-Activated Calcium Modulator 1 |
| PA | phosphatidic acid |
| PAM | plasma membrane -associated membrane |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PFO | perfringolysin O |
| PI | phosphatidylinositol |
| PM | plasma membrane |
| PMCA1 | PM Ca(2+)-ATPase 1 |
| PS | phosphatidylserine |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR |
| RT | room temperature |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| SREBP | sterol regulatory element-binding protein |
| VDAC1 | voltage-dependent anion channel |
References
- Klose, C.; Surma, M.A.; Simons, K. Organellar lipidomics—Background and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, V.; Liu, J.; Culty, M. Is there a mitochondrial signaling complex facilitating cholesterol import? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 265–266, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.G. Biological membranes: The importance of molecular detail. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.S.; Koeppe, R.E., 2nd. Bilayer thickness and membrane protein function: An energetic perspective. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007, 36, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1666, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rone, M.B.; Midzak, A.S.; Issop, L.; Rammouz, G.; Jagannathan, S.; Fan, J.; Ye, X.; Blonder, J.; Veenstra, T.; Papadopoulos, V. Identification of a dynamic mitochondrial protein complex driving cholesterol import, trafficking, and metabolism to steroid hormones. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1868–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Midzak, A.; Papadopoulos, V. Adrenal Mitochondria and Steroidogenesis: From Individual Proteins to Functional Protein Assemblies. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issop, L.; Fan, J.; Lee, S.; Rone, M.B.; Basu, K.; Mui, J.; Papadopoulos, V. Mitochondria-associated membrane formation in hormone-stimulated Leydig cell steroidogenesis: Role of ATAD3. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Prinz, W.A.; Rapoport, T.A. Weaving the web of ER tubules. Cell 2011, 147, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Cholesterol feedback: From Schoenheimer’s bottle to Scap’s MELADL. J. Lipid. Res. 2009, 50, S15–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E. MAM (mitochondria-associated membranes) in mammalian cells: Lipids and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, D.A. Cyclic AMP mediated modification of cholesterol traffic in Leydig tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 13061–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, L.; Freeman, D.A. Effect of cholesterol transport inhibitors on steroidogenesis and plasma membrane cholesterol transport in cultured MA-10 Leydig tumor cells. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porpaczy, Z.; Tomasek, J.J.; Freeman, D.A. Internalized plasma membrane cholesterol passes through an endosome compartment that is distinct from the acid vesicle-lysosome compartment. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 234, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocze, P.M.; Freeman, D.A. Plasma membrane cholesterol is utilized as steroidogenic substrate in Y-1 mouse adrenal tumor cells and normal sheep adrenal cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1993, 209, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, D.A. Plasma membrane cholesterol: Removal and insertion into the membrane and utilization as substrate for steroidogenesis. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, S.; Martinez-Arguelles, D.B.; Chebbi, S.; Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Papadopoulos, V. Plasma membrane origin of the steroidogenic pool of cholesterol used in hormone-induced acute steroid formation in Leydig cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26109–26125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, B.; Shen, W.-J.; Dong, D.; Azhar, S.; Kraemer, F.B. Plasma membrane cholesterol trafficking in steroidogenesis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, F.; Maronde, E.; Genieser, H.-G.; Jastorff, B. Cyclic nucleotide analogs as biochemical tools and prospective drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 87, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suski, J.M.; Lebiedzinska, M.; Wojtala, A.; Duszynski, J.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P.; Wieckowski, M.R. Isolation of plasma membrane-associated membranes from rat liver. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieckowski, M.R.; Giorgi, C.; Lebiedzinska, M.; Duszynski, J.; Pinton, P. Isolation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondria from animal tissues and cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziel, K.; Lebiedzinska, M.; Szabadkai, G.; Onopiuk, M.; Brutkowski, W.; Wierzbicka, K.; Wilczyński, G.; Pinton, P.; Duszyński, J.; Zabłocki, K.; et al. Plasma membrane associated membranes (PAM) from Jurkat cells contain STIM1 protein is PAM involved in the capacitative calcium entry? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, H.; Gaigg, B.; Hrastnik, C.; Achleitner, G.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Zellnig, G.; Perktold, A.; Daum, G. A subfraction of the yeast endoplasmic reticulum associates with the plasma membrane and has a high capacity to synthesize lipids. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigg, B.; Simbeni, R.; Hrastnik, C.; Paltauf, F.; Daum, G. Characterization of a microsomal subfraction associated with mitochondria of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Involvement in synthesis and import of phospholipids into mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1234, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paolo, G.; De Camilli, P. Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 2006, 443, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farese, R.V.; Am, S.; Sl, V.; Re, L. Are polyphosphoinositides the cycloheximide-sensitive mediator in the steroidogenic actions of adrenocorticotropin and adenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate? J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 5728–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, T.P.; Pittman, R.C. A plasma membrane pool of cholesteryl esters that may mediate the selective uptake of cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1002, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midzak, A.; Papadopoulos, V. Binding domain-driven intracellular trafficking of sterols for synthesis of steroid hormones, bile acids and oxysterols. Traffic 2014, 15, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casares, D.; Escribá, P.V.; Rosselló, C.A. Membrane Lipid Composition: Effect on Membrane and Organelle Structure, Function and Compartmentalization and Therapeutic Avenues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, K.; Lucki, N.C.; Sewer, M.B. Silencing diacylglycerol kinase-theta expression reduces steroid hormone biosynthesis and cholesterol metabolism in human adrenocortical cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwun, C.; Patel, A.; Pletcher, S.; Lyons, B.; Abdelrahim, M.; Nicholson, D.; Morris, E.; Salata, K.; Francis, G.L. Ceramide increases steroid hormone production in MA-10 Leydig cells. Steroids 1999, 64, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, D.R. Genetic and biochemical analysis of non-vesicular lipid traffic. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 827–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Bose, H.S. Early steps in steroidogenesis: Intracellular cholesterol trafficking. J. Lipid. Res. 2011, 52, 2111–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Midzak, A.; Rone, M.; Aghazadeh, Y.; Culty, M.; Papadopoulos, V. Mitochondrial protein import and the genesis of steroidogenic mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 336, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, M. Detergent-resistant microdomains determine the localization of sigma-1 receptors to the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria junction. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Area-Gomez, E.; Rone, M.; Aghazadeh, Y.; Culty, M.; Papadopoulos, V. Upregulated function of mitochondria-associated ER membranes in Alzheimer disease. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4106–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucki, N.C.; Sewer, M.B. Multiple roles for sphingolipids in steroid hormone biosynthesis. Subcell. Biochem. 2008, 49, 387–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, Y.; Onguka, O.; Itoh, K.; Endo, T.; Iijima, M.; Claypool, S.M.; Sesaki, H. Phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis in mitochondria: Phosphatidylserine (PS) trafficking is independent of a PS decarboxylase and intermembrane space proteins UPS1P and UPS2P. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43961–43971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, Y.; Onguka, O.; Hobbs AE, A.; Jensen, R.E.; Iijima, M.; Claypool, S.M.; Sesaki, H. Role for two conserved intermembrane space proteins, Ups1p and Ups2p, [corrected] in intra-mitochondrial phospholipid trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15205–15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7248–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuta, T.; Scharwey, M.; Langer, T. Mitochondrial lipid trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Poetsch, T.; Ju, J.; Eyler, D.E.; Dang, Y.; Bhat, S.; Merrick, W.C.; Green, R.; Shen, B.; Liu, J.O. Inhibition of eukaryotic translation elongation by cycloheximide and lactimidomycin. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, V.L.; Xu, T.; Lambeth, J.D. Cholesterol trafficking in steroidogenic cells. Reversible cycloheximide-dependent accumulation of cholesterol in a pre-steroidogenic pool. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 216, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, B.A.; Janszen, F.H.; Clotscher, W.F.; Van Der Molen, H.J. Effect of protein-synthesis inhibitors on testosterone production in rat testis interstitial tissue and Leydig-cell preparations. Biochem. J. 1975, 150, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramnath, H.I.; Peterson, S.; Michael, A.E.; Stocco, D.M.; Cooke, B.A. Modulation of steroidogenesis by chloride ions in MA-10 mouse tumor Leydig cells: Roles of calcium, protein synthesis, and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyev, A.Y.; Fahy, E.; Guan, Z.; Kelly, S.; Li, X.; McDonald, J.G.; Milne, S.; Myers, D.; Park, H.; Ryan, A.; et al. Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR-4-activated macrophages. J. Lipid. Res. 2010, 51, 2785–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, W.L. StAR search—what we know about how the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein mediates mitochondrial cholesterol import. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoller, L.C.; Malamed, S. Acute effects of ACTH on dissociated adrenocortical cells: Quantitative changes in mitochondria and lipid droplets. Anat. Rec. 1975, 182, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.A.