Abstract
(-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG) is a polyphenolic compound similar to (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) which is abundant in green tea. Numerous workers have proposed that EGCG protects epidermal cells against UVB-induced damage. However, little has been known about whether ECG protects keratinocytes against UVB-induced damage. We decided to investigate the protective effects and underlying mechanisms of ECG on UVB-induced damage. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. Activation of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK was analyzed by Western blotting. Intracellular H2O2 production and DNA content was analyzed by flow cytometry. Lipid peroxidation was assayed by colorimetry. In our study, we found that ECG dose-dependently attenuated UVB-induced keratinocyte death. Moreover, ECG markedly inhibited UVB-induced cell membrane lipid peroxidation and H2O2 generation in keratinocytes, suggesting that ECG can act as a free radical scavenger when keratinocytes were photodamaged. In parallel, H2O2-induced the activation of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK in keratinocytes could be inhibited by ECG. UVB-induced pre-G1 arrest leading to apoptotic changes of keratinocytes were blocked by ECG. Taken together, we provide here evidence that ECG protects keratinocytes from UVB-induced photodamage and H2O2-induced oxidative stress, possibly through inhibition of the activation of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK and/or scavenging of free radicals.
Introduction
Solar ultraviolet radiation, particularly ultraviolet B (UVB) with a wavelength range between 290 and 320 nm, elicits many adverse effects in the skin, which include generation of skin cancer [1], suppression of the immune system [2,3] and photoaging [4]. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated by ultraviolet radiation, resulting in oxidative damage to cellular components such as mitochondria, as well as nuclear DNA damage, which in turn accelerates aging and contributes to skin cancers [5]. Antioxidants play an important role that protects skin against ROS-induced injury. Numerous antioxidants, such as ascorbic acid [6], α-tocopherol [7] and a mixture of dietary antioxidants [8] have been reported to inhibit UV-induced skin carcinogenesis..
Green tea catechins have attracted much attention because of their relative high antioxidant capacity and their abundance in human diet [9,10]. In several publications, it has been demonstrated that topical application or oral feeding of a polyphenolic fraction prepared from green tea (GTP) prevents photocarcinogenesis [11,12,13]. The major green tea catechins are (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG; 9-13%), (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC; 3-6%), (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG; 3-6%), (-)-epicatechin (EC; 1-3%), and (+)-catechin (C; less than 1%). Several catechins found in green tea have been shown to have antioxidant activities [14,15] and display cutaneous photoprotection [16]. A previous study showed that the galloyl catechins, especially EGCG, are an effective protectant against the oxidative stress of UVB radiation [17]. Topical treatment of mouse and human skin with EGCG before UV exposure significantly reduced UVB-induced erythema development, hydrogen peroxide production and leukocyte infiltration [18,19]. In addition, EGCG have been shown to protect against UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis in mice [20,21,22]. These data suggest that the galloylcatechins have the potential to reduce the risk of UV-induced, oxidative stress-mediated skin diseases in humans. Although ECG is the third major catechin in green tea, it shows strong biological activity in several areas [23]. It was reported that EGCG and ECG have anticancer activities, but not EGC or EC. Thus, both EGCG and ECG may play an important role in green tea-induced anti-tumorigenesis [23]. Recently, our laboratory demonstrated that ECG protects skin cells against UVA-induced damage [24]. However, ECG has not been studied in detail regarding UVB photoprotection. Several studies have shown that EGCG are photoprotectant in skin cells, but little input has been directed to evaluating the photoprotective effects by ECG. In this study, effect of ECG on UVB-induced skin cell damage was investigated. Our results indicate that ECG may act through inhibition of UVB-induced intracellular hydrogen peroxide production and MAPK signaling pathway.
Results and Discussion
ECG inhibits UVB-induced keratinocyte death
To clarify the protective effect of ECG, HaCaT keratinocytes were pretreated with different concentrations of ECG and exposed to UVB. A UVB dose at 50mJ/cm2 was used in this study because it caused about 40~50% decrease of cell viability, as determined by the MTT assay. After a further incubation for 24 h in the presence or absence of ECG, cell viability was measured by this assay. We found that ECG dose-dependently reversed UVB-induced cell death. (Figure 1), ECG at 1 μM is sufficient to exert its inhibitory effect. The effect was not due to ECG’s proliferative activity because ECG alone did not affect the cell viability [24]. The result suggests that ECG prevents human keratinocytes from UVB-induced damage. Our laboratory has shown that ECG also prevents UVA-induced keratinocyte death [24]. However, it appears that ECG exerted a pronounced inhibitory effect on UVB-induced keratinocyte death at the same tested concentrations, suggesting its differential effects on UV irradiation-induced cell damage.
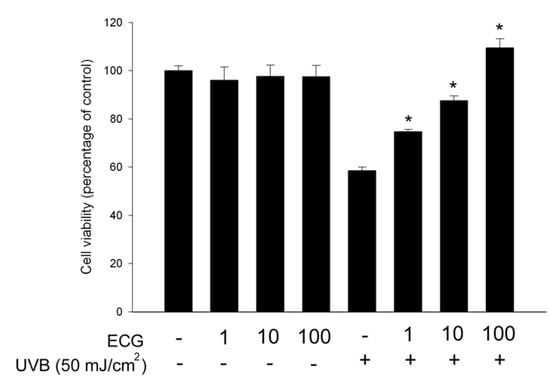
Figure 1.
