Combined Iron-Loaded Zeolites and Ozone-Based Process for the Purification of Drinking Water in a Novel Hybrid Reactor: Removal of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fe-Zeolite Characterization
2.1.1. Drinking-Water Quality Analysis in the Selected Areas
2.1.2. Human Health Risk Assessment Model
2.2. Treatment of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic
2.2.1. Treatment of Faecal Coliforms
Comparison between Single Ozonation and O3/Fe-ZA Process
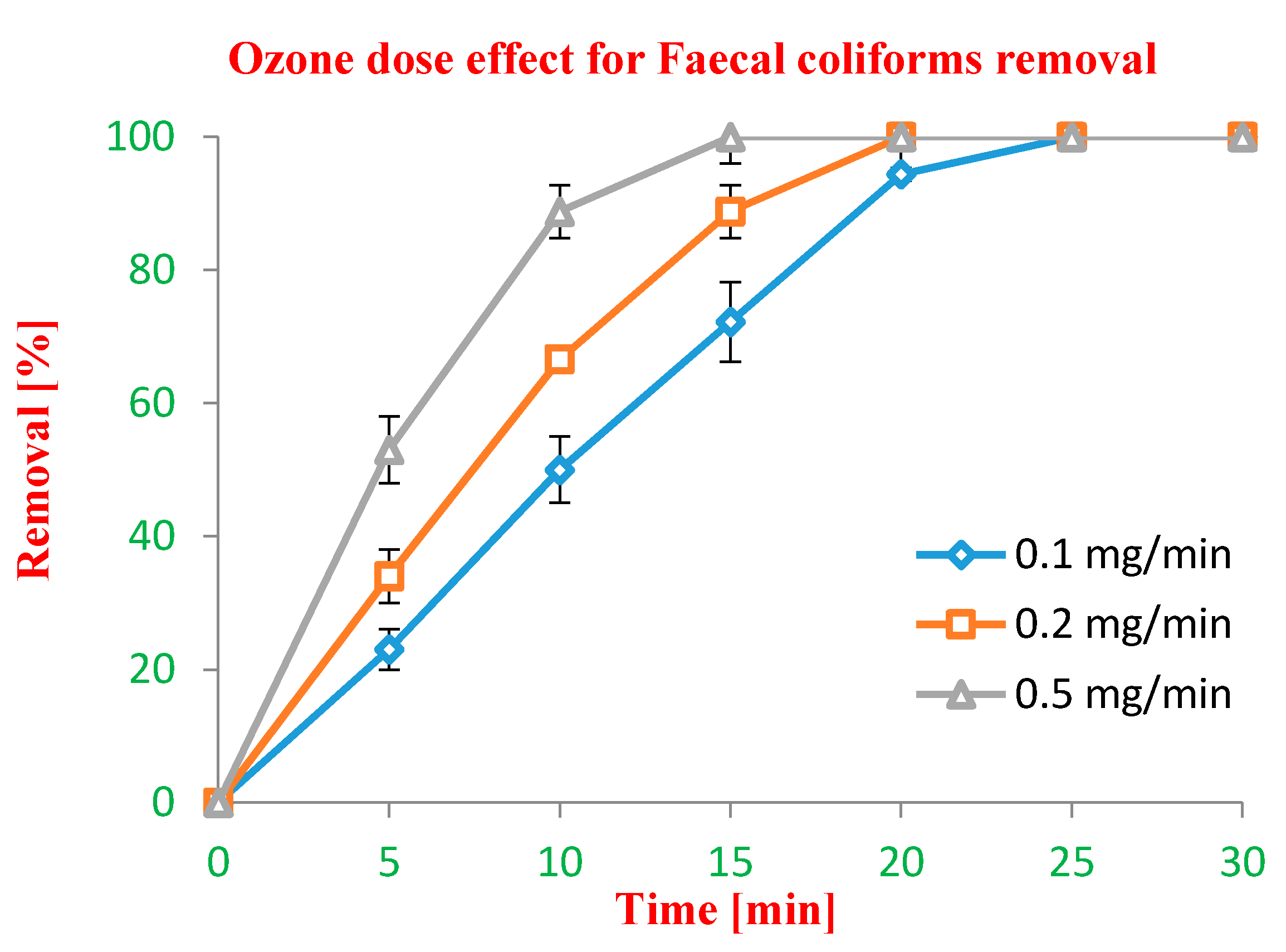
Ozone Dose Effect
Fe-Zeolite Dose Effect
2.2.2. Treatment of Arsenic
Comparison between Single Ozonation, Adsorption and O3/Fe-ZA Processes
Ozone Dose Effect
Fe-Zeolite Dose Effect
Effect of Hydroxyl Radical Scavenger on Water Disinfection and Arsenic Removal
Mechanism of Water Disinfection and Arsenic Removal on Fe-Zeolite A
3. Materials and Methods
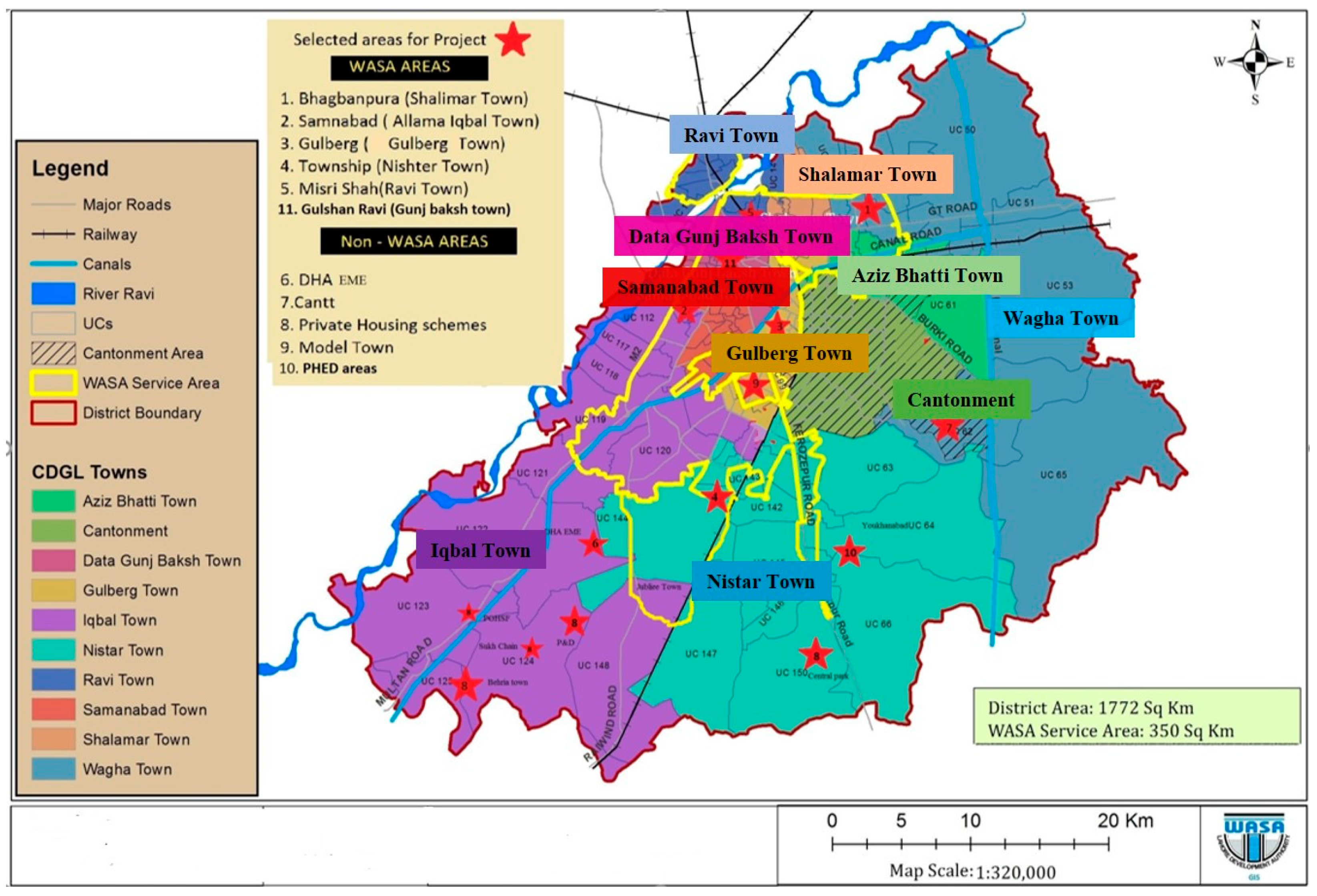
3.1. Study Area
3.1.1. Sampling Locations
3.1.2. Sample Collection, Storage and Analytical Procedures
3.2. Health Risk Assessment Model
3.2.1. Daily Intake of Metals
3.2.2. Health Quotient
3.3. Experimental Setup
3.3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3.3. Experimental Procedure for Single Ozonation and Catalytic Ozonation
3.3.4. Ozone Dose
- A = Titrant (Na2S2O3) used for Reactor (I) in mL
- B = Titrant (Na2S2O3) used for Reactor (II) in mL
- N = Normality of titrant (Na2S2O3)
- T = Total time of ozonation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinrichsen, D.; Tacio, H. The Linkages between population and water. In The Coming Freshwater Crisis is Already Here—Finding the Source; Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars: Washington, DC, USA; ESCP Publication: Paris, France; Spring: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: http://www.sciepub.com/reference/169629 (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Trace organic chemicals contamination in ground water recharge. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Lee, H.K.; Khan, M.A. Domestic water contamination in rapidly growing megacities of Asia: Case of Karachi, Pakistan. In Proceedings of the Environmental Monitoring and Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 44, pp. 339–360. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgrami, K.S.; Kumar, S. Bacterial contamination in water of the River Ganga and its risk to human health. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1998, 8, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shah, I.A.; Muhammad, S.; Malik, R.N.; Shah, M.T. Arsenic and Heavy Metal Concentrations in Drinking Water in Pakistan and Risk Assessment: A Case Study. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Xiao, T.; Farooqi, A.; Shafeeque, M.; Masood, S.; Ali, S.; Fahad, S.; Nasim, W. Arsenic and heavy metal contaminations in the tube well water of Punjab, Pakistan and risk assessment: A case study. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Sobsey, M.D. Microbiological effectiveness of locally produced ceramic filters for drinking water treatment in Cambodia. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clasen, T.; Edmondson, P. Sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) tablets as an alternative to sodium hypochlorite for the routine treatment of drinking water at the household level. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2006, 209, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applications of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Drinking Water Treatment|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007%2F978-3-319-76882-3 (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) Applied for Wastewater and Drinking Water Treatment. Elimination of Pharmaceuticals. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/index.php?id_clanak_jezik=103247&show=clanak (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y. Catalytic Oxidation Process for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, J.; Frasson, D.