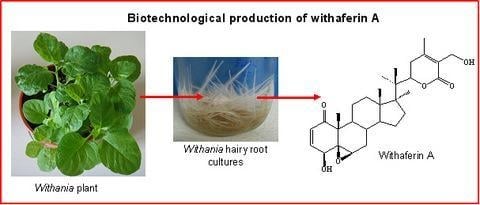
Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine
Abstract
Share and Cite
Mirjalili, M.H.; Moyano, E.; Bonfill, M.; Cusido, R.M.; Palazón, J. Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine. Molecules 2009, 14, 2373-2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072373
Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Cusido RM, Palazón J. Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine. Molecules. 2009; 14(7):2373-2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072373
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirjalili, Mohammad Hossein, Elisabeth Moyano, Mercedes Bonfill, Rosa M. Cusido, and Javier Palazón. 2009. "Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine" Molecules 14, no. 7: 2373-2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072373
APA StyleMirjalili, M. H., Moyano, E., Bonfill, M., Cusido, R. M., & Palazón, J. (2009). Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine. Molecules, 14(7), 2373-2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072373