ECG inhibition of UVB irradiation-induced keratinocyte death.
Figure 1.
ECG inhibition of UVB irradiation-induced keratinocyte death.
Results are expressed as percentage of control and are mean ± SE (n=4). * P < 0.05 vs. UVB-exposed cells without ECG treatment
ECG inhibits lipid peroxidation (LPO) by UVB irradiation
The hallmarks of UVB-induced oxidative damage are the oxidation of biomacromolecules like lipids. As cell death is strongly associated with lipid peroxidation (LPO) of cell membranes, we assessed whether ECG affected LPO of keratinocytes. Human HaCaT keratinocytes were pretreated with ECG for 2 h and then exposed to UVB irradiation. This exposure increased LPO, as compared to non-UVB-exposed control cells. Treatment of keratinocytes with ECG (1, 10 and 100 μM) obviously inhibited UVB-induced LPO in keratinocytes (Figure 2).
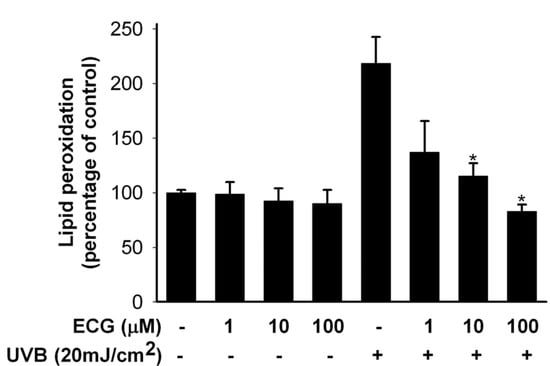
Figure 2.
Protective effect of ECG on UVB-induced lipid peroxidation in human keratinocytes.
Figure 2.
Protective effect of ECG on UVB-induced lipid peroxidation in human keratinocytes.
Lipid peroxidation was detemined by measuring MDA content in cell lysates, as described in experimental section and the results were expressed as MDA per total proteins (n=5). * P < 0.01 vs. UVB-exposed cells without ECG treatment.
LPO is highly detrimental to cell membrane structure and function, and its elevated levels have been linked to damaging effects such as loss of fluidity, inactivation of membrane enzymes, increased cell membrane permeability to ions, and finally rupture of cell membrane leading to release of cell organelles [25,26,27]. Thus, a strong inhibition of LPO by ECG would result in reduction of the risk factors associated with UVB radiation.
ECG inhibits UVB-induced H2O2 generation in keratinocytes
Hydrogen peroxide is generated in cultured human skin cells during UVB irradiation [17,28]. We therefore suspected that ECG affected UVB-induced intracellular H2O2 production. To further elucidate the possible action mechanisms of ECG in inhibiting UVB-induced keratinocyte death and lipid peroxidation, we measured intracellular H2O2 in keratinocytes by using dihydrorhodamine 123. The dye has been shown to react with H2O2 in the presence of peroxidase and is extensively used as a probe for the detection of intracellular H2O2 [17,29].
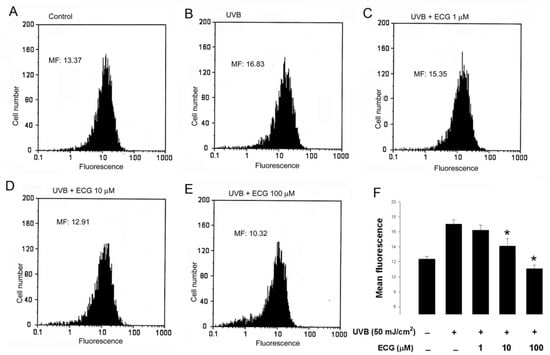
Figure 3.
ECG inhibits intracellular H2O2 production in keratinocytes.
Figure 3.
ECG inhibits intracellular H2O2 production in keratinocytes.
