Ultrasound in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Diseases: Own Experiences and a Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Technical Aspects
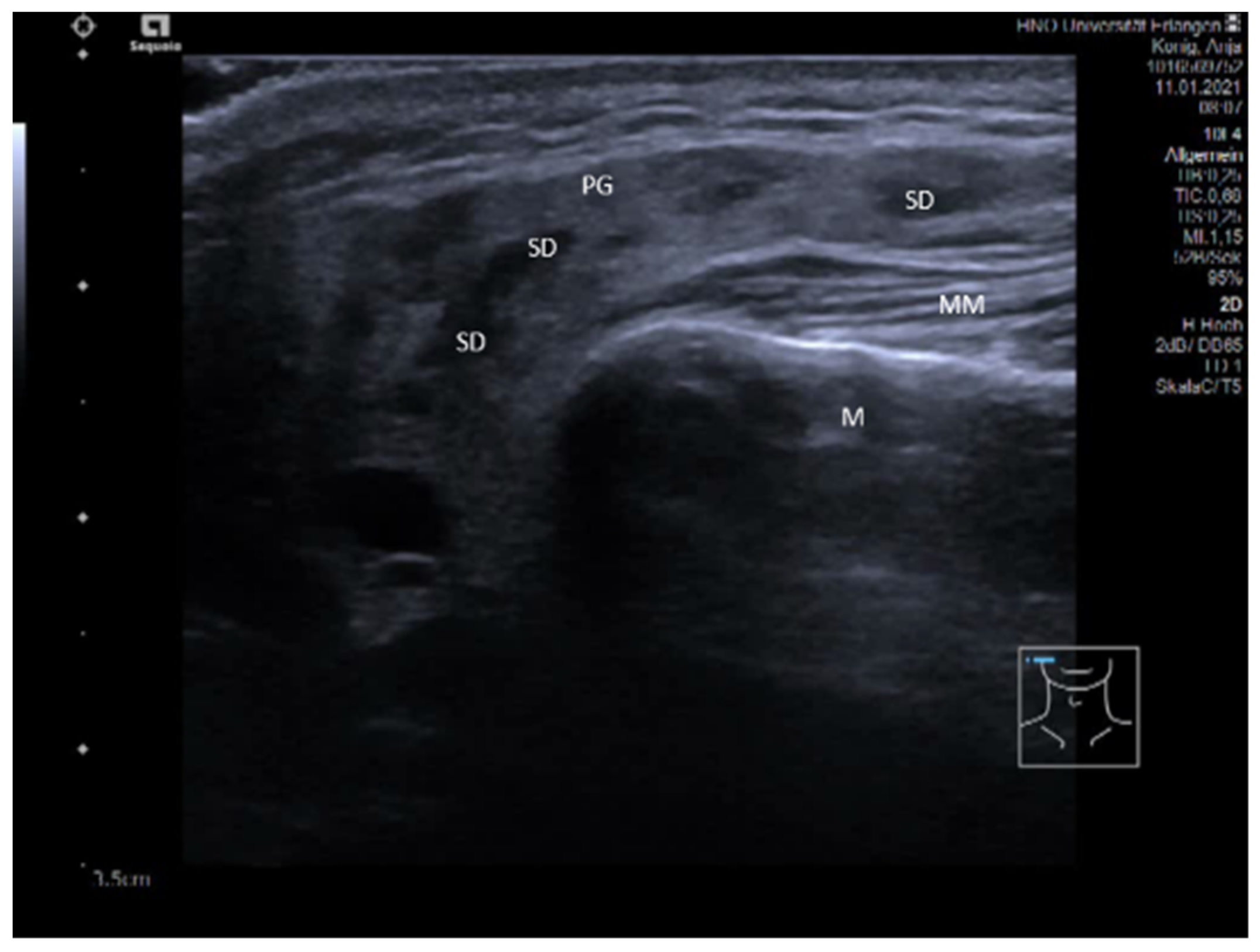
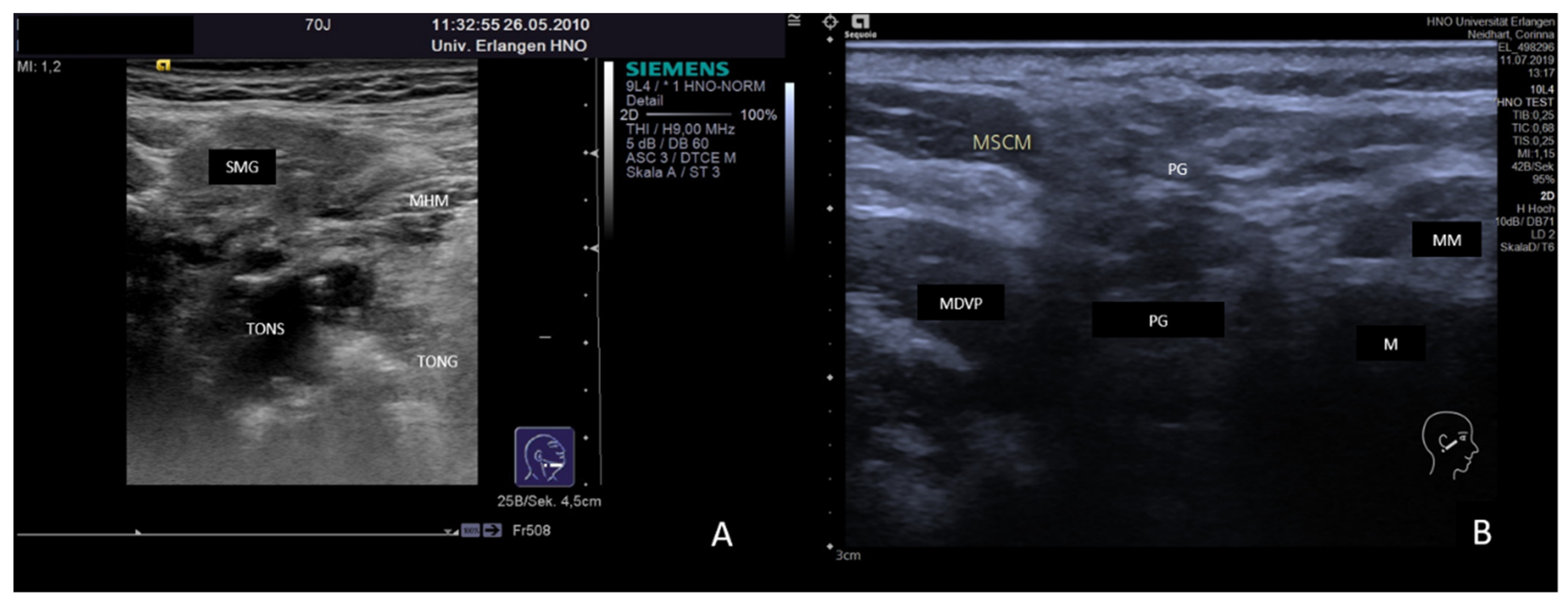
3.2. Findings in Normal Anatomy in Major Salivary Glands
3.3. Ultrasonographic Signs of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory and Obstructive Sialadenitis
3.3.1. Acute or Subacute Primary Non-Obstructive Microbial Sialadenitis
3.3.2. Obstructive Sialadenitis Caused by Sialolithiasis
3.3.3. Non-Sialolithiasis-Caused Unspecific Sialadenitis with Sialodochitis and/or Duct Stenosis with Primary or Secondary Obstruction
3.4. Disease-Associated Inflammatory Sialadenitis with Sialodochitis (and Possible Secondary Obstruction)
3.4.1. Chronic fibrinous Sialodochitis
3.4.2. Chronic Recurrent Juvenile Parotitis
3.4.3. Sjoegren’s Syndrome/Disease
3.4.4. IgG4-Associated Involvement of Salivary Glands
3.4.5. Sarcoidosis with Sialadenitis
3.5. Ultrasound in Monitoring Gland Function at the Follow-up Examination in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Disease
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, S.; Ossoinig, K.C. Ultrasonic evaluation of salivary glands. Trans. Sect. Otolaryngol. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1977, 84 Pt 1, 750–762. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Kohirazawa, H.; Tomita, K. Ultrasonographic analysis of diseases requiring oral surgery. Shikai Tenbo 1984, 63, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwerk, W.B.; Schroeder, H.G.; Eichhorn, T. High-resolution real-time sonography in salivary gland diseases. I: Inflammatory diseases. HNO 1985, 33, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wittich, G.R.; Scheible, W.F.; Hajek, P.C. Ultrasonography of the salivary glands. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 1985, 23, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rengo, S.; De Fazio, P.; Fortunato, L.; Mignogna, A.; Di Capua, V.; Rengo, C. Diagnosis of sialopathies. I. Echography. Minerva Stomatol. 1986, 35, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohndorf, K.; Lonnecken, I.; Zanella, F.; Lanfermann, L. Value of sonography and sialography in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Rofo 1987, 147, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurawitzki, H.; Gritzmann, N.; Fezoulidis, J.; Karnel, F.; Kramer, J. Value and indications for high-resolution real-time sonography in nontumor salivary gland diseases. Rofo 1987, 146, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, W. Ultrasonic diagnosis. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. Suppl. 1989, 1, 71–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gritzmann, N. Sonography of the salivary glands. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1989, 153, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovic, N.; Cvetinovic, M.; Mijatovic, D.; Stosic, S. Value of ultrasound and sialography in diagnosis of chronic inflammatory diseases of the parotid salivary glands. Dtsch. Stomatol. 1990, 40, 498–500. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, P. Value of echography in salivary pathology. J. Radiol. 1991, 72, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schemelzeisen, R.; Milbradt, H.; Reimer, P.; Gratz, P.; Wittekind, C. Sonography and scintigraphy in the diagnosis of diseases of the major salivary glands. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1991, 49, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxler, M.; Schurawitzki, H.; Ulm, C.; Solar, P.; Blahout, R.; Piehslinger, E.; Schadlbauer, E. Sonography of nonneoplastic disorders of the salivary glands. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 21, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneton, J.N.; Mourou, M.Y. Ultrasound in salivary gland disease. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 1993, 55, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausegger, K.W.; Krasa, H.; Pelzmann, W.; Grasser, R.K.; Frisch, C.; Simon, H. Sonography of the salivary glands. Ultraschall Med. 1993, 14, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, G.; Ouimet-Oliva, D.; Nicolet, V.; Bourdon, F. Imaging of the salivary glands. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 1993, 44, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kordylewska, M.; Dziamska, K.; Citowicki, W. The ultrasound examination of salivary gland. Otolaryngol. Pol. 1993, 47, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiurin, E.I.; Dobromyslova, N.A.; Matina, V.N. Comprehensive radiologic examination in the diagnosis of parotid salivary gland diseases. Vestn. Rentgenol. Radiol. 1993, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, E. Ultrasound imaging of the salivary glands. Radiologe 1994, 34, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinoli, C.; Derchi, L.E.; Solbiati, L.; Rizzatto, G.; Silvestri, E.; Giannoni, M. Color Doppler sonography of salivary glands. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 163, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritzmann, N.; Rettenbacher, T.; Hollerweger, A.; Macheiner, P.; Hubner, E. Sonography of the salivary glands. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyas, F.; Lewis, K.; Williams, M.; Moody, A.B.; Wong, K.T.; Ahuja, A.T.; Howlett, D.C. Diseases of the submandibular gland as demonstrated using high resolution ultrasound. Br. J. Radiol. 