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Carman, G.M. Metabolism and regulation of glycerolipids in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2012, 190, 317–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, C.; Voelker, D.R.; Langer, T. Making heads or tails of phospholipids in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athenstaedt, K.; Daum, G. Phosphatidic acid, a key intermediate in lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liscovitch, M.; Amsterdam, A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates phospholipase D in ovarian granulosa cells. Possible role in signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 11762–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, C.; Tatsuta, T.; König, T.; Haag, M.; Wai, T.; Aaltonen, M.J.; Langer, T. TRIAP1/PRELI complexes prevent apoptosis by mediating intramitochondrial transport of phosphatidic acid. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E. Newly made phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine are preferentially translocated between rat liver mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, D.R. Phosphatidylserine functions as the major precursor of phosphatidylethanolamine in cultured BHK-21 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozbay, T.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Sewer, M.B. ACTH regulates steroidogenic gene expression and cortisol biosynthesis in the human adrenal cortex via sphingolipid metabolism. Endocr. Res. 2004, 30, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porn, M.I.; Tenhunen, J.; Slotte, J.P. Increased steroid hormone secretion in mouse Leydig tumor cells after induction of cholesterol translocation by sphingomyelin degradation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1093, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, S.B.; Pellizzari, E.H.; Cánepa, D.F.; Cigorraga, S.B. Possible involvement of ceramide in the regulation of rat Leydig cell function. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 75, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.; Llanes, L.; Hernandez, I.; Gonzalez-Robayna, I.; Tabraue, C.; Gonzalez-Reyes, J.; Quintana, J.; Estevez, F.; de Galarreta, C.M.R.; Fanjul, L.F. Interleukin-1 beta stimulates sphingomyelin hydrolysis in cultured granulosa cells: Evidence for a regulatory role of ceramide on progesterone and prostaglandin biosynthesis. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 2480–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degnan, B.M.; Bourdelat-Parks, B.; Daniel, A.; Salata, K.; Francis, G.L. Sphingomyelinase inhibits in vitro Leydig cell function. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1996, 26, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawatzki, P.; Kolter, T.; Bittman, R.; London, E. Effect of ceramide N-acyl chain and polar headgroup structure on the properties of ordered lipid domains (lipid rafts). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar]
- FluoView, Version 3.1; Olympus Corporation: Center Valley, PA, USA, 2018.
- Image-Pro Plus, Version 6.3; Media Cybernetics, Inc.: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009.
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prism, Version 5.0; GraphPad Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007.
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MultiQuant™, Version 3.03; SCIEX: Singapore, 2017.
- Simons, B.; Kauhanen, D.; Sylvänne, T.; Tarasov, K.; Duchoslav, E.; Ekroos, K. Shotgun Lipidomics by Sequential Precursor Ion Fragmentation on a Hybrid Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer. Metabolites 2012, 2, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LipidView™, Version 1.1; SCIEX: Singapore, 2017.


| Cytosol | ER | Mito | MAM | PM | PAM | WH | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Categories | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C | Ctl | cAMP | C+C |
| Glycerophospholipids | 42 | 42 | 42 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 173 | 173 | 173 | 172 | 172 | 172 | 164 | 164 | 164 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 183 | 183 | 183 |
| Sphingolipids | 10 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Sterol lipids | 11 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| Ceramides | 5 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Total | 68 | 68 | 68 | 184 | 184 | 184 | 201 | 201 | 201 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 198 | 198 | 198 | 213 | 213 | 213 | 221 | 221 | 221 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venugopal, S.; Galano, M.; Chan, R.; Sanyal, E.; Issop, L.; Lee, S.; Taylor, L.; Kaur, P.; Daly, E.; Papadopoulos, V. Dynamic Remodeling of Membranes and Their Lipids during Acute Hormone-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052554
Venugopal S, Galano M, Chan R, Sanyal E, Issop L, Lee S, Taylor L, Kaur P, Daly E, Papadopoulos V. Dynamic Remodeling of Membranes and Their Lipids during Acute Hormone-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052554
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenugopal, Sathvika, Melanie Galano, Rachel Chan, Esha Sanyal, Leeyah Issop, Sunghoon Lee, Lorne Taylor, Pushwinder Kaur, Edward Daly, and Vassilios Papadopoulos. 2021. "Dynamic Remodeling of Membranes and Their Lipids during Acute Hormone-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052554
APA StyleVenugopal, S., Galano, M., Chan, R., Sanyal, E., Issop, L., Lee, S., Taylor, L., Kaur, P., Daly, E., & Papadopoulos, V. (2021). Dynamic Remodeling of Membranes and Their Lipids during Acute Hormone-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052554







