Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a prime cause of liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The current drugs clinically available are nucleot(s)ide analogues that inhibit viral reverse transcriptase activity. Most drugs of this class are reported to have viral resistance with breakthrough. Recent advances in methods for in silico virtual screening of chemical libraries, together with a better understanding of the resistance mechanisms of existing drugs have expedited the discovery and development of novel anti-viral drugs. This review summarizes the current status of knowledge about and viral resistance of HBV drugs, approaches for the development of novel drugs as well as new viral and host targets for future drugs.
Abbreviations
| cccDNA | covalently closed circular DNA |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| GASP | Genetic Algorithm Similarity Program |
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e antigen |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HBx | HBV X protein |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HNF | hepatocyte nuclear factor |
| RT | reverse transcriptase |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WHV | woodchuck hepatitis virus |
1. Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV), the prototype of the Hepadnaviridae family, is a small virus harboring only four open reading frames. The genome of HBV comprises a partially double-stranded 3.2-kb DNA. Chronic HBV infection is strongly associated with liver diseases like chronic hepatic insufficiency, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [1,2,3,4]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there are currently 400 million individuals worldwide who are chronically infected with HBV, of whom 100 million eventually will die of chronic liver diseases or HCC [5,6]. Although vaccination and drugs against HBV have been introduced successfully, the level of global chronic infection still calls for development of new drugs for the control of HBV infection.
Infection with HBV in hepatocytes results in the formation of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) in the nucleus, which is the template transcribed to generate four major RNA species. HBV expresses four major viral antigens: precore/core, surface, polymerase and HBV X protein (HBx). Among these HBV-encoded proteins, viral polymerase is the key protein for genome replication and consists of terminal protein (following a spacer), reverse transcriptase (RT), and RNAse H domains. The RT domain is responsible for the minus strand DNA synthesis, the first step in HBV replication, from the pregenomic RNA template [7,8]. Therefore, RT is a fascinating target for anti-HBV drugs.
All the clinically available HBV drugs are nucleotide or nucleoside analogues that target the activity of viral RT. All drugs approved as anti-HBV agents are reported to have viral resistance due to specific mutations in the RT domain, which encourage the development of novel anti-HBV agents targeting non-polymerase viral or host proteins. In this review we summarize the current status of anti-HBV agents with their viral resistance and the novel small chemical anti-HBV agents targeting non-polymerase proteins.
2. Anti-HBV Drugs
The currently available anti-HBV agents are all nucleotide or nucleoside analogues RT inhibitors. These are summarized in Table 1.
2.1. Current anti-HBV drugs
2.1.1. Lamivudine
Lamivudine [(-)2′,3′-dideoxy-3′-thiacytidine, commonly called 3TC, Zeffix®) was initially developed for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Lamivudine is a synthetic nucleoside analogue, with activity against HBV and HIV. It is sequentially phosphorylated to lamivudine triphosphate by cellular kinases. After removal of the diphosphate group, lamivudine 5′-monophosphate is incorporated into the growing viral DNA chain at the 3’-end by HBV polymerase. The incorporation of lamivudine into the viral DNA chain induces premature chain termination due to the absence of 3’-OH, which is essential for chain polymerization.

Table 1.
Approved anti-HBV drugs.
| Molecule | Structure | Brand name | Mechanism | Company | Year of FDA approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamivudine |  | Zeffix, Heptovir, Epivir, and Epivir-HBV | Nucleoside analogue/RT Inhibitor | GlaxoSmithKline | 1998 (for adults) and 2000 (for children) in US |
| Adefovir | 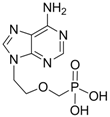 | Preveon and Hepsera | Nucleotide analogue/RT Inhibitor | Gilead | 2002 (US) |
| Entecavir | 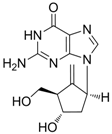 | Baraclude | Nucleoside analogue/RT Inhibitor | Bristol Meyers Squibb | 2005 (US) |
| Telbivudine | 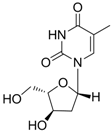 | Sebivo (Europe) Tyzeka (US) | Nucleoside analogue/RT Inhibitor | Idenix, Novartis | 2006 (US) |
| Clevudine | 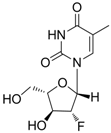 | Levovir and Revovir | Nucleoside analogue/RT Inhibitor. | Bukwang Pharm | 2006 (KOREA) |
| Tenofovir | 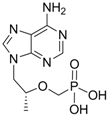 | Viread | Nucleotide analogue/RT Inhibitor | Gilead | 2008 (US) |
In vitro antiviral activity of lamivudine against HBV was assessed in HBV DNA-transfected cells and IC50 values ranged between 0.01 μM and 3.3 μM, depending on the duration of exposure of cells to lamivudine, the cell model system, and the protocol used [9].
2.1.2. Adefovir Dipivoxil
Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera®, 9-[2-[[bis[(pivaloyloxy)methoxy]-phosphinyl]-methoxy]ethyl]-adenine) is an acyclic nucleotide analog with activity against HBV. Adefovir was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the treatment of hepatitis B in September 2002 and by the European Union in March 2003. Because adefovir is an analog of adenosine monophosphate, it can be easily phosphorylated to the active metabolite adefovir diphosphate by cellular kinases. Adefovir diphosphate inhibits HBV DNA polymerase by competing with the natural substrate deoxyadenosine triphosphate. The incorporation of adefovir diphosphate into the growing viral DNA causes premature DNA chain termination similar to lamivudine [10]. The inhibition constant (Ki) for adefovir diphosphate for HBV DNA polymerase is 0.1 μM. In vitro antiviral activity of adefovir against HBV was assessed in HBV DNA-transfected human hepatoma cell lines and the IC50 values ranged between 0.2 μM and 6.3 μM depending on the assay conditions [9].
2.1.3. Entecavir
Entecavir (Baraclude®, 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(1S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylenecyclopentyl]-6H-purin-6-one monohydrate) is a guanosine nucleoside analogue with selective activity against HBV. Entecavir was approved by the U.S. FDA in March 2005 for the treatment of hepatitis B infection. Entecavir is a guanosine nucleoside analogue and is efficiently phosphorylated to the active triphosphate form. By competing with the natural substrate deoxyguanosine triphosphate, entecavir triphosphate functionally inhibits the activities of HBV polymerase.
Entecavir was more efficacious than other previous agents and had low side effects [11]. Entecavir inhibited HBV DNA synthesis by 50% at a concentration of 3.75 nM in in vitro assays [12]. Lamivudine-resistant HBV (rtL180M, rtM204V) was also susceptible to entecavir treatment with high efficacy in vitro [13]. Clinical trials revealed that entecavir was superior compared to lamivudine in vivo for both hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive and HBeAg-negative patients [14,15]. Chronic hepatitis B patients who were refractory to lamivudine treatments showed improved virologic and serology outcomes [16,17].
2.1.4. Telbivudine
Telbivudine [Tyzeka®, LdT, 1-(2-deoxy-β-L-ribofuranosyl)-5-methyluracil)] is a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue with activity against HBV. Telbivudine is the unmodified L-isomer of the naturally occurring nucleoside, thymidine; therefore, phosphorylation to the active telbivudine triphosphate form by cellular kinases is easily accomplished. The telbivudine 5'-triphosphate eventually inhibits HBV DNA polymerase by competing with the natural substrate, thymidine 5'-triphosphate. Incorporation of telbivudine 5'-triphosphate into replicating HBV DNA causes premature DNA chain termination. In vitro antiviral activity of telbivudine against HBV replication was assessed in HBV-stable cell line, hepG2 2.2.15 human hepatoma cells, and the IC50 values were around 0.19 μM [18]. Telbivudine was not active against HIV-1 at concentrations of up to 100 μM in vitro. Clinical trials have shown that telbivudine is superior to lamivudine or adefovir in patients with chronic hepatitis B [19,20,21].
