The Basolateral Amygdala Mediates the Role of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Integrating Fear Memory Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Virus Vector Construct
2.3. Surgical Procedures
2.4. Experimental Procedures
2.5. Optogenetic Stimulation
2.6. Sleep Scoring
2.7. Electroencephalograph (EEG) Analysis
2.8. Scoring of Freezing
2.9. Evaluation of Body Temperature
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histological Verification of Stimulation Sites
3.2. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (REM) + L, but Not Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (NREM) + L, Attenuated Freezing Tested at 24 h and 48 h after Fear Conditioning
3.3. Fear Conditioning and Stress-Induced Hyperthermia
3.4. Stress and Fear-Conditioned Alterations in Sleep
3.5. REM + L Attenuated Post-Re-Exposure REM-θ Reduction
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pace-Schott, E.F.; Germain, A.; Milad, M.R. Effects of sleep on memory for conditioned fear and fear extinction. Psychol. Bull. 2015, 141, 835–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M. The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1992, 15, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Rison, R.A.; Fanselow, M.S. Effects of amygdala, hippocampus, and periaqueductal gray lesions on short- and long-term contextual fear. Behav. Neurosci. 1993, 107, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.W.; Han, J.S.; Kim, J.J. Selective neurotoxic lesions of basolateral and central nuclei of the amygdala produce differential effects on fear conditioning. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7654–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maren, S. Overtraining does not mitigate contextual fear conditioning deficits produced by neurotoxic lesions of the basolateral amygdala. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3088–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, H.C.; Pare, D. Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 419–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitkanen, A. Connectivity of the rat amygdaloid complex. In The Amygdala; Aggleton, J.P., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 31–115. [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen, M.; Ronkko, S.; Savander, V.; Insausti, R.; Pitkanen, A. Projections from the lateral, basal, and accessory basal nuclei of the amygdala to the hippocampal formation in rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 403, 229–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Maren, S. Hippocampal involvement in contextual modulation of fear extinction. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.B.; Vertes, R.P. Anatomical analysis of afferent projections to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Struct. Funct. 2007, 212, 149–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirk, G.J.; Mueller, D. Neural mechanisms of extinction learning and retrieval. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pare, D.; Quirk, G.J.; Ledoux, J.E. New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeDoux, J.E. Emotion circuits in the brain. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 23, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeDoux, J.E. Emotional memory systems in the brain. Behav. Brain Res. 1993, 58, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.; Whalen, P.J. The amygdala: Vigilance and emotion. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machida, M.; Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick Bs, M.E.; Hallum Bs, O.; Sutton Bs, A.M.; Lonart, G.; Sanford, L.D. Brief Optogenetic Inhibition of the Basolateral Amygdala in Mice Alters Effects of Stressful Experiences on Rapid Eye Movement Sleep. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Machida, M.; Sanford, L.D. The basolateral amygdala determines the effects of fear memory on sleep in an animal model of PTSD. Exp. Brain Res. 2014, 232, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Yang, L.; Ambrozewicz, M.A.; Machida, M.; Sanford, L.D. Basolateral amygdala and the regulation of fear-conditioned changes in sleep: Role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Sleep 2013, 36, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Hallum, O.Y.