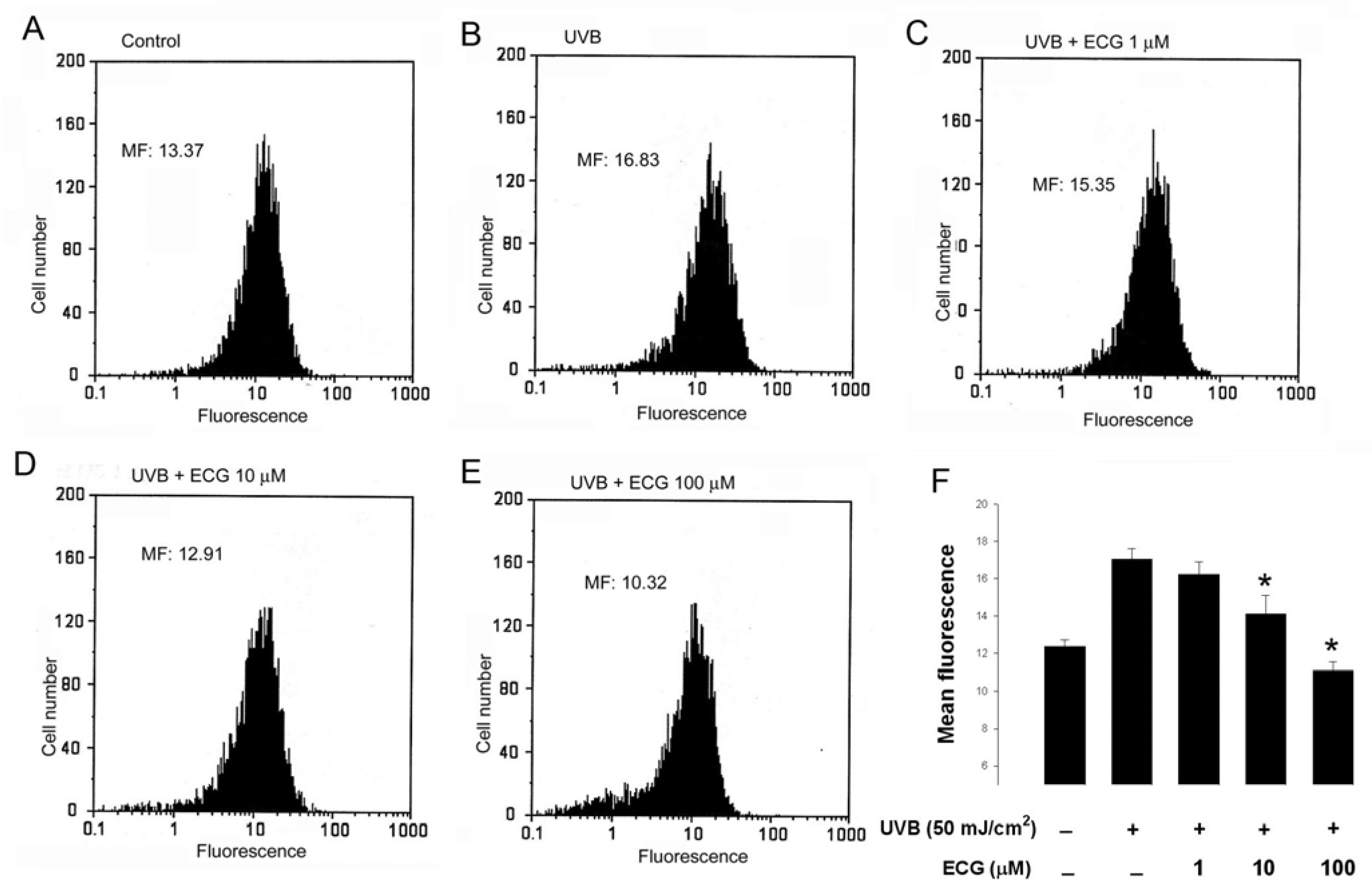
Human HaCaT keratinocytes preincubated with PBS (A and B) or the indicated concentrations of ECG (C-E) were loaded with DHR 123. After UVB irradiation (B-E), cells were collected and subjected to flow cytometric analysis for the measurement of intracellular H2O2. Results were presented as histograms of cell number versus fluorescence intensity. Each histogram is the representative of four similar independent experiments. (F) Quantitative analysis of intracellular H2O2 production in keratinocytes. * P < 0.05 vs. UVB-exposed cells without ECG treatment.
As previously reported [17], in our system, flow cytometric analysis showed that mean fluorescence, i.e. H2O2 production, was increased in UVB-treated cells than in control untreated cells (Figure 3, panels A and B). However, the increase of intracellular H2O2 was inhibited by the treatment of ECG in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 3 panels C, D, E and F), indicating that ECG has a potent scavenging activity towards H2O2. Taken together, our present and previous data reveal that ECG can prevent both UVA and UVB-induced intracellular H2O2 production in human keratinocytes.
ECG inhibits UVB-induced ERK1/2, JNK andp38 activation
It has been shown that various signaling pathways are activated during or after UV exposure. For example, UV irradiation leads to the activation of MAPKs, including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 [17,30]. We next examined ECG’s effect on UVB-induced MAPKs phosphorylation. As shown in Figure 4, JNK, ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation increased at 30 min after UVB irradiation in keratinocytes. However, the activation of ERK1/2, JNK and p38 was reduced by treatment of ECG (Figure 4, upper panels). The decrease of phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK and p38 was not due to uneven loading because expression of each total protein was about the same (lower panels). Interestingly, it was found that JNK activation induced by UVB irradiation was inhibited by low and higher concentrations of ECG, whereas ERK1/2 and p38 activation was only affected by ECG at 100 μM. Taken together, the results showed that ECG can inhibit UVB irradiation-induced JNK, ERK1/2 and p38 activation in human keratinocytes.
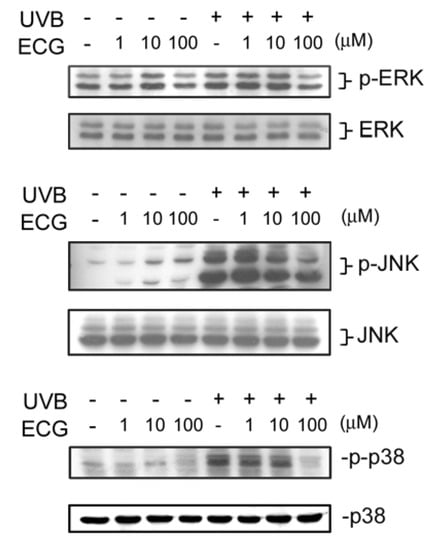
Figure 4.
Effect of ECG on UVB-induced ERK1/2, JNK and p38 activation.
Figure 4.
Effect of ECG on UVB-induced ERK1/2, JNK and p38 activation.