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.; Matos, A.; Martins, R. Removal of Enteric Pathogens from Real Wastewater Using Single and Catalytic Ozonation. Water 2019, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Tao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Noguchi, H. Performance of an integrated process combining ozonation with ceramic membrane ultra-filtration for advanced treatment of drinking water. Desalination 2014, 335, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhate, C.V.; Srivastava, J.K. Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater—A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.H.; Yuan, C.Z.; Zou, H.Y.; Cheang, T.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Qazi, U.Y.; Zhong, S.L.; Wang, L.; Xu, A.W. Bimetallic phosphide hollow nanocubes derived from a prussian-blue-analog used as high-performance catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Kawasaki, S.; Ookawara, R.; Sato, K.; Nishioka, M.; Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, T.M. Continuous Dehydrogenation of Aqueous Formic Acid under Sub-Critical Conditions by Use of Hollow Tubular Reactor Coated with Thin Palladium Oxide Layer. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2013, 46, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Kawanami, H.; Chatterjee, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, T.M. Fabrication of microtubular reactors coated with thin catalytic layer (M = Pd, Pd-Cu, Pt, Rh, Au). Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Kawasaki, S.I. Highly efficient decomposition of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using tubular reactor coated with thin layer of PdO. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qazi, U.Y.; Javaid, R. A Review on Metal Nanostructures: Preparation Methods and Their Potential Applications. Adv. Nanoparticles 2016, 5, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javaid, R.; Kawanami, H.; Chatterjee, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, T.M. Sonogashira C–C coupling reaction in water using tubular reactors with catalytic metal inner surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Zhou, X.; Ullah, N.; Liu, Y.-N.; Zeb, A.; Jiang, N.; Qazi, U.Y.; Yuan, C.-Z.; Xu, A.-W. Catalytic Conversion of Biomass into Hydrocarbons over Noble-Metal-Free VO-Substituted Potassium Salt of Phosphotungstic Acid. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 8625–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Kawasaki, S.I.; Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, T.M. Simple and rapid hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol with aqueous formic acid in catalytic flow reactors. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabasum, A.; Alghuthaymi, M.; Qazi, U.Y.; Shahid, I.; Abbas, Q.; Javaid, R.; Nadeem, N.; Zahid, M. UV-Accelerated Photocatalytic Degradation of Pesticide over Magnetite and Cobalt Ferrite Decorated Graphene Oxide Composite. Plants 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Urata, K.; Furukawa, S.; Komatsu, T. Factors affecting coke formation on H-ZSM-5 in naphtha cracking. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 491, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanba, T.; Nagata, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Javaid, R.; Atsumi, R.; Nishi, M.; Mochizuki, T.; Manaka, Y.; Kojima, H.; Tsujimura, T.; et al. Explorative Study of a Ru/CeO2 Catalyst for NH3 synthesis from renewable hydrogen and demonstration of NH3 synthesis under a range of reaction conditions. J. Japan Pet. Inst. 2021, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-Z.; Sun, Z.-T.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Yang, Z.-K.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, Z.-W.; Qazi, U.Y.; Zhang, W.-H.; Xu, A.