The Stability, Sustained Release and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
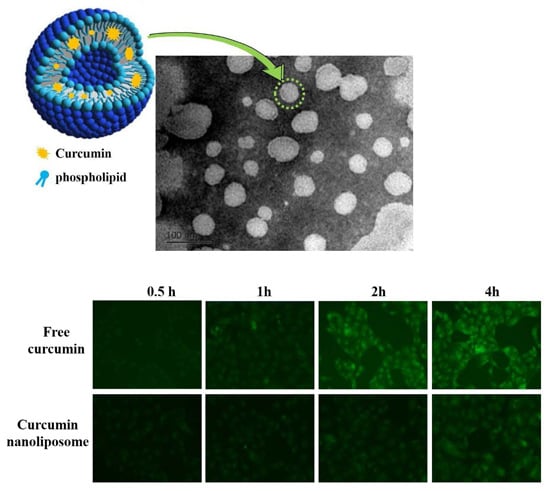
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization and Morphology of Curcumin Nanoliposomes



2.2. In Vitro Drug Release of Curcumin Nanoliposome


2.3. Stability Studies of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
2.3.1. Stability against pH of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
| pH | Samples | 0 min | 20 min | 40 min | 60 min | 120 min | 180 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin residual rate | 6.5 | Cur-F | 101.3 ± 2.7 a | 97.2 ± 5.4 a | 98.7 ± 5.6 a | 99.3 ± 2.1 a | 97.7 ± 3.2 a | 98.7 ± 0.7 a |
| Cur-N | 99.5 ± 0.6 a | 99.1 ± 1.5 a | 99.5 ± 5.7 a | 99.3 ± 2.0 a | 99.6 ± 4.6 a | 98.7 ± 2.8 a | ||
| 7.4 | Cur-F | 99.6 ± 3.6 a | 21.8 ± 4.4 b | 16.0 ± 0.8 b,c | 15.2 ± 1.2 b,c | 14.0 ± 1.5 b,c | 12.1 ± 1.2 c | |
| Cur-N | 99.3 ± 7.5 a | 94.2 ± 2.7 a | 97.7 ± 2.7 a | 100.5 ± 8.1 a | 97.7 ± 4.9 a | 99.3 ± 7.5 a | ||
| 8.0 | Cur-F | 102.5 ± 9.8 a | 21.4 ± 2.0 c | 19.9 ± 0.9 c | 17.6 ± 0.7 c | 16.9 ± 1.9 c | 15.3 ± 0.7 c | |
| Cur-N | 100.1 ± 7.1 a,b | 96.9 ± 5.8 a,b | 96.8 ± 4.3 a,b | 94.4 ± 7.0 a,b | 89.7 ± 9.9 b | 90.8 ± 10.6 a,b | ||
| 10.0 | Cur-F | 99.9 ± 9.0 a | 74.3 ± 4.9 b,c | 51.1 ± 5.0 e,f | 37.7 ± 6.5 g | 19.2 ± 2.4 h | 17.2 ± 2.3 h | |
| Cur-N | 96.8 ± 6.0 a | 80.5 ± 8.2 b | 64.9 ± 10.1 c,d | 64.0 ± 10.0 c,d | 54.9 ± 4.2 e,d | 40.1 ± 10.0 f,g | ||
| 12.0 | Cur-F | 97.2 ± 18.4 a,b | 84.8 ± 3.7 b,c | 75.2 ± 7.9 c,d | 65.2 ± 7.0 d | 47.1 ± 5.7 e | 37.1 ± 1.9 e,f | |
| Cur-N | 99.3 ± 7.1 a | 81.9 ± 9.3 c | 67.7 ± 2.2 d | 46.0 ± 2.5 e | 32.5 ± 5.0 f,g | 22.2 ± 4.1 g |
2.3.2. Stability against Metal Ions of Curcumin Nanoliposomes