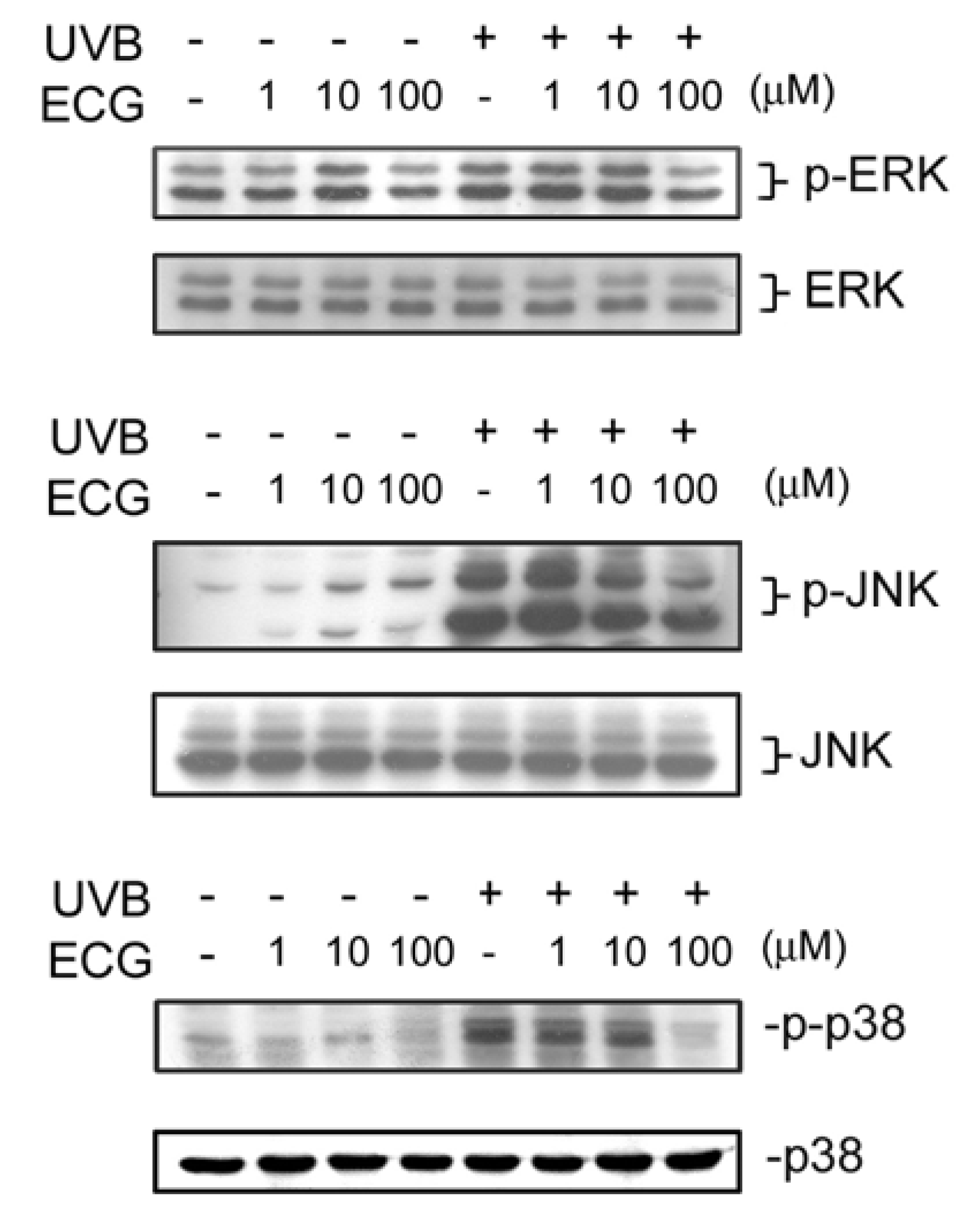
Control and UVB-irradiated keratinocytes treated with PBS or ECG were collected and lysed. Cell lysates were subjected to be analyzed by Western blotting. All results shown above are the representatives from three to four independent experiments.ECG inhibits8 H2O2 -induced ERK1/2, JNK andp38 activation
It has been reported that H2O2 is required for UVB-induced activation of the EGF receptor and downstream signaling pathway(s) [28]. Moreover, several studies demonstrated that H2O2 treatment induces phosphorylation of MAPKs in keratinocytes [17], suggesting that it causes an oxidative stress on skin cells. We next tested if ECG affects H2O2-induced signaling in keratinocytes. It was also found that JNK activation induced by H2O2 treatment was inhibited by low and higher concentrations of ECG, whereas ERK1/2 and p38 activation was only affected by ECG at 100 μM. (Figure 5).
Exposure of solar UV radiation results in an increased generation of ROS that overwhelms the antioxidant defense mechanisms of skin. This condition of disequilibrium is defined as ‘‘oxidative stress’’. Thus, intervention of antioxidative agents is expected to exhibit a protective effect on the skin photoaging. In this study we found that ECG possesses a strong inhibitory effect on UVB-induced H2O2 production and 10 μM of ECG is sufficient to exert its inhibitory effect (Figure 3). Moreover, ECG inhibited H2O2-induced MAPKs activation. It has been shown that UVB-induced ROS formation is responsible for the activation of MAPKs [28]. Therefore, exogenous H2O2 may directly activate MAPKs signaling pathway through penetrate cell membrane. If ECG inhibits UVB-induced H2O2 production through a direct scavenging of intracellular H2O2, ECG may have relatively strong anti-oxidant activity on exogenous H2O2, which is a large amount (200 μM) in our study. The antioxidant activity was also observed on that ECG could prevent keratinocytes from hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase-induced damage, which was previously demonstrated by our lab [24].
