Rehardening and the Protective Effect of Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste on Surface-Etched Enamel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
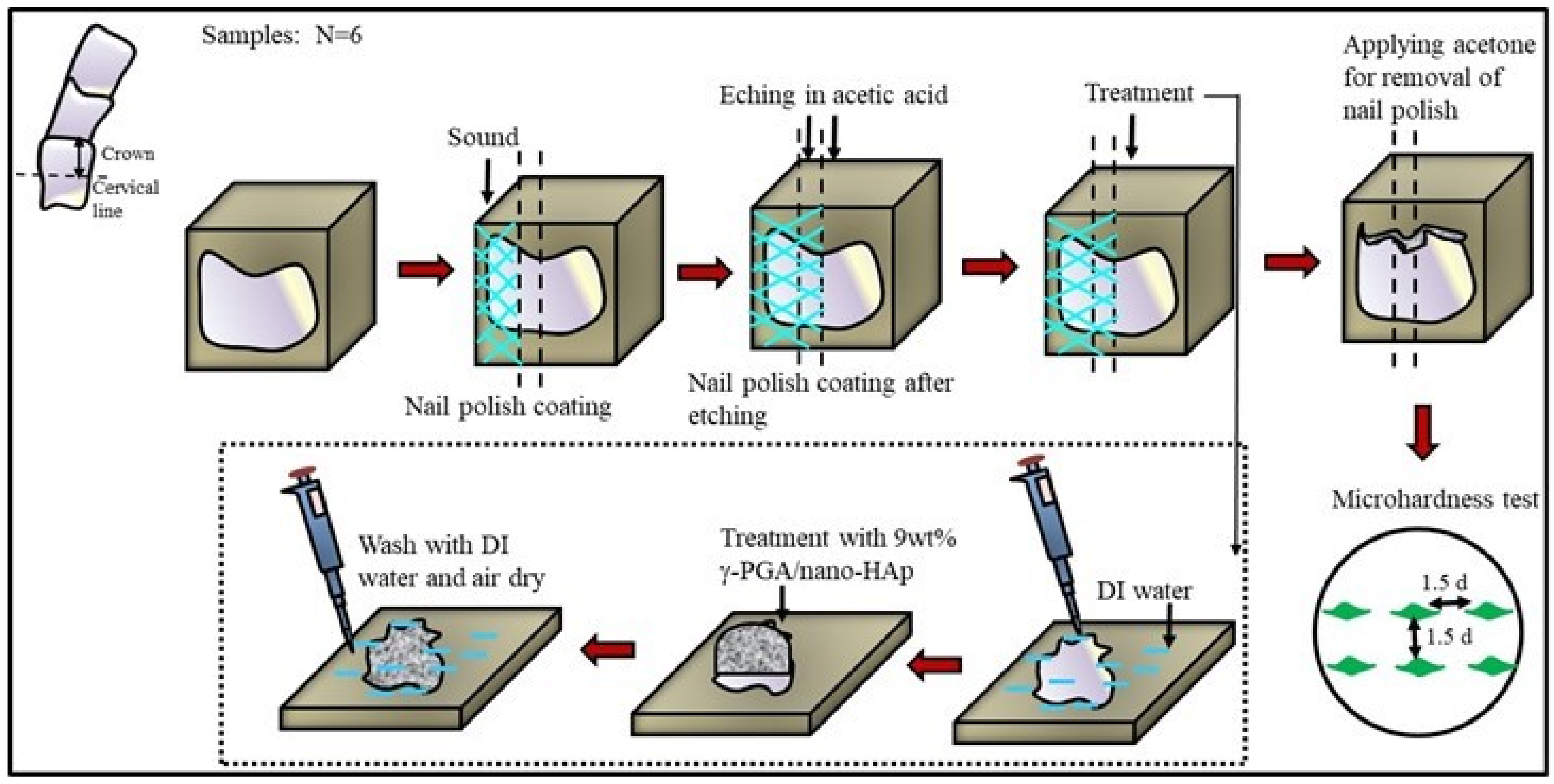
2.1. Preparation of Tooth-Repairing Paste
2.2. Etched Enamel Preparation
2.3. Surface Microhardness Recovery (SMHR) Measurement
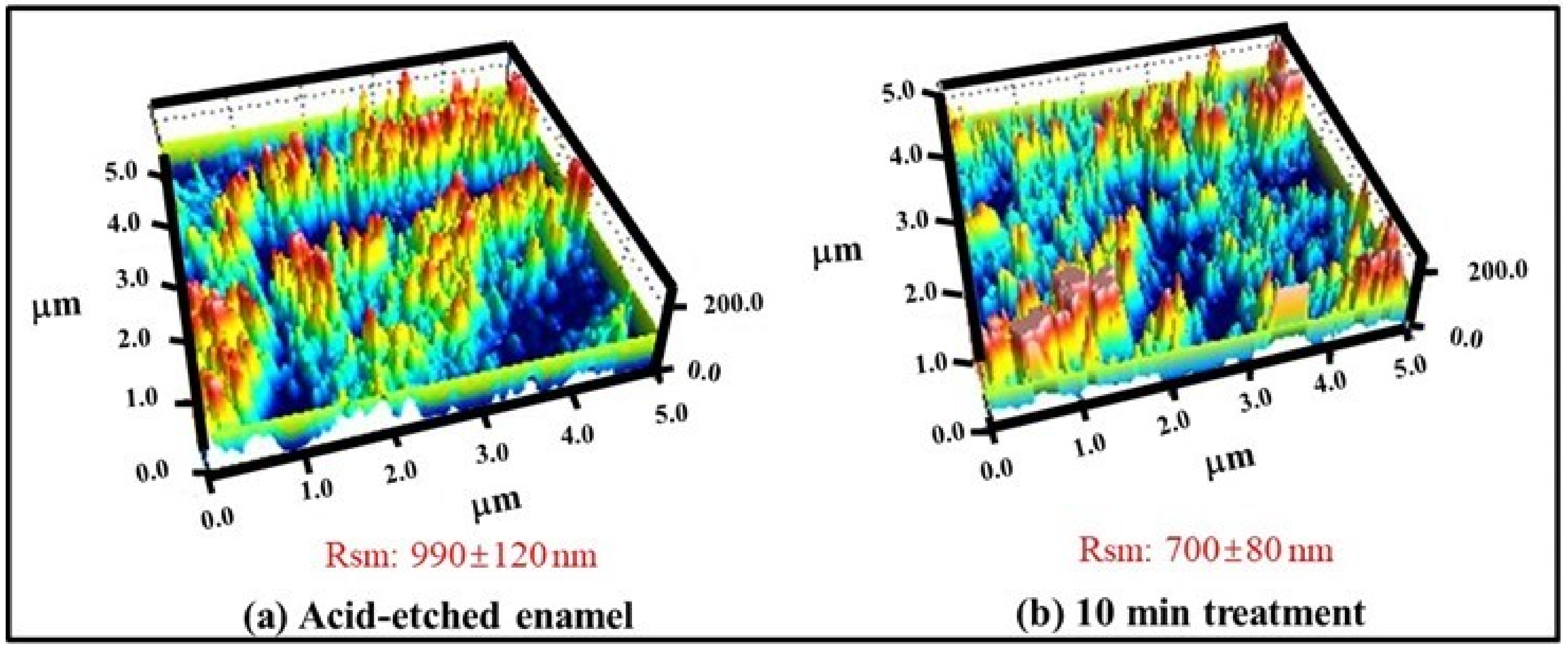
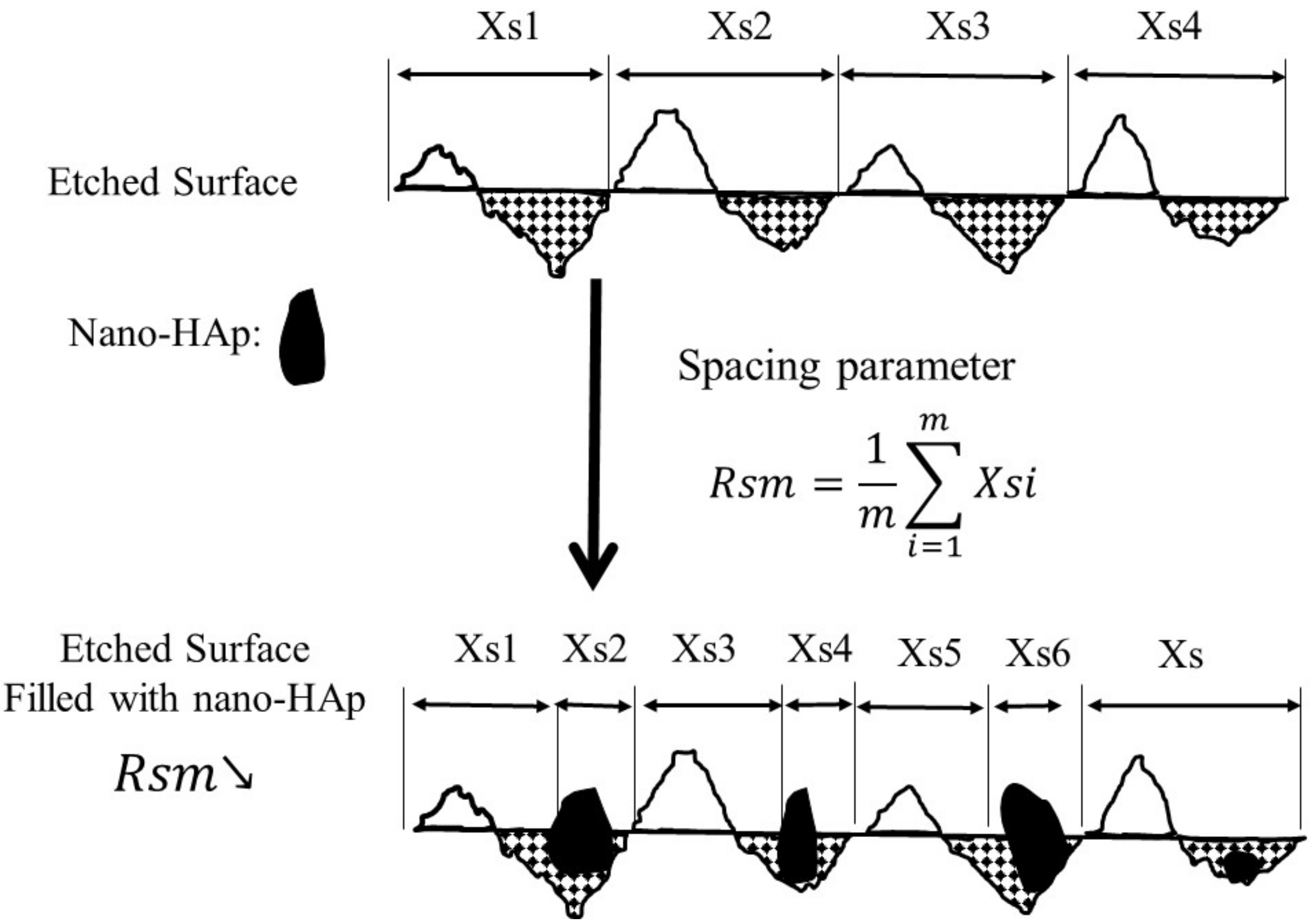
2.4. Surface Profile Measurement by Atomic Force Microscopy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Percent Surface Microhardness Recovery (SMHR%) Analysis
3.2. Effect of γ-PGA/Nano-HAp Paste on AFM Surface Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldassarri, M.; Margolis, H.; Beniash, E. Compositional determinants of mechanical properties of enamel. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, Y.-R.; Lin, T.-T.; Shieh, D.-B. Nanotribological characterization of tooth enamel rod affected by surface treatment. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Cate, A.; Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology: Development, Structure, and Function; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, J.K.; Chiego, D.J. Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology: A Clinical Approach; Mosby Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, J.; Walsh, D.; Fowler, C.E.; Mann, S. Electrospun mats of PVP/ACP nanofibres for remineralization of enamel tooth surfaces. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2011, 13, 3692–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyas, M.J.; Anusavice, K.J.; Frencken, J.E.; Mount, G.J. Minimal intervention dentistry—A review* FDI Commission Project 1–97. Int. Dent. J. 2000, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, L. Dentine hypersensitivity: A review of its aetiology, pathogenesis and management: Clinical. S. Afr. Dent. J. 2007, 62, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.; Shore, R.C.; Brookes, S.J.; Strafford, S.; Wood, S.; Kirkham, J. The chemistry of enamel caries. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2000, 11, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bynum, A.M.; Donly, K.J. Enamel de/remineralization on teeth adjacent to fluoride releasing materials without dentifrice exposure. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1999, 66, 89–92, 84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, M.; Bishop, K. Tooth surface loss: Tooth surface loss: An overview. Br. Dent. J. 1999, 186, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, C. Managing dental erosion. BDJ. Team 2014, 1, 14109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poggio, C.; Lombardini, M.; Dagna, A.; Chiesa, M.; Bianchi, S. Protective