The (U-Th)/He Chronology and Geochemistry of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths Formed in the Paleochannel Environments at the Garden Well Gold Deposit, Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: Implications for Landscape Evolution and Geochemical Exploration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths in Context of Landscape of the Yilgarn Craton
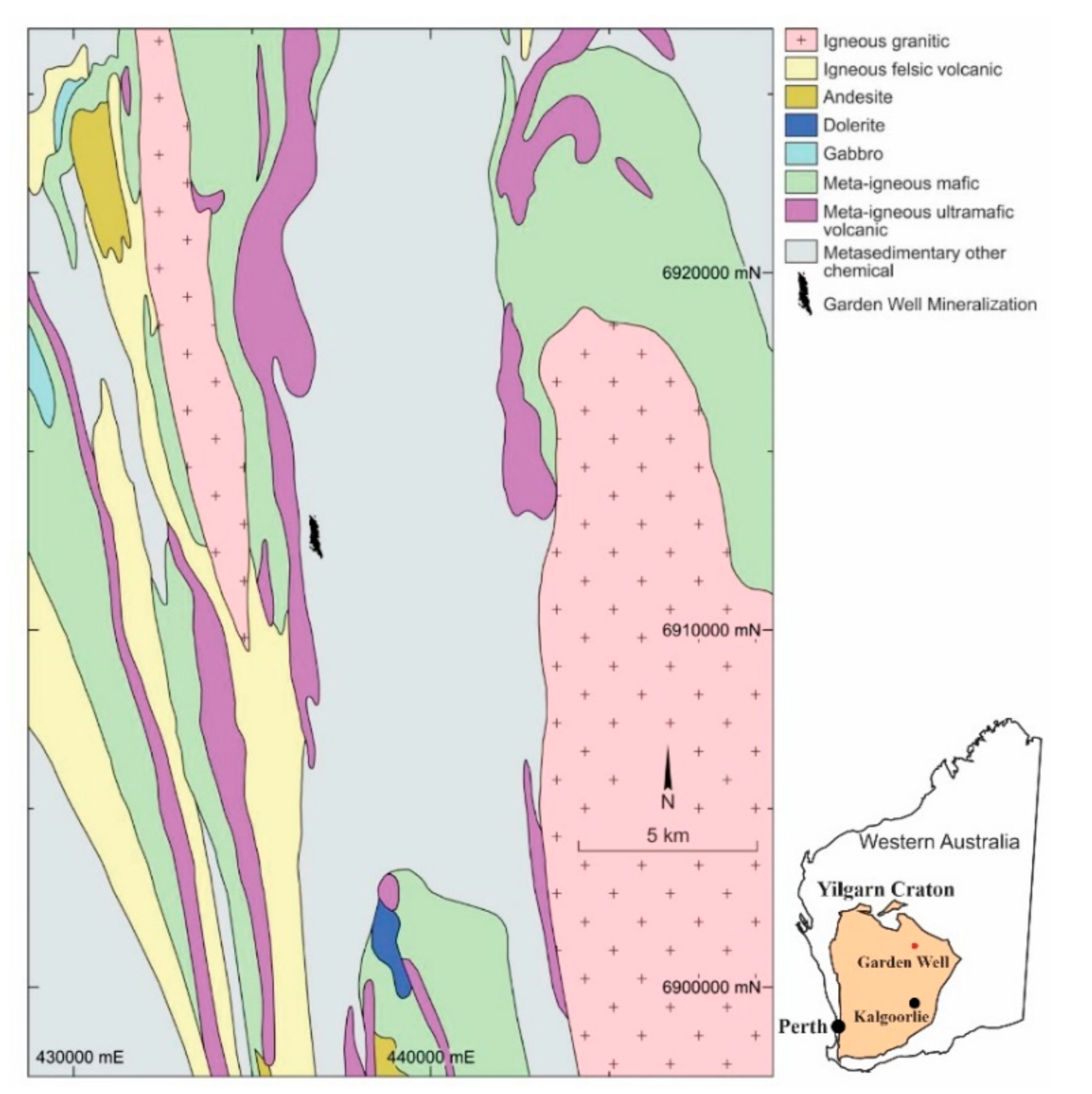
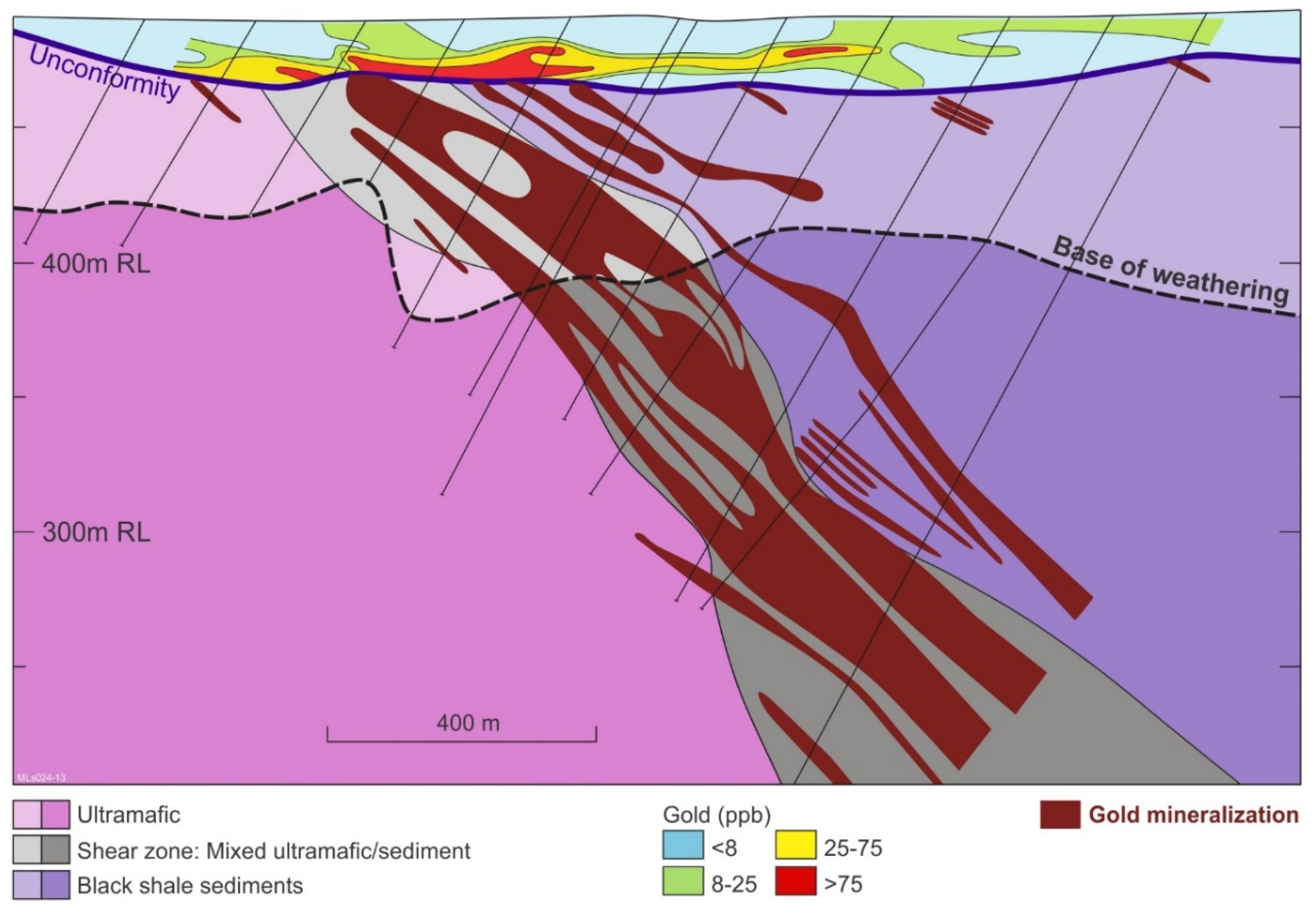
3. Geology and Mineralization
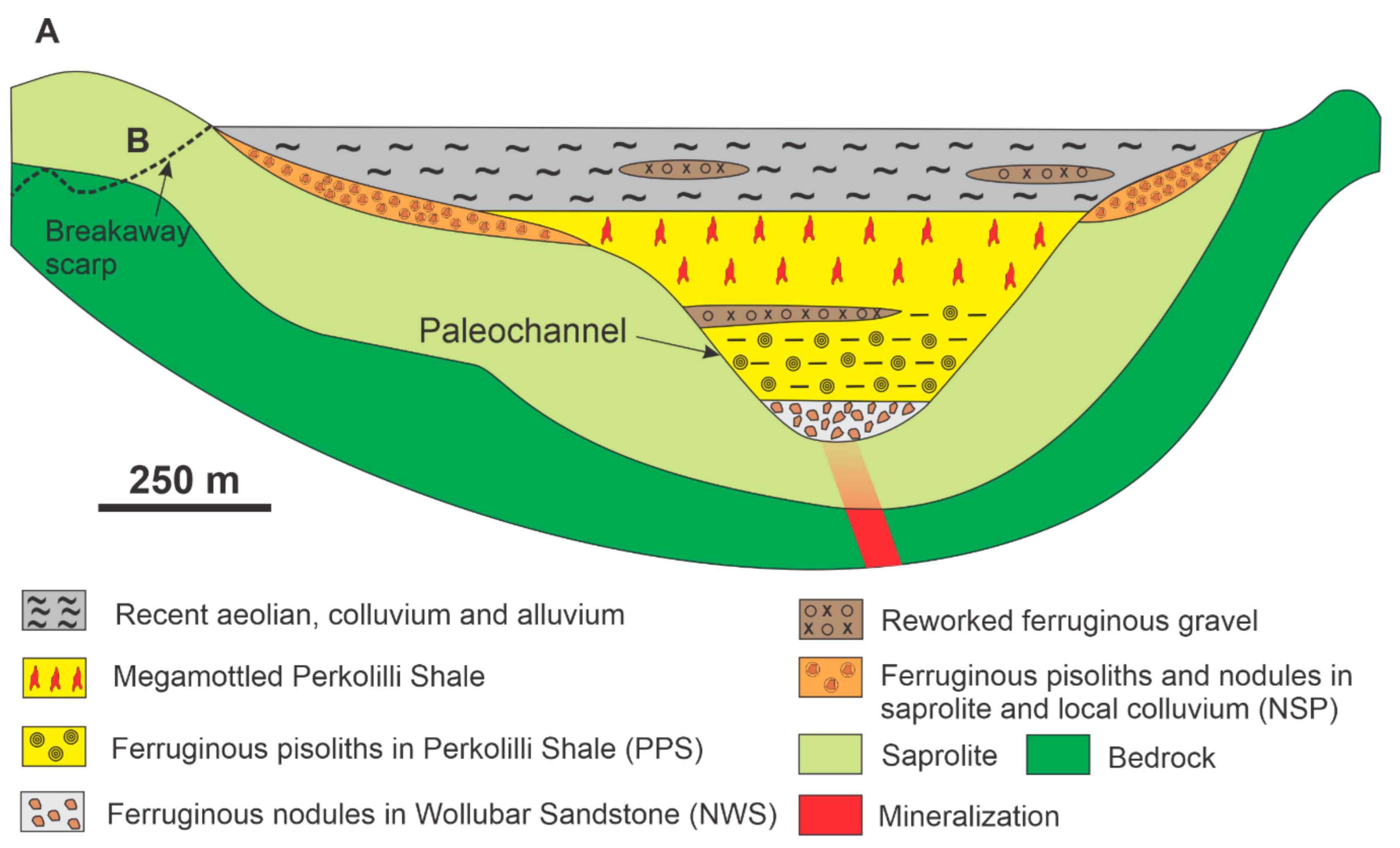
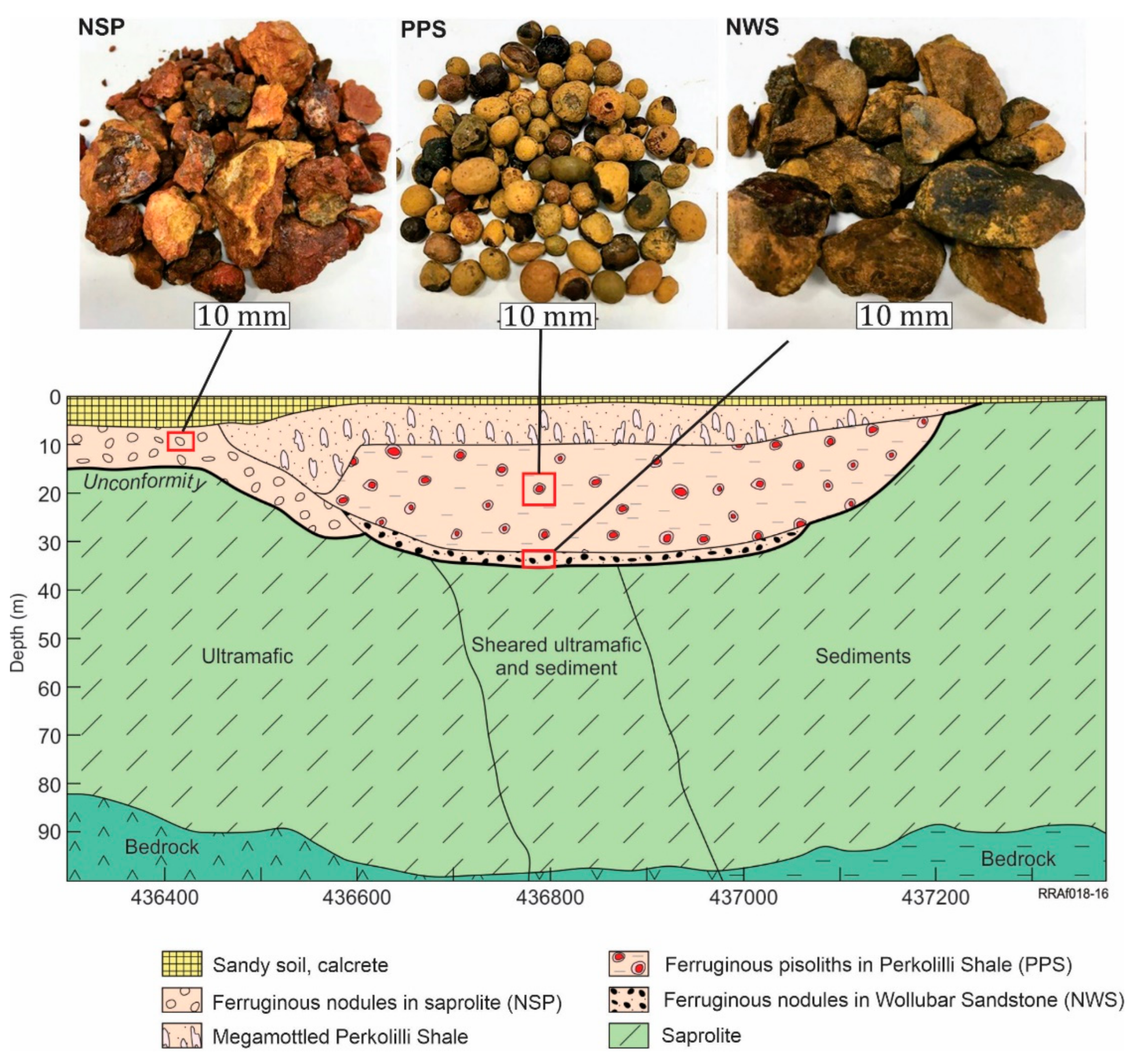
4. Geomorphology and Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths in the Garden Well Deposit and its Nearby Environments
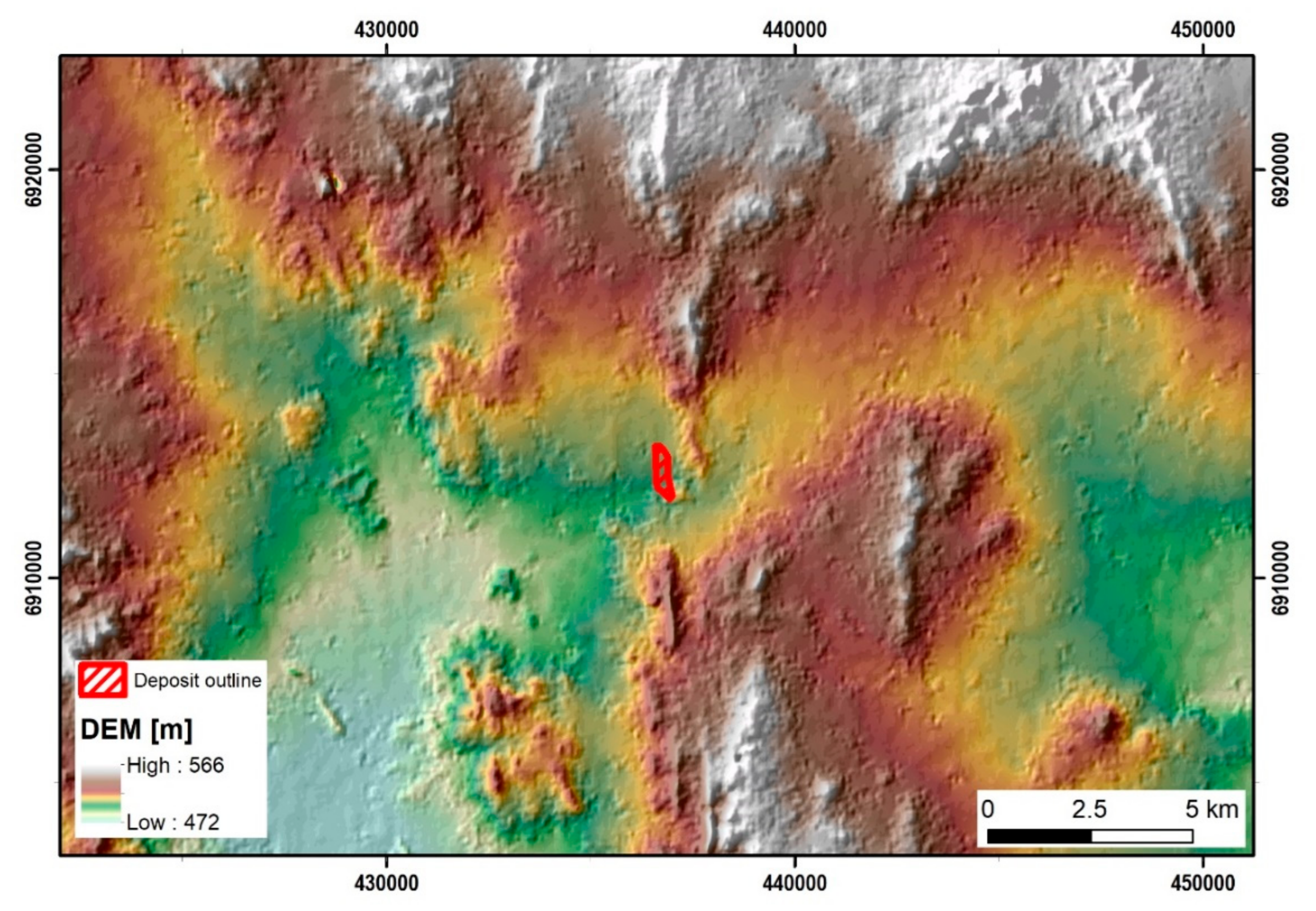
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sample Collection
5.2. Whole Sample Mineral Identification
5.3. Whole Sample Chemical Analyses
5.4. In Situ Chemical Analyses
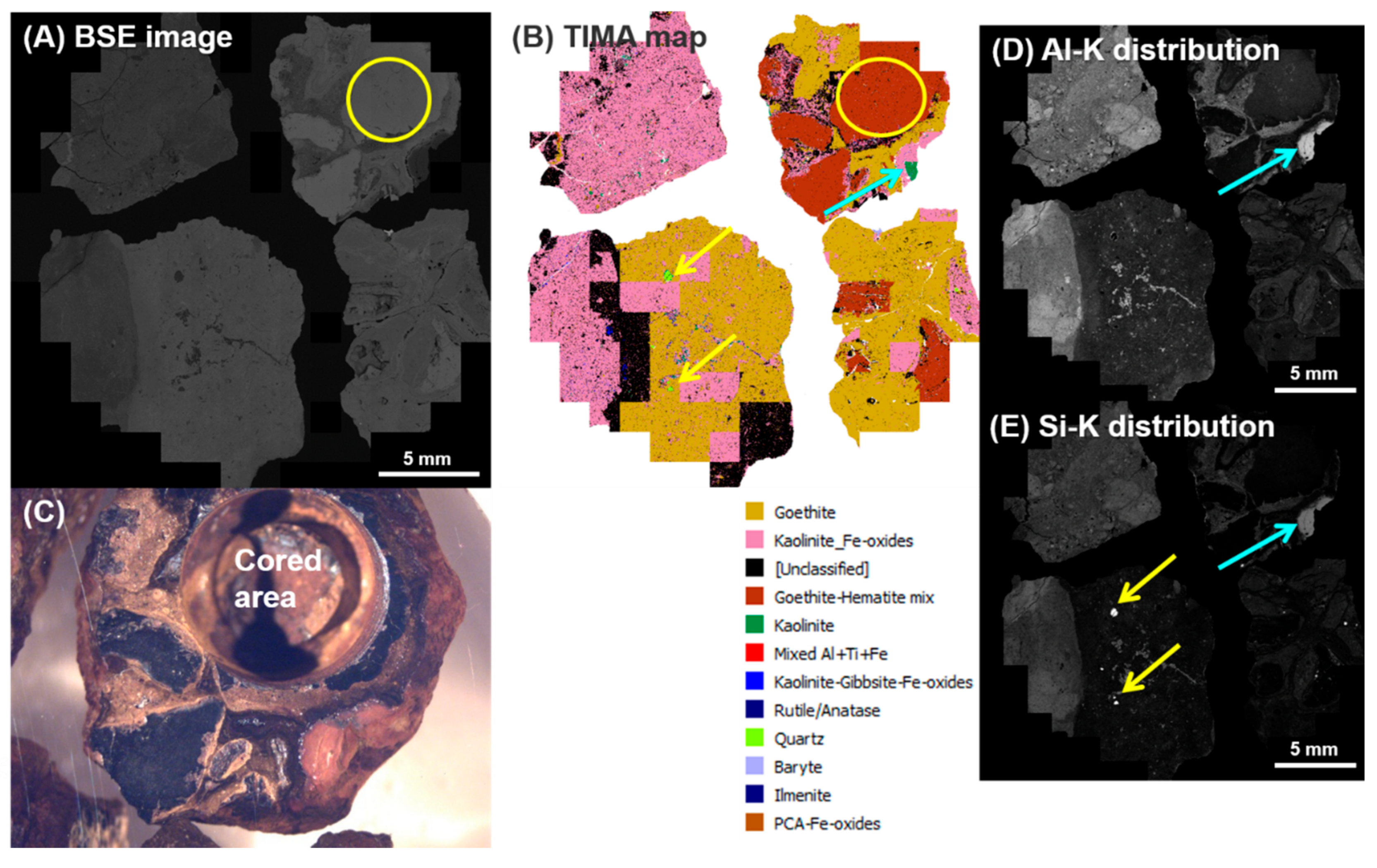
5.5. TIMA Mineral Mapping of Selected Samples for Dating
5.6. (U–Th)/He Dating
6. Results