2.1.5. Clevudine
Clevudine (Levovir®, 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-arabinofuranosyl)thymine, also known as L-FMAU), is a pyrimidine analog with potent antiviral activity against HBV [22]. Like other nucleoside analogues, clevudine inhibits HBV polymerase by competing with the natural substrate, thymidine. Clevudine has been approved in Korea and the Philippines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B patients and is now under Phase 3 clinical studies in China. Clevudine inhibits the DNA-dependent DNA activity of HBV polymerase as well as reverse transcription and priming [23,24].
The in vitro antiviral activity of clevudine against HBV was assessed in HBV DNA-transfected human hepatoma cells and the IC50 value was 0.9 μM [9]. Phase III clinical trial results showed that clevudine therapy for 24 weeks has a potent and sustained antiviral effect in both HBeAg-positive and -negative chronic hepatitis B patients [25,26].
2.1.6. Tenofovir
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread®, 9-[(R)-2-[[bis[[(isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy]methoxy]-phosphinyl]methoxy]propyl] adenine fumarate) is an acyclic nucleotide analog with activity in vitro against retroviruses, including HIV-1, HIV-2, and HBV. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is an orally bioavailable ester prodrug of tenofovir (also known as PMPA). Tenofovir is a methyl derivative of adefovir and shows a very similar mechanism of action and antiviral resistance pattern to adefovir. Therefore, like adefovir, tenofovir exhibits antiviral activity against lamivudine-resistant HBV in vivo and in vitro [27,28,29].
Tenofovir was approved by the U.S. FDA in October 2001 for the treatment of HIV and in August 2008 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Like adefovir, tenofovir is rapidly metabolized intracellularly into the active metabolite, tenofovir diphosphate, by cellular kinases. Tenofovir diphosphate inhibits HBV DNA polymerase RT by competing with the natural substrate, deoxyadenosine triphosphate, causing the termination of the growing DNA chain since it lacks a 3' hydroxyl group. The Ki for viral DNA polymerase is 0.02 μM, 5-fold lower than the Ki of adefovir.
In vitro antiviral activity of tenofovir against HBV replication was assessed using HBV-transfected human hepatoma cell lines and the IC50 value was 2.5 μM [9]. Phase III clinical trial results showed that tenofovir therapy for 48 weeks at a daily dose of 300 mg had superior antiviral efficacy with a similar safety profile compared with adefovir dipivoxil at a daily dose of 10 mg [30].
2.2. Adverse effects of current HBV drugs
The major adverse effects of long-term administration of nucleotide or nucleoside RT inhibitors are nephrotoxicity and myopathy [31,32]. Nephrotoxicity is characterized by gradual increases in serum creatinine and decreases in serum phosphorus due to the inhibition (or toxicity) of kidney function. Adefovir and tenofovir (structural analogue of adefovir) are reported to be associated with nephrotoxicity at higher doses in HIV-infected patients and in chronic hepatitis B patients [31,33,34]. In the case of adefovir, the FDA did not approve the drug due to concerns about the severity and frequency of kidney toxicity when dosed at 60 or 120 mg for the treatment of HIV infection [35]. However, Gilead Sciences continued its development for HBV treatment, for which it is effective at a much lower dose of 10 mg. Because the long-term administration of adefovir may increase the overall risk of nephrotoxicity, it is important to monitor renal function for all patients during treatment with adefovir and tenofovir.
The major human DNA polymerases include DNA polymerases alpha, beta, gamma, delta and epsilon. Most of the nucleotide or nucleoside analogues are weak inhibitors of mammalian alpha-, beta-, and gamma-DNA polymerases [36]. This inhibition is likely related to drug-induced adverse effects. Among these, DNA polymerase gamma is located in mitochondria whereas other polymerases are found in the nucleus. The mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma is reported to have both DNA- and RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity similar to those of viruses such as HBV and HIV. The functional similarity between viral polymerase and mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma is likely responsible for the nucleoside drug-induced toxicity. DNA polymerase gamma is reported to have higher affinity for nucleotide or nucleoside RT inhibitors. The incorporation of nucleoside inhibitors into the mitochondrial DNA induces premature genome termination, resulting in mitochondrial DNA deletions (see review by references [37,38]).
Myopathy characterized by muscle pain, muscle weakness or muscle tenderness is observed in patients who have received long-term treatment of clevudine and telbivudine [38,39]. Seok et al. [39] reported that seven patients who received 8-13 months of clevudine therapy showed severe evidence of myopathy with elevated creatine kinase levels. Muscle biopsies and molecular studies showed that the myopathy is associated with the depletion of mitochondria DNA and myonecrosis, possibly due to the inhibition of polymerase gamma by clevudine. These findings indicate that long-term treatment with structurally similar telbivudine and clevudine (fluoro-telbivudine) may lead to mitochondrial toxicity-mediated myopathy [32].
3. Viral Resistance to HBV Drugs
3.1. Molecular mechanism of resistance
Like other viral polymerases, the reverse transcriptase of HBV polymerase lacks proofreading activity on the newly synthesized viral genome, resulting in the introduction of random mutations into the progeny HBV DNA. The error rate of HBV polymerase is approximately 1 per 105 to 107 base synthesis due to the error-prone nature of HBV RT [40,41]. The HBV quasispecies produced by the infidelity of HBV RT could account for the emergence of the many natural mutants with point substitutions [42]. Under selection pressure from the host immune system or administration of antiviral agents, these quasispecies can converge into a dominant HBV mutant that can escape the selection pressure. The molecular mechanisms of resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogue drugs and the clinical importance of resistance for chronic hepatitis B have been comprehensively reviewed recently [43,44]. The well established and documented escape mutants against long-term antiviral treatment are as follows.
3.1.1. Lamivudine resistance
The incidence of resistance during lamivudine treatment increases progressively at rates of 14 to 32% annually, approaching 80% after 48 months of treatment [45]. Genotypic analysis of viral isolates obtained from patients who showed breakthrough of HBV replication while receiving lamivudine enabled the identification of the primary resistance mutations to lamivudine. The element for primary resistance to lamivudine was mapped to mutations in the YMDD motif, a common active site in reverse transcriptase, in the C domain of HBV Polymerase. The rtM204I and rtM204V mutations, resulting in YIDD and YVDD, respectively, have been identified as primary resistance elements to lamivudine treatment [46]. The YMDD mutation is usually accompanied by a compensatory mutation, rtL180M, which enhances the viral replication of replication-defective rtM204I/V mutants [47]. Other compensatory mutations, L80I/V and V173L, in combination with rtM204I/V with or without rtL180M have also been identified [48,49]. In vitro drug susceptibility assays showed that mutations that confer resistance to lamivudine decrease the drug sensitivity by 100- to 1000-fold. Lamivudine resistance does not confer cross-resistance to adefovir dipivoxil or tenofovir. The molecular mechanisms of drug resistance have been predicted based on the crystal structure and molecular modeling [50,51].
3.1.2. Adefovir Dipivoxil resistance
The rate of HBV resistance to adefovir is less frequent compared to the resistance to lamivudine. After two years of adefovir monotherapy in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis, approximately 2% of patients were reported to have drug resistance. However, the rate of resistance increased considerably to 30% after five years of adefovir monotherapy [52,53].
Genotypic analysis has revealed that adefovir resistance is conferred by the substitution of threonine for asparagine at codon 236 (rtN236T) in the D domain, and alanine for threonone or valine at codon 181 (rtA181T/V) in the B domain of HBV polymerase RT [54]. In vitro drug susceptibility assays showed that the rtN236T mutation does not affect sensitivity to lamivudine, telbivudine and entecavir; however, rtA181T mutation decreased susceptibility to lamivudine (<10-fold), adefovir (2- to 8-fold) and tenofovir (2- to 3-fold) [55,56].