effect on enamel demineralization of a CPP-ACP paste: An AFM in vitro study. J. Dent. 2009, 37, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemingway, C.A.; Parker, D.M.; Addy, M.; Barbour, M.E. Erosion of enamel by non-carbonated soft drinks with and without toothbrushing abrasion. Br. Dent. J. 2006, 201, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Taji, S.; Seow, W.K. A literature review of dental erosion in children. Aust. Dent. J. 2010, 55, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussi, A.; Schlüter, N.; Rakhmatullina, E.; Ganss, C. Dental erosion—An overview with emphasis on chemical and histopathological aspects. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Cai, F.; Huq, N.L.; Burrow, M.F.; Reynolds, E.C. New approaches to enhanced remineralization of tooth enamel. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Xiao, S.; Weir, M.D.; Bao, C.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Xu, H.H. Poly (amido amine) dendrimer and dental adhesive with calcium phosphate nanoparticles remineralized dentin in lactic acid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 2414–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, E.C. Anticariogenic complexes of amorphous calcium phosphate stabilized by casein phosphopeptides: A review. Spec. Care Dentist. 1998, 18, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.E.; Manton, D.J.; Parashos, P.; Wong, R.H.; Singleton, W.; Holden, J.A.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Reynolds, E.C. Biocompatibility and Osteogenic/Calcification Potential of Casein Phosphopeptide-amorphous Calcium Phosphate Fluoride. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Pan, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, R. Roles of amorphous calcium phosphate and biological additives in the assembly of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13410–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Amorphous calcium (ortho) phosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4457–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, V.M.; Uskoković, V. Is there a relationship between solubility and resorbability of different calcium phosphate phases in vitro? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, I.; Moheet, I.A.; Imran, Z.; Farooq, U. A review of novel dental caries preventive material: Casein phosphopeptide–amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP–ACP) complex. Saudi J. Dent. Res. 2013, 4, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, N.; Shen, P.; Byrne, S.; Walker, G.; Adams, G.; Yuan, Y.; Reynolds, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Dashper, S.; Reynolds, E. Remineralisation