-W. One-Step In Situ Growth of Iron-Nickel Sulfide Nanosheets on FeNi Alloy Foils: High-Performance and Self-Supported Electrodes for Water Oxidation. Small 2017, 13, 1604161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Javed, F.; Akram, A.; Qazi, U.Y.; Masood, Z.; Ahmed, T.; Arshad, Z.; Khalid, S.; Qi, F. Treatment of leachate through constructed wetlands using Typha angustifolia in combination with catalytic ozonation on Fe-zeolite A. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Sahar, S.; Qazi, U.Y.; Odda, A.H.; Ullah, N.; Liu, Y.N.; Qazi, I.A.; Xu, A.W. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity and enhanced photo-Fenton reactivity of iron-substituted polyoxometallate nanostructures. Dalt. Trans. 2018, 47, 7344–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Imran, M.; Liang, K.; Yuan, C.Z.; Zeb, A.; Jiang, N.; Qazi, U.Y.; Sahar, S.; Xu, A.W. Highly dispersed ultra-small Pd nanoparticles on gadolinium hydroxide nanorods for efficient hydrogenation reactions. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13800–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Nanba, T. MgFe2O4-Supported Ru Catalyst for Ammonia Synthesis: Promotive Effect of Chlorine. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 4312–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.Y.; Yuan, C.Z.; Ullah, N.; Jiang, Y.F.; Imran, M.; Zeb, A.; Zhao, S.J.; Javaid, R.; Xu, A.W. One-Step Growth of Iron-Nickel Bimetallic Nanoparticles on FeNi Alloy Foils: Highly Efficient Advanced Electrodes for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28627–28634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Tanaka, D.A.P.; Kawanami, H.; Suzuki, T.M. Silica Capillary with Thin Metal (Pd and Pt) Inner Wall: Application to Continuous Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.Y.; Javaid, R.; Tahir, N.; Jamil, A.; Afzal, A. Design of advanced self-supported electrode by surface modification of copper foam with transition metals for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 33396–33406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Kawasaki, S.-I. Efficient and Continuous Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide Using a Silica Capillary Coated with a Thin Palladium or Platinum Layer. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javaid, R.; Nanba, T. Effect of reaction conditions and surface characteristics of Ru/CeO2 on catalytic performance for ammonia synthesis as a clean fuel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Aoki, Y.; Nanba, T. Highly efficient Ru/MgO–Er2O3 catalysts for ammonia synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 146, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hao, G.X.; Luo, H.D.; Ke, C.X.; Shi, G.; Lin, J.; Lin, X.M.; Qazi, U.Y.; Cai, Y.P. Bifunctional 2D Cd(II)-Based Metal-Organic Framework as Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Formation of C–C Bond. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 2883–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, B.S.; Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J. Removal of Escherichia coli after Treatment Using Ozonation-Ultrafiltration with Iron Oxide-Coated Membranes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2007, 29, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Galeano, L.A.; Vicente, M.Á. (Eds.) Applications of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Drinking Water Treatment. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 67, ISBN 978-3-319-76881-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Waheed, S.; Joya, K.S.; Kazmi, M. Catalytic ozonation of paracetamol on zeolite A: Non-radical mechanism. Catal. Commun. 2018, 112, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Fang, G.; Chen, Y.; Chan, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, C. Degradation of Cyanotoxin-Nodularin in Drinking Water by Catalytic Ozonation Using a Ag-TiO2 Hybrid Catalyst. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zong, P.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, B.; Sun, Q. Adsorption and bio-sorption of nickel ions and reuse for 2-chlorophenol catalytic ozonation oxidation degradation from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackulak, T.; Nagyová, K.; Faberová, M.; Grabic, R.; Koba, O.; Gál, M.; Birošová, L. Utilization of Fenton-like reaction for antibiotics and resistant bacteria elimination in different parts of WWTP. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, N.H.; Belen, R. Aqueous phase disinfection with power ultrasound: Process kinetics and effect of solid catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1885–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, G.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous catalytic ozonation degradation of metronidazole and removal of heavy metal from aqueous solution using nano-magnesium hydroxide. Environ. Technol. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yoza, B.A.; Li, Q.X.; Kou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Catalytic Ozonation of Recalcitrant Organic Chemicals in Water Using Vanadium Oxides Loaded ZSM-5 Zeolites. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Anis, M.; Javed, F.; Ghani, H.; Muhammad, H.; Munir, S.; Ijaz, K. Catalytic ozonation for the treatment of municipal wastewater by iron loaded zeolite A. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 152, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Catalytic oxidation of benzene with ozone over Mn ion-exchanged zeolites. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsorption and Removal of Arsenic(V) from Drinking Water by Aluminum-Loaded Shirasu-Zeolite—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389402000201?casa_token=puuxUG54KzoAAAAA:9VSUawrAySmSk2armDocmr2Gj0qg0YguQN-PJ7RYIFp_WMVq-3T52kwPKTJ0wzBP96o62Pz77MQ (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Li, Z.; Jean, J.S.; Jiang, W.T.; Chang, P.H.; Chen, C.J.; Liao, L. Removal of arsenic from water using Fe-exchanged natural zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, K.; Abdel-Fattah, T. Adsorption of Arsenate and Arsenite by Iron-Treated Activated Carbon and Zeolites: Effects of pH, Temperature, and Ionic Strength. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2005, 40, 723–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, M.S. Sorption Kinetics of Arsenic onto Iron-Conditioned Zeolite. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2003, 36, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Umetsu, Y. Oxidative precipitation of arsenic(III) with manganese(II) and iron(II) in dilute acidic solution by ozone. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 62, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Nriagu, J. Oxidation of arsenite in groundwater using ozone and oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rosal, R.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Mezcua, M.; Agüera, A.; Hernando, M.D.; Letón, P.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Calvo, E. Ozone-Based Technologies in Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Emerging Contaminants from Industrial and Municipal Waste; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5, pp. 127–175. [Google Scholar]