3.1.3. Entecavir resistance
Entecavir is the most potent of the currently available anti-HBV agents. Resistance to entecavir was not reported in early clinical trials because the incidence of resistance in treatment-naïve patients was very low, less than 1% at 2 years [57]. Long-term monitoring of entecavir resistance has revealed that the resistance rate was only 1.2% even after five years of therapy in treatment-naïve patients [58]. However, when lamivudine-failure patients, who had lamivudine resistance, were treated with entecavir, the incidence of resistance to entecavir dramatically increased to 14% at two years and 51% at five years [58].
The mutations associated with the primary resistance to entecavir are the most complex and have not been fully established in patients. Mutations in the viral polymerase associated with the emergence of entecavir resistance have been mapped to the B domain (rtI169T, rtL180M, rtS184G), C domain (rtM204I/V, rtS202I), and E domain (rtM250V). The lamivudine mutations, rtM204I/V with or without rtL180M, along with other mutations are frequently detected in patients who exhibit entecavir resistance [59]. In vitro cell-based drug susceptibility assays also showed that the presence of lamivudine-resistant mutations leads to several hundredfold increases in entecavir resistance. Entecavir resistance does not confer cross-resistance to adefovir dipivoxil and tenofovir [44].
3.1.4. Telbivudine resistance
The cumulative frequency of genotypic resistance to telbivudine in HBeAg-positive patients at 52 and 104 weeks was 5% and 25.1%, respectively, whereas, in HBeAg-negative patients, the resistance incidence was 2.2% and 10.8%, respectively [19,20]. The resistance rate at two years was lower than that of lamivudine (42%) and higher than those of adefovir (3%) and entecavir (<1%) [60].
Genotypic analysis from telbivudine-treatment failure isolates showed that the rtM204I/V substitution was associated with virologic failure and rebound. The rtM204I substitution confers the primary resistance to telbivudine treatment and was frequently found with substitutions rtL80I/V and rtL180M. In vitro drug susceptibility assays showed that rtM204I, rtL180M + rtM204V, rtI169T/rtM250V and rtT184G/rtS202I mutations exerted strong resistance to telbivudine treatment [61]. Because telbivudine is an L-nucleoside analogue, telbivudine resistance does not confer cross-resistance to adefovir, tenofovir, and entecavir [62].
3.1.5. Clevudine resistance
As an L-nucleoside analogue, clevudine (a fluorinated telbivudine) has a similar resistance profile to lamivudine and telbivudine. Because clevudine was approved very recently, long-term cumulative data on the incidence and genotypic mutations that cause clevudine resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients is not available.
The rtM204I mutation was identified during week 32 of clevudine therapy in woodchuck HBV [63]. In vitro studies using site-directed mutagenesis have also demonstrated that clevudine is not active against HBV harboring a single rtM204I mutant [64,65]. Recently, Kwon et al. [9] identified several conserved mutations in RT domain during viral BT from four clevudine-failure patients, with rtM204I being the most common. In vitro phenotypic analysis showed that mutation rtM204I was predominantly associated with clevudine resistance, whereas rtL229V was a compensatory mutation for the impaired replication of the rtM204I mutant. They found that a quadruple mutant (rtL129M + rtV173L + rtM204I + rtH337N) conferred greater replicative ability and strong resistance to both clevudine and lamivudine. All of the clevudine-resistant clones were also lamivudine-resistant, but were susceptible to adefovir, entecavir, and tenofovir except for one mutant clone [9].
3.1.6. Tenofovir resistance
Tenofovir is an adefovir analogue, methyl adefovir, presenting a similar mechanism of action and characteristics to adefovir. Tenofovir was approved for chronic hepatitis B treatment very recently; therefore the resistance mutation and resistance rate of tenofovir has not been well studied yet.
The substitution rtA194T, along with rtL180M + rtM204V, has been found in patients with HIV-HBV co-infection who showed resistance to tenofovir treatment [66]. A recent in vitro drug susceptibility assay demonstrated that the rtA194T mutation is associated with partial tenofovir resistance (5- to7-fold increase), regardless of rtL180M + rtM204V mutation, and negatively impacts the replication competence of HBV constructs. Viral replication of rtA194T mutant can be restored to WT levels, if this mutation occurs together with precore or basic core promoter substitutions found in HBeAg-negative hepatitis B [67]. No genotypic substitutions in RT associated with phenotypic resistance to tenofovir were detected during 48-week treatment [30]. Limited in vivo and in vitro studies on the antiviral activity of tenofovir showed that lamivudine- and adefovir-resistant mutants are susceptible to tenofovir [9,28,29,62].
3.2. Molecular modeling study of drug-resistant HBV
The currently available anti-HBV drugs show potent antiviral activity in patients with chronic hepatitis B; however, the resistance and cross-resistance to the drugs is a major obstacle in long-term treatment. Many studies have been conducted to understand the molecular basis of drug resistance, and the mechanistic characterization and molecular modeling of anti-HBV drugs complexed with HBV RT have been reported. Although the three-dimensional X-ray structure of HBV polymerase is not available, its homology model has been reported using the X-ray structure of HIV RT as a template [48,51,68,69,70]. Even though the homology models may not be accurate due to the low sequence homology between the overall HIV and HBV polymerase, the sequence conservation between the RT domains of HIV and HBV polymerase enables molecular modeling of HBV RT [71]. In particular, the residues around the active site that are responsible for recognizing the template-primer or an incoming nucleoside triphosphate are highly conserved. Nucleoside analogue HBV polymerase inhibitors cause chain termination after incorporation into the growing chain in the active site of HBV polymerase and consequently inhibit viral reverse transcriptase. Thus, the HBV homology model structure based on the crystal structure of HIV polymerase serves as a useful guide for understanding the molecular basis of HBV resistance to drugs.
Molecular dynamics studies on the homology model structure of HBV can provide useful information regarding mutations associated with resistance to inhibitors of HBV polymerase. Daga et al. [72] built a stereochemically significant homology model of HBV polymerase and suggested a significant role for conserved Lys 32 residue in HBV RT, which corresponds to Lys 65 in HIV RT, in binding of nucleotides and known HBV RT inhibitors. Their homology model of HBV polymerase had two main differences from previous reports: They aligned the sequence by using the proper match of a conserved Lys residue in HIV-1 RT, which has important salt bridge interactions with the γ-phosphate of the incoming nucleotide. Secondly, they used a different template structure of HIV-1 RT (PDB code: 1T05) that was a higher resolution crystal structure compared to the previously used template (PDB code: 1RTD). Based on this modeling result, they provided an explanation for the various resistant mutants of HBV polymerase and successfully predicted binding conformations of known HBV inhibitors [72].
Das K et al. [51] constructed a three-dimensional homology model of the catalytic core of HBV polymerase based on the crystal structure of HIV-1 RT. Molecular modeling studies using the HBV polymerase homology model suggest that steric hindrance between the mutant amino acid side chain and lamivudine or emtricitabine, anti-HBV-drug, could account for the resistance phenotype. Specifically, steric conflict between the Ile or Val at position rt204 in HBV polymerase and the sulfur atom in the oxathiolane ring of lamivudine and emtricitabine is proposed to account for the resistance observed with rtM204I or rtM204V mutation. The effects of the rtL180M mutation, which also occurs near the HBV polymerase active site, appeared to be less direct, potentially involving rearrangement of the deoxynucleoside triphosphate-binding pocket residues.