by chewing sugar-free gums in a randomised, controlled in situ trial including dietary intake and gauze to promote plaque formation. Caries Res. 2012, 46, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebayo, O.; Burrow, M.; Tyas, M. An SEM evaluation of conditioned and bonded enamel following carbamide peroxide bleaching and casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) treatment. J. Dent. 2009, 37, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penumatsa, N.V.; Kaminedi, R.R.; Baroudi, K.; Barakath, O. Evaluation of remineralization capacity of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on the carbamide peroxide treated enamel. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7 (Suppl. 2), S583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.; Margaritis, A. Poly(glutamic acid) for biomedical applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2001, 21, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwata, H.; Matsuda, S.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Itoh, E.; Ikada, Y. A novel surgical glue composed of gelatin and N-hydroxysuccinimide activated poly(L-glutamic acid): Part 1. Synthesis of activated poly(L-glutamic acid) and its gelation with gelatin. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chung, C.K.; Chen, C.T.; Liang, H.F.; Chen, S.C.; Sung, H.W. Preparation of nanoparticles composed of chitosan/poly-gamma-glutamic acid and evaluation of their permeability through Caco-2 cells. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Hu, W.-k.; Li, H.; Jing, Y.-h.; Kang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C. Preparation and characterization of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels as potential tissue engineering scaffolds. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhan, S.; Yi, M.; Chi, B.; Xu, H.; Mao, C. Degradation performance of polyglutamic acid and its application of calcium supplement. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, H.; Fox, T.; Eagles, J.; Satoh, H.; Nozawa, H.; Okiyama, A.; Morinaga, Y.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J. Acute effect of poly-gamma-glutamic acid on calcium absorption in post-menopausal women. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Al-Bayatee, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shavandi, A.; Brunton, P.; Ratnayake, J.J.M. Hydroxyapatite in Oral Care Products—A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivrak, N.; Taş, A.C. Synthesis of calcium hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate (HA-TCP) composite bioceramic powders and their sintering behavior. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Midha, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Maurya, R.; Nigam, V.K.; Ghosh, S.; Balani, K. Antioxidant and antibacterial hydroxyapatite-based biocomposite for orthopedic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 88, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.; Rahman, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Sefat, F.; Kumar, N. Effect of Nanostructures on the Properties of Glass Ionomer Dental Restoratives/Cements: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Materials 2021, 14, 6260. [Google Scholar]
- Roveri, N.; Foresti, E.; Lelli, M.; Lesci, I.G. Recent advancements in preventing teeth health hazard: The daily use of hydroxyapatite instead of fluoride. Recent Pat. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Tao, J.; Xu, X.; Mao, C.; Gu, X.; Tang, R. Repair of enamel by using hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as the building blocks. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4079–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghgoo, R.; Ahmadvand, M.; Moshaverinia, S. Remineralizing Effect of Topical NovaMin and Nano-hydroxyapatite on caries-like Lesions in Primary teeth. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2016, 17, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Yu, H. Remineralization potential of nano-hydroxyapatite on initial enamel lesions: An in vitro study. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyavhare, S.; Sharma, D.S.; Kulkarni, V. Effect of three different pastes on remineralization of initial enamel lesion: An in vitro study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2015, 39, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarajan, J.; Janardhanam, P.; Jayakumar, P. Deepika, Efficacy of CPP-ACP and CPP-ACPF on enamel remineralization—An in vitro study using scanning electron microscope and DIAGNOdent®. Indian J. Dent. Res. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Dent. Res. 2011, 22, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstone, L.M. Remineralization of Human Enamel In Vitro; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Qamar, Z.; Rahim, Z.B.H.A.; Neon, G.S.; Chew, H.P.; Zeeshan, T. Effectiveness of poly-γ-glutamic acid in maintaining enamel integrity. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 106, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Yu, H. Combined effects of nano-hydroxyapatite and Galla chinensis on remineralisation of initial enamel lesion in vitro. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, O.Y.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Lo, E.C.; Chu, C.H. A Review of the Common Models Used in Mechanistic Studies on Demineralization-Remineralization for Cariology Research. Dent. J. 2017, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-J.; Takahashi, R.; Lin, P.