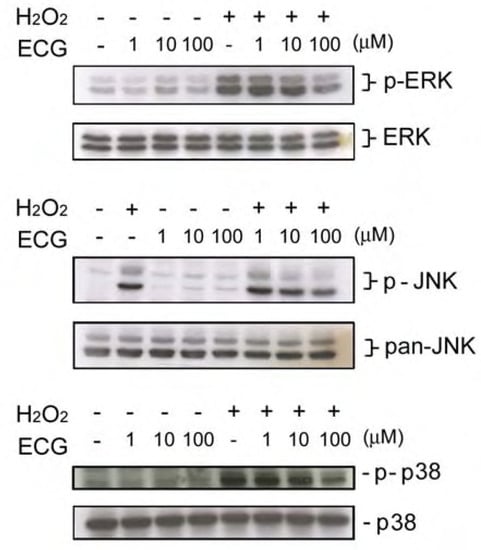
Figure 5.
Effect of ECG on H2O2-induced ERK1/2, JNK and p38 activation.
Figure 5.
Effect of ECG on H2O2-induced ERK1/2, JNK and p38 activation.
Human HaCaT keratinocytes pretreated with the PBS or ECG (1-100 μM) were treated by H2O2 (200 μM). After a further incubation for 30 min, cells were lysed and (A) ERK1/2, (B) JNK and (C) p38 phosphorylation (upper panels) and expression (lower panels) were analyzed by Western blotting. Each blot shown above is the representative from three to four independent experiments.
UV radiation induces the release of ROS, which has been implicated in cutaneous aging as well as in skin cancer and various cutaneous inflammatory disorders [31]. Transcription of many genes is mediated by the sequential activation of cytoplasmic protein kinases, and the MAP kinase plays a major role in triggering and coordinating these gene responses [32]. Peus et al. [29,33] have shown the activation and regulation of MAPKs, namely ERK1/2, JNK, and p38, in normal human epidermal keratinocytes following exposure to UVB radiation. It is suggested that a transient activation of ERK1/2 is responsible for proliferation and differentiation [34] and stimulation of JNK and p38 can mediate differentiation, inflammatory responses and cell death [34,35,36,37]. Therefore MAP kinase signaling cascades are important targets in cells [38,39,40]. Our study provides evidence showing that ECG can inhibit both UVB-induced and H2O2-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK. However, ECG seems to differentially inhibit on UVB- and H2O2-induced MAPKs (Figure 4 and Figure 5). JNK activation induced by UVB irradiation and H2O2 treatment were inhibited by low and higher concentrations of ECG, whereas ERK1/2 and p38 activation were only affected by ECG at 100 μM. These results indicate that the inhibition of JNK by ECG may be predominant to reverse UVB-induced cell death. On the other hand, ECG’s inhibitory effect on ERK activation suggests that it possesses relatively weak antiproliferative activity.
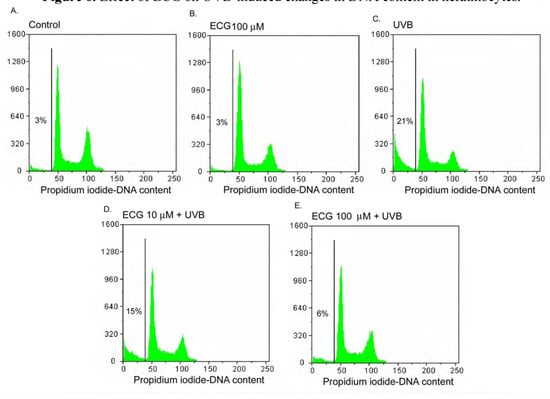
Figure 6.
Effect of ECG on UVB-induced changes in DNA content in keratinocytes.
Figure 6.
Effect of ECG on UVB-induced changes in DNA content in keratinocytes.