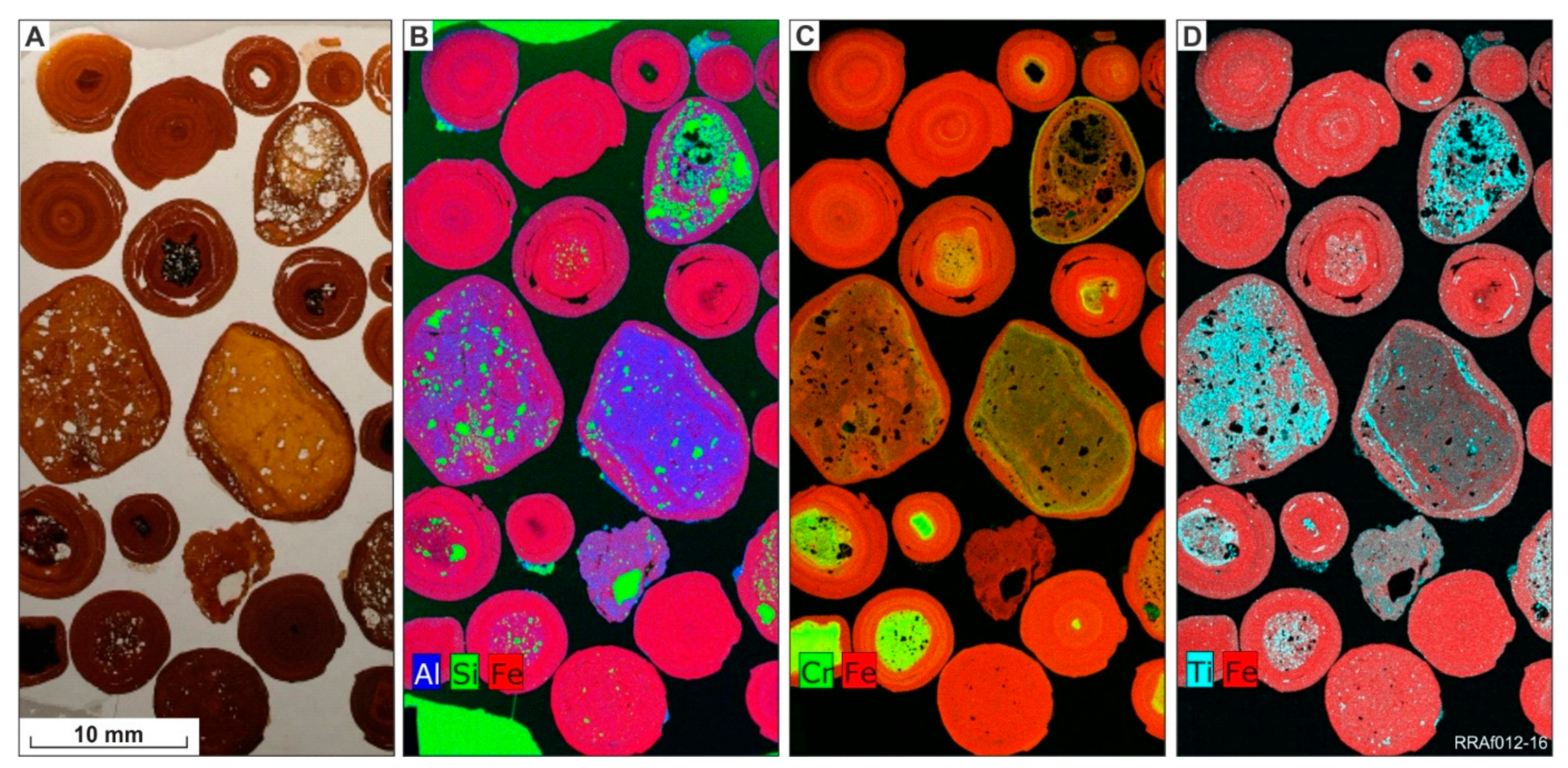
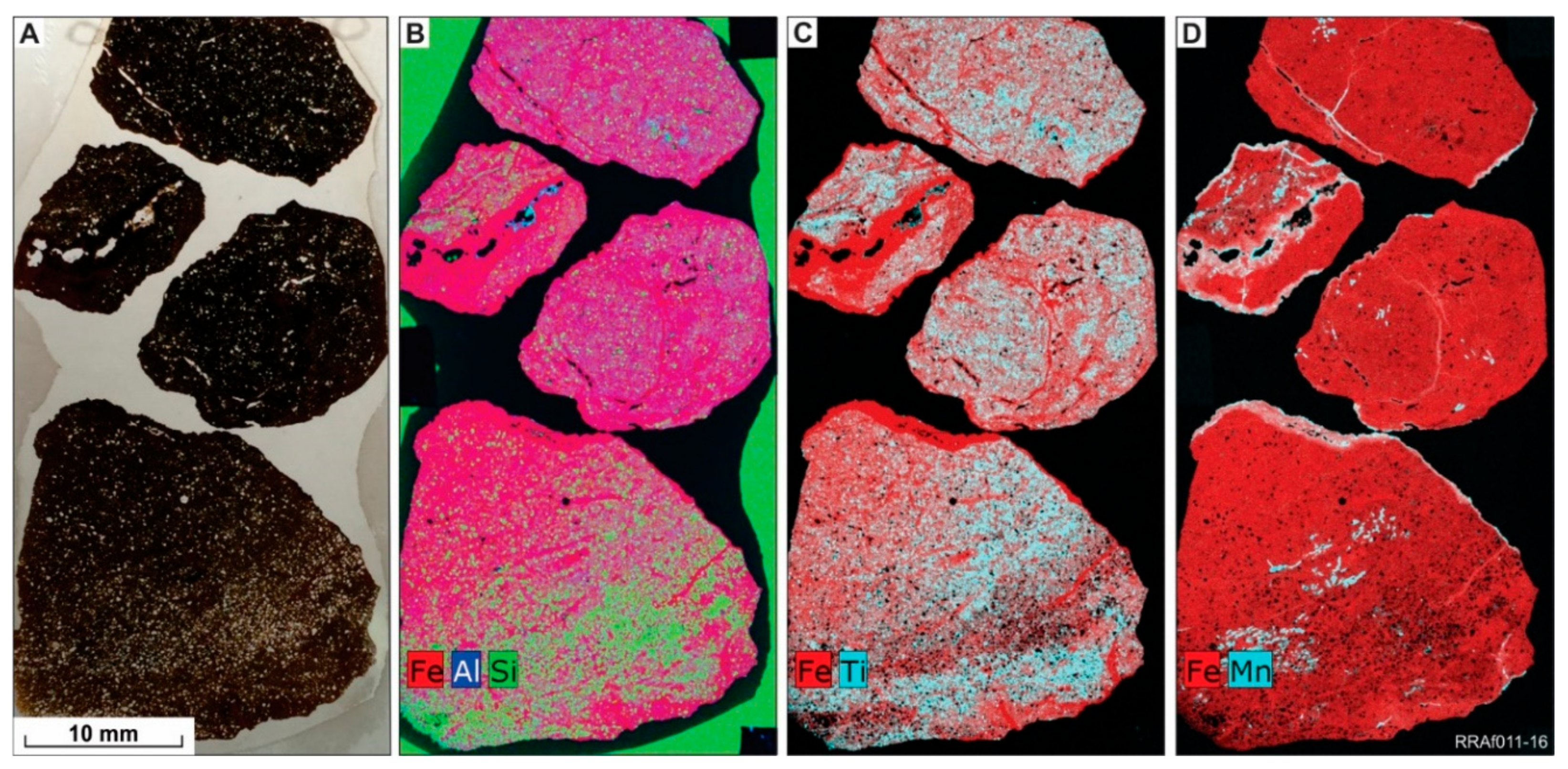
6.1. Ferruginous Pisoliths in the Perkolilli Shale (PPS)
6.2. Ferruginous Nodules in the Wollubar Sandstone (NWS) and in Saprolite (NSP)
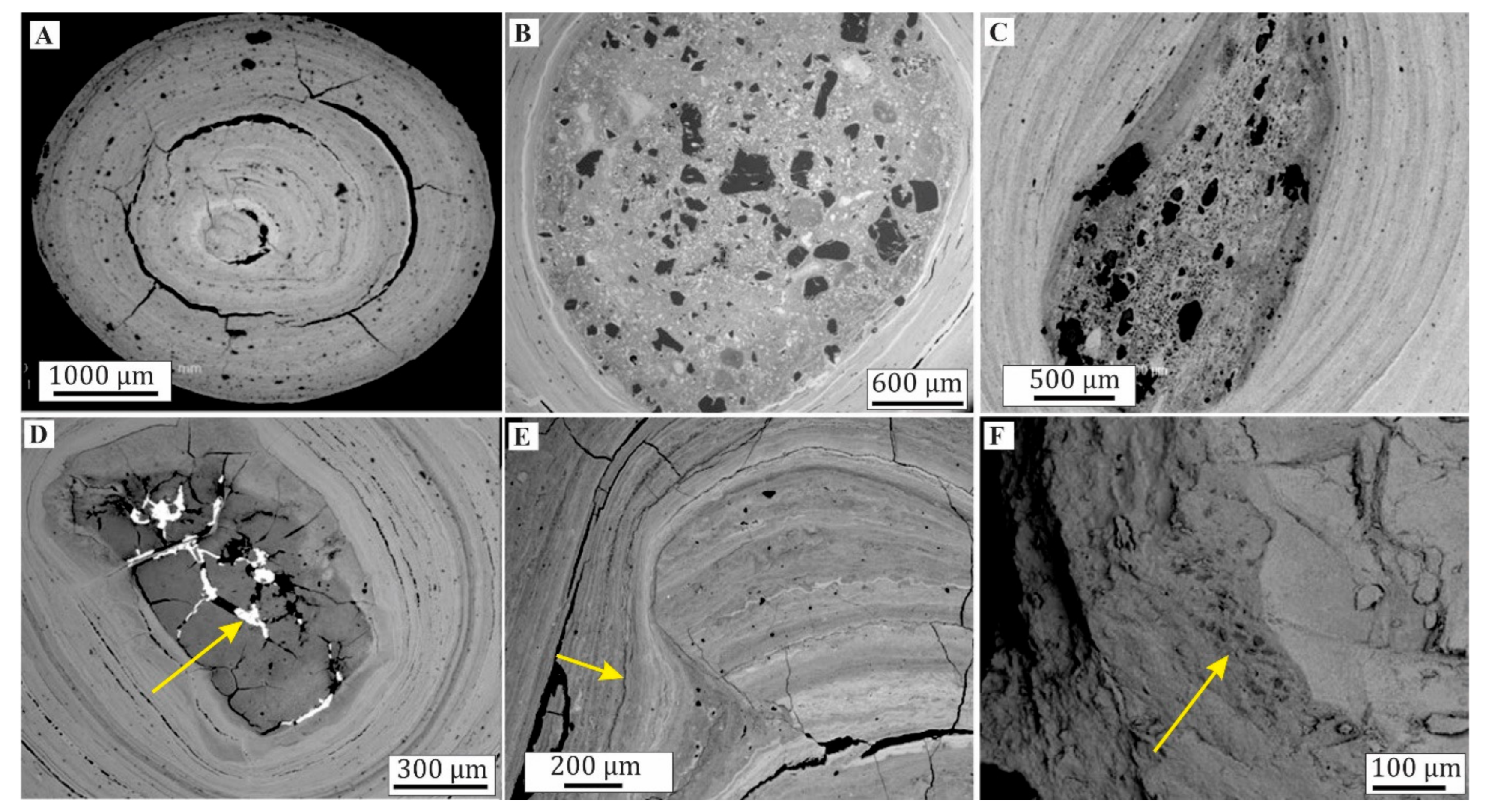
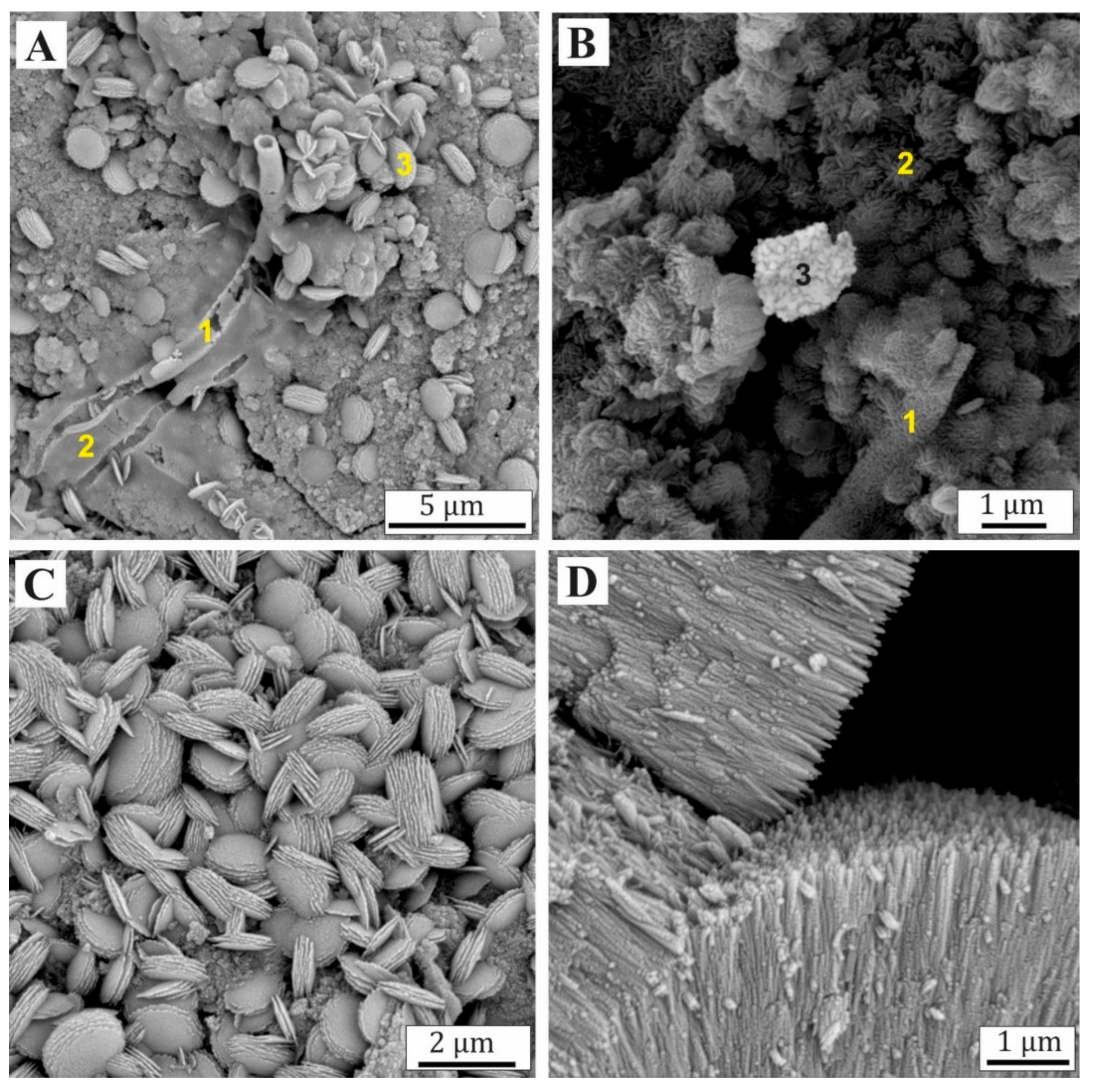
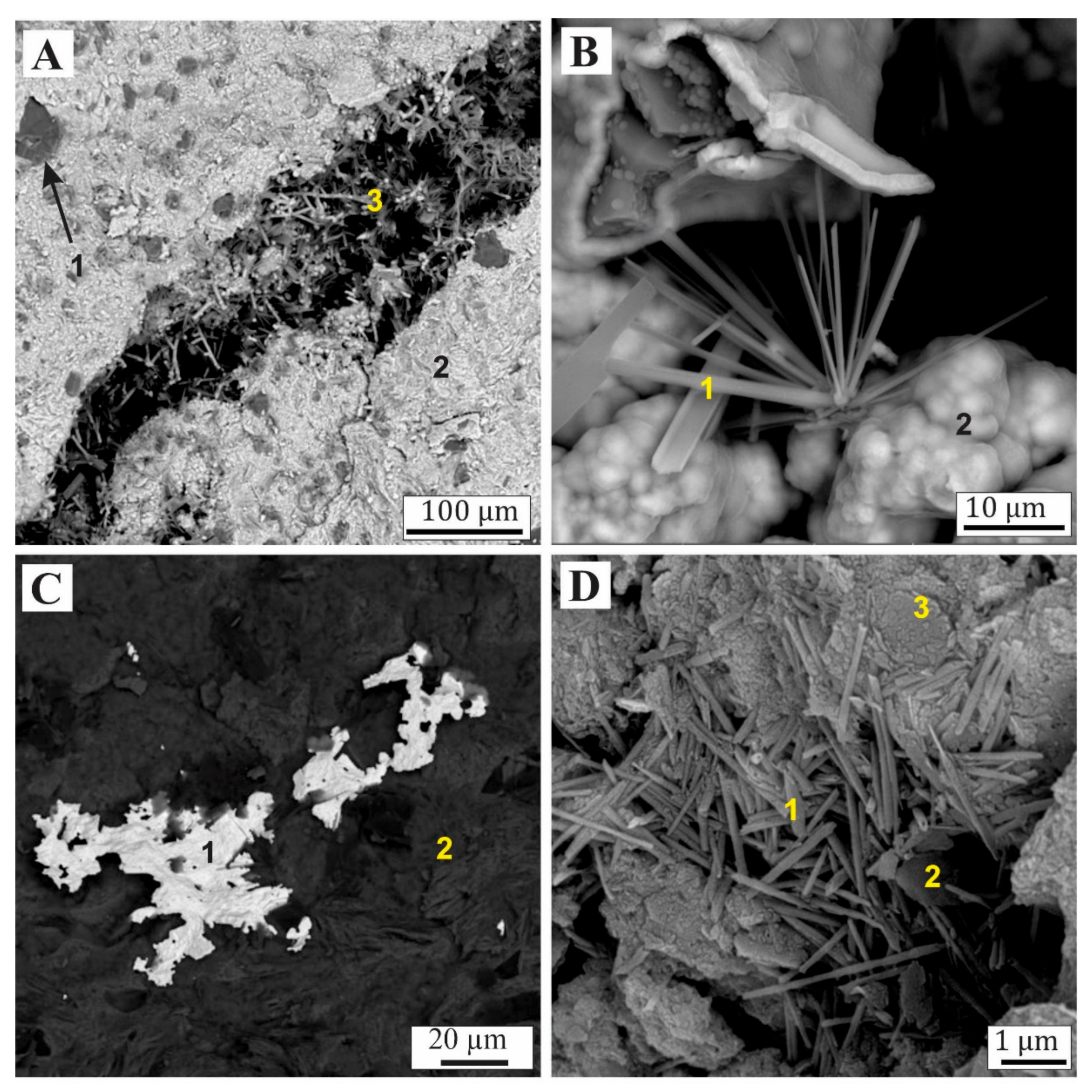
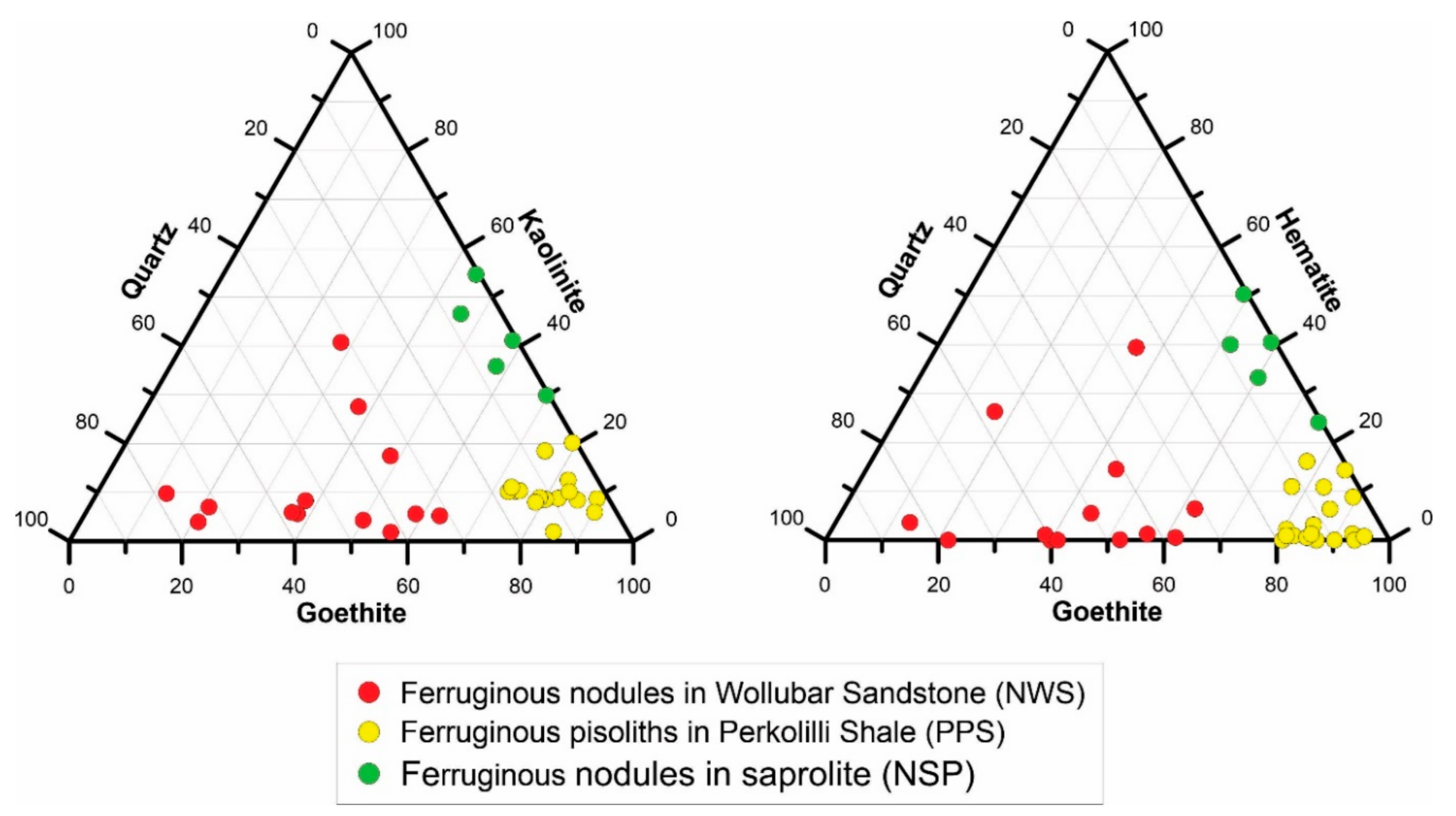
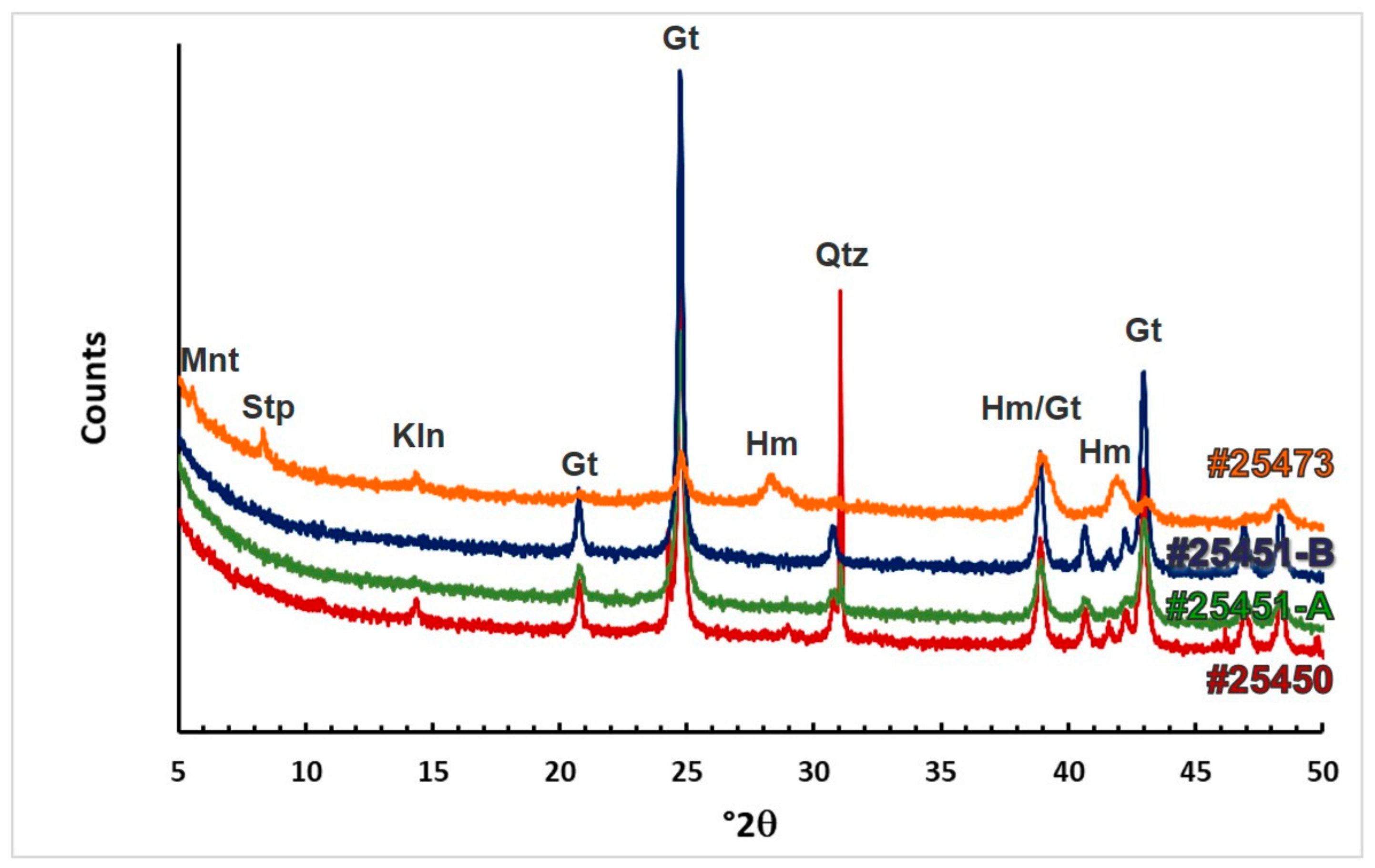
6.3. Mineralogical Differentiation of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths
6.4. Whole-Rock Geochemistry of Selected Ore-Related Elements in the PPS, NWS and NSP
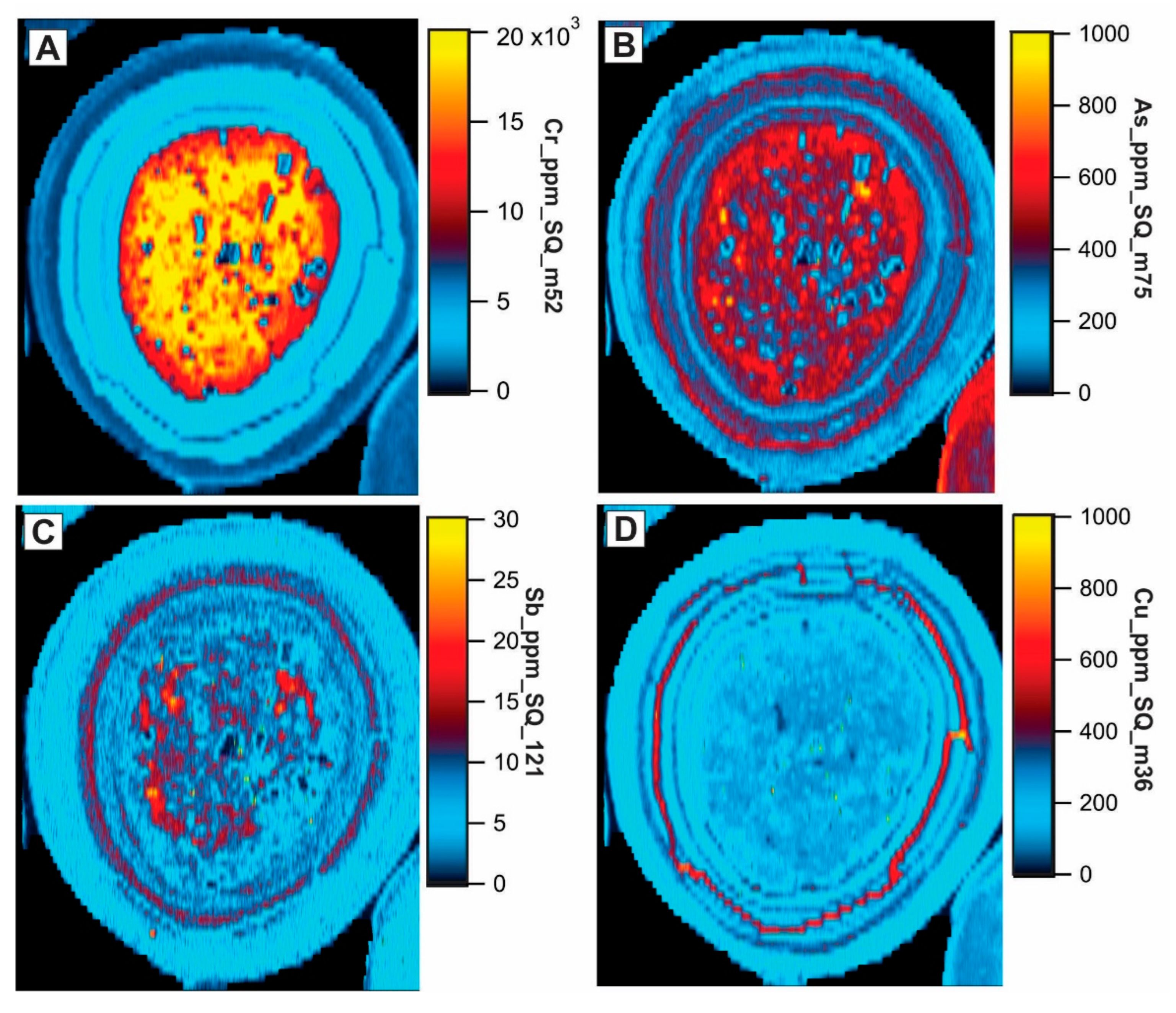
6.5. Laser Ablation ICP-MS Mapping of Elements
6.6. Mineralogy of Dated Samples
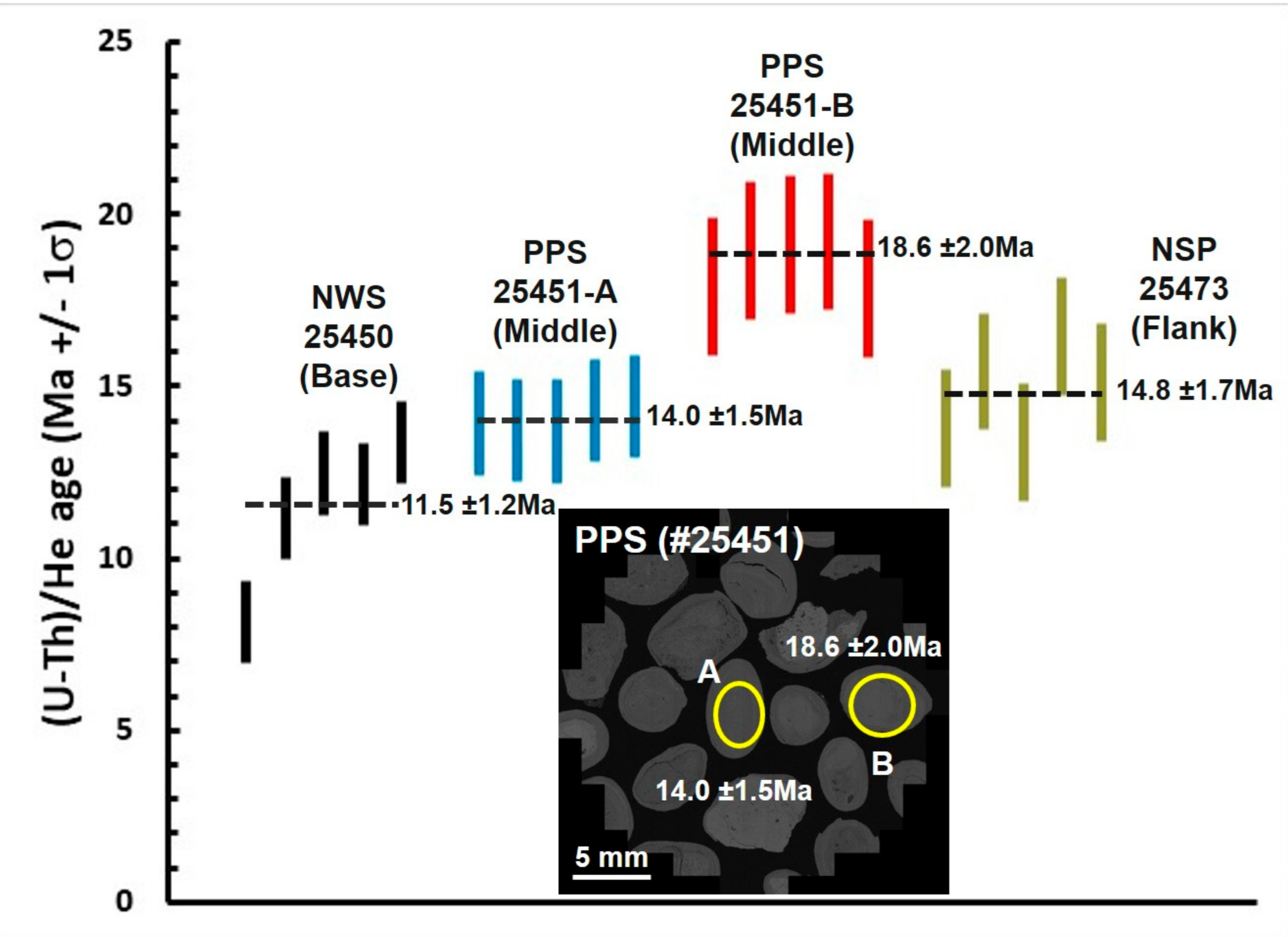
6.7. (U–Th)/He Dating
7. Discussion
7.1. Formation of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths and Landscape Evolution
7.2. Geochemical Dispersion Processes
8. Conclusions and Implications to Exploration