Sharon et al. [70] constructed a homology model structure of HBV polymerase, which is used for minimization, conformational search and induced fit docking followed by binding energy calculation for wild-type and mutant HBV polymerases (rtL180M, rtM204V, rtM204I, rtL180M + rtM204V, rtL180M + rtM204I). Their studies suggest a significant correlation between the fold resistance and the binding affinity of five anti-HBV agents: lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir, telbivudine and clevudine. Also, they analyzed different binding modes for synthetic nucleoside analogue drugs as well as natural nucleosides. Although their studies may not fully explain the difference of quantitative binding affinity, they showed detailed resistance mechanisms for anti-HBV drugs against wild-type and mutant HBV.
Adefovir is active against wild-type and lamivudine-resistant strains of HBV [73]. In contrast to lamivudine therapy, adefovir is associated with delayed and uncommon selection of drug-resistant viruses [74]. Long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil leads to the rtN236T mutation, which displays reduced susceptibility to adefovir but remains sensitive to lamivudine [75]. Yadav V et al. [76] presented the molecular basis of the mechanism of adefovir-diphosphate against lamivudine-resistant mutants and its decrease in susceptibility for rtN236T HBV polymerase mutants. These molecular dynamics studies demonstrated that the rtN236T HBV polymerase mutation does not affect the binding affinity of the natural substrate (dATP), but it decreases the binding affinity of adefovir-diphosphate toward the rtN236T HBV polymerase. The lamivudine-resistant mutations, rtM204V and rtM204I, result in increased van der Waals contacts between adefovir-diphosphate and the mutated residues, which accounts for the better binding affinity of adefovir-diphosphate toward these mutants. The second lamivudine-related mutation, rtL180M, also results in increased van der Waals interactions between adefovir-diphosphate and the final residue of the primer strand, which accounts for the better binding affinity of adefovir-diphosphate in these mutants.
Warner et al. [48] determined the prevalence of rtL80V/I mutation in lamivudine-resistant HBV isolates and characterized the in vitro phenotype of the mutants. Although L80I increases sensitivity to lamivudine and imparts a replication defect, it enhances the in vitro replication of lamivudine-resistant (rtM204I) HBV. Molecular modeling revealed that Leu 80 does not interact directly with the enzyme’s substrates. Molecular models of HBV reverse transcriptase showed that, although Leu 80 is located distal to the enzyme’s dNTP binding pocket, substitution of isoleucine for leucine at this site partially restores replication efficiency by sufficiently changing the overall spatial alignment of other residues that are important for catalysis. These results imply that the presence of rtL80I decreases the enzyme’s affinity for both dNTPs and lamivudine triphosphate and that the decrease in affinity for lamivudine triphosphate is greater than the decrease in affinity for the natural substrate, dCTP.
As mentioned above, using the homology model structure of HBV polymerase, the amino acid changes resulting from mutations that give antiviral resistance can be mapped to functional regions to provide a better understanding of the molecular mechanism of resistance [51,71]. The HBV polymerase consists of four different domains: terminal protein, a space region, a catalytic RT domain and RNase H domain. We constructed and refined the model structure of HBV RT based on the homology to HIV-1 RT according to the reported method [72].
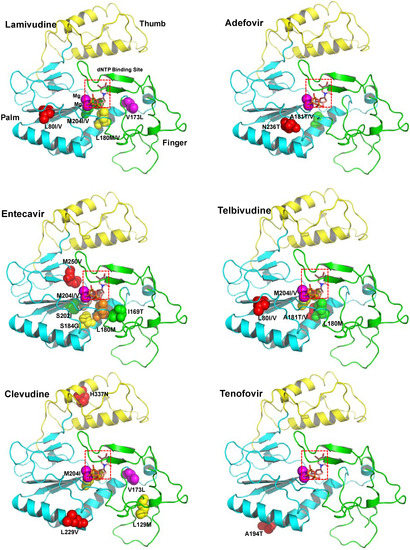
Figure 1.
The ribbon diagram of homology model structure of HBV RT shows the location of the major mutations that confer resistance to clinically available six drugs. The HBV RT model structure was constructed and refined as previously reported [72]. HBV RT consists of three sub-domains: fingers (amino acid 1 to 49 and 90 to 172, in green), palm (amino acid 50 to 89 and 173 to 267, in cyan), and thumb (amino acid 268 to 351, in yellow). The locations of the mutations are indicated with the sphere model.
Figure 1.
The ribbon diagram of homology model structure of HBV RT shows the location of the major mutations that confer resistance to clinically available six drugs. The HBV RT model structure was constructed and refined as previously reported [72]. HBV RT consists of three sub-domains: fingers (amino acid 1 to 49 and 90 to 172, in green), palm (amino acid 50 to 89 and 173 to 267, in cyan), and thumb (amino acid 268 to 351, in yellow). The locations of the mutations are indicated with the sphere model.
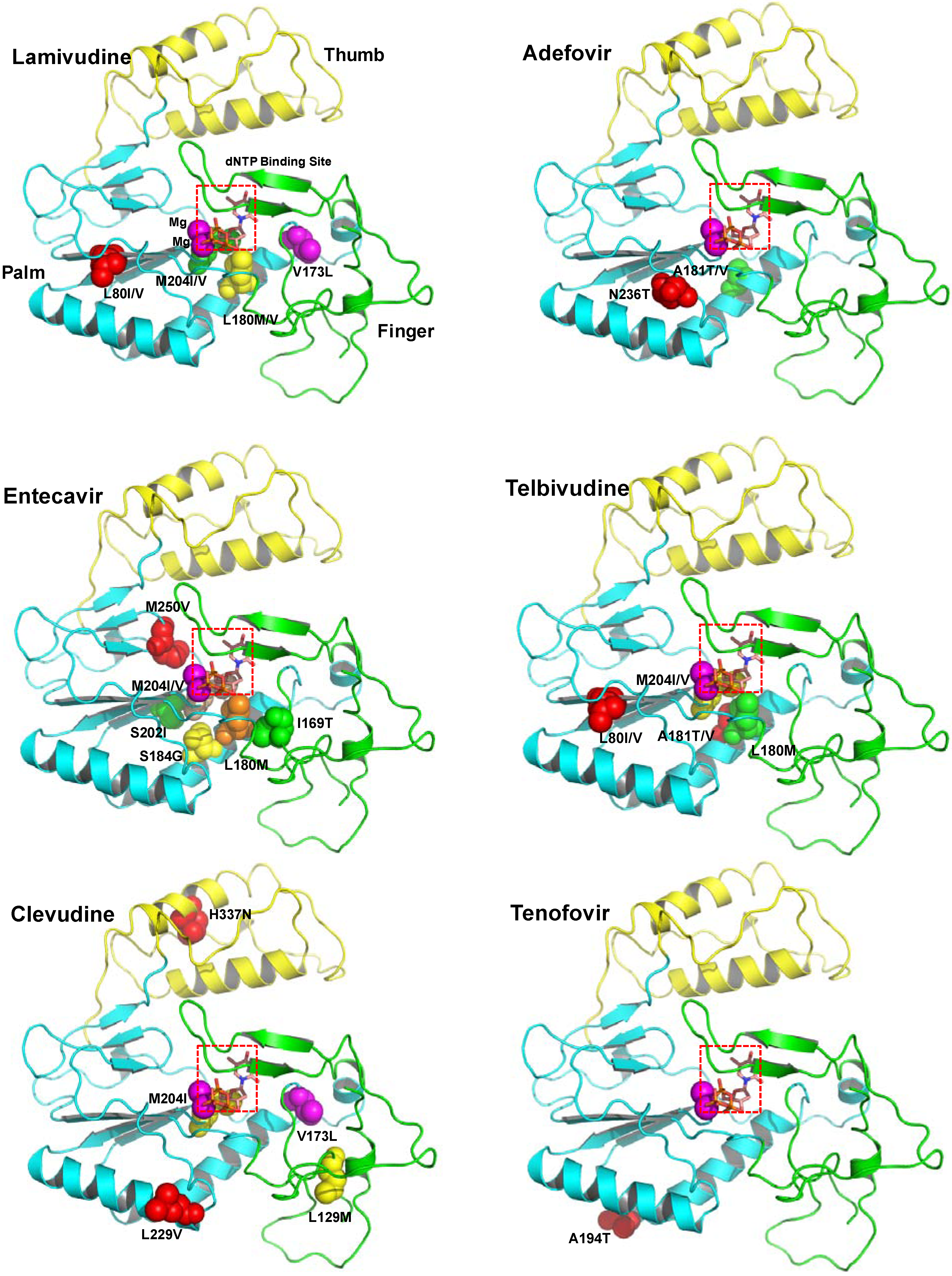
Figure 1 shows the location of the major mutations in RT that confer resistance to clinically available drugs. Detailed analysis of the model structure reveals that most of the drug-resistant mutations alter the conformation of at least one of the following sites: dNTP binding site, primer binding site, template binding site, dNTP incoming region, dNTP binding pocket, and magnesium ions binding site (highly conserved YMDD).