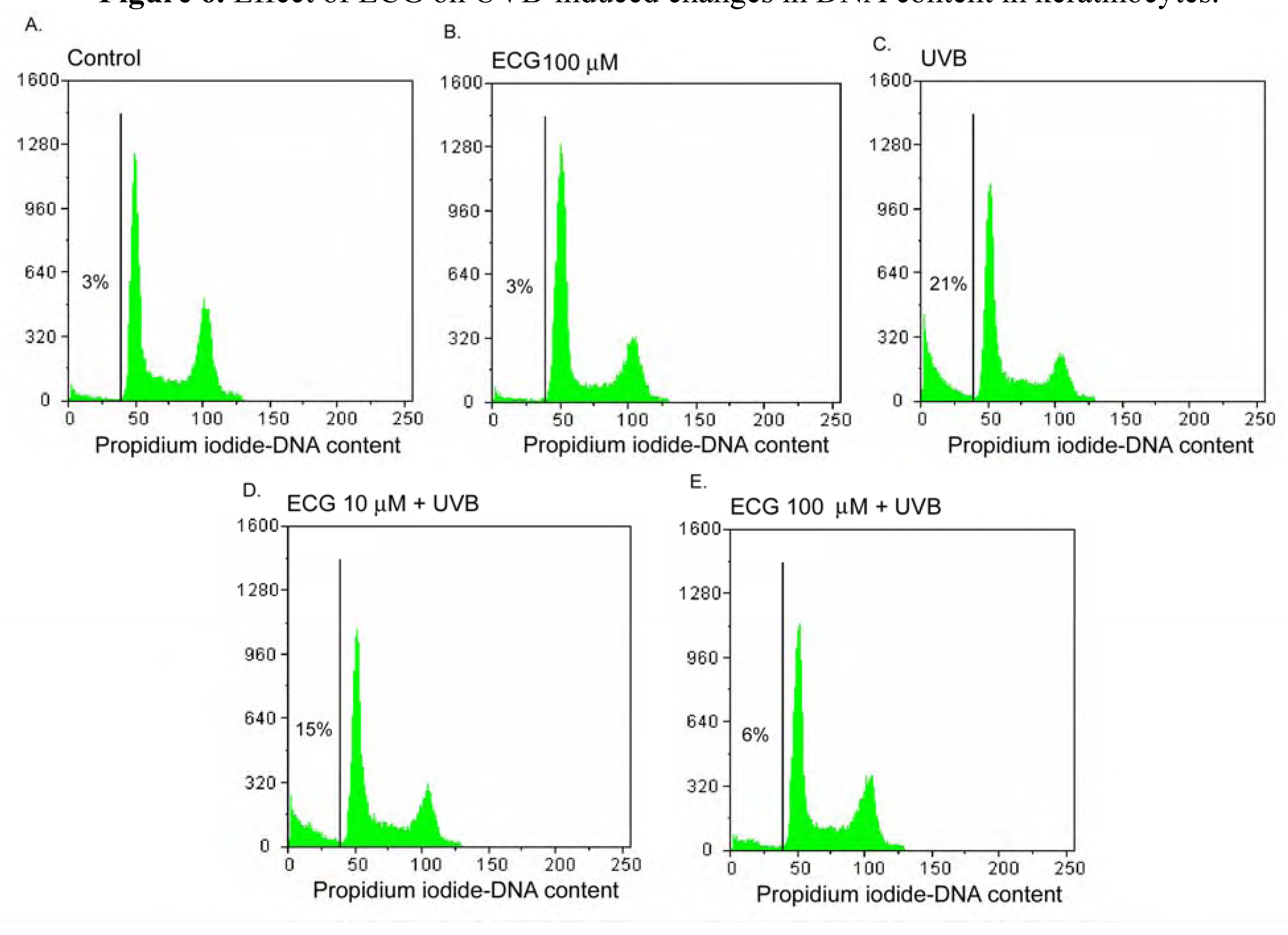
Human keratinocytes treated with PBS or ECG for 2h and were then incubated at 37oC or exposed to UVB (50mJ/cm2). After additional 24h incubation, cellular DNA was stained with PI staining solution and analyzed by flowcytometry. Data shown here are from a representative experiment repeated three times with similar results.
Effect of ECG on DNA content in human keratinocytes
Since the induction of apoptosis by UVB irradiation may be mediated through cell cycle regulation of, we next examined by flow cytometry the effect of ECG on cell cycle perturbation. As shown in Figure 6A and Figure 6B, DNA content was not changed in basal and ECG-treated cells. However, UVB irradiation resulted in an appreciable arrest in pre-G1 phase and a peculiar pre-G1 peak in DNA content, causing 21% of increase of a fractional DNA content in pre-G1 phase (Figure 6C. Cells treated with ECG at 10 and 100 μM before UVB irradiation resulted in a decrease of apoptotic DNA oligonucleosomic strand-breaks to 15 % and 6 %, respectively (Figure 6D and Figure 6E). The mechanism of ECG against UVB-induced apoptosis and cell cycle deregulation may be caused by the inhibition of intracellular ERK1/2, JNK and p38 phosporylation.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the data presented in this study demonstrate that ECG can protect keratinocytes against UVB-induced damage by inhibiting intracellular H2O2 generation, lipid peroxidation and MAPKs activation. This is the first time that mechanisms of action of ECG against UVB damage in keratinocytes has been demonstrated. ECG appears to act on keratinocytes similarly to another galloylcatechin, EGCG, in protecting UVB-induced damage. However, in addition to its anti-UVB-induced ability, ECG also elicited an inhibitory effect on H2O2-induced MAPKs activation, suggesting ECG not only protects keratinocytes from UVB- but also possibly H2O2-induced damage. In view of structure, our data also suggest that the catechins with a galloyl ring structure, including ECG and EGCG, possess bioactivities that can prevent skin photoaging.
Experimental
Materials
ECG, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), aprotinin, leupeptin, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), sodium fluoride (NaF) sodium orthovanadate and propidium iodide were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St Louis, MO). Antibodies raised against p38 and p-JNK were from Cell Signalling Technology (Beverly, MA). Antibodies raised against JNK, ERK1/2 and p-p38 were from R&D System, Inc. (Minneapolis, MN). Antibodies raised against p-ERK1/2 were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Dihydrorhodamine 123 (DHR 123) was from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR).
Cell Culture
Spontaneously immortalized human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT cells) were a gift from Dr. Nan-Lin Wu at HsinChu Mackay Memorial Hospital. They were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal calf serum (GibcoBRL, UK), 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrish, UK). The cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2.