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, R.R.; Paine, M. Regolith geology of the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Implications for exploration. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2002, 49, 3–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidgeon, R.T.; Brander, T.; Lippolt, H.J. Late Miocene (U+Th)–4He ages of ferruginous nodules from lateritic duricrust, Darling Range, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2004, 51, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.; Danišík, M.; McInnes, B.; Morris, P. (U-Th)/He-dating of ferruginous duricrust: Insight into laterite formation at Boddington, WA. Chem. Geol. 2019, 522, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillans, B. Geochronology of the Australian regolith. In Regolith Landscape Evolution Across Australia; Anand, R.R., de Broekert, P., Eds.; CRC LEME: Perth, Australia, 2005; pp. 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, H.S.; Vasconcelos, P.M.; Farley, K.A.; Spier, C.; Mello, C.L. (U–Th)/He geochronology of goethite and the origin and evolution of cangas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 131, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, A.M.; Commander, P. Cainozoic stratigraphy in the Roe Palaeodrainage of the Kalgoorlie region, Western Australia. Prof. Pap. 34 Geol. Surv. West. Aust. 1993, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.D.A. Stratigraphy of the Lefroy and Cowan palaeodrainages, Western Australia. J. Proc. R. Soc. West. Aust. 1993, 76, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- De Broekert, P.; Sandiford, M. Buried inset-valleys in the Eastern Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Geomorphology, age and allogenic control. J. Geol. 2005, 113, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorne, R.; Anand, R.; Suvorova, A. The formation of fluvio-lacustrine ferruginous pisoliths in the extensive palaeochannels of the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Sediment. Geol. 2014, 313, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, R.A. Glossary of Regolith-Surficial Geology, Soils and Landscape; CRC LEME: Perth, Australia, 