4. Development of Anti-HBV Agents
The development of antiviral agents is compelled by the need to overcome life-threatening viruses such as HIV. Recently, greater understanding of viral life cycles and more advanced development tools have enabled us to discover and develop novel antiviral agents faster and more easily. The strategies and rationale in the design of antiviral drugs have been comprehensively reviewed [10]. The anti-HBV drugs in clinical trials and HBV inhibitors of antigens or replication are summarized in Table 2 and discussed in the following.
4.1. Drugs in clinical trials for HBV
There are several new drug candidates that are in clinical trials for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Lagociclovir valactate (known as MIV-210), a prodrug of 3′-fluoro-2′,3′-dideoxyguanosine with high oral bioavailability in humans and potent activity against hepatitis B virus, is currently in phase 1 and 2 clinical studies in Europe and Asia. MIV-210 is known to have activity against lamivudine-, adefovir-, and entecavir-resistant HBV variants. In the woodchuck model of HBV, treatment with MIV-210 at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day or 60 mg/kg/day was well tolerated and caused rapid and pronounced virological woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) DNA reduction as well as appreciable decreases in hepatic WHV cccDNA levels [77].

Table 2.
Anti-HBV drugs in clinical trials.
| Molecule | Structure | Brand name | Mechanism | Company | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lagociclovir valactate | 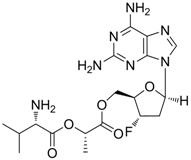 | - | Nucleoside analogue/RT inhibitor/Prodrug | Medvir AB | Phase II 2005 (Sweden) |
| Elvucitabine | 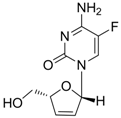 | - | Nucleoside analogue/RT Inhibitor | Achillion Pharmaceuticals | 2001 (US) |
| B-80380 | 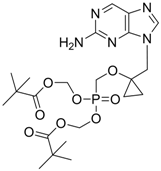 | - | Nucleotide analogue/RT Inhibitor | LG Chem Ltd | Phase II 2003 (KOREA) |
| radefovir |  | - | Nucleotide analogue/RT inhibitor/Prodrug | Metabasis Therapeutics | Phase II 2007 (US) |
| altorcitabine | 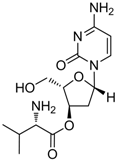 | Nucleoside analogue/RT inhibitor/Prodrug | Idenix Pharmaceuticals/Novartis | Phase II 2003 (US) |
Elvucitabine [2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-β-L(-)-5-fluorocytidine] is a nucleoside analogue RT inhibitor developed by Achillion Pharmaceuticals. In vitro studies and several phase I/phase II clinical trials have demonstrated that elvucitabine has significant potency against HIV. It also showed strong anti-HBV activity for the treatment of chronic HBV [78]. In the initial Phase 2 clinical trial for HIV, doses of 50 mg or greater per day were associated with an unacceptable reduction in patients’ white and red blood cells. Recently, the clinical trial was discontinued and the program was placed on hold while determination of the appropriate dosing regimen for elvucitabine was made for hepatitis B in the USA.
LB-80380 is a nucleotide analogue RT inhibitor developed by LG Life Sciences, Ltd., in Korea for the treatment of HBV infection [79]. In vitro antiviral activity against wild-type and lamivudine-resistant mutants (rtM204I/V, rtL180M + rtM204I/V) showed similar EC50 values to adefovir [80]. LB80380 is currently in phase 2 clinical studies for chronic HBV patients in South Korea. The results of the clinical study suggest that LB80380 at doses of up to 240 mg for a period of 12 weeks is safe, well tolerated, and effective at reducing viral load in chronic hepatitis B patients with lamivudine-resistant virus [81,82].
Pradefovir, a selectively liver-activated prodrug of adefovir dipivoxil was developed by Metabasis Therapeutics. Pradefovir was developed to overcome the renal toxicity of adefovir dipivoxil and showed the delivery of adefovir and its metabolites to the liver with a 12-fold improvement in the liver/kidney ratio over adefovir dipivoxil [83].
Valtorcitabine, a well-absorbed prodrug of L-deoxycytidine, has also demonstrated potent suppression of serum HBV DNA in HBeAg-positive patients in a phase I/II study. Valtorcitabine was well-tolerated in all patient cohorts, with a safety profile comparable to that of placebo and synergistic with telbivudine for inhibiting HBV replication in vitro and in the woodchuck hepadnavirus model [84].
4.2. Novel non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors
As described above, all currently available anti-HBV drugs are nucleoside or nucleotide analogues and inevitably associated with the development of HBV resistance to drugs because they inhibit the RT by competing with the natural dNTPs. Therefore, agents that can interfere with other targets in the viral life cycle are strongly needed for combination therapies, such as those used for the treatment of HIV. In this regard, many research groups are dedicated to developing non-nucleoside anti-HBV agents that exert different modes of action than nucleoside or nucleotide inhibitors. In this section, we divided the HBV inhibitors into two subgroups according to the mode of action: HBV inhibitors targeting viral antigens or replication. Table 3 summarizes the characteristics of non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors that target viral antigens.
Zhang et al. [85,86,87] synthesized a series of alisol A derivatives and evaluated their anti-HBV activities and cytotoxicities in vitro using lamivudine as a positive control. Their results demonstrate that simple modifications to the parent structure of alisol A resulted in inhibitory potency against secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), such as compound 1 (Table 1). Ellagic acid isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria (compound 2) showed unique anti-HBV activities. Ellagic acid did not inhibit HBV replication or HBsAg secretion; rather, it blocked HBeAg secretion very effectively in HepG2 2.2.15 cells [88]. Compound 3 is a selective, potent inhibitor of secretion of both subviral and DNA-containing viral particles [89]. It did not affect the viral replication and HBeAg secretion. Further analysis showed that compound 3 is a specific inhibitor of HBsAg secretion. Although the exact mechanism of action of compound 3 remains to be elucidated, these observations suggest that its effects occur through direct action on the HBV viral and subviral particles themselves, the antigens that they contain, or the cellular processes or factors that are uniquely required for the secretion of these particles. Su et al. [90] found that the natural pyranocoumarin derivatives (compound 4) suppressed the secretion of HBsAg in HepA2 cells and also showed cytotoxic activity against four human cancer cell lines (A549, MCF7, KB, and KB-VIN). The most interesting result in the cytotoxicity assay was that compound 4 showed significant activity only against KB-VIN cells, the multi-drug resistant cell line; on the other hand, they showed marginal or no activity against the other three cell lines.