2005, 78, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaleska-Dorobisz, U.; Kuzniar, J.; Badowski, R.; Cudenko, R.; Pospiech, L.; Moron, K. Usefulness of imaging in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski 2005, 19, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bialek, E.J.; Jakubowski, W.; Zajkowski, P.; Szopinski, K.T.; Osmolski, A. US of the major salivary glands: Anatomy and spatial relationships, pathologic conditions, and pitfalls. Radiographics 2006, 26, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Argalia, G.; Salera, D.; Giuseppetti, G.M.; Grassi, W. Usefulness of ultrasonography and color Doppler sonography in the diagnosis of major salivary gland diseases. Reumatismo 2006, 58, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalma, J.; Olasz, L.; Toth, M.; Acs, P.; Szabo, G. Diagnostic value of radiographic and ultrasonic examinations in patients with sialoadenitis and sialolithiasis. Fogorv. Sz. 2007, 100, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, R. Clinic and ultrasound of salivary gland diseases—Part I. Praxis 2008, 97, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, R. Clinic and ultrasound of salivary gland diseases—Part II. Praxis 2008, 97, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritzmann, N. Ultrasound of the salivary glands. Laryngorhinootologie 2009, 88, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, P.; Hartl, D.M.; Guerre, A. Clinical ultrasound of the salivary glands. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 42, 973–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenk, J.; Iro, H.; Klintworth, N.; Lell, M. Diagnostic imaging in sialadenitis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 21, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.J.; Thomas, R.H.; Howlett, D. Imaging the major salivary glands. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 49, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanchuk, V.A.; Pererva, V.V.; Loganovskaia, E.N.; Guch, A.A. Early differential diagnostics of sialadenitis in the parotid salivary glands by ultrasonography methods. Lik. Sprava 2013, 5, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Onkar, P.M.; Ratnaparkhi, C.; Mitra, K. High-frequency ultrasound in parotid gland disease. Ultrasound Q. 2013, 29, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, M.A.; Pistorio, V.; Guerra, P.A. Ultrasound in sialadenitis. J. Ultrasound 2013, 16, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengel, P.; Schrotzlmair, F.; Reichel, C.; Paprottka, P.; Clevert, D.A. Sonography: The leading diagnostic tool for diseases of the salivary glands. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2013, 34, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandage, S.G.; Kachewar, S.G. An Imaging Panorama of Salivary Gland Lesions as seen on High Resolution Ultrasound. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, RC01–RC13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotti, M.; Ciapetti, A.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; Salaffi, F. Ultrasonography of the salivary glands: The role of grey-scale and colour/power Doppler. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. S80), S61–S70. [Google Scholar]
- Ugga, L.; Ravanelli, M.; Pallottino, A.A.; Farina, D.; Maroldi, R. Diagnostic work-up in obstructive and inflammatory salivary gland disorders. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.S.S.; Dai, Y.L. Routine and Advanced Ultrasound of Major Salivary Glands. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.T.; Pagedar, N.A. Ultrasound-Guided Salivary Gland Techniques and Interpretations. Atlas. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, K.; Fukuhara, T.; Matsuda, E.; Donishi, R.; Hirooka, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Kato, M. Impact of Screening for Salivary Gland by Ultrasonography. Yonago Acta Med. 2020, 63, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederich, S.; Roos, N.; Bick, U.; Hidding, J.; Birke, D. Diagnostic imaging of the salivary glands in children and adolescents. Radiologe 1991, 31, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben Kheder, N.; Daghfous, M.H.; Chebbi, K.; Nagi, S.; Hached, M.; Ben Hajel, H. Echography and lithiasis of the submaxillary glands. Tunis. Med. 1993, 71, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.J.; Flores, P.A.; Arce, J.D.; Chuaqui, B.; Schwartz, D.S. Ultrasonography in the study of salivary gland lesions in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 1998, 28, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Ussmuller, J.; Donath, K.; Yoshiura, K.; Ban, S.; Kanda, S.; Ozeki, S.; Shinohara, M. Sonographic analysis of recurrent parotitis in children: A comparative study with sialographic findings. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 86, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlieli, O.; Eliav, E.; Hasson, O.; Zagury, A.; Baruchin, A.M. Pediatric sialolithiasis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 90, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlieli, O.; Shacham, R.; Shlesinger, M.; Eliav, E. Juvenile recurrent parotitis: A new method of diagnosis and treatment. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Bijoor, R. Imaging (computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, sialography) in a case of recurrent parotitis in children. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitheeque, M.; Sivachandran, Y.; Varathan, V.; Ariyawardana, A.; Ranasinghe, A. Juvenile recurrent parotitis: Clinical, sialographic and ultrasonographic features. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2007, 17, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerena, J.; Sancho, M.A.; Caceres, F.; Krauel, L.; Parri, F.; Morales, L. Salivary calculi in children. Cir. Pediatr. 