- Cole-Hamilton, D.J.; Tooze, R.P. (Eds.) Catalyst Separation, Recovery and Recycling; Catalysis by Metal Complexes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 30, ISBN 978-1-4020-4086-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, G.H.; Jiang, L.; Li, P. Mass-transfer limitations for immobilized enzyme catalyzed kinetic resolution of racemate in a batch reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4054–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekbaş, M.; Yatmaz, H.C.; Bektaş, N. Heterogeneous photo-Fenton oxidation of reactive azo dye solutions using iron exchanged zeolite as a catalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carter, J.E.; Parker, A. Towards the characterisation of heavy metals in dredged canal sediments and an appreciation of “availability”: Two examples from the UK. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Olmos, R.; Roland, U.; Toufar, H.; Kopinke, F.D.; Georgi, A. Fe-zeolites as catalysts for chemical oxidation of MTBE in water with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 89, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Othman, O.M.; Abu Amr, S.S. The performance of Electro-Fenton oxidation in the removal of coliform bacteria from landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, A.; El-Gohary, F.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. The influence of physical-chemical and biological factors on the removal of faecal coliform through down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) system treating UASB reactor effluent. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.K.; Mariñas, B.J. Inactivation of Escherichia coli with ozone: Chemical and inactivation kinetics. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Chung, H.; Yoon, J. Disinfection of water containing natural organic matter by using ozone-initiated radical reactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.; Raston, C.L. Role of hydroxyl radicals and mechanism of Escherichia coli inactivation on Ag/AgBr/TiO2 nanotube array electrode under visible light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4042–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, S.; Majumder, S.K.; Ghosh, P. Oxidation of As(III) to As(V) using ozone microbubbles. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.K.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Sharma, V.K.; Ray, A.K. Photocatalytic oxidation of arsenic(III): Evidence of hydroxyl radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.V.; Andrade, C.V.; De Angelis, L.E.; Jacobo, S.E. Adsorption and catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants using Fe-zeolite. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sidra, S.; Nasir, Z.A.; Colbeck, I. Air quality (particulate matter) at heavy traffic sites in Lahore, Pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Landreth, S. Achieving Universal Access to Water and Sanitation Services: The Role of Political Will in Implementation Practices, a Study of Pakistan and India. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Colorado, Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Rice, E.W.; Greenberg, A.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Available online: http://www.sciepub.com/reference/195183 (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Farooq, R.; Khan, S.; Shahbaz, S.; Khan, M.A.; Sadique, M. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals for Population via Consumption of Vegetables. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sato, T.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, N.K.; Hameed, B.H. Decolorization of Acid Red 1 by Fenton-like process using rice husk ash-based catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, P.; Javaid, R. A review of ammonia as a compression ignition engine fuel. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 7098–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanba, T.; Javaid, R.; Matsumoto, H. Ammonia synthesis catalyst development for renewable energy storage. Fine Chem. 2019, 48, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nanba, T.; Javaid, R.; Matsumoto, H. Ammonia synthesis by using hydrogen produced from renewable energy. Catalysis 2019, 16, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Nanba, T. Influence of Reaction Conditions and Promoting Role of Ammonia Produced at Higher Temperature Conditions in Its Synthesis Process over Cs-Ru/MgO Catalyst. Chem. Sel. 2019, 4, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Properties of Zeolite. | Typical Formula | Pore Size (Å) | Thermal Decomposition (°C) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Fe [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2Na2O–Al2O3–1.75SiO2–6H2O | 4 | 700 | 91.21 | 10 |
| Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Codes | pH | TDS a (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) | Chlorides (mg/L) | Residual Chlorine (mg/L) | Faecal Coliforms MPN/100 mL | Arsenic (ppb) | |
| Township Area | ||||||||
| ST-1 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 835 ± 15 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 38 ± 11 | 0.07 | 9 ± 3 | 68 ± 8 | |
| ST-2 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 829 ± 12 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 39 ± 13 | 0.07 | 5 ± 4 | 45 ± 4 | |
| Ichra | ||||||||
| SI-1 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 237 ± 12 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 33 ± 8 | 0 | 16 ± 5 | 44 ± 5 | |
| SI-2 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | 215 ± 15 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 36 ± 8 | 0 | 10 ± 5 | 69 ± 12 | |
| Gulshan RaviArea | ||||||||
| SG-1 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 209 ± 11 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 24 ± 5 | 0 | 21 ± 4 | 72 ± 8 | |
| SG-2 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | 212 ± 15 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 22 ± 3 | 0 | 22 ± 7 | 49 ± 6 | |
| Bagbanpura Area | ||||||||
| SB-1 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 392 ± 13 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 48 ± 11 | 0 | 20 ± 5 | 41 ± 11 | |
| SB-2 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 270 ± 11 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 55 ± 4 | 0 | 3 ± 2 | 58 ± 4 | |
| Misri Shah Area | ||||||||
| SM-1 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 340 ± 14 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 40 ± 7 | 0 | 18 ± 4 | 45 ± 4 | |
| SM-2 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 330 ± 12 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 37 ± 12 | 0 | 10 ± 4 | 42 ± 2 | |
| WHO Guideline | 6.5–8.5 | <1000 | <5 | 250 | 0.2–5.0 | 0 | 10 | |
| NSDWQ Guideline | 6.5–8.5 | <1000 | <5 | <250 | 0.2–5.0 | 0 | 50 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikhlaq, A.; Fatima, R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Javaid, R.; Akram, A.; Ibn Shamsah, S.; Qi, F. Combined Iron-Loaded Zeolites and Ozone-Based Process for the Purification of Drinking Water in a Novel Hybrid Reactor: Removal of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic. Catalysts 2021, 11, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030373
Ikhlaq A, Fatima R, Qazi UY, Javaid R, Akram A, Ibn Shamsah S, Qi F. Combined Iron-Loaded Zeolites and Ozone-Based Process for the Purification of Drinking Water in a Novel Hybrid Reactor: Removal of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic. Catalysts. 2021; 11(3):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030373
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkhlaq, Amir, Rida Fatima, Umair Yaqub Qazi, Rahat Javaid, Asia Akram, Sami Ibn Shamsah, and Fei Qi. 2021. "Combined Iron-Loaded Zeolites and Ozone-Based Process for the Purification of Drinking Water in a Novel Hybrid Reactor: Removal of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic" Catalysts 11, no. 3: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030373
APA StyleIkhlaq, A., Fatima, R., Qazi, U. Y., Javaid, R., Akram, A., Ibn Shamsah, S., & Qi, F. (2021). Combined Iron-Loaded Zeolites and Ozone-Based Process for the Purification of Drinking Water in a Novel Hybrid Reactor: Removal of Faecal Coliforms and Arsenic. Catalysts, 11(3), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030373