Table 3.
Summary of non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors that target viral antigens.
| Compound (Target) | Structure | Activity | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (HBsAg, HBeAg) | 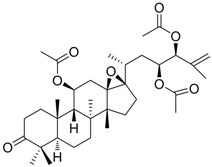 | CC50 : >2.6mM HBsAg(IC50): 0.024 mM HBeAg(IC50): 0.028 mM | Inhibition of HBsAg and HBeAg secretion | [85] |
| 2 (HBeAg) | 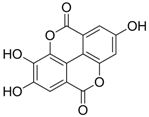 | IC50: 0.07 μg/mL | Inhibition of HBeAg secretion in HepG2 2.2.15 cell line | [88] |
| 3 (HBsAg) | 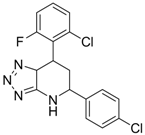 | EC50: 1.5 μM | Inhibition of HBsAg secretion | [89] |
| 4 (HBsAg) | 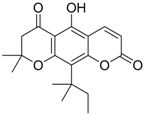 | EC50: 1.14 μM | Inhibition of HBsAg secretion | [90] |
| 5 (Virion secretion) | 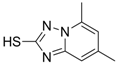 | IC50: 0.12 μM | Inhibition of the interaction between core and surface protein | [91] |
| 6 (Virion secretion) | 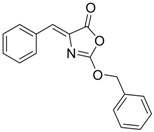 | IC50: 5.4 μM | Inhibition of the interaction between core and surface protein | [91] |
| 7 (Capsid formation) | 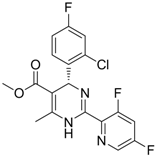 | IC50: 0.05 μM | Inhibition of replication by nucleocapsid depletion | [92] |
Using chemical library screening, Asif-Ullah et al. [91] identified compounds 5 and 6, which inhibit the interaction between the core protein and PreS region of the surface protein. These compounds prevented the production of HBV particles from transiently HBV-producing HuH7 cells. The IC50 values of these compounds for inhibition of HBV production in HuH7 cells were 0.12 and 5.4 μM for compound 5 and compound 6, respectively. Although these compounds showed promising anti-HBV activity, the detailed mechanism of how the compounds interfere with the surface and core protein interactions requires further investigation.
Compound 7 inhibits HBV nucleocapsid maturation leading to potent in vitro and in vivo antiviral activity [92]. It displayed a highly specific antiviral principle, namely, inhibition of capsid formation, concomitant with a reduced half-life of the core protein. This compound may become a valuable addition to future therapy in light of its specific mechanism of action. In vitro cell studies as well as HBV transgenic mice models showed a suitable preclinical pharmacokinetic and toxicology profile with high efficacy.
The characteristics of non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors targeting viral replication are summarized in Table 4. The phenylpropenamide derivatives are potent inhibitors of in vitro HBV replication in stably or transiently transfected HepG2 cells [93,94]. These compounds showed no significant differences in sensitivity between wild-type and nucleoside analogue-resistant (rtL180M, rtM204I, and rtL180M + rtM204V) HBV. Although the mechanism of action of compound 8 is not clearly understood, it appears to be independent of interference with the RNA- or DNA-dependent activities of the HBV polymerase. Recently, Feld and colleagues found that compound 8 decreased the amount of RNA-containing cytoplasmic HBV core particles, suggesting that this compound blocks HBV replication at the level of viral RNA packaging [95].
A series of non-nucleoside ethyl 6-hydroxyquinoline-3-carboxylate derivatives (compound 9 in Table 4) were synthesized and evaluated for anti-HBV activity in HepG2.2.15 cells [96]. Compound 9 derivatives inhibited the expression of viral antigens HBsAg or HBeAg at low concentration and displayed excellent intracellular inhibitory activity and selectivity towards the replication of HBV DNA. Of these ethyl 6-hydroxyquinoline-3-carboxylate derivatives, compound 9 was the most potent and highly specific inhibitor of HBV DNA replication in cell culture.

Table 4.
Summary of non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors that target viral replication.
| Compound | Structure | Activity | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 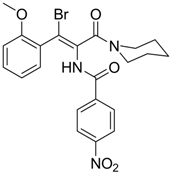 | IC50: 2.4 μM in HepG2 cells | Inhibition of replication by blocking RNA packaging | [93,94,95] |
| 9 | 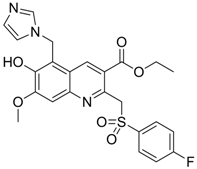 | IC50: 4.7 μM (Replication)
IC50: 26.2 μM (HBsAg) IC50: 98.1 μM (HBeAg) in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication, HBsAg and HBeAg secretion | [96] |
| 10 | 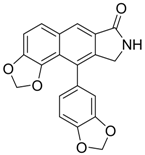 | IC50: 0.08 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication by down-regulation of HNF-3 and 4 | [97,98] |
| 11 |  | IC50: 0.9 μM in HepG2 cells
CC50: >1000 μM | Inhibition of replication | [99] |
| 12 | 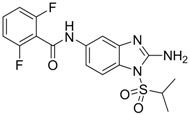 | IC50: 0.7 μM
CC50: 192 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication | [100] |
| 13 | 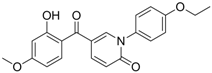 | IC50: 0.206 μM
CC50: >109.6 μM in HepG2 cells | Inhibition of replication | [101] |
| 14 | 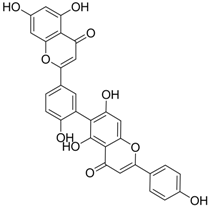 | IC50: 0.25 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication | [102] |
| 15 | 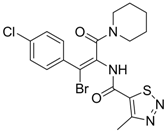 | IC50: 3.59 μg/mL in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication | [103] |
| 16 | 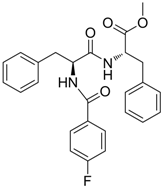 | IC50: 1.40 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication, HBsAg and HBeAg secretion | [104] |
| 17 | 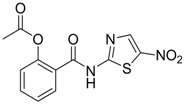 | EC50: 0.12 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of replication | [105] |
| 18 | 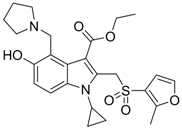 | IC50: 1.52 μg/mL in HepG2 2.2.15 | Inhibition of replication | [106] |
| 19 | 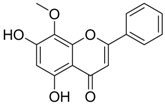 | IC50: 0.57 μg/mL in DHBV replication.
IC50: 4.0 μg/mL (HBsAg, HBeAg) | Inhibition of replication, HBsAg and HBeAg secretion | [107] |
| 20 | 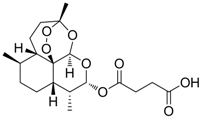 | IC50: 2.3 μM (HBsAg)
IC50: 0.5 μM (replication) | Inhibition of replication and HBsAg secretion | [108] |
| 21 | 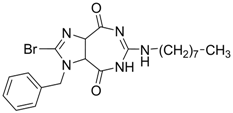 | EC50: 1.7 μM,
CC50: 286 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 cells | Inhibition of virion secretion and replication | [109] |
| 22 | 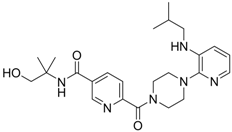 | IC50: ~0.01 μg/mL | Inhibition of RT | [110] |
| 23 | 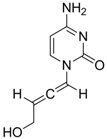 | IC50:0.08 μM in HepG2 2.2.15 | Inhibition of replication | [111] |
Helioxanthin and its derivative 5-4-2 (compound 10), a novel class of compounds, were reported to have potent anti-HBV activities in HepG2.2.15 cells, with EC50s of 1 and 0.08 μM, respectively [97]. The lamivudine-resistant rtL180M/M204V double mutant HBV strain was also sensitive to helioxanthin and compound 10. This class of compounds not only inhibited HBV DNA, but also decreased HBV mRNA and core protein expression. A recent study has demonstrated that compound 10 suppresses HBV replication by post-transcriptional down-regulation of critical transcription factors, which are essential for HBV gene expression, hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 4 and 3 [98]. Compound 10 was a potential novel anti-HBV agent that possesses a different mechanism of action from existing therapeutic drugs.