2007, 20, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Quenin, S.; Plouin-Gaudon, I.; Marchal, F.; Froehlich, P.; Disant, F.; Faure, F. Juvenile recurrent parotitis: Sialendoscopic approach. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, Z.T.; Goud, A.R.; Lowe, L.H.; Shao, L. Pediatric salivary gland imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2009, 39, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, S.; Giordano, J.; La Tona, G.; De Grazia, E.; Barresi, B.; Lo Casto, A. Pediatric sialolithiasis distinctive characteristic in radiological imaging. Minerva Stomatol. 2011, 60, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, K.S.; Bartlett, M.; Prabhu, N.K. Role of high resolution ultrasound in parotid lesions in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 75, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Gonzalez, J.C.; Monteagudo, I.; Bello, N.; Martinez-Estupinan, L.; Naredo, E.; Carreno, L. Salivary gland ultrasound in children: A useful tool in the diagnosis of juvenile Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schorr, B.; Mandel, L. Diagnosing Juvenile Recurrent Parotitis. Case Reports. N. Y. State Dent. J. 2016, 82, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capaccio, P.; Canzi, P.; Gaffuri, M.; Occhini, A.; Benazzo, M.; Ottaviani, F.; Pignataro, L. Modern management of paediatric obstructive salivary disorders: Long-term clinical experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioz Habibi, H.; Memis Durmaz, E.S.; Qarayeva, V.; Kandemirli, S.G.; Kalyoncu Ucar, A.; Aslan, M.; Apaydin, G.; Kurugoglu, S.; Adaletli, I. Quantitative Assessment of Thyroid, Submandibular, and Parotid Glands Elasticity With Shear-Wave Elastography in Children. Ultrasound Q. 2018, 34, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, E.; Patino, M.O.; Udayasankar, U.K. Imaging of Pediatric Salivary Glands. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guissa, V.R.; Martinelli, E.L.; Brandao, L.; Garcia, L.D.; Provenza, J.R.; Mendonca, J.A. Sonographic evaluation of salivary glands in juvenile Sjogren’s syndrome. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2018, 43, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Aburiziza, A.J. Primary Juvenile Sjogren’s Syndrome in a 3-Year-Old Pediatric Female Patient: Diagnostic Role of Salivary Gland Ultrasonography: Case Report. Open Access Rheumatol. 2020, 12, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.T.; Dai, E.Y.L.; Tang, E.W.K.; Cho, C.C.M.; Wong, K.T. Diagnostic ultrasound: Head and Neck, 2nd ed.; Ahuja, A.T., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-323-62572-2. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich Iro, H.; Bozzato, A.; Zenk, J. Atlas of Head and Neck Ultrasound, 1st ed.; Iro, H., Bozzato, A., Zenk, J., Eds.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vogl, T.J.; Al-Nawas, B.; Beutner, D.; Geisthoff, U.; Gutinas-Lichius, O.; Naujoks, C.; Reich, R.; Schroder, U.; Sproll, C.; Teymoortash, A.; et al. Updated S2K AWMF guideline for the diagnosis and follow-up of obstructive sialadenitis--relevance for radiologic imaging. Rofo 2014, 186, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nawas, B.; Beutner, D.; Geisthoff, U.; Naujoks, C.; Reich, R.; Schroder, U.; Sproll, C.; Teymoortash, A.; Ussmuller, J.; Vogl, T.; et al. The new S2k AWMF guideline for the treatment of obstructive sialadenitis in commented short form. Laryngorhinootologie 2014, 93, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustabasioglu, F.E.; Korkmaz, S.; Ilgen, U.; Solak, S.; Kula, O.; Turan, S.; Emmungil, H. Quantitative Assessment of Salivary Gland Parenchymal Vascularization Using Power Doppler Ultrasound and Superb Microvascular Imaging: A Potential Tool in the Diagnosis of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Balkan Med. J. 2020, 37, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengel, P.; Berghaus, A.; Weiler, C.; Reiser, M.; Clevert, D.A. Intraductally applied contrast-enhanced ultrasound (IA-CEUS) for evaluating obstructive disease and secretory dysfunction of the salivary glands. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedek, V.; Clevert, D.A.; Rytvina, M.; Ihrler, S.; Klotz, L.V.; Berghaus, A.; Strieth, S. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for monitoring effects of extracorporeal shock wave sialolithotripsy in sialolithiasis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedek, V.; Rytvina, M.; Klotz, L.V.; Berghaus, A.; Clevert, D.A.; Strieth, S. Validation of contrast-enhanced ultrasound-derived intensity-time gradients in submandibular gland sialolithotomy patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jecker, P.; Pfeiffer, J. Lesions of the submandibular glands-contrast-enhanced ultrasound for non-invasive diagnosis. Laryngorhinootologie 2014, 93, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strieth, S.; Siedek, V.; Rytvina, M.; Gurkov, R.; Berghaus, A.; Clevert, D.A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound for differential diagnosis of submandibular gland disease. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluzny, J.; Wierzbicka, M.; Kopec, T.; Szyfter, W.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Stangierski, A.; Gurgul, E.; Ruchala, M.; Milecki, P. The sonoelastography of major salivary glands in chosen pathological conditions. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2012, 66 (Suppl. S4), 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengel, P.; Schrotzlmair, F.; Schwarz, F.; Paprottka, P.; Kramer, M.; Berghaus, A.; Clevert, D.A. Elastography: A new diagnostic tool for evaluation of obstructive diseases of the salivary glands; primary results. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 50, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badea, A.F.; Tamas Szora, A.; Ciuleanu, E.; Chioreanu, I.; Baciut, G.; Lupsor Platon, M.; Badea, R. ARFI quantitative elastography of the submandibular glands. Normal measurements and the diagnosis value of the method in radiation submaxillitis. Med. Ultrason. 2013, 15, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashiri, S.Y.; Nishino, A.; Nakamura, H.; Origuchi, T.; Aoyagi, K.; Kawakami, A. The stiff elastographic change of submandibular glands rapidly improves after the introduction of glucocorticoid treatment in patients with IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengel, P.; Reichel, C.A.; Vincek, T.; Clevert, D.A. Ultrasound elastography in diagnosis and follow-up for patients with chronic recurrent parotitis. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2017, 67, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura-Hayama, E.; Criales-Vera, S.; Azpeitia-Espinosa, L.; Pacheco-Molina, C.; Reyes, E.; Lima, G.; Hernandez-Ramirez, D.; Llorente, L.; Hernandez-Molina, G. Elastographic ultrasound: An additional image tool in Sjogren’s syndrome. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, C.A.; Vincek, T.; Gellrich, D.; Schrotzlmair, F.; Clevert, D.; Zengel, P. Ultrasound elastography in diagnosis and follow-up for patients with sialolithiasis. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2018, 47, 20170424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeblawy, Y.M.; Eshaq Amer Mohamed, M. Strain and shear wave ultrasound elastography in evaluation of chronic inflammatory disorders of major salivary glands. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2020, 49, 20190225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.M.; Wen, M.H.; Hsu, W.L.; Chang, C.M.; Hou, P.Y.; Liao, L.J. Ultrasonographic and elastographic biometry in adult major salivary glands: A preliminary case-control report. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheipers, U.; Konig, K.; Sommerfeld, H.J.; Garcia-Schurmann, M.; Senge, T.; Ermert, H. Sonohistology-ultrasonic tissue characterization for prostate cancer diagnostics. Cancer Biomark. 2008, 4, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheipers, U.; Siebers, S.; Gottwald, F.; Ashfaq, M.; Bozzato, A.; Zenk, J.; Iro, H.; Ermert, H. Sonohistology for the computerized differentiation of parotid gland tumors. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Escudier, M.P.; Whaites, E.J.; Drage, N.A.; Ng, S.Y. Intra-oral ultrasound imaging of a submandibular duct calculus. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 1997, 26, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.; Lim, D.; Park, H. Transoral sonographic diagnosis of submandibular duct calculi. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2014, 42, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapher, M.; Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Transoral ultrasound: A helpful and easy diagnostic method in obstructive salivary gland diseases. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3635–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, K.; Nakhyama, E.; Ban, S.; Kawazu, T.; Chikui, T.; Shimizu, M.; Kanda, S. Submandibular gland duct endoscopy. Diagnostic value for salivary duct disorders in comparison to conventional radiography, sialography, and ultrasonography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1997, 84, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadel, A.; Wagner, W. Ultrasound diagnosis as a complement to sialography. Laryngol. Rhinol. Otol. 1986, 65, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, S.; Wernecke, K.; Peters, P.E. Sialographic and sonographic diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Radiologe 1987, 27, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.X. Comparison of the diagnostic value between sialography and ultrasonography in salivary lesions (analysis of 101 cases). Zhonghua Fang She Xue Za Zhi 1987, 21, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Landwehr, P.; Hohmann, D.; Krahe, T.; Lackner, K. The value of digital subtraction sialography compared to conventional sialography, salivary gland sonography and surgical findings. Rofo 1992, 156, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccio, P.; Cuccarini, V.; Ottaviani, F.; Minorati, D.; Sambataro, G.; Cornalba, P.; Pignataro, L. Comparative ultrasonographic, magnetic resonance sialographic, and videoendoscopic assessment of salivary duct disorders. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2008, 117, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, E.; Schulz, H.G.; Neumann, T. Diagnosis of diseases of the large salivary glands of the head by ultrasound, sialography and CT-sialography. A comparison of methods. HNO 1993, 41, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.E.; Buckenham, T.M.; Joseph, A.E. The role of ultrasound in screening patients referred for sialography: A possible protocol. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1996, 21, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbaren, P.; Ducommun, J.C. Diagnosis of salivary gland disease using ultrasound and sialography: A comparison. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1989, 14, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, I.; Esmer, N.; Gerceker, M.; Aytac, S.; Erden, I.; Akan, H. Sialographic and ultrasonographic analyses of major salivary glands. Acta Otolaryngol. 