Drug treatment and UVB irradiation
Cell reaching a 90%~95% of confluency were starved and synchronized in serum-free DMEM for 24 h before ECG pretreatment and UVB irradiation. Keratinocytes cultured on 1.5-cm or 3.5-cm culture dishes (Costar, NY) were pretreated with various concentrations of ECG for 2 h. After two washes with DMEM, cells were then incubated with 1 or 2 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). UVB irradiation was performed immediately as suggested by the manufacturer. Briefly, cells were irradiated in a VL Bio-Sun system illuminator (Vilber Lourmat, France) with a UV peak at 312 nm. UVB was supplied by a closely spaced array of two UVB lamps, which delivered uniform irradiation at a distance of 10-cm. UVB irradiation doses were 50 mJ/cm2. After UVB exposure, cells were fed with fresh DMEM containing various concentrations of ECG and then incubated for an additional 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay [24] (see below).
Cell viability assay (MTT assay)
Briefly, MTT (0.5 mg/mL in DMEM) was used for the quantification of living metabolically active cells. Mitochondrial dehydrogenases metabolized MTT to a purple formazan dye, which is measured photometrically at 550 nm. Cell viability is proportional to the absorbance measured. Otherwise where indicated, cell viability was calculated as the percentage of control.
Lipid peroxidation assay
Cells were collected and resuspended in cold PBS. Cell homogenate was prepared with the homogenizer. After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed and malondialdehyde (MDA), a terminal product of lipid peroxidation (LPO), was measured to estimate the extent of lipid peroxidation. The levels of MDA were determined by addition of thiobarbituric acid (TBA). Briefly, supernatant of each sample (0.15 mL) was mixed with 3% SDS, 0.1N HCl, 10% phosphtungstic acid and 0.7% TBA, and then incubated at 95°C for 45 min. After centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was removed and measured by a microplate by Wallac Victor 3 1420 multilabel counter (Perkin Elmer, Turku, Finland) using excitation and emission wavelength at 485 and 535 nm, respectively.
Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular H2O2
Briefly, confluent keratinocytes starved with DMEM were pretreated with various concentrations of ECG for 2 h. Cells were washed with PBS and DMEM and then treated with dihydrorhodamine 123 (10 μg/mL) in DMEM for 30 mins. After a brief wash, cells were irradiated with UVB and then were collected by scraping and centrifugation. The cell pellets were resuspended in PBS (1 mL) and then analyzed immediately by flow cytometry (Partech GmBH, Munster, Germany) at excitation and emission wavelengths of 488 and 525 nm, respectively. Fluorescence signals of 10,000 cells were collected to calculate mean fluorescence intensity of a single cell.
Cell lysate preparation and Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, JNK and p38
Keratinocytes treated with or without UVB were washed twice with PBS. Cells were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer [17 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA. 1 mM sodium fluoride, 1% Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM PMSF and 1 μg/mL aprotinin and freshly prepared leupeptin]. After sonication, the lysate was centrifuged (14,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C), and supernatant was removed. The protein content was quantified by Pierce protein assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Total protein was separated by electrophoresis on 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gels (SDS-PAGE) and the proteins were electroblotted onto PVDF membranes and then probed using respective specific antibodies such as p-ERK1/2 (0.2 μg/mL), ERK1/2 (0.5 μg/ml), p-JNK, JNK, p-p38, p38. Immunoblots were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence (Chemiluminescence Reagent Plus from NEN, Boston, MA). For reprobing, the PVDF membrane was stripped at 60oC for 30 min with a striping buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.7, 2% SDS and 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol) and probed with the indicated Abs.
Flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle
Cells were collected and fixed overnight in 70% ethanol at 4 °C. After centrifugation, cellular DNA was stained with PI-staining solution (100 μg/mL PI, 0.1% Triton-X, 1mM EDTA in PBS, 100 μg/mL DNase-free RNase). Cell-cycle determination was performed using a Partec CyFlow ML flow cytometer (Partech GmBH, Munster, Germany). Flow cytometric histograms were analyzed by defining borders between pre-G1, G1, S and G2+M from an asynchronous population and using these boundaries in analyses of the experimental samples.
Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise indicated, data were expressed as mean ± standard errors (SE). Comparison of means of two groups of data was made by using the unpaired, two-tailed Student t-test. All data are analyzed by SigmaPlot 2002 for Windows Version 8.0.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant of Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital and the National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan.