Compounds 11 ~ 23 in Table 4 and their derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their anti-HBV activity and cytotoxicity in vitro (see references in Table 4). All compounds exhibited strong activity against HBV replication with low cytotoxicity in vitro. However, the stages of the viral life cycle or the targets involved in their mechanisms of action have not been determined. Further studies on the mechanisms of action and preclinical evaluations using animal models are therefore needed to describe this novel class of anti-HBV drug candidates.
4.3. Virtual screening, modeling and rational drug design
Virtual screening is an efficient method for identifying drug candidates in silico from large chemical compound databases. Virtual screening, particularly receptor-based or ligand-based virtual screening, has emerged as a reliable, inexpensive method for identifying lead compounds. Advances in computational techniques have enabled virtual screening to be a powerful tool in the drug discovery process. Its usefulness has been verified by current applications in which hit and lead identifications against various disease targets were successfully retrieved (reviewed in reference [112]). There have been great advances in molecular modeling techniques that have resulted in the excavation of a large number of potential therapeutic drugs that are relevant to biological functions. The growth in the number of potential target molecules has increased the demand for reliable target validation as well as for technologies that can rapidly identify optimal lead candidates.
Antiviral compounds have also recently been successfully identified by virtual screening. Many laboratories have investigated inhibitors of HIV-1 and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) using various targets and virtual screening methods [113,114,115,116,117,118]. Applications and examples of pharmacophore-based antiviral drug design are comprehensively reviewed recently [112].
However, unfortunately, there has been no report of an HBV inhibitor study by virtual screening methods. This may partly be due to the lack of an X-ray crystal structure of HBV polymerase, which is needed to obtain reliable virtual screening results. Recently, a pharmacophore model of the synthesized compounds was proposed by the genetic algorithm similarity program (GASP) program [119] to give useful information for further structural modification [101]. Lv and colleagues synthesized the 2-pyridone derivatives and tested for their in vitro anti-HBV activity [101]. Because the target of 2-pyridone derivatives is unknown, the construction a pharmacophore model would be useful for further structural optimization and could also be used in virtual screening and for identifying new lead structures.
The refined homology model structure of HBV based on the crystal structure of HIV-1 RT has successfully demonstrated the molecular mechanism of drug resistance to corresponding drugs [120]. The homology models provide mechanistic insight into HBV resistance that is consistent with the biological studies, although it still lacks the validation of direct structural data. Until the 3D structure of HBV polymerase is defined, the homology model structure will serve as a useful tool for better understanding the molecular mechanism of replication and resistance and for the investigation of anti-HBV lead compounds.
4.4. Targets for future drugs
As described earlier, all current anti-HBV drugs are RT inhibitors of nucleoside or nucleotide analogues, leading to a high possibility of developing drug-resistant HBV. Treatment with multiple drugs having different mechanisms of action is therefore needed to improve viral clearance and prevent resistance. Thus, small molecule inhibitors that target the viral life cycle proteins other than polymerase are strongly needed for combination therapy.
RT inhibitors suppress viral replication very efficiently but do not eliminate the existing virus and cccDNA. If the episomal cccDNA in hepatocytes is not eliminated, HBV can rebound if the conditions are suitable for virion production. Recently, a fundamental understanding of the regulation of cccDNA has been elucidated by some groups [121,122,123,124]. The main features of their findings on cccDNA regulation are the involvement of HBx and the epigenetic control of cccDNA-bound histones and cccDNA itself. These efforts will allow development of future drugs that can control the biogenesis and regulation of cccDNA, the ultimate goal of HBV eradication.
The inhibitors that have been reported to exert specific and potent anti-HBV activity with non-polymerase viral targets in vivo and in vitro warrant further evaluation in clinical trials. Small molecule inhibitors such as compound 7 (in Table 3) and compound 8 (in Table 4) efficiently block the nucleocapsid maturation [92] and pregenomicRNA encapsidation [93,94,95], respectively. HBV entry inhibitors that utilized the pre-S1 peptides, which are essential for virus entry into the hepatocytes, successfully prevent viral infection [125]. Introduction of intact or modified small-interfering RNA produces strong and persistent anti-HBV activity in vivo and in vitro [126,127,128]. The chemical inhibitors (compounds 5 and 6 in Table 3), which block the interaction between core and surface protein, exert strong anti-HBV activity [91]. The inhibition of this interaction will eventually block the maturation of virion assembly and virion secretion. Along with these inhibitors, materials that can block viral and host targets that are essential for HBV life cycle, such as HBx [129], HNF [98] and unidentified HBV receptor(s) [130], are candidates for future drugs against HBV.
5. Conclusions
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B patients depends on anti-HBV drugs. Even though the currently approved anti-HBV drugs, nucleos(t)ide analogues, show potent and fast antiviral response, several problems remain to be solved. These include the development of resistance and the side effects such as myopathy, which is induced by mitochondrial damage. Based on advances in the development of antiviral agents along with newly discovered drug candidates and combination therapy, resistance should not be a great concern in the near future. However, combination therapy for effective control of HBV requires the development of novel drugs that have different mechanisms of action.
The mitochondrial damage is mainly due to the high affinity of nucleos(t)ide RT inhibitors for mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma. Therefore, alleviation of side effects should be considered in the development of future nucleos(t)ide drugs. In this regard, the fine crystal structure of polymerase gamma was reported recently [131,132]. The elucidation of the polymerase gamma structure establishes a foundation for understanding the molecular basis of the toxicity of anti-retroviral drugs targeting HBV and HIV and the cause of cellular toxicity induced by some antiviral nucleoside analogs. Eventually, these fundamental studies in conjunction with advanced drug development tools will provide valuable information for the development of novel drugs without side effects.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project (A084826 to K.H.K, A085105 to B.L.S), Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Korea.