1991, 111, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pniak, T.; Strympl, P.; Stanikova, L.; Zelenik, K.; Matousek, P.; Kominek, P. Sialoendoscopy, sialography, and ultrasound: A comparison of diagnostic methods. Open Med. 2016, 11, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frallonardo, P.; Ramonda, R.; Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Andretta, M.; Zucchetta, P.; Dorigo, A.; Campana, C.; Contessa, C.; Iagnocco, A.; et al. Sjogren’s syndrome: Comparison among the main imaging techniques in the study of major salivary glands. Reumatismo 2008, 60, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.W.; Douglas, J.E.; Rassekh, C.H. Accuracy of Ultrasonography and Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Patients Undergoing Sialendoscopy for Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.; Kabbasch, C.; Scheer, M.; Mikolajczak, S.; Beutner, D.; Luers, J.C. Comparative analysis of sialendoscopy, sonography, and CBCT in the detection of sialolithiasis. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, F.; Sumbullu, M.A.; Miloglu, O.; Akgul, H.M. Are all soft tissue calcifications detected by cone-beam computed tomography in the submandibular region sialoliths? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, e1531–e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, L.; Menauer, F.; Holzknecht, N.; Scholz, V.; Grevers, G.; Reiser, M. Sialolithiasis: MR sialography of the submandibular duct--an alternative to conventional sialography and US? Radiology 2000, 216, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Schapher, M.L.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Goncalves, M.; Iro, H. Simultaneous Application of Ultrasound and Sialendoscopy and its Value in the Management of Sialolithiasis. Ultraschall Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Schapher, M.; Goncalves, M.; Iro, H.; Mantsopoulos, K. Simultaneous application of ultrasound and sialendoscopy: Experience in the management of stenosis and other non-sialolithiasis-related salivary gland disorders. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, A.R.; Aubin-Pouliot, A.; Delagnes, E.; Zheng, M.; Chang, J.L.; Ryan, W.R. Surgeon-Performed Ultrasound for Chronic Obstructive Sialadenitis Helps Predict Sialendoscopic Findings and Outcomes. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 157, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzato, A.; Hertel, V.; Bumm, K.; Iro, H.; Zenk, J. Salivary simulation with ascorbic acid enhances sonographic diagnosis of obstructive sialadenitis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2009, 37, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzato, A.; Hertel, V.; Koch, M.; Zenk, J.; Iro, H. Vitamin C as contrast agent in diagnosis of salivary duct obstruction. Laryngorhinootologie 2009, 88, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Ultrasound in the diagnosis of parotid duct obstruction not caused by sialolithiasis: Diagnostic value in reference to direct visualization with sialendoscopy. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.A.; Lazarz, D.P.; Pekala, J.R.; Skinningsrud, B.; Lauritzen, S.S.; Solewski, B.; Pekala, P.A.; Walocha, J.A.; Tomaszewski, K.A. The Accessory Parotid Gland and its Clinical Significance. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, P.; Kaiser, S. Ultrasonographic biometry in salivary glands. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1997, 23, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrina, J.; Muller, W.; Gebbers, J.O. Enlargement of salivary glands in bulimia. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1994, 108, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzato, A.; Burger, P.; Zenk, J.; Uter, W.; Iro, H. Salivary gland biometry in female patients with eating disorders. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 265, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, T.L.; Chan, T.T.; Choi, C.Y.; Lam, S.H. Kuttner’s tumour (chronic sclerosing sialadenitis) of the submandibular gland: A clinical perspective. Hong Kong Med. J. 2008, 14, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantino, L.; Giorgio, A.; De Stefano, G.; Farella, N. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of post-pubertal epidemic parotitis and its complications. Radiol. Med. 2000, 99, 461–464. [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell, K.L.; Trought, W.S.; Shearin, J.C. The use of ultrasound to localize calculi within the parotid gland. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1978, 1, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellina, P.V., Jr. Diagnostic use of ultrasound in sialolithiasis of the parotid gland. J. La State Med. Soc. 1982, 134, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gritzmann, N.; Hajek, P.; Karnel, F.; Fezoulidis, J.; Turk, R. Sonography in salivary calculi--indications and status. Rofo 1985, 142, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danic, D.; Milkovic, Z.; Marinkovic, M. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of sialolithiasis of the major salivary glands. Chir. Maxillofac. Plast. 1988, 18, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Odagawa, T. Sonographic examination of sialolithiasis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1989, 47, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelelli, G.; Favia, G.; Macarini, L.; Lacaita, M.G.; Laforgia, A. Echography in the study of sialolithiasis. Radiol. Med. 1990, 79, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Eistert, B.; Glanz, H. Examination technique in ultrasound calculus detection in the submandibular gland. HNO 1992, 40, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fodra, C.; Kaarmann, H.; Iro, H. Sonography and plain roentgen image in diagnosis of salivary calculi—Experimental studies. HNO 1992, 40, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, A.; Strauss, S.; Eviatar, E.; Segal, S. Ultrasonography of an infected parotid gland in an elderly patient: Detection of sialolithiasis during the acute attack. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1995, 104 Pt 1, 736–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, R.; Pennisi, F.; Politi, G.; Speranza, V. Sialolithiasis with an unusual dilatation of the submandibular duct. A color Doppler echographic study of a case. Radiol. Med. 1999, 98, 536–537. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, A.S.; Ahuja, A.T.; King, A.D.; Tse, G.M.; Metreweli, C. Comparison of the sonographic features of acalculous and calculous submandibular sialadenitis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2001, 29, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terraz, S.; Poletti, P.A.; Dulguerov, P.; Dfouni, N.; Becker, C.D.; Marchal, F.; Becker, M. How reliable is sonography in the assessment of sialolithiasis? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, W104–W109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizides, A.; Gruber, H. Reliability of sonography in the assessment of sialolithiasis: Is the fishnet mesh too small? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, W119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.G.; Hurst, N.D.; Magajna, P.W. Bedside emergency ultrasound in a case of acute parotid duct sialolithiasis. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 47, e49–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerni, M.; Foletti, J.M.; Collet, C.; Chossegros, C. Evaluation of the prevalence of residual sialolith fragments after transoral approach of Wharton’s duct. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.L.; Zenk, J.; Bozzato, A.; Kuenzel, J.; Zengel, P.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Interrater Reliability of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 40, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.; Schapher, M.; Iro, H.; Wuest, W.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Koch, M. Value of Sonography in the Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis: Comparison With the Reference Standard of Direct Stone Identification. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Ultrasound Supplemented by Sialendoscopy: Diagnostic Value in Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.J.; Hashemi, S.; Joshi, A.S. Sonopalpation: A novel application of ultrasound for detection of submandibular calculi. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.L.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Response to Letter to the editor: Interrater Reliability of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis: Methodological Issues. Interrater Reliability of Ultrasound: Methodological Issues. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 40, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Zenk, J.; Bozzato, A.; Bumm, K.; Iro, H. Sialoscopy in cases of unclear swelling of the major salivary glands. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 133, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapher, M.; Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Transoral Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Obstructive Salivary Gland Pathologies. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badger, C.D.; Patel, S.; Romero, N.J.; Fuson, A.; Joshi, A.S. In Vivo Accuracy of Ultrasound for Sizing Salivary Ductal Calculi. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 164, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisthoff, U.W.; Lehnert, B.K.; Verse, T. Ultrasound-guided mechanical intraductal stone fragmentation and removal for sialolithiasis: A new technique. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Ultrasound-guided transoral removal of impalpable hilar submandibular salivary stones. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisthoff, U.W.; Maune, S. Ultrasound-guided mechanical fragmentation of sialoliths (sonoguide forceps). Head Neck 2010, 32, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, W.W.; Walvekar, R.R.; Gillespie, M.B. Transfacial ultrasound-guided gland-preserving resection of parotid sialoliths. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Sood, A.J. Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization during Open Parotid Sialolithotomy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, U.; Nair, S.; Mishra, A. Ultrasonography-guided minimally invasive removal of parotid calculi: A prudent approach. Ear Nose Throat J. 2016, 95, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero, N.J.; Fuson, A.; Kieliszak, C.R.; Joshi, A.S. Sonolocation during submandibular sialolithotomy. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2716–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.M.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, G.T.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, E.H. Ultrasound-guided sialo-irrigation for the treatment of chronic sialodochitis with sialolithiasis. Oral Radiol. 2021, 37, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Lohia, S. Ultrasound indicators of persistent obstruction after submandibular sialolithotomy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Ultrasound in the Assessment of Parotid Duct Stenosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2935–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, L. Ultrasound findings in HIV-positive patients with parotid gland swellings. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatokhin, A.I. HIV-related salivary gland diseases: Diagnostics and treatment. Stomatologiia 2010, 89, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, W.R.; Chang, J.L.; Eisele, D.W. Surgeon-performed ultrasound and transfacial sialoendoscopy for complete parotid duct stenosis. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, A.N.; Okuhama, A.; Eisele, D.W.; Tversky, J.R.; Gniadek, T.J. Eosinophilic sialodochitis: Redefinition of ‘allergic parotitis’ and ‘sialodochitis fibrinosa’. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.; Koch, M.; Kunzel, J.; Gillespie, M.B.; Grundtner, P.; Iro, H.; Zenk, J. Juvenile recurrent parotitis: A retrospective comparison of sialendoscopy versus conservative therapy. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Katagiri, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Imai, F.; Ohno, S.; Doi, Y. A case of sarcoidosis associated with Sjogren’s syndrome. Arerugi 1992, 41, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, A.T.; Metreweli, C. Ultrasound features of Sjogren’s syndrome. Australas. Radiol. 1996, 40, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Argalia, G.; Carotti, M.; Giannini, F.B.; Palombi, C. Salivary gland ultrasonography in the evaluation of primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Comparison with minor salivary gland biopsy. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carotti, M.; Salaffi, F.; Manganelli, P.; Argalia, G. Ultrasonography and colour doppler sonography of salivary glands in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2001, 20, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornec, D.; Jamin, C.; Pers, J.O. Sjogren’s syndrome: Where do we stand, and where shall we go? J. Autoimmun. 2014, 51, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorri, E.; Sutcliffe, N.; Richards, P.S.; Suchak, K.; Pitzalis, C.; Bombardieri, M.; Tappuni, A.R. Ultrasound of the salivary glands is a strong predictor of labial gland biopsy histopathology in patients with sicca symptoms. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapi, A.; Horisberger, A.; Francois, S.; Ribi, C. Sjogren’s syndrome: When to suspect and how to confirm? Rev. Med. Suisse 2016, 12, 698–702. [Google Scholar]
- Carotti, M.; Salaffi, F.; Di Carlo, M.; Barile, A.; Giovagnoni, A. Diagnostic value of major salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: The role of grey-scale and colour/power Doppler sonography. Gland Surg. 2019, 8 (Suppl. S3), S159–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringhieri, G.; Izzetti, R.; Vitali, S.; Ferro, F.; Gabriele, M.; Baldini, C.; Caramella, D. Ultra-high frequency ultrasound (UHFUS) applications in Sjogren syndrome: Narrative review and current concepts. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 2248–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad Magalhaes, C.; de Souza Medeiros, P.B.; Oliveira-Sato, J.; Custodio-Domingues, M.A. Clinical presentation and salivary gland histopathology of paediatric primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M.; Okamura, K.; Kise, Y.; Takeshita, Y.; Furuhashi, H.; Weerawanich, W.; Moriyama, M.; Ohyama, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Effectiveness of imaging modalities for screening IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialadenitis (Mikulicz’s disease) and for differentiating it from Sjogren’s syndrome (SS), with an emphasis on sonography. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumrey-Langkammerer, M.; Haas, J.P. Salivary gland ultrasound in the diagnostic workup of juvenile Sjogren’s syndrome and mixed connective tissue disease. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2020, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Luciano, N.; Tarantini, G.; Pascale, R.; Sernissi, F.; Mosca, M.; Caramella, D.; Bombardieri, S. Salivary gland ultrasonography: A highly specific tool for the early diagnosis of primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Song, S.; Wu, S.; Duan, T.; Chen, L.; Ye, J.; Xiao, J. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasonography with different scoring systems in Sjogren’s syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: Nomenclature, clinical features, and treatment. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 29, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.Y.; Hong, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4double ended arrowrelated sialadenitis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2019, 51, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, L.Y.; Pu, Y.P.; Zhou, H.H.; Xie, L.S.; Shi, H.; Yu, C.Q. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of immunoglobulin g4-related sclerosing sialadenitis. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xie, X.Y.; Su, J.Z.; Hong, X.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yu, G.Y. Ultrasonographic Features of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sialadenitis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S.M.; Liu, Y.Y. Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2019, 51, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, M.; Moriyama, M.; Shimizu, M.; Chinju, A.; Mochizuki, K.; Munemura, R.; Ohyama, K.; Maehara, T.; Ogata, K.; Ohta, M.; et al. The diagnostic utility of submandibular gland sonography and labial salivary gland biopsy in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialadenitis: Its potential application to the diagnostic criteria. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Joshi, D.; Khurana, A.; Gupta, V.; Kapoor, N. Bilaterally enlarged parotids and sicca symptoms as a presentation of sarcoidosis: Pivotal role of aspiration cytology in diagnosis. J. Cytol. 2015, 32, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.K. Isolated Parotid Gland Sarcoidosis Mimicking Parotid Tumor. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 644–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, S.; Brown, M.; Seegobin, K.; Isache, C. Sarcoidosis presenting with facial swelling (Heerfordt syndrome). Clin. Case Rep. 2018, 6, 2023–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, A.T.; Loke, T.K.; Mok, C.O.; Chow, L.T.; Metreweli, C. Ultrasound of Kimura’s disease. Clin. Radiol. 1995, 50, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeishi, M.; Makino, Y.; Nishioka, H.; Miyawaki, T.; Kurihara, K. Kimura disease: Diagnostic imaging findings and surgical treatment. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2007, 18, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Akker, H.P.; Busemann-Sokole, E. Submandibular gland function following transoral sialolithectomy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral. Pathol. 1983, 56, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osailan, S.M.; Proctor, G.B.; Carpenter, G.H.; Paterson, K.L.; McGurk, M. Recovery of rat submandibular salivary gland function following removal of obstruction: A sialometrical and sialochemical study. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Xu, J.H.; Liao, G.Q.; Zheng, G.S.; Cheng, M.H.; Han, L.; Shan, H. Salivary gland functional recovery after sialendoscopy. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
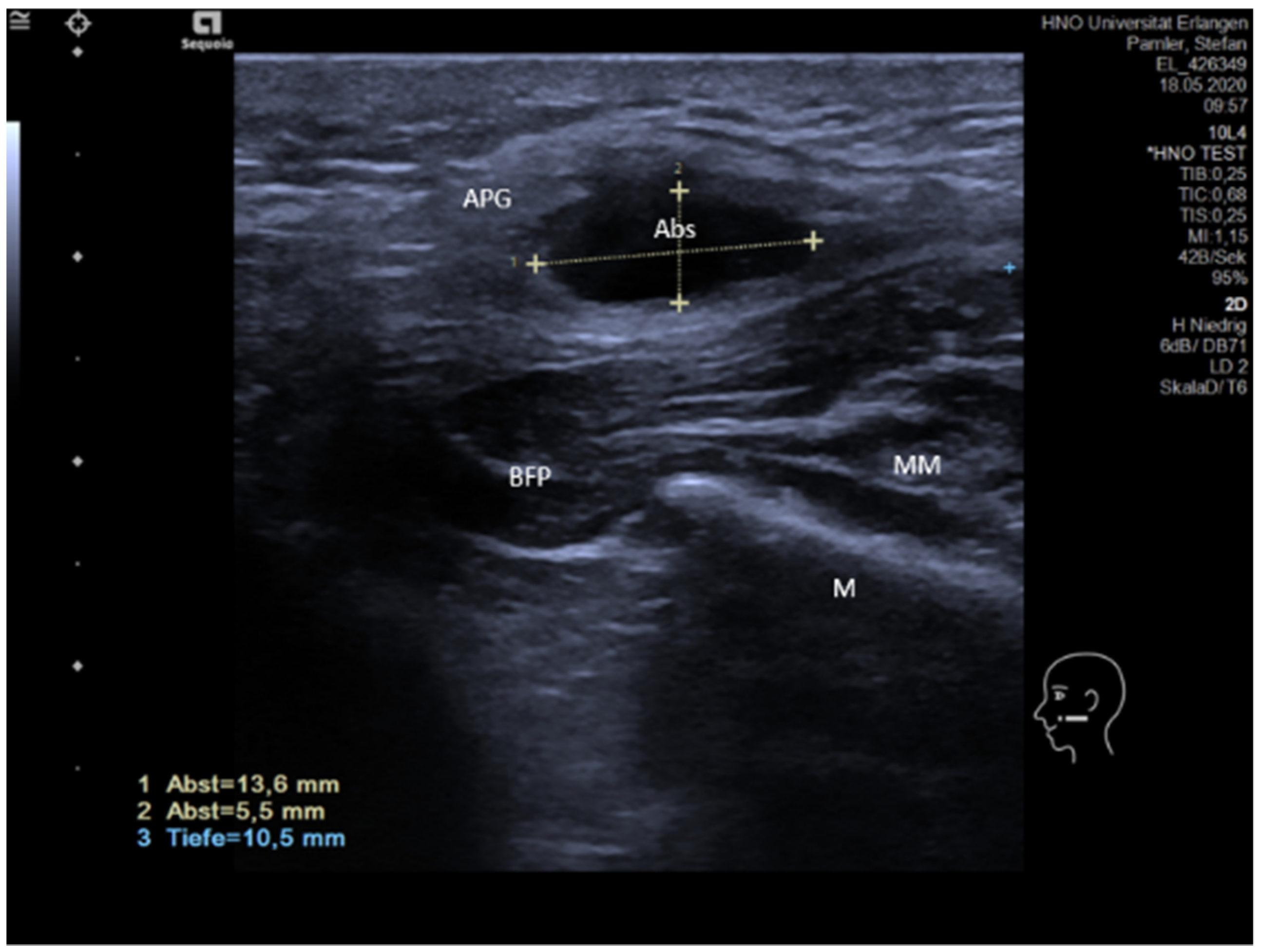


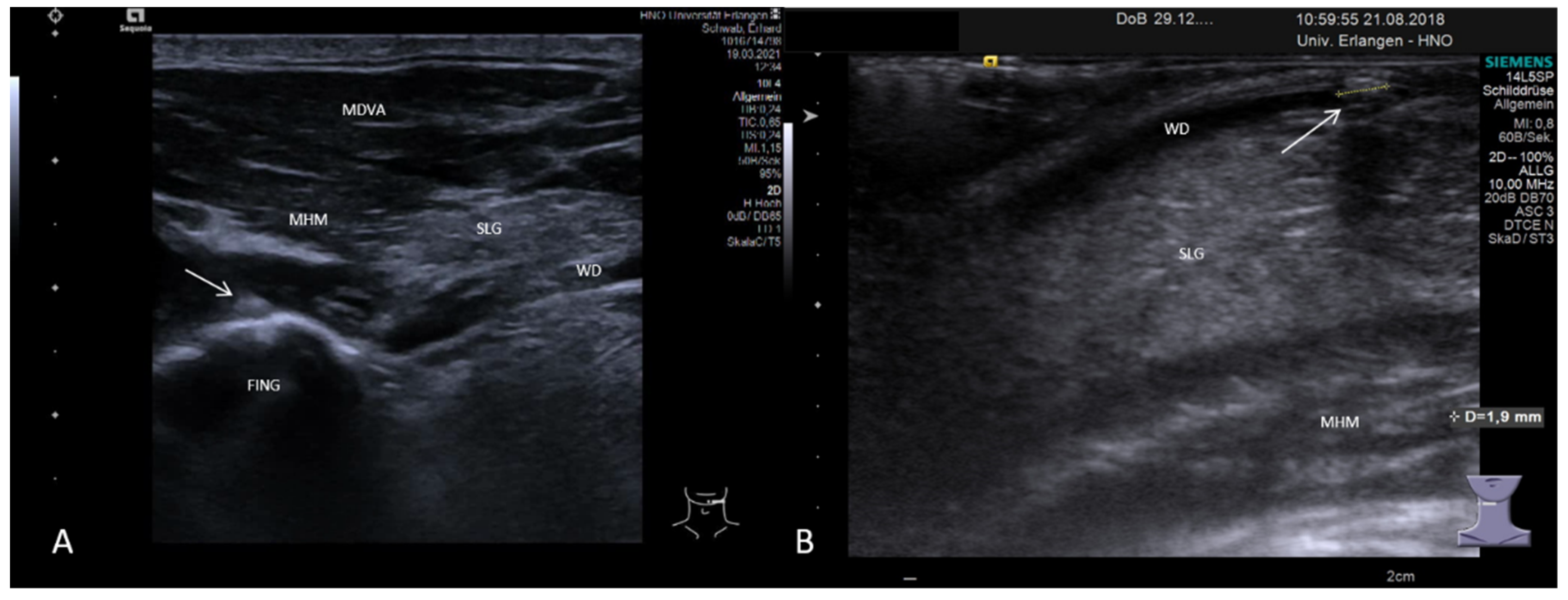


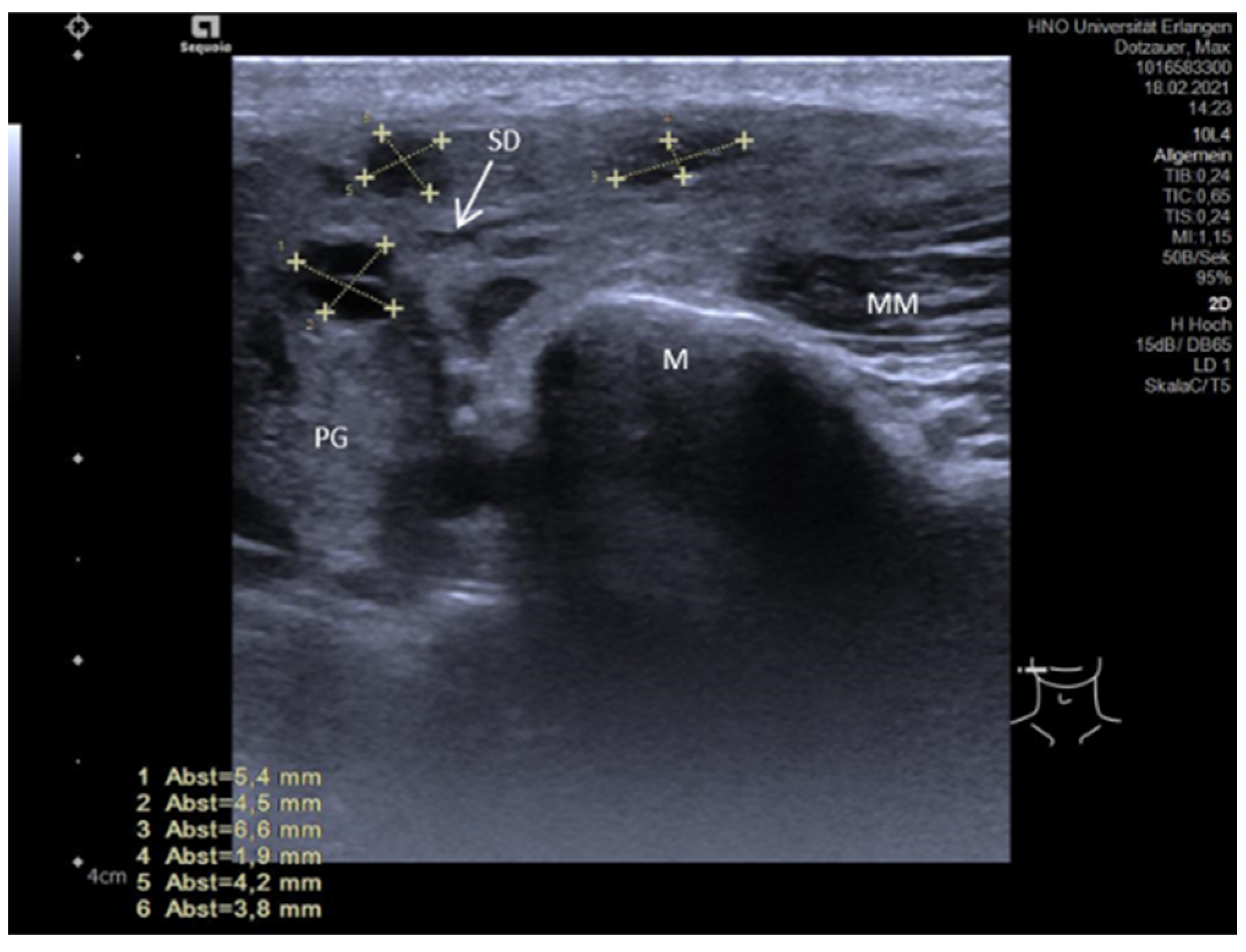

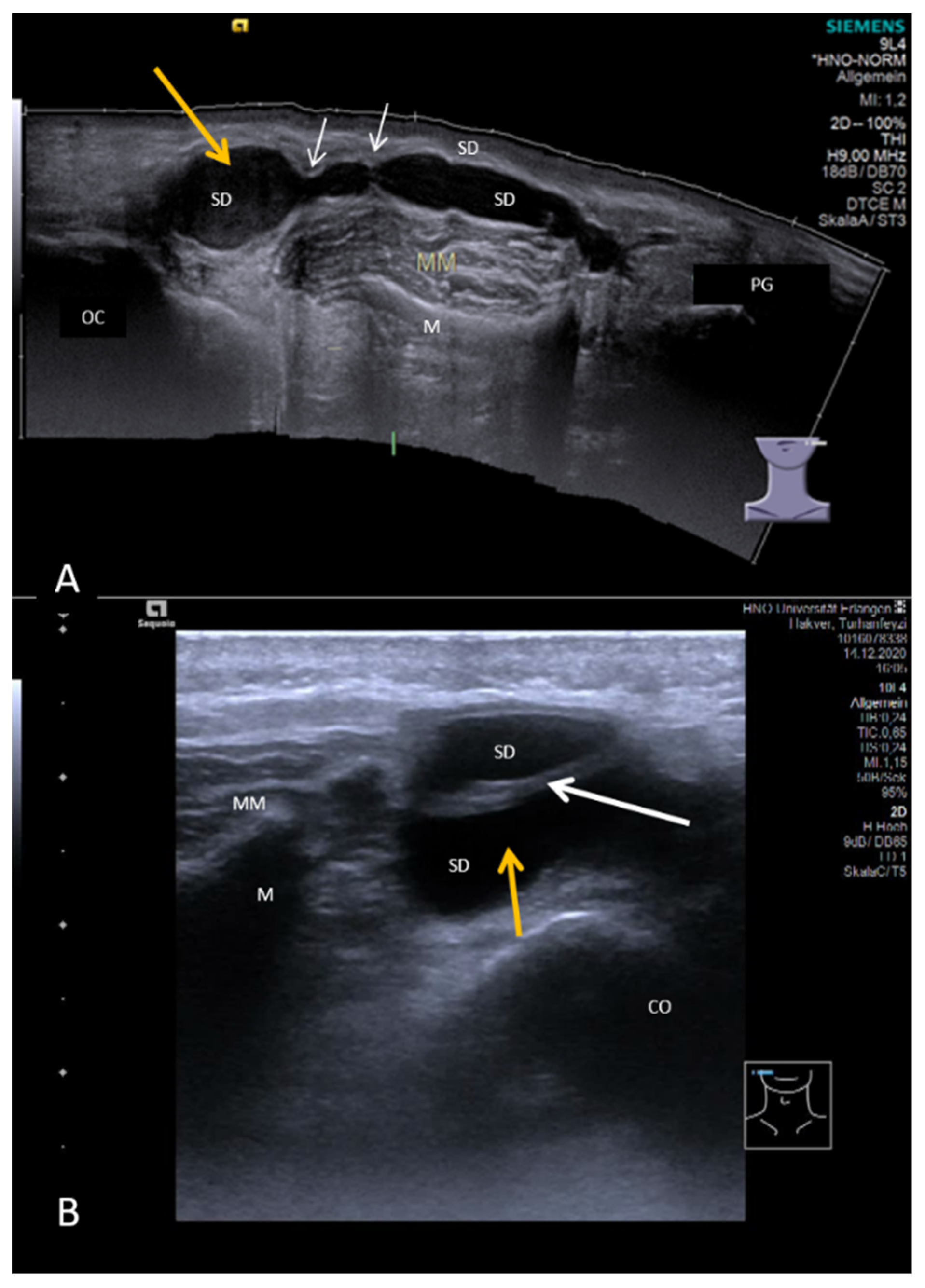









| Stenoses | Ultrasound Feature | Duct Dilation (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Webs | Duct Kinking | Megaducts | Normal Echogenicity | ||
| Without duct anomalies (n = 90) | 7.8% (n = 7) | 3.3% (n = 3) | 15.6% (n = 14) | 25.6% (n = 23) | 3.27 ± 2.17 (n = 90) |
| With duct anomalies (n = 40) | 82.5% (n = 33) | 75.0% (n = 30) | 87.5% (n = 35) | 77.5% (n = 31) | 9.19 ± 3.65 (n = 40) |
| Fisher’s exact test/χ2 test | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Disease | VD | HIV | craS (SD) ° | craS (Sten) ° | ESD | cjrP | SS | IgG4 | SA | RTiS/RITiS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. US-Feature | ||||||||||
| Gland volume | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ # | ↑ optional ↓ (late stages) # | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ optional ↓ (late stages) | ↑ optional ↓ (late stages) | ↑ | ↑ (early stages) ↓ (late stages) |
| Parenchyma: echopoor | optional | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes (focal) | no | yes |
| Parenchyma: heterogeneous | no | no | no | optional | optional | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes (late stages) |
| Tissue aspect: spongy | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Tissue aspect: leopard-skin-like | no | no | no | no | no | yes | yes | optional | no | no |
| Tissue aspect: polycystic | optional | yes | optional | optional | yes | yes | optional (late stages) | no | no | no |
| Tissue aspect: echopoor foci | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| Tissue aspect: coarse | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | optional | yes | no |
| Tissue aspect: honey-comb-like | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes (acute progress) | optional (focal infiltration) | optional (focal infiltration) | no |
| Tissue aspect: space occupying lesion-like | no | no | no | no | no | no | optional (MALT-lymphoma) | optional (focal infiltration) | optional (focal infiltration) | no |
| Tissue aspect: atrophy | no | no | no # | optional (late stages) # | no | optional (late stages) | yes (late stages) | yes (late stages) | no | yes (late stages) |
| Tissue aspect: Perfusion increased | yes | no | optional | optional | optional | optional | optional | optional | no | no |
| Duct dilation | no | no | yes | yes | yes | no | no | optional | no | optional |
| Formation of megaduct | no | no | optional | optional (no duct anomaly); yes (with duct anomaly) | yes | no | no | optional | no | no |
| Lympadenopathy: significant | optional | optional | no | no | no | no | Optional (MALT) | no | yes | no |
| II. Additional diagnostics: Blood tests | no | Yes (PCR) | no | no | yes (eosinophils) | no | yes (ANA, SS-A, SS-B) | yes (IgG4) | yes (ACE, Calcium) | no |
| III. Additional diagnostics: Gland biopsy | no | no | no | no | yes (eosinophilic inflammation) | no | yes (ANA, SS-A, SS-B) | yes (IgG4:IgG > 40%) | yes | no |
| IV. Additional diagnostics: LN-biopsy | no | no | no | no | no | no | no * | no | yes | no |
| V. Additional diagnostics: Imaging (CT, MRI) | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | CT human/MRI human | CT Thorax | no |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koch, M.; Sievert, M.; Iro, H.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M. Ultrasound in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Diseases: Own Experiences and a Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163547
Koch M, Sievert M, Iro H, Mantsopoulos K, Schapher M. Ultrasound in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Diseases: Own Experiences and a Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163547
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoch, Michael, Matti Sievert, Heinrich Iro, Konstantinos Mantsopoulos, and Mirco Schapher. 2021. "Ultrasound in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Diseases: Own Experiences and a Review of the Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163547
APA StyleKoch, M., Sievert, M., Iro, H., Mantsopoulos, K., & Schapher, M. (2021). Ultrasound in Inflammatory and Obstructive Salivary Gland Diseases: Own Experiences and a Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163547