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Sanford, L.D. Individual Differences in Animal Stress Models: Considering Resilience, Vulnerability, and the Amygdala in Mediating the Effects of Stress and Conditioned Fear on Sleep. Sleep 2016, 39, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Hallum, O.Y.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Sanford, L.D. The basolateral amygdala can mediate the effects of fear memory on sleep independently of fear behavior and the peripheral stress response. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 137, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Machida, M.; Sanford, L.D. Antagonism of corticotropin releasing factor in the basolateral amygdala of resilient and vulnerable rats: Effects on fear-conditioned sleep, temperature and freezing. Horm. Behav. 2018, 100, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Sweeten, B.L.W.; Adkins, A.M.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Basolateral Amygdala Regulates EEG Theta-activity During Rapid Eye Movement Sleep. Neuroscience 2021, 468, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G.; Leung, L.W.; Vanderwolf, C.H. Cellular bases of hippocampal EEG in the behaving rat. Brain Res. 1983, 287, 139–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesting, J.; Narayanan, R.T.; Kluge, C.; Sangha, S.; Seidenbecher, T.; Pape, H.C. Patterns of coupled theta activity in amygdala-hippocampal-prefrontal cortical circuits during fear extinction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pape, H.C.; Narayanan, R.T.; Smid, J.; Stork, O.; Seidenbecher, T. Theta activity in neurons and networks of the amygdala related to long-term fear memory. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G. The hippocampo-neocortical dialogue. Cereb. Cortex 1996, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzsaki, G. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron 2002, 33, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pare, D.; Collins, D.R.; Pelletier, J.G. Amygdala oscillations and the consolidation of emotional memories. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, R.; Glasgow, S.D.; Williams, S.; Adamantidis, A. Causal evidence for the role of REM sleep theta rhythm in contextual memory consolidation. Science 2016, 352, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwolf, C.H. Hippocampal electrical activity and voluntary movement in the rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1969, 26, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stujenske, J.M.; Likhtik, E.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Fear and safety engage competing patterns of theta-gamma coupling in the basolateral amygdala. Neuron 2014, 83, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, A.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Synchronized activity between the ventral hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex during anxiety. Neuron 2010, 65, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidenbecher, T.; Laxmi, T.R.; Stork, O.; Pape, H.C. Amygdalar and hippocampal theta rhythm synchronization during fear memory retrieval. Science 2003, 301, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machida, M.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Differential behavioral, stress, and sleep responses in mice with different delays of fear extinction. Sleep 2019, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, A.J. REM sleep deprivation affects extinction of cued but not contextual fear conditioning. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 84, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Li, P.; Ouyang, X.; Gu, C.; Song, Z.; Gao, J.; Han, L.; Feng, S.; Tian, S.; Hu, B. Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation selectively impairs recall of fear extinction in hippocampus-independent tasks in rats. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Yang, L.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Effects of stressor predictability on escape learning and sleep in mice. Sleep 2013, 36, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.P.; Boyden, E.S.; Deisseroth, K. Channelrhodopsin-2 and optical control of excitable cells. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuber, G.D.; Sparta, D.R.; Stamatakis, A.M.; van Leeuwen, W.A.; Hardjoprajitno, J.E.; Cho, S.; Tye, K.M.; Kempadoo, K.A.; Zhang, F.; Deisseroth, K.; et al. Excitatory transmission from the amygdala to nucleus accumbens facilitates reward seeking. Nature 2011, 475, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Sanford, L.D. Telemetric recording of sleep and home cage activity in mice. Sleep 2002, 25, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, R.J.; Blanchard, D.C. Passive and active reactions to fear-eliciting stimuli. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1969, 68, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkers, C.H.; van Oorschot, R.; Olivier, B.; Groenink, L. Stress-Induced Hyperthermia in the Mouse. In Mood and Anxiety Related Phenotypes in Mice, Neuromethods; Gould, T.D., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wehr, T.A. A brain-warming function for REM sleep. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, L.D.; Yang, L. Differential Effects of Controllable and Uncontrollable Footshock Stress on Sleep in Mice. Sleep 2010, 33, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellman, L.L.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.; Sanford, L.D. Contextual fear extinction ameliorates sleep disturbances found following fear conditioning in rats. Sleep 2008, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, L.A.; Heller, E.A.; Pack, A.I.; Abel, T. Sleep deprivation selectively impairs memory consolidation for contextual fear conditioning. Learn. Mem. 2003, 10, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warlow, S.M.; Robinson, M.J.F.; Berridge, K.C. Optogenetic Central Amygdala Stimulation Intensifies and Narrows Motivation for Cocaine. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8330–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Warlow, S.M.; Berridge, K.C. Optogenetic excitation of central amygdala amplifies and narrows incentive motivation to pursue one reward above another. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 16567–16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Guo, Y.; Jia, X.; Choe, H.K.; Grena, B.; Kang, J.; Park, J.; Lu, C.; Canales, A.; Chen, R.; et al. One-step optogenetics with multifunctional flexible polymer fibers. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, M.L.; Miller, R.L.; Deisseroth, K.; Moorman, D.E.; LaLumiere, R.T. Posttraining optogenetic manipulations of basolateral amygdala activity modulate consolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3597–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, J.P.; Hamanaka, H.; Monfils, M.H.; Behnia, R.; Deisseroth, K.; Blair, H.T.; LeDoux, J.E. Optical activation of lateral amygdala pyramidal cells instructs associative fear learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12692–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popescu, A.T.; Popa, D.; Pare, D. Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, E.P.; Paz, R.; Pare, D. Gamma oscillations coordinate amygdalo-rhinal interactions during learning. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9369–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, I.; Furini, C.R.; Myskiw, J.C. Fear Memory. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 695–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Orchard, S.M.; Sanford, L.D. Home cage activity and behavioral performance in inbred and hybrid mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, X.; Sanford, L.D. Strain differences in the influence of open field exposure on sleep in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 154, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, K.C. The relation between fear induced by novel stimulation and exploratory behavior. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1955, 48, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, W.R.; Naugle, N.W. Oscillatory electrographic activity in the hippocampus: A mathematical model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1980, 4, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siapas, A.G.; Lubenov, E.V.; Wilson, M.A. Prefrontal phase locking to hippocampal theta oscillations. Neuron 2005, 46, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirota, A.; Montgomery, S.; Fujisawa, S.; Isomura, Y.; Zugaro, M.; Buzsaki, G. Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 2008, 60, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popa, D.; Duvarci, S.; Popescu, A.T.; Lena, C.; Pare, D. Coherent amygdalocortical theta promotes fear memory consolidation during paradoxical sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6516–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitkanen, A.; Pikkarainen, M.; Nurminen, N.; Ylinen, A. Reciprocal connections between the amygdala and the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, and postrhinal cortex in rat. A review. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2000, 911, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvet, M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science 1969, 163, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Saha, S.; Prutzman, S.L.; Mullins, O.J.; Mavanji, V. Pontine-wave generator activation-dependent memory processing of avoidance learning involves the dorsal hippocampus in the rat. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Datta, S.; O’Malley, M.W. Fear extinction memory consolidation requires potentiation of pontine-wave activity during REM sleep. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4561–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, L.D.; Tejani-Butt, S.M.; Ross, R.J.; Morrison, A.R. Amygdaloid control of alerting and behavioral arousal in rats: Involvement of serotonergic mechanisms. Arch. Ital. Biol. 1995, 134, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deboer, T.; Sanford, L.D.; Ross, R.J.; Morrison, A.R. Effects of electrical stimulation in the amygdala on ponto-geniculo-occipital waves in rats. Brain Res. 1998, 793, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboer, T.; Ross, R.J.; Morrison, A.R.; Sanford, L.D. Electrical stimulation of the amygdala increases the amplitude of elicited ponto-geniculo-occipital waves. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



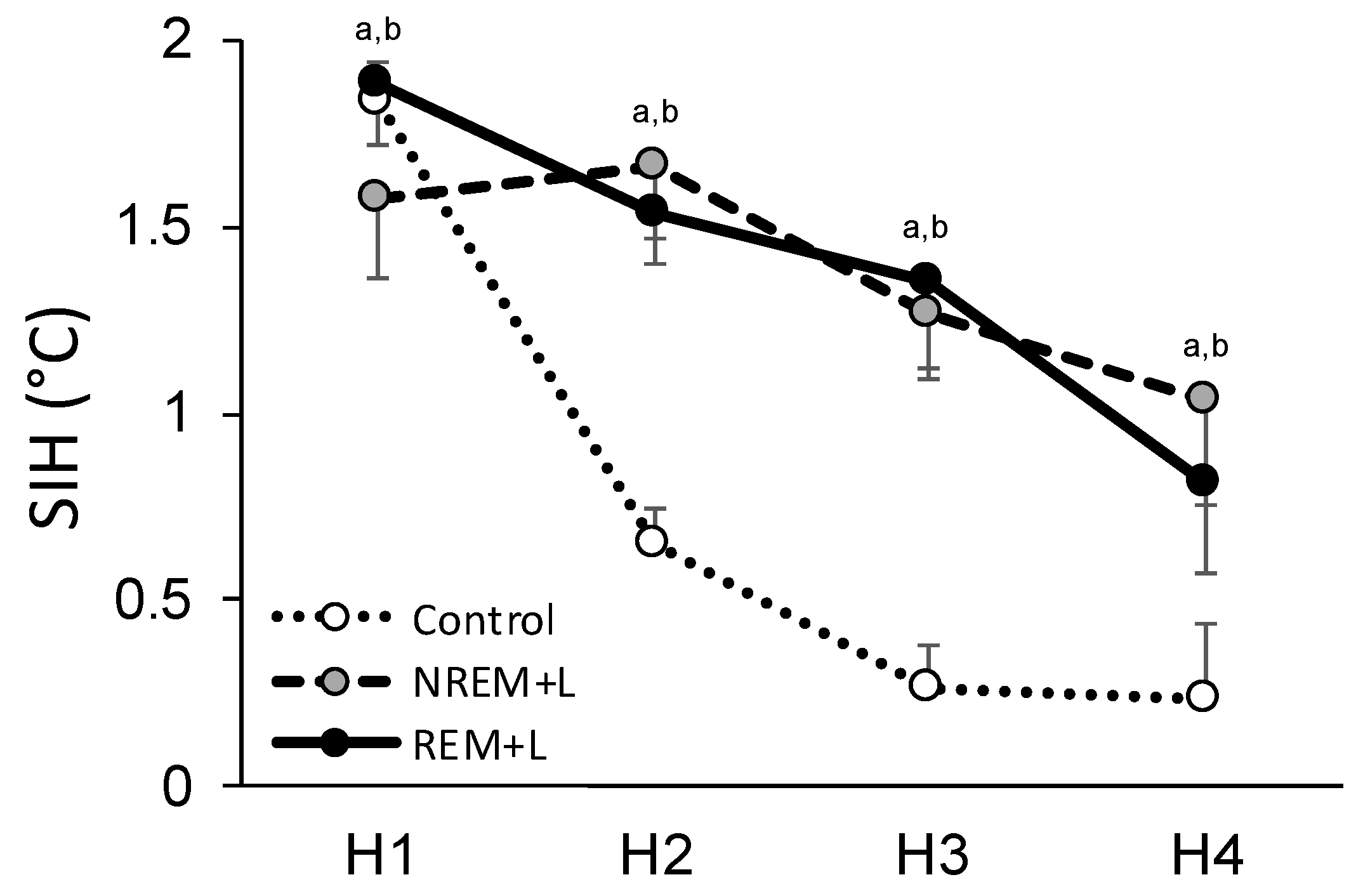


| Day | Hour | Control | NREM + L | REM + L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | H1 | 1.83 ± 0.11 * | 1.57 ± 0.21 * | 1.89 ± 0.17 * |
| H2 | 0.64 ± 0.10 | 1.66 ± 0.19 * | 1.54 ± 0.14 * | |
| H3 | 0.26 ± 0.12 | 1.27 ± 0.15 * | 1.35 ± 0.26 * | |
| H4 | 0.24 ± 0.20 | 1.04 ± 0.28 | 0.82 ± 0.24 * | |
| 24 H | H1 | 1.54 ± 0.16 * | 1.26 ± 0.19 * | 1.51 ± 0.13 * |
| H2 | 0.54 ± 0.09 | 0.74 ± 0.12 | 0.69 ± 0.17 | |
| H3 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | 0.40 ± 0.17 | 0.30 ± 0.21 | |
| H4 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.24 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | |
| 48 H | H1 | 1.39 ± 0.16 * | 1.11 ± 0.21 * | 1.27 ± 0.16 * |
| H2 | 0.35 ± 0.14 | 0.66 ± 0.10 | 0.71 ± 0.18 | |
| H3 | 0.00 ± 0.08 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.41 ± 0.22 | |
| H4 | 0.06 ± 0.09 | 0.22 ± 0.16 | 0.28 ± 0.22 | |
| 1 WK | H1 | 1.28 ± 0.19 * | 0.86 ± 0.30 * | 1.17 ± 0.14 * |
| H2 | 0.29 ± 0.13 | 0.38 ± 0.11 | 0.45 ± 0.19 | |
| H3 | −0.01 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 0.00 ± 0.19 | |
| H4 | 0.05 ± 0.09 | 0.01 ± 0.20 | 0.02 ± 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machida, M.; Sweeten, B.L.W.; Adkins, A.M.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. The Basolateral Amygdala Mediates the Role of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Integrating Fear Memory Responses. Life 2022, 12, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010017
Machida M, Sweeten BLW, Adkins AM, Wellman LL, Sanford LD. The Basolateral Amygdala Mediates the Role of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Integrating Fear Memory Responses. Life. 2022; 12(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachida, Mayumi, Brook L. W. Sweeten, Austin M. Adkins, Laurie L. Wellman, and Larry D. Sanford. 2022. "The Basolateral Amygdala Mediates the Role of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Integrating Fear Memory Responses" Life 12, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010017
APA StyleMachida, M., Sweeten, B. L. W., Adkins, A. M., Wellman, L. L., & Sanford, L. D. (2022). The Basolateral Amygdala Mediates the Role of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Integrating Fear Memory Responses. Life, 12(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010017