2.3.3. Storage Stability of Curcumin Nanoliposomes

2.4. Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes

2.5. Cellular Uptake Assays of Curcumin Nanoliposomes


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Curcumin Nanoliposome Preparation
3.3. The Solubility of Curcumin in Nanoliposomes
3.4. Physicochemical Characterization and Morphology of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.6. Curcumin Nanoliposome Stability Studies
3.6.1. pH Stability of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.6.2. Stability of Curcumin Nanoliposomes against Metal Ions
3.6.3. Storage Stability of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.7. Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.8. Cellular Uptake Assays of Curcumin Nanoliposomes
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilken, R.; Veena, M.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. Curcumin: A review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R.; Bassi, R.; Green, C.J. Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Du, Z. Curcumin, Inflammation, and Chronic Diseases: How Are They Linked? Molecules 2015, 20, 9183–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Ji, H.F. The pharmacology of curcumin: Is it the degradation products? Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, N.P.; Shim, M.; Lee, I.; Lee, Y.; Im, M.H.; Ko, S. Curcumin and Genistein Coloaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: In Vitro Digestion and Antiprostate Cancer Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Ke, D.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; An, X.; Shen, W. Temperature-dependent stability and DPPH scavenging activity of liposomal curcumin at pH 7.0. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotto-Filho, A.; Coradini, K.; Braganhol, E.; Schröder, R.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Simões-Pires, A.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Forcelini, C.M. Curcumin-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules as a strategy to improve pharmacological efficacy of curcumin in glioma treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, C.; Qian, Z.; Wei, Y. Curcumin loaded polymeric micelles inhibit breast tumor growth and spontaneous pulmonary metastasis. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Elremaily, M.A.; Hernández-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Divinyl sulfone cross-linked cyclodextrin-based polymeric materials: Synthesis and applications as sorbents and encapsulating agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Q. Improving the oral bioavailability of curcumin using novel organogel-based nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5373–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chai, S.; Chen, Z.; An, X.; Shen, W. Effects of curcumin concentration and temperature on the spectroscopic properties of liposomal curcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Uechi, S.; Takara, K.; Asikin, Y.; Wada, K. Evaluation of an oral carrier system in rats: Bioavailability and antioxidant properties of liposome-encapsulated curcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9141–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L. Preparation of curcumin-loaded liposomes and evaluation of their skin permeation and pharmacodynamics. Molecules 2012, 17, 5972–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L.; Gan, Q.; Le, X. Temperature-dependent structure stability and in vitro release of chitosan-coated curcumin liposome. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Bhandari, B. Encapsulation of polyphenols—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.S.; Singh, S. Targeted nanomedicines: Effective treatment modalities for cancer, AIDS and brain disorders. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Pan, M.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Lin, L.I.; Ho, Y.S.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, J.K. Stability of curcumin in buffer solutions and characterization of its degradation products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 15, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Jiang, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, P. Interaction of curcumin with Zn (II) and Cu (II) ions based on experiment and theoretical calculation. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 984, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matloob, A.H.; Mourtas, S.; Klepetsanis, P.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Increasing the stability of curcumin in serum with liposomes or hybrid drug-in-cyclodextrin-in-liposome systems: A comparative study. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saengkrit, N.; Saesoo, S.; Srinuanchai, W.; Phunpee, S.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. Influence of curcumin-loaded cationic liposome on anticancer activity for cervical cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 114, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, Y.F.; He, X.J.; Jiang, M.Y. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of glycyrrhetinic acid-modified curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Molecules 2014, 19, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.L.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.M.; Yang, S.B.; Liu, J.H.; Zheng, H.J.; Su, K.M. Medium-chain fatty acid nanoliposomes suppress body fat accumulation in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Liang, R.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Niu, J.; Liu, Z. Characterization and bioavailability of tea polyphenol nanoliposome prepared by combining an ethanol injection method with dynamic high-pressure microfluidization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Peng, S.; Liu, W.; Gan, L.; Liu, W.; Liang, R.; Liu, C.; Niu, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z. Improved in vitro digestion stability of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate through nanoliposome encapsulation. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. β-Cyclodextrin-curcumin self-assembly enhances curcumin delivery in prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 79, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramera, E.I.; Konteles, S.J.; Karathanos, V.T. Microencapsulation of curcumin in cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, H.K.; Liew, K.B.; Loh, G.O.K.; Peh, K.K. Stability indicating HPLC-UV method for detection of curcumin in Curcuma longa extract and emulsion formulation. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Gao, Y.; Guo, C.; Cao, F.; Song, Z.; Xi, Y.; Yu, A.; Li, A.; Zhai, G. Enhancement of transport of curcumin to brain in mice by poly (n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticle. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 3111–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.; Emam-jomeh, Z.; Kalbasi, A.; Razavi, S.; Karimi, M.; Kokini, J. The effect of different desolvating agents on BSA nanoparticle properties and encapsulation of curcumin. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Zheng, F.; Zhong, S.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Yao, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, G. Self-Assembled Nanoparticles of Glycyrrhetic Acid-Modified Pullulan as a Novel Carrier of Curcumin. Molecules 2014, 19, 13305–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, J.; Shi, K.; Huang, Q. Structure of modified ε-polylysine micelles and their application in improving cellular antioxidant activity of curcuminoids. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, M.; Isacchi, B.; van Bloois, L.; Torano, J.S.; Ket, A.; Wu, X.; Broere, F.; Metselaar, J.M.; Rijcken, C.J.; Storm, G. Improving solubility and chemical stability of natural compounds for medicinal use by incorporation into liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, J.; Fritz, M.; Brender, J.R.; Smith, P.E.; Lee, D.K.; Ramamoorthy, A. Determining the effects of lipophilic drugs on membrane structure by solid-state NMR spectroscopy: The case of the antioxidant curcumin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4490–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.H.; Colangelo, H.; Kee, T.W. Encapsulation of curcumin in cationic micelles suppresses alkaline hydrolysis. Langmuir 2008, 24, 5672–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Prasad, S.; Kim, J.H.; Patchva, S.; Webb, L.J.; Priyadarsini, I.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Multitargeting by curcumin as revealed by molecular interaction studies. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 1937–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, L.; Ng, A. Curcumin interaction with copper and iron suggests one possible mechanism of action in Alzheimer’s disease animal models. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2004, 6, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Zou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, R.; Chen, J. Storage stability and skin permeation of vitamin C liposomes improved by pectin coating. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 117, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, T.; Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin. Chem. Biol. Int. 2008, 174, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, A.; Barik, A.; Mishra, B.; Rathinasamy, K.; Pandey, R.; Priyadarsini, K. Quantitative cellular uptake, localization and cytotoxicity of curcumin in normal and tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Un, K.; Sakai-Kato, K.; Oshima, Y.; Kawanishi, T.; Okuda, H. Intracellular trafficking mechanism, from intracellular uptake to extracellular efflux, for phospholipid/cholesterol liposomes. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Liang, W. Cellular uptake and elimination of lipophilic drug delivered by nanocarriers. Die Pharm. 2010, 65, 737–742. [Google Scholar]
- Pellequer, Y.; Ollivon, M.; Barratt, G. Methodology for assaying recombinant interleukin-2 associated with liposomes by combined gel exclusion chromatography and fluorescence. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 783, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, T.; Liu, C. Improved physical and in vitro digestion stability of a polyelectrolyte delivery system based on layer-by-layer self-assembly alginate-chitosan-coated nanoliposomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4133–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oetari, S.; Sudibyo, M.; Commandeur, J.N.; Samhoedi, R.; Vermeulen, N.P. Effects of curcumin on cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.L.; Liu, R.H. Cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay for assessing antioxidants, foods, and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8896–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Ting, Y.; Zeng, X.; Huang, Q. Bioactive peptides/chitosan nanoparticles enhance cellular antioxidant activity of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the curmin nanoliposomes are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zou, L.-Q.; Niu, J.; Liu, W.; Peng, S.-F.; Liu, C.-M. The Stability, Sustained Release and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes. Molecules 2015, 20, 14293-14311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814293
Chen X, Zou L-Q, Niu J, Liu W, Peng S-F, Liu C-M. The Stability, Sustained Release and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes. Molecules. 2015; 20(8):14293-14311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814293
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xing, Li-Qiang Zou, Jing Niu, Wei Liu, Sheng-Feng Peng, and Cheng-Mei Liu. 2015. "The Stability, Sustained Release and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes" Molecules 20, no. 8: 14293-14311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814293
APA StyleChen, X., Zou, L.-Q., Niu, J., Liu, W., Peng, S.-F., & Liu, C.-M. (2015). The Stability, Sustained Release and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanoliposomes. Molecules, 20(8), 14293-14311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814293