2001; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Balkau, J.; Walker, D.; McCracken, S.; Hawker, A.; Carver, R.; Taylor, T.; Ion, J. The discovery and resource development of the Moolart Well gold deposit. In Proceedings of the New Generation of Gold Mines Conference (January 2007), Perth, Australia, 15–16 November; Paydirt Media Pty. Ltd.: Perth, Australia, 2007; pp. 833–855. [Google Scholar]
- Geological Survey of Western Australia. East Yilgarn Western Australia 1:100,000 Geological Information Series; Department of Primary Industry and Resources, Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2011. Available online: http://www.dmp.wa.gov.au (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Balkau, J.; French, T.; Ridges, T. Moolart Well, Garden Well and Rosemont gold deposits. In Australian Ore Deposits; Phillips, G.N., Ed.; The Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, Australia, 2017; pp. 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lintern, M.; Anand, R.R.; Reid, N. Exploration Geochemistry at Garden Well Gold Deposit NE Yilgarn Craton (Western Australia); CSIRO Report No EP1310007; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2013; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, K. Development, sedimentation and economic potential of palaeoriver systems of the Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia. Sediment. Geol. 1993, 85, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, I.D.M.; Phang, C.; Munday, T. The regolith geology around the Harmony gold deposit, Peak Hill, W.A. In Proceedings of the Regolith ‘98, New Approaches to an Old Continent, Kalgoorlie, Australia, 2–9 May 1998; Taylor, G., Pain, C., Eds.; CRCLEME: Perth, Australia, 1999; pp. 283–298. [Google Scholar]
- De Broekert, P. Origin of Tertiary Inset-Valleys and Their Fills, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. Ph.D. Thesis, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Geoscience Australia Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of Australia Derived from LiDAR 5 Metre Grid. Available online: https://ecat.ga.gov.au/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/89644 (accessed on 14 November 2020).