-Y.; Kuo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Matin, K.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Shimada, Y.; Tagami, J. Anti-Demineralization Effects of Dental Adhesive-Composites on Enamel-Root Dentin Junction. Polymers 2021, 13, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargul, B.; Altinok, B.; Welbury, R. The effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on enamel surface rehardening. An in vitro study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2012, 13, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hua, F.; Yan, J.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; He, H. In vitro remineralization of enamel white spot lesions with a carrier-based amorphous calcium phosphate delivery system. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rao, A.; Shenoy, R.; Suprabha, B.S. Comparative evaluation of Nano-hydroxyapatite and casein Phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on the remineralization potential of early enamel lesions: An in vitro study. J. Orofac. Sci. 2017, 9, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Kunam, D.; Sampath, V.; Manimaran, S.; Sekar, M. Effect of indigenously developed nano-hydroxyapatite crystals from chicken egg shell on the surface hardness of bleached human enamel: An In Vitro study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, V.; Bhatia, A.; Varma, H. Development, characterization and comparison of two strontium doped nano hydroxyapatite molecules for enamel repair/regeneration. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Mai, S.; Lin, H.-C.; Zhi, Q.-H. Effect of poly (γ-glutamic acid)/tricalcium phosphate (γ-PGA/TCP) composite for dentin remineralization in vitro. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 40, 2019–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahamid, J.; Aichmayer, B.; Shimoni, E.; Ziblat, R.; Li, C.; Siegel, S.; Paris, O.; Fratzl, P.; Weiner, S.; Addadi, L. Mapping amorphous calcium phosphate transformation into crystalline mineral from the cell to the bone in zebrafish fin rays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6316–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, R. Amorphous calcium phosphate phase-mediated crystal nucleation kinetics and pathway. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 179, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.S.; Patel, A.N.; Al Botros, R.; Snowden, M.E.; McKelvey, K.; Unwin, P.R.; Ashcroft, A.T.; Carvell, M.; Joiner, A.; Peruffo, M. Measurement of the efficacy of calcium silicate for the protection and repair of dental enamel. J. Dent. 2014, 42, S21–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, D.; Jaiswal, A.K. Synthesis and characterization of human bone-like hydroxyapatite using Schiff’s base. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9401–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, M.; Mirando, M.; Beltrami, R.; Chiesa, M.; Poggio, C. Protective effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on enamel erosion: Atomic force microscopy studies. Scanning 2015, 37, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionysopoulos, D.; Tolidis, K.; Sfeikos, T. Effect of CPP-ACPF and nano-hydroxyapatite preventive treatments on the susceptibility of enamel to erosive challenge. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2019, 17, 357–364. [Google Scholar]

| Group | 9 wt%-γPGA/Nano-HAp | GC Tooth Mousse | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHN | SMHR% | VHN | SMHR% | |
| Sound enamel | 361.16 ± 9.21 a | 332.95 ± 2.05 a | ||
| Etched enamel | 218.41 ± 6.87 b | 208.29 ± 2.01 b | ||
| Treat 10 min | 261.31 ± 0.32 c | 30.10 ± 5.53 | 221.77 ± 0.62 c | 10.81 ± 1.13 |
| 20 min | 270.11 ± 2.21 c | 36.27 ± 6.95 | 223.15 ± 1.81 c | 11.92 ± 0.17 |
| 30 min | 274.84 ± 1.75 c | 39.59 ± 6.69 | 223.65 ± 2.21 c | 12.32 ± 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, N.-C.; Pandey, A.; Hsu, W.-H.; Huang, C.-S.; Lee, W.-F.; Lee, T.-H.; Yang, T.C.-K.; Yang, T.-S.; Yang, J.-C. Rehardening and the Protective Effect of Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste on Surface-Etched Enamel. Polymers 2021, 13, 4268. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234268
Teng N-C, Pandey A, Hsu W-H, Huang C-S, Lee W-F, Lee T-H, Yang TC-K, Yang T-S, Yang J-C. Rehardening and the Protective Effect of Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste on Surface-Etched Enamel. Polymers. 2021; 13(23):4268. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234268
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Nai-Chia, Aditi Pandey, Wei-Hsin Hsu, Ching-Shuan Huang, Wei-Fang Lee, Tzu-Hsin Lee, Thomas Chung-Kuang Yang, Tzu-Sen Yang, and Jen-Chang Yang. 2021. "Rehardening and the Protective Effect of Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste on Surface-Etched Enamel" Polymers 13, no. 23: 4268. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234268
APA StyleTeng, N.-C., Pandey, A., Hsu, W.-H., Huang, C.-S., Lee, W.-F., Lee, T.-H., Yang, T. C.-K., Yang, T.-S., & Yang, J.-C. (2021). Rehardening and the Protective Effect of Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste on Surface-Etched Enamel. Polymers, 13(23), 4268. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234268







