A20 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation by Regulating TRAF6 Polyubiquitination in Rainbow Trout
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence and Characteristics of OmA20
2.2. OmA20 Expression in Fish Tissues and RTH-149 Cells Stimulated with LPS
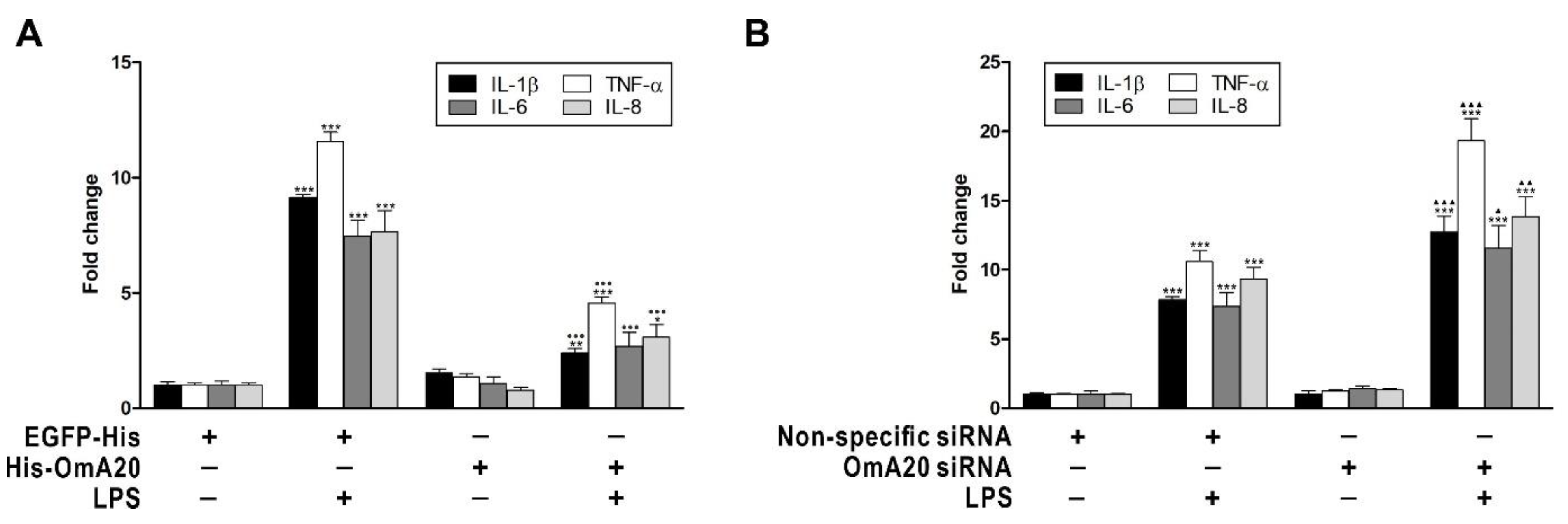
2.3. Involvement of OmA20 on MAPK and NF-κB Activation in RTH-149 Cells Stimulated with LPS
2.4. Effect of OmA20 on the Ubiquitination of TRAF6 in LPS-Stimulated RTH-149 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Line and Reagents
4.2. cDNA Cloning of the Gene Encoding OmA20
4.3. Sequence Analysis
4.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Construction of Expression Plasmids
4.7. Overexpression of OmA20 and OmA20 Mutants in RTH-149 Cells
4.8. Silencing of OmA20 Expression in RTH-149 Cells
4.9. Dual-Luciferase Activity Assay
4.10. Immunoprecipitation
4.11. Ubiquitination Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimbrell, D.A.; Beutler, B. The evolution and genetics of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Bhoj, V.; Seth, R.B. Ubiquitin, TAK1 and IKK: Is there a connection? Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, A.; Lamothe, B.; Campos, A.D.; Webster, W.K.; Maddineni, U.; Lin, S.C.; Wu, H.; Darnay, B.G. TAK1-dependent signaling requires functional interaction with TAB2/TAB3. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3918–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liew, F.Y.; Xu, D.; Brint, E.K.; O’Neill, L.A. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jia, H.; Jing, Z.; Liu, D. Recognition of pathogen-associated nucleic acids by endosomal nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, L.A. When signaling pathways collide: Positive and negative regulation of toll-like receptor signal transduction. Immunity 2008, 29, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Dissecting negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, C.M.; Eddins, M.J. Ubiquitin: Structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1695, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pickart, C.M.; Fushman, D. Polyubiquitin chains: Polymeric protein signals. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, A.; Heller, H.; Elias, S.; Ciechanover, A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 8206–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D. The emerging complexity of protein ubiquitination. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37 Pt 5, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S.; Komander, D. Breaking the chains: Deubiquitylating enzyme specificity begets function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.L.; Turer, E.E.; Lee, E.G.; Ahmad, R.C.; Wheeler, M.T.; Tsui, C.; Hurley, P.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Hitotsumatsu, O.; et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, S.M.; Moynagh, P.N. Regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 signalling by A20 zinc finger protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, Y.; Asai, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Mizumura, K.; Jibiki, I.; Machino, T.; Ra, C.; Horie, T. A20 inhibits toll-like receptor 2- and 4-mediated interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, I.E.; O’Rourke, K.M.; Zhou, H.; Eby, M.; Aravind, L.; Seshagiri, S.; Wu, P.; Wiesmann, C.; Baker, R.; Boone, D.L.; et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 2004, 430, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D.; Barford, D. Structure of the A20 OTU domain and mechanistic insights into deubiquitination. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.C.; Chung, J.Y.; Lamothe, B.; Rajashankar, K.; Lu, M.; Lo, Y.C.; Lam, A.Y.; Darnay, B.G.; Wu, H. Molecular basis for the unique deubiquitinating activity of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Priem, D.; van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. A20 and Cell Death-driven Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P.C. Regulation of pro-inflammatory signalling networks by ubiquitin: Identification of novel targets for anti-inflammatory drugs. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2005, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shembade, N.; Ma, A.; Harhaj, E.W. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 2010, 327, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vereecke, L.; Beyaert, R.; van Loo, G. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of immunopathology. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabilleau, G.; Chappard, D.; Sabokbar, A. Role of the A20-TRAF6 axis in lipopolysaccharide-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oehlers, S.H.; Flores, M.V.; Hall, C.J.; Swift, S.; Crosier, K.E.; Crosier, P.S. The inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) susceptibility genes NOD1 and NOD2 have conserved anti-bacterial roles in zebrafish. Dis. Model. Mech. 2011, 4, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merour, E.; Jami, R.; Lamoureux, A.; Bernard, J.; Bremont, M.; Biacchesi, S. A20 (tnfaip3) is a negative feedback regulator of RIG-I-Mediated IFN induction in teleost. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikima, J.I.; Morita, M.; Kinoshita, S.; Basu, M.; Biswas, G.; Kono, T.; Sakai, M. Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-induced Protein 3 (TNFAIP3/A20) Gene from Japanese Pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Fish Pathol. 2017, 52, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cultrone, D.; Zammit, N.W.; Self, E.; Postert, B.; Han, J.Z.R.; Bailey, J.; Warren, J.; Croucher, D.R.; Kikuchi, K.; Bogdanovic, O.; et al. A zebrafish functional genomics model to investigate the role of human A20 variants in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.; Jang, M.J.; Cho, J.H. PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palti, Y. Toll-like receptors in bony fish: From genomics to function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, P.E.; Mellon, M.T.; Kim, C.H. Functional characterization of full-length TLR3, IRAK-4, and TRAF6 in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, E.F.; O’Neill, L.A. Signalling adaptors used by Toll-like receptors: An update. Cytokine 2008, 43, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstrom, M. The TAK1-TRAF6 signalling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turer, E.E.; Tavares, R.M.; Mortier, E.; Hitotsumatsu, O.; Advincula, R.; Lee, B.; Shifrin, N.; Malynn, B.A.; Ma, A. Homeostatic MyD88-dependent signals cause lethal inflamMation in the absence of A20. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Arron, J.R. TRAF6, a molecular bridge spanning adaptive immunity, innate immunity and osteoimmunology. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamothe, B.; Campos, A.D.; Webster, W.K.; Gopinathan, A.; Hur, L.; Darnay, B.G. The RING domain and first zinc finger of TRAF6 coordinate signaling by interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide, and RANKL. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24871–24880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, S.; Dong, X.; Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Ruan, J.; Peng, J.; Xu, A. Emergence of the A20/ABIN-mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling via modifying the ubiquitinated proteins in a basal chordate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6720–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, G.M.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 2003, 300, 1524–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S. Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38105–38108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coornaert, B.; Carpentier, I.; Beyaert, R. A20: Central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8217–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.G.; Boone, D.L.; Chai, S.; Libby, S.L.; Chien, M.; Lodolce, J.P.; Ma, A. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 2000, 289, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal Uddin, M.; Joe, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Oh Jeong, S.; Ryter, S.W.; Pae, H.O.; Chung, H.T. IRG1 induced by heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide inhibits LPS-mediated sepsis and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Xiong, J.; Takeuchi, M.; Kurama, T.; Goeddel, D.V. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 1996, 383, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, C.; Spencer, E.; Yang, L.; Braun, A.; You, J.; Slaughter, C.; Pickart, C.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell 2000, 103, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, A.; Malynn, B.A. A20: Linking a complex regulator of ubiquitylation to immunity and human disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of TRAF6 and TAK1 in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of deubiquitinase CYLD in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 101, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.C.; Ovaa, H.; Hamon, M.; Kilshaw, P.J.; Hamm, S.; Bauer, S.; Ploegh, H.L.; Smith, T.S. Zinc-finger protein A20, a regulator of inflammation and cell survival, has de-ubiquitinating activity. Biochem. J. 2004, 378 Pt 3, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.N.; Hunt, H.D.; Horton, R.M.; Pullen, J.K.; Pease, L.R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 1989, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.; Jung, I.Y.; Cho, J.H. A20 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation by Regulating TRAF6 Polyubiquitination in Rainbow Trout. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189801
Jang JH, Kim H, Jung IY, Cho JH. A20 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation by Regulating TRAF6 Polyubiquitination in Rainbow Trout. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189801
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Ju Hye, Hyun Kim, In Young Jung, and Ju Hyun Cho. 2021. "A20 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation by Regulating TRAF6 Polyubiquitination in Rainbow Trout" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189801
APA StyleJang, J. H., Kim, H., Jung, I. Y., & Cho, J. H. (2021). A20 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation by Regulating TRAF6 Polyubiquitination in Rainbow Trout. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189801