- Ubide, T.; McKenna, C.A.; Chew, D.; Kamber, B.S. High-resolution LA-ICP-MS trace element mapping of igneous minerals: In search of magma histories. Chem. Geol. 2015, 409, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, I.; Merigot, K.; McInnes, B.I.A. Application of quantitative mineralogical analysis in archaeological micromorphology: A case study from Barrow Island, Western Australia. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2018, 25, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrstka, T.; Gottlieb, P.; Skála, R.; Breiter, K.; Motl, D. Automated mineralogy and petrology—Applications of TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer (TIMA). J. Geosci. 2018, 63, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danišík, M.; Evans, N.J.; Ramanaidou, E.R.; McDonald, B.J.; Mayers, C.; McInnes, B.I. (U–Th)/He chronology of the Robe River channel iron deposits, Hamersley Province, Western Australia. Chem. Geol. 2013, 354, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Hough, R.; Salama, W.; Aspandiar, M.; Butt, C.; González-Álvarez, I.; Metelka, V. Gold and pathfinder elements in ferricrete gold deposits of the Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: A review with new concepts. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 104, 294–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaidou, E.R.; Wells, M.A.; Morris, R.C.; Duclaux, G.; Evans, N.; Danišík, M. Channel iron deposits of the Pilbara. In Australian Ore Deposits; Phillips, G.N., Ed.; The Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, Australia, 2017; pp. 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R.C.; Ramanaidou, E. Genesis of the channel iron deposits (CID) of the Pilbara region, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 54, 733–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, R.; Schwertmann, U. Al-substituted goethite—An indicator of pedogenic and other weathering environments in South Africa. Geoderma 1982, 27, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.L.; Evans, B.W. Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am. Miner. 2009, 95, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, J.A.; Vasconcelos, P.M.; Shuster, D.L.; Farley, K.A.; Broadbent, G. Dating paleochannel iron ore by (U-Th)/He analysis of supergene goethite, Hamersley province, Australia. Geology 2006, 34, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R. Evolution, classification and use of ferruginous regolith materials in exploration, Yilgarn Craton. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2001, 1, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, S.; Cohen, D.R.; Dunlop, A.C. Characteristics of magnetic and non-magnetic lag in the Cobar area. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 58, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusci, M.E. Regolith-Landform Evolution of the Black Flag Area with Emphasis on the Upper Reaches of the Roe Palaeochannel System, Western Australia. Honours Thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Perth, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Colman, S.M.; Dethier, D.P. Rates of Chemical Weathering of Rocks and Minerals. Soil Sci. 1987, 143, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A.; Achenbach, L.A.; Coates, J.D. Microorganisms pumping iron: Anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 4, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arocena, J.M.; Pawluk, S. The nature and origin of nodules in Podzolic soils from Alberta. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1991, 71, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Karathanasis, A.D. Characterization of iron manganese concretions in Kentucky Alfisols with perched water tables. Clays Clay Miner. 1997, 45, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanin, V.F.; Ivanov, D.E.; Pukhov, D.E.; Shipilin, A.M. Magnetic properties of concretions in surface-gleyed poszolic soils. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2000, 33, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, M.; Vivit, D.; Schulz, C.; Fitzpatrick, J.; White, A. Biological origin of iron nodules in a marine terrace chronosequence, Santa Cruz, California. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R.; Verrall, M. Biological origin of minerals in pisoliths in the Darling Range of Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 58, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A.; Spanbauer, T.; Wacey, D.; Kilburn, M.R.; Loope, D.B.; Kettler, R.M. Biosignature link microorganisms to iron mobilization in a paleoaquifer. Geology 2012, 40, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, A.; Gagen, E.; Shuster, J.; Rintoul, L.; Tobin, M.; Vongsvivut, J.; Bambery, K.; Vasconcelos, P.; Southam, G. Evidence of biogeochemical processes in iron duricrust formation. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2016, 71, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dequincey, O.; Chabaux, F.; Clauer, N.; Sigmarsson, O.; Liewig, N.; Leprun, J.C. Chemical mobilizations in laterites; evidence from trace elements and 238U-234U-230Th disequilibria. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, P.; Heim, J.A.; Farley, K.A.; Monteiro, H.; Waltenberg, K. 40Ar/39Ar and (U–Th)/He – 4He/3He geochronology of landscape evolution and channel iron deposit genesis at Lynn Peak, Western Australia. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.D.; Anand, R.R. Anomalies in insect nest structures at the Garden Well gold deposit: Investigation of mound-forming termites, subterranean termites and ants. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 140, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.M.; Butt, C.R.M.; Fischer-Buhner, J. The crystallography, metallography and composition of Gold. Elements 2009, 5, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.W. Mobility of gold and silver in lateritic weathering profiles; some observations from Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 1984, 79, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, C.R.M. Supergene gold deposits. AGSO J. Geo. Geophys. 1998, 17, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, C.; Lintern, M.; Anand, R. Evolution of regoliths and landscapes in deeply weathered terrain—Implications for geochemical exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2000, 16, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R.; Butt, C. A guide for mineral exploration through the regolith in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 57, 1015–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gleuher, M.; Anand, R.R.; Eggleton, R.A.; Radford, N. Mineral hosts for gold and trace metals in regolith at Boddington gold deposit and Scuddles massive copper–zinc sulphide deposit, Western Australia: An LA-ICP-MS study. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2008, 8, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquin, C.; Freyssinet, P.; Zeegers, H.; Tardy, Y. Element distribution patterns in laterites of southern Mali: Consequence for geochemical prospecting and mineral exploration. Appl. Geochem. 1990, 5, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L. Lateritisation as a major process of ore deposit formation in the Amazon region. Exp. Mining Geol. 1997, 6, 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, C.G. Geochemical exploration challenges in the regolith dominated Igarapé Bahia gold deposit, Carajás, Brazil. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