References
- Lyons, N.M.; O'Brien, N.M. Modulatory effects of an algal extract containing astaxanthin on UVA-irradiated cells in culture. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Rae, V.; Bruins-Slot, W.; Van den Berg, J.W.; Taylor, J.R.; Streilein, J.W. Susceptibility to effects of UVB radiation on induction of contact hypersensitivity as a risk factor for skin cancer in humans. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1990, 95, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Donawho, C.K.; Muller, H.K.; Bucana, C.D.; Kripke, M.L. Enhanced growth of murine melanoma in ultraviolet-irradiated skin is associated with local inhibition of immune effector mechanisms. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Goihman-Yahr, M. Skin aging and photoaging: an outlook. Clin. Dermatol. 1996, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, Y. Photoaging from an oxidative standpoint. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1995, 9, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, W.B.; Zuckerkandl, E.; Reynolds, R.; Willoughby, R.; Marcuson, R.; Barth, R.; Pauling, L. Effects of intake of L-ascorbic acid on the incidence of dermal neoplasms induced in mice by ultraviolet light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1982, 79, 7532–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensler, H.L.; Magdaleno, M. Topical vitamin E inhibition of immunosuppression and tumorigenesis induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Nutr. Cancer 1991, 15, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.S.; Chan, J.T. Suppression of ultraviolet light-induced tumor formation by dietary antioxidants. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1975, 65, 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, H.N. Green tea composition, consumption, and polyphenol chemistry. Prev. Med. 1992, 21, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaq, F.; Adhami, V.M.; Mukhtar, H. Photochemoprevention of ultraviolet B signaling and photocarcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2005, 571, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaq, F.; Mukhtar, H. Photochemoprevention by botanical antioxidants. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2002, 15, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F'guyer, S.; Afaq, F.; Mukhtar, H. Photochemoprevention of skin cancer by botanical agents. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2003, 19, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Elmets, C.A. Green tea polyphenolic antioxidants and skin photoprotection (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 18, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Afaq, F.; Perez, A.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate treatment of human skin inhibits ultraviolet radiation-induced oxidative stress. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmets, C.A.; Singh, D.; Tubesing, K.; Matsui, M.; Katiyar, S.; Mukhtar, H. Cutaneous photoprotection from ultraviolet injury by green tea polyphenols. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 44, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Afaq, F.; Azizuddin, K.; Mukhtar, H. Inhibition of UVB-induced oxidative stress-mediated phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 176, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate treatment to mouse skin prevents UVB-induced infiltration of leukocytes, depletion of antigen-presenting cells, and oxidative stress. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Hursting, S.D.; Slaga, T.J.; Fischer, S.M.; DiGiovanni, J.; Phang, J.M. Mechanism-based cancer prevention approaches: targets, examples, and the use of transgenic mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Elmets, C.A.; Agarwal, R.; Mukhtar, H. Protection against ultraviolet-B radiation-induced local and systemic suppression of contact hypersensitivity and edema responses in C3H/HeN mice by green tea polyphenols. Photochem. Photobiol. 1995, 62, 855–861. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Katiyar, S.K.; Khan, S.G.; Mukhtar, H. Protection against ultraviolet B radiation-induced effects in the skin of SKH-1 hairless mice by a polyphenolic fraction isolated from green tea. Photochem. Photobiol. 1993, 58, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Agarwal, R.; Bickers, D.R.; Mukhtar, H. Protection against ultraviolet B radiation-induced photocarcinogenesis in hairless mice by green tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Fang, J.Y.; Wu, W.B.; Chiang, H.S.; Wei, Y.J.; Hung, C.F. Protective effects of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate on UVA-induced damage in HaCaT keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2005, 296, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Lee, S.H.; Song, M.H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoon, J.H.; Choi, E.C.; Baek, S.J. Growth inhibition and apoptosis by (−)-epicatechin gallate are mediated by cyclin D1 suppression in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 3260–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Fang, J.Y.; Wu, W.B.; Chiang, H.S.; Wei, Y.J.; Hung, C.F. Protective effects of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate on UVA-induced damage in HaCaT keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2005, 296, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, S.; Thibault, L.; Lepage, G.; Seidman, E.G.; Dube, N.; Levy, E. Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum-bound cholesterol regulatory enzymes by iron/ascorbate-mediated lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Riley, D.P.; Caputi, A.P.; Salvemini, D. Antioxidant therapy: a new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 135–159. [Google Scholar]
- Afaq, F.; Syed, D.N.; Malik, A.; Hadi, N.; Sarfaraz, S.; Kweon, M.H.; Khan, N.; Zaid, M.A.; Mukhtar, H. Delphinidin, an anthocyanidin in pigmented fruits and vegetables, protects human HaCaT keratinocytes and mouse skin against UVB-mediated oxidative stress and apoptosis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peus, D.; Meves, A.; Vasa, R.A.; Beyerle, A.; O'Brien, T.; Pittelkow, M.R. H2O2 is required for UVB-induced EGF receptor and downstream signaling pathway activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peus, D.; Vasa, R.A.; Beyerle, A.; Meves, A.; Krautmacher, C.; Pittelkow, M.R. UVB activates ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways via reactive oxygen species in cultured keratinocytes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziere, C.; Conte, M.A.; Leborgn, L.; Levade, T.; Hornebeck, W.; Santus, R.; Maziere, J.C. UVA radiation stimulates ceramide production: relationship to oxidative stress and potential role in ERK, JNK, and p38 activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, D.; Fridovich, I. Free radicals in cutaneous biology. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Karin, M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16483–16486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peus, D.; Vasa, R.A.; Meves, A.; Beyerle, A.; Pittelkow, M.R. UVB-induced epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation is critical for downstream signaling and keratinocyte survival. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 72, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M.H.; Goldsmith, E.J. How MAP kinases are regulated. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14843–14846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y.T.; Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-from inflammation to development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998, 10, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Borchers, A.H.; Dong, Z.; Powell, M.B.; Bowden, G.T. UVB irradiation-induced activator protein-1 activation correlates with increased c-fos gene expression in a human keratinocyte cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32176–32181. [Google Scholar]
- Guyton, K.Z.; Gorospe, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Holbrook, N.J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation by butylated hydroxytoluene hydroperoxide: implications for cellular survival and tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Holbrook, N.J. The cellular response to oxidative stress: influences of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways on cell survival. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmer, W.A.; Tan, L.C.; Dickerson, J.A.; Danne, M.; Rovin, B.H. Interleukin-1beta induction of mitogen-activated protein kinases in human mesangial cells. Role of oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10877–10881. [Google Scholar]
- Sample availability: Contact the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
