Dextromethorphan Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Uremic Artery Calcification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
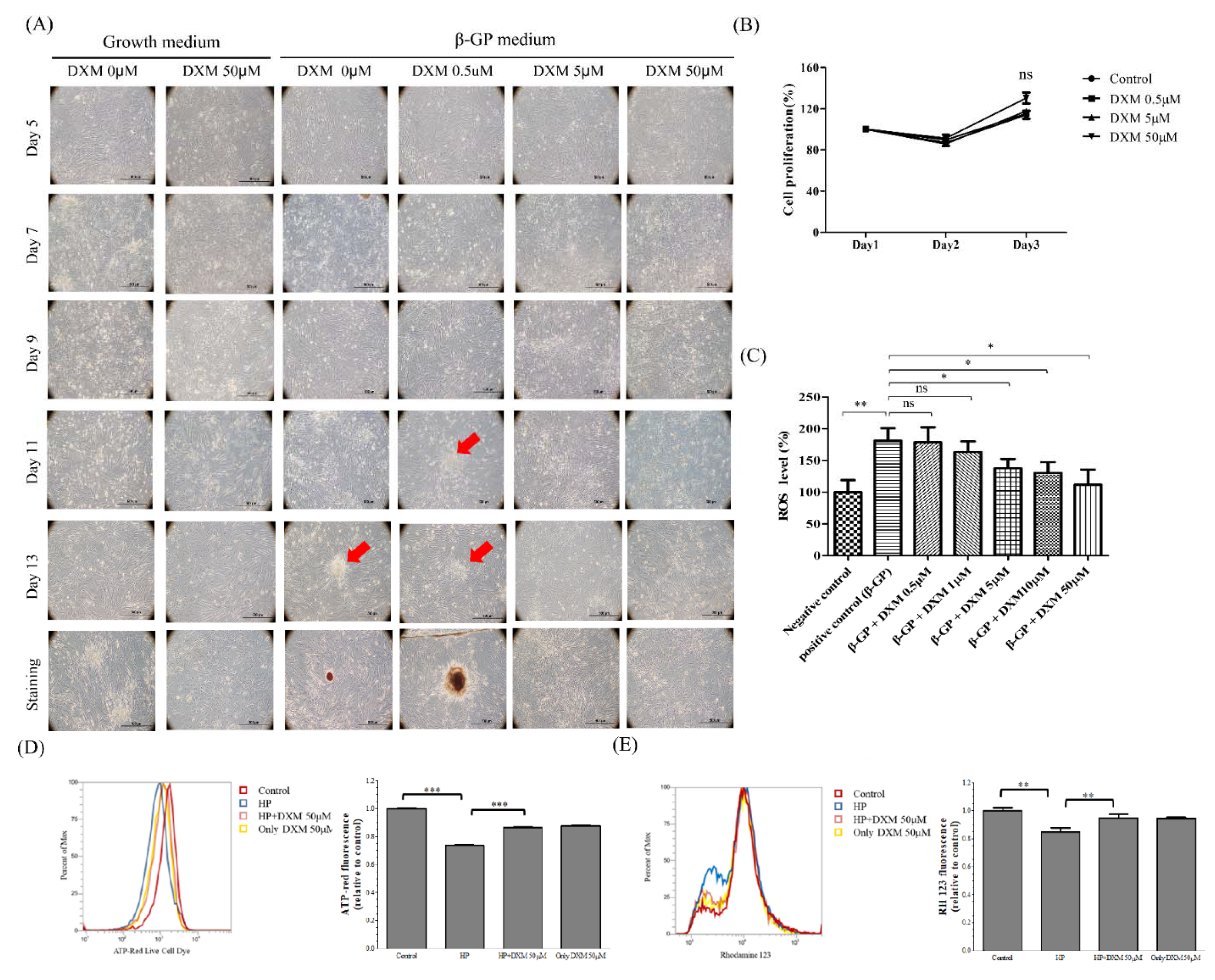
2.1. Effect of High-Phosphate Medium on Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Effect of DXM on High-Phosphate Medium in Rat Smooth Vascular Cells
2.2. Effect of High-Phosphate Medium on Human Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
2.3. Effects of DXM on Adenine Rat Models
2.4. DXM Reduces Vascular Calcification in a Rat Model of CKD with Hyperphosphatemia
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Culture and Osteoblast Differentiation
4.1.1. MTT (3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 Diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide) Assay
4.1.2. Measurement of ROS Levels
4.1.3. Measurement of Mitochondria ATP Generation
4.1.4. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.1.5. Detection of Mineralization
4.2. Primary Human Aorta Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Culture and Osteoblast Differentiation
4.3. Animal Model
4.3.1. Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Measurement
4.3.2. Biochemical Analysis
4.3.3. Histological Assessment
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32 (Suppl. 3), S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Renal Data System. USRDS 2010 Annual Data Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States; United States Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health—National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Division of Kidney, Urology, and Hematologic Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Muntner, P.; He, J.; Astor, B.C.; Folsom, A.R.; Coresh, J. Traditional and non-traditional risk factors predict coronary heart disease in chronic kidney disease: Results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, L.; Brundage, B.; Crouse, J.; Detrano, R.; Fuster, V.; Maddahi, J.; Rumberger, J.; Stanford, W.; White, R.; Taubert, K. Coronary Artery Calcification: Pathophysiology, Epidemiology, Imaging Methods, and Clinical Implications. Circulation 1996, 94, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demer, L.L.; Tintut, Y. Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Genetic Mechanisms of Vascular Calcification. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.C.; Leopold, J.A.; Loscalzo, J. Vascular calcification: Pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boström, K.I.; Rajamannan, N.M.; Towler, D.A. The Regulation of Valvular and Vascular Sclerosis by Osteogenic Morphogens. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccarty, M.F.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. The Molecular Biology and Pathophysiology of Vascular Calcification. Postgrad. Med. 2014, 126, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Balogh, E.; Jeney, V. Antioxidants Regulation of Vascular Calcification by reactive oxygen species. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faverman, L.; Mikhaylova, L.; Malmquist, J.; Nurminskaya, M. Extracellular transglutaminase 2 activates beta-catenin signaling in calcifying vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hioi, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Jono, S.; Koyama, H.; Hosoi, M.; Morii, H. Beta glycerophosphate accelerates calcification in cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazaña-Pérez, V.; Cidad, P.; Donate-Correa, J.; Martin-Nuñez, E.; Lopez-Lopez, J.R.; Perez-Garcia, M.T.; Giraldez, T.; Navarro-González, J.F.; De La Rosa, D.A. Phenotypic Modulation of Cultured Primary Human Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Uremic Serum. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neven, E.; D’Haese, P.C. Vascular calcification in chronic renal failure: What have we learned from animal studies? Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Ivanovski, O.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Angulo, J.; Szumilak, D.; Mothu, N.; Phan, O.; Daudon, M.; Lacour, B.; Drüeke, T.B.; et al. Uremia Accelerates both Atherosclerosis and Arterial Calcification in Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 16, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Apocynin attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cells osteogenic switching via suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83588–83600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Du, Q.; Gu, C.; Black, S.M.; Han, Y.; Tang, H. Salusin-beta Promotes Vascular Calcification via Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate/Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Klotho Downregulation. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2019, 31, 1352–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.; Chen, H.; Brown, A.T. Hcy-induced vascular dysregulation is mediated by the NMDA receptor. Vasc. Med. 2005, 10, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Qin, L.; Gao, H.M.; Wilson, B.; Ali, S.F.; Zhang, W.; Hong, J.S.; Liu, B. Neuroprotective effect of dextromethorphan in the MPTP Parkinson’s disease model: Role of NADPH oxidase. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Shi, G.-Y.; Tang, S.-H.; Jiang, S.-J.; Huang, C.-W.; Liu, P.-Y.; Hong, J.-S.; Wu, H.-L. Dextromethorphan reduces oxidative stress and inhibits atherosclerosis and neointima formation in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.-C.; Chao, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, J.-W. Low-Dose Dextromethorphan, a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor, Reduces Blood Pressure and Enhances Vascular Protection in Experimental Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, I.R.; Wendling, W.W.; Chen, D.; Wendling, K.S.; Harakal, C.; Carlsson, C. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists--S(+)-ketamine, dextrorphan, and dextromethorphan--Act as calcium antagonists on bovine cerebral arteries. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2008, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzer, T.; Schlinzig, T.; Krohn, K.; Meinertz, T.; Munzel, T. Endothelial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2001, 104, 2673–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touyz, R.M. Reactive oxygen species, vascular oxidative stress, and redox signaling in hypertension: What is the clinical significance? Hypertension 2004, 44, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zalba, G.; Beaumont, F.J.; José, G.S.; Fortuño, A.; Fortuño, M.-A.; Etayo, J.-C.; Diez, J. Vascular NADH/NADPH Oxidase Is Involved in Enhanced Superoxide Production in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2000, 35, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzik, T.J.; West, N.E.; Black, E.; McDonald, D.; Ratnatunga, C.; Pillai, R.; Channon, K.M. Vascular superoxide production by NAD(P)H oxidase: Association with endothelial dysfunction and clinical risk factors. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, E85–E90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landmesser, U.; Dikalov, S.; Price, S.R.; McCann, L.; Fukai, T.; Holland, S.M.; Mitch, W.E.; Harrison, D.G. Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to uncoupling of endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase in hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Okamoto, K.; Eger, B.T.; Pai, E.F.; Nishino, T. Mammalian xanthine oxidoreductase—Mechanism of transition from xanthine dehydrogenase to xanthine oxidase. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3278–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, Z.; Heymes, C.; Ohan, J.; Faggin, E.; Lesèche, G.; Tedgui, A. Expression of interleukin-10 in advanced human atherosclerotic plaques: Relation to inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and cell death. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byon, C.H.; Javed, A.; Dai, Q.; Kappes, J.C.; Clemens, T.L.; Darley-Usmar, V.; McDonald, J.M.; Chen, Y. Oxidative Stress Induces Vascular Calcification through Modulation of the Osteogenic Transcription Factor Runx2 by AKT Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15319–15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsumata, K.; Kusano, K.; Hirata, M.; Tsunemi, K.; Nagano, N.; Burke, S.K.; Fukushima, N. Sevelamer hydrochloride prevents ectopic calcification and renal osteodystrophy in chronic renal failure rats. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reissig, C.J.; Carter, L.P.; Johnson, M.W.; Mintzer, M.Z.; Klinedinst, M.A.; Griffiths, R.R. High doses of dextromethorphan, an NMDA antagonist, produce effects similar to classic hallucinogens. Psychopharmacology 2012, 223, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carliss, R.; Radovsky, A.; Chengelis, C.; O’Neill, T.; Shuey, D. Oral administration of dextromethorphan does not produce neuronal vacuolation in the rat brain. NeuroToxicology 2007, 28, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hung, C.-H. Systemic dextromethorphan and dextrorphan are less toxic in rats than bupivacaine at equianesthetic doses. Can. J. Anaesth. 2010, 58, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilde, E.; Aubdool, A.A.; Thakore, P.; Baldissera, L.; Alawi, K.M.; Keeble, J.; Nandi, M.; Brain, S.D. Tail-Cuff Technique and Its Influence on Central Blood Pressure in the Mouse. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Wen, S.-W.; Lai, C.-C.; Cheng, P.-W.; Tseng, C.-J. Excessive Fructose Intake Impairs Baroreflex Sensitivity and Led to Elevated Blood Pressure in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, E.-S.; Chen, N.-C.; Jao, T.-M.; Chen, C.-L. Dextromethorphan Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Uremic Artery Calcification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212277
Liu E-S, Chen N-C, Jao T-M, Chen C-L. Dextromethorphan Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Uremic Artery Calcification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212277
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, En-Shao, Nai-Ching Chen, Tzu-Ming Jao, and Chien-Liang Chen. 2021. "Dextromethorphan Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Uremic Artery Calcification" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212277
APA StyleLiu, E.-S., Chen, N.-C., Jao, T.-M., & Chen, C.-L. (2021). Dextromethorphan Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Uremic Artery Calcification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212277