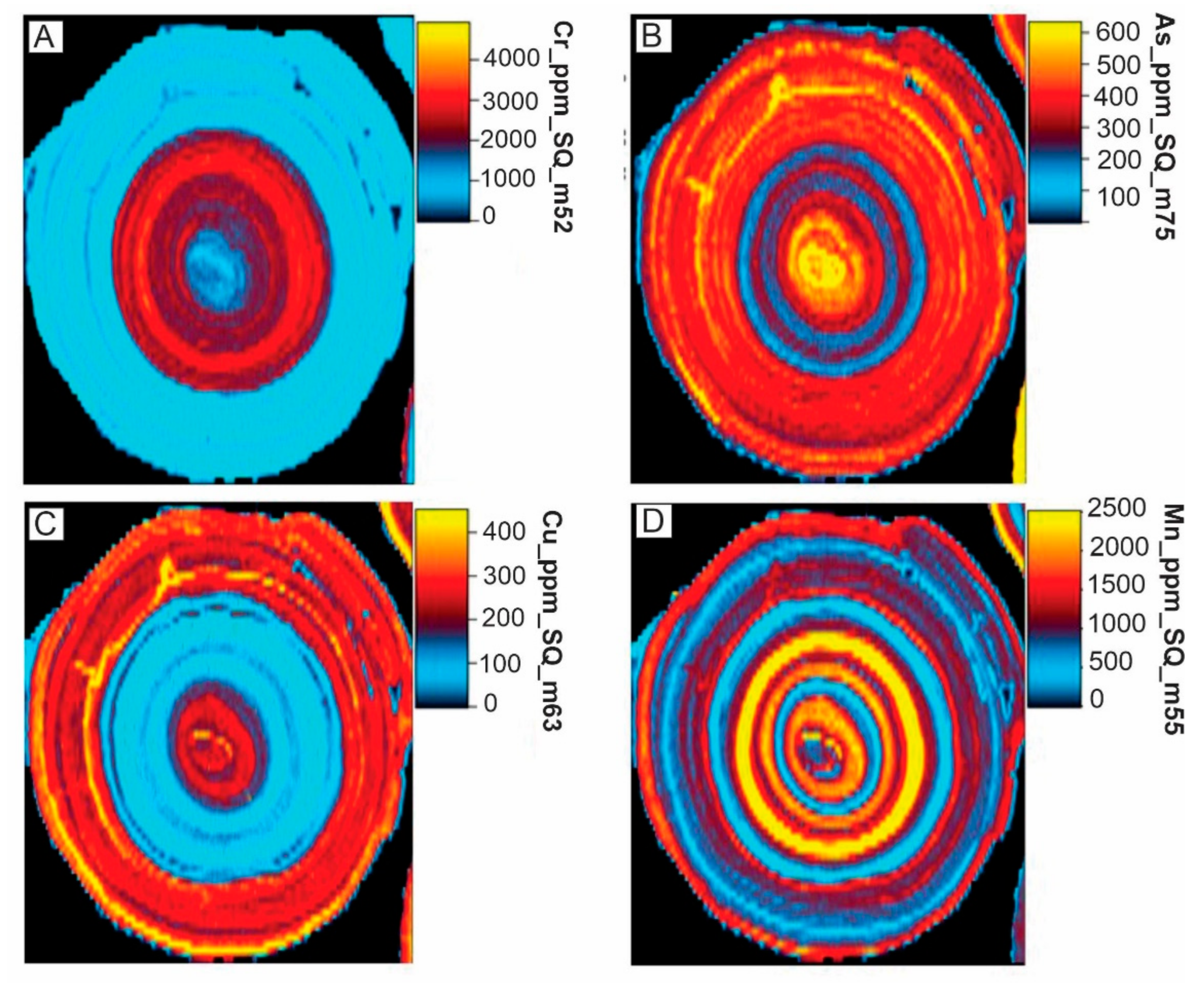




| PPS over Mineralization (N = 11) | PPS over Background (N = 7) | |||||||
| Element | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Min | Max | Mean | Median |
| As-ppm | 151 | 1340 | 330 | 280 | 66 | 129 | 97 | 87 |
| Au-ppb | 4 | 436 | 124 | 68 | 1 | 16.6 | 6.9 | 6.4 |
| Bi-ppm | 0.6 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.48 | 0.5 |
| Cu-ppm | 97 | 381 | 170 | 142 | 52 | 86 | 66 | 63 |
| In-ppm | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.1 |
| S-ppm | 785 | 1310 | 1014 | 1020 | 147 | 505 | 323 | 336 |
| Sb-ppm | 3 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 5.6 | 3.5 | 3 |
| Se-ppm | 1.98 | 4.66 | 3.39 | 3.42 | 1.05 | 1.58 | 1.35 | 1.3 |
| NWS over Mineralization (N = 9) | NWS over Background (N = 4) | |||||||
| Element | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Min | Max | Mean | Median |
| As-ppm | 33 | 5480 | 1124 | 470 | 90 | 1520 | 536 | 268 |
| Au-ppb | 6.6 | 11,700 | 2679 | 515 | 3.6 | 55.4 | 21.7 | 14 |
| Bi-ppm | 0.05 | 2.9 | 0.95 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.17 | 0.1 |
| Cu-ppm | 37 | 1741 | 401 | 249 | 49 | 159 | 84 | 64 |
| In-ppm | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| S-ppm | 201 | 715 | 455 | 456 | 25 | 226 | 131 | 136 |
| Sb-ppm | 2 | 8 | 3.7 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1 |
| Se-ppm | 1 | 15.7 | 4.04 | 1.85 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.64 |
| Sample | Mineralogy |
|---|---|
| NSP (#25473) | Hematite, goethite (maj); kaolinite, stilpnomelane, smectite (min) |
| NWS (#25450) | Goethite (maj); quartz (min); kaolinite, paragonite (tr) |
| PPS (#25451-A) | Goethite (maj); quartz (tr) |
| PPS (#25451-B) | Goethite (maj) |
| Sample | 232Th | ± | 238U | ± | He | ± | TAU# | Th/U | Raw Age | ±1σ | Ft | ± | Cor. Age | ±1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | (ng)* | (%) | (ng) | (%) | (ncc)^ | (%) | (%) | (Ma) | (Ma) | (%) | (Ma) | (Ma) | ||
| NWS | ||||||||||||||
| 25450-1 | 0.010 | 2.5 | 0.079 | 2.8 | 0.081 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 0.13 | 8.2 | 0.3 | 1.00 | 10 | 8.2 | 0.9 |
| 25450-2 | 0.007 | 5.7 | 0.110 | 2.2 | 0.151 | 2.7 | 3.5 | 0.07 | 11.2 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 11.2 | 1.2 |
| 25450-3 | 0.012 | 4.2 | 0.116 | 2.2 | 0.181 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 0.10 | 12.5 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 12.5 | 1.3 |
| 25450-4 | 0.006 | 8.3 | 0.105 | 2.3 | 0.157 | 2.7 | 3.5 | 0.05 | 12.1 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 12.1 | 1.3 |
| 25450-5 | 0.003 | 2.5 | 0.055 | 2.8 | 0.091 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 0.05 | 13.4 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.4 | 1.4 |
| 11.5 | 1.2 | |||||||||||||
| PPS | ||||||||||||||
| 25451-A-1 | 0.192 | 1.7 | 0.328 | 2.3 | 0.634 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 0.58 | 13.9 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.9 | 1.5 |
| 25451-A-2 | 0.361 | 1.7 | 0.422 | 2.2 | 0.848 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 0.85 | 13.7 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.7 | 1.4 |
| 25451-A-3 | 0.451 | 1.7 | 0.677 | 2.2 | 1.305 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 0.66 | 13.7 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.7 | 1.4 |
| 25451-A-4 | 0.702 | 2.5 | 0.687 | 2.8 | 1.484 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 1.02 | 14.3 | 0.5 | 1.00 | 10 | 14.3 | 1.5 |
| 25451-A-5 | 0.679 | 1.7 | 0.669 | 2.3 | 1.455 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 1.01 | 14.4 | 0.5 | 1.00 | 10 | 14.4 | 1.5 |
| 14.0 | 1.5 | |||||||||||||
| PPS | ||||||||||||||
| 25451-B-1 | 0.053 | 2.0 | 0.417 | 2.3 | 0.936 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 0.13 | 17.9 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 10 | 17.9 | 1.9 |
| 25451-B-2 | 0.104 | 1.8 | 0.254 | 2.2 | 0.642 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 0.41 | 19.0 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 10 | 19.0 | 2.0 |
| 25451-B-3 | 0.033 | 2.6 | 0.231 | 2.8 | 0.557 | 2.6 | 3.8 | 0.14 | 19.1 | 0.7 | 1.00 | 10 | 19.1 | 2.0 |
| 25451-B-4 | 0.118 | 1.8 | 0.364 | 2.2 | 0.917 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 0.32 | 19.2 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 10 | 19.2 | 2.0 |
| 25451-B-5 | 0.048 | 2.0 | 0.405 | 2.3 | 0.904 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 0.12 | 17.8 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 10 | 17.8 | 1.9 |
| 18.6 | 2.0 | |||||||||||||
| NSP | ||||||||||||||
| 25473-1 | 0.203 | 1.7 | 0.073 | 2.3 | 0.203 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 2.75 | 13.8 | 0.7 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.8 | 1.6 |
| 25473-2 | 0.196 | 2.4 | 0.052 | 2.8 | 0.185 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 3.74 | 15.4 | 0.8 | 1.00 | 10 | 15.4 | 1.8 |
| 25473-3 | 0.122 | 1.8 | 0.038 | 2.6 | 0.108 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 3.23 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 1.00 | 10 | 13.4 | 1.5 |
| 25473-4 | 0.084 | 1.8 | 0.096 | 2.3 | 0.232 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 0.87 | 16.5 | 0.9 | 1.00 | 10 | 16.5 | 1.9 |
| 25473-5 | 0.063 | 1.9 | 0.196 | 2.3 | 0.387 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 0.32 | 15.1 | 0.8 | 1.00 | 10 | 15.1 | 1.7 |
| 14.8 | 1.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anand, R.R.; Wells, M.A.; Lintern, M.J.; Schoneveld, L.; Danišík, M.; Salama, W.; Noble, R.R.P.; Metelka, V.; Reid, N. The (U-Th)/He Chronology and Geochemistry of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths Formed in the Paleochannel Environments at the Garden Well Gold Deposit, Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: Implications for Landscape Evolution and Geochemical Exploration. Minerals 2021, 11, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070679
Anand RR, Wells MA, Lintern MJ, Schoneveld L, Danišík M, Salama W, Noble RRP, Metelka V, Reid N. The (U-Th)/He Chronology and Geochemistry of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths Formed in the Paleochannel Environments at the Garden Well Gold Deposit, Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: Implications for Landscape Evolution and Geochemical Exploration. Minerals. 2021; 11(7):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070679
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnand, Ravi R., Martin A. Wells, Melvyn J. Lintern, Louise Schoneveld, Martin Danišík, Walid Salama, Ryan R. P. Noble, Vasek Metelka, and Nathan Reid. 2021. "The (U-Th)/He Chronology and Geochemistry of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths Formed in the Paleochannel Environments at the Garden Well Gold Deposit, Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: Implications for Landscape Evolution and Geochemical Exploration" Minerals 11, no. 7: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070679
APA StyleAnand, R. R., Wells, M. A., Lintern, M. J., Schoneveld, L., Danišík, M., Salama, W., Noble, R. R. P., Metelka, V., & Reid, N. (2021). The (U-Th)/He Chronology and Geochemistry of Ferruginous Nodules and Pisoliths Formed in the Paleochannel Environments at the Garden Well Gold Deposit, Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: Implications for Landscape Evolution and Geochemical Exploration. Minerals, 11(7), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070679








