- Article
Exploring the Activity of a Novel N-Glycosidase (EndoBI-2): Recombinant Production to Release Bioactive Glycans
- Hatice Duman,
- İzzet Avcı and
- Bekir Salih
- + 3 authors
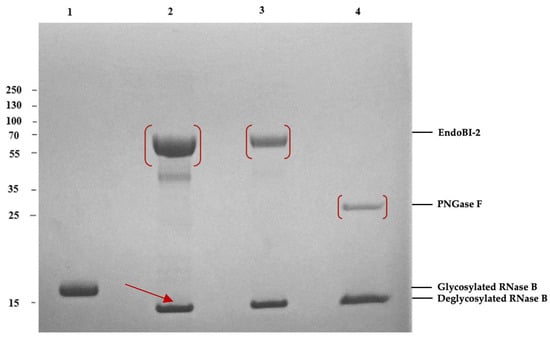
The gut microbiome evolves in response to host development, health state, lifestyle, nutrition, and microbial interactions. The survival of gut microbiota depends on its ability to utilize its host-indigestible complex oligosaccharides. Certain gut microbes produce glycosidases that cleave N-glycoproteins to release N-glycans that are then used as a carbon source. However, commercial glycosidases are inefficient and, thus, require improved deglycosylation strategies to study their functions and scale up their production. Therefore, the main objective of this study was to recombinantly produce and characterize the novel endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase 2 (EndoBI-2) from Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (B. infantis) and to evaluate its enzymatic performance for controlled N-glycan release. Furthermore, the optimum reaction conditions for EndoBI-2 were investigated on model glycoprotein RNAse B using model glycoprotein. The released N-glycans were profiled by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection-quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-FLD-QTOF-MS/MS). We demonstrated that EndoBI-2 possesses a strong temperature tolerance and efficiently cleaves N-glycans under mild reaction conditions, exhibiting high activity at pH 5. These findings highlight EndoBI-2 as a robust and efficient biocatalyst for the production of bioactive N-glycans from diverse N-glycoproteins, with potential applications in glycobiotechnology.
28 December 2025