References
- Tiollais, P.; Charnay, P.; Vyas, G.N. Biology of hepatitis B virus. Science 1981, 213, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, W.S. Molecular events in the pathogenesis of hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Med. 1994, 45, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremsdorf, D.; Soussan, P.; Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Brechot, C. Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechot, C. Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Old and new paradigms. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, C.; Zoulim, F.; Mason, W.S. Hepadnaviruses. In Fields Virology, 5th; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2977–3029. [Google Scholar]
- Ganem, D.; Schneider, R.J. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. In Fields Virology, 4th; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 2923–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.H.; Seeger, C. Novel mechanism for reverse transcription in hepatitis B viruses. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6507–6512. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.H.; Seeger, C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell 1992, 71, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Cho, E.S.; Choe, W.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, B.K.; Ko, S.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Park, E.S.; Shin, G.C.; Kim, K.H. Identification and characterization of clevudine-resistant mutants of hepatitis B virus isolated from chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4494–4503. [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq, E. Strategies in the design of antiviral drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, C.E.; Hamatake, R.K.; Colonno, R.J.; Tenney, D.J. Entecavir for treatment of hepatitis B virus displays no in vitro mitochondrial toxicity or DNA polymerase gamma inhibition. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innaimo, S.F.; Seifer, M.; Bisacchi, G.S.; Standring, D.N.; Zahler, R.; Colonno, R.J. Identification of BMS-200475 as a potent and selective inhibitor of hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.; Hernandez, D.; Yamanaka, G.; Zhang, S.; Rose, R.; Weinheimer, S.; Colonno, R.J. Efficacies of entecavir against lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus replication and recombinant polymerases in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T. A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Shouval, D.; Lok, A.S.; Chang, T.T.; Cheinquer, H.; Goodman, Z.; DeHertogh, D.; Wilber, R.; Zink, R.C.; Cross, A.; Colonno, R.; Fernandes, L. BEHoLD AI463027 Study Group. Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.; Yurdaydin, C.; Sollano, J.; Silva, M.; Liaw, Y.F.; Cianciara, J.; Boron-Kaczmarska, A.; Martin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Colonno, R.; Cross, A.; Denisky, G.; Kreter, B.; Hindes, R. AI463026 BEHoLD Study Group. Entecavir for the treatment of lamivudine-refractory, HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.; Yurdaydin, C.; Simsek, H.; Silva, M.; Liaw, Y.F.; Rustgi, V.K.; Sette, H.; Tsai, N.; Tenney, D.J.; Vaughan, J.; Kreter, B.; Hindes, R. AI463026 Benefits of Entecavir for Hepatitis B Liver Disease (BEHoLD) Study Group. Entecavir therapy for lamivudine-refractory chronic hepatitis B: Improved virologic, biochemical, and serology outcomes through 96 weeks. Hepatology 2008, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, M.L.; Bridges, E.G.; Placidi, L.; Faraj, A.; Loi, A.G.; Pierra, C.; Dukhan, D.; Gosselin, G.; Imbach, J.L.; Hernandez, B.; Juodawlkis, A.; Tennant, B.; Korba, B.; Cote, P.; Marion, P.; Cretton-Scott, E.; Schinazi, R.F.; Sommadossi, J.P. Antiviral L-nucleosides specific for hepatitis B virus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Gane, E.; Leung, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Wang, Y.; Lai, C.L.; Heathcote, E.J.; Manns, M.; Bzowej, N.; Niu, J.; Han, S.H.; Hwang, S.G.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Tong, M.J.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Chen, Y.; Brown, N.A.; Albanis, E.; Galil, K.; Naoumov, N.V. GLOBE Study Group. 2-Year GLOBE trial results: Telbivudine is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.L.; Gane, E.; Liaw, Y.F.; Hsu, C.W.; Thongsawat, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Heathcote, E.J.; Rasenack, J.; Bzowej, N.; Naoumov, N.V.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Zeuzem, S.; Moon, Y.M.; Goodman, Z.; Chao, G.; Constance, B.F.; Brown, N.A. Globe Study Group. Telbivudine versu lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2576–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.L.; Leung, N.; Teo, E.K.; Tong, M.; Wong, F.; Hann, H.W.; Han, S.; Poynard, T.; Myers, M.; Chao, G.; Lloyd, D.; Brown, N.A. Telbivudine Phase II Investigator Group. A 1-year trial of telbivudine, lamivudine, and the combination in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, CK.; Ma, T.; Shanmuganathan, K.; Wang, C.; Xiang, Y.; Pai, S.B.; Yao, G.Q.; Sommadossi, J.P.; Cheng, Y.C. Use of 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta-L-arabinofuranosyluracil as a novel antiviral agent for hepatitis B virus and Epstein-Barr virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna Pai, S.; Liu, S.H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Chu, C.K.; Cheng, Y.C. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by a novel L-nucleoside, 2’-fluor-5-methyl-beta L-arabinofuranosyl uracil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 380–386. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Grove, K.L.; Cheng, Y.C. Unique metabolism of a novel antiviral L-nucleoside analog, 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta-L-arabinofuranosyluracil: A substrate for both thymidine kinase and deoxycytidine kinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 833–839. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, B.C.; Kim, J.H; Kim, T.H.; Koh, K.C.; Um, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.S.; Han, B.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Byun, K.S.; Hwang, S.G.; Kim, B.I.; Cho, M.; Yoo, K.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Yang, J.M.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, D.G.; Chung, Y.H.; Cho, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Lee, H.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Yoo, H.W.; Lee, H.S. Clevudine is highly efficacious in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B with durable off-therapy viral suppression. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, K.S.; Paik, S.W.; Ryu, S.H.; Han, B.H.; Han, J.Y.; Byun, K.S.; Cho, M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Cho, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Um, S.H.; Hwang, S.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Chon, C.Y.; Kim, B.I.; Lee, Y.S.; Yang, J.M.; Kim, H.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Choi, S.K.; Kweon, Y.O.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Yoo, K.; Yoo, H.W.; Lee, H.S. Twenty-four-week clevudine therapy showed potent and sustained antiviral activity in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar]
- van Bommel, F.; Wunsche, T.; Mauss, S.; Reinke, P.; Bergk, A.; Schurmann, D.; Wiedenmann, B.; Berg, T. Comparison of adefovir and tenofovir in the treatment of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, F.; Zollner, B.; Sarrazin, C.; Spengler, U.; Huppe, D.; Moller, B.; Feucht, H.H.; Wiedenmann, B.; Berg, T. Tenofovir for patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and high HBV DNA level during adefovir therapy. Hepatology 2006, 44, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, W.E.; Ray, A.S.; Yang, H.; Qi, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Miller, M.D. Intracellular metabolism and in vitro activity of tenofovir against hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, P.; Heathcote, E.J.; Buti, M.; Gane, E.; de Man, R.A.; Krastev, Z.; Germanidis, G.; Lee, S.S.; Flisiak, R.; Kaita, K.; Manns, M.; Kotzev, I.; Tchernev, K.; Buggisch, P.; Weilert, F.; Kurdas, O.O.; Shiffman, M.L.; Trinh, H.; Washington, M.K.; Sorbel, J.; Anderson, J.; Snow-Lampart, A.; Mondou, E.; Quinn, J.; Rousseau, F. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2442–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, S.K.; Lok, A.S. Drug insight: Nucleoside and nucleotide analog inhibitors for hepatitis B. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 1, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.D.; Lok, A.S. Myopathy and neuropathy associated with nucleos(t)ide analog therapy for hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, M.; Perazella, M.A. Nephrotoxicity associated with antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients. Curr. Drug Saf. 2007, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, N.; Tanji, K.; Kambham, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Bell, A.; D'agati, V.D. Adefovir nephrotoxicity: Possible role of mitochondrial DNA depletion. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.; Lagakos, S.; Wulfsohn, M.; Cherng, D.; Miller, M.; Cherrington, J.; Hardy, D.; Beall, G.; Cooper, R.; Murphy, R.; Basgoz, N.; Ng, E.; Deeks, S.; Winslow, D.; Toole, J.J.; Coakley, D. Efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil with antiretroviral therapy: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999, 282, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.L.; Brown, C.E.; Matthews-Davis, N.; Reardon, J.E. Effects of antiviral nucleoside analogs on human DNA polymerases and mitochondrial DNA synthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuda, T.N. Pharmacology of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor-induced mitochondrial toxicity. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Day, B.J.; Copeland, W.C. Mitochondrial toxicity of NRTI antiviral drugs: An integrated cellular perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2003, 2, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.I.; Lee, D.K.; Lee, C.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jo, H.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.S. Long-term therapy with clevudine for chronic hepatitis B can be associated with myopathy characterized by depletion of mitochondrial DNA. Hepatology 2009, 49, 2080–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girones, R.; Miller, R.H. Mutation rate of the hepadnavirus genome. Virology 1989, 170, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Hill, A.M.; Boehme, R.; Thomas, H.C.; McDade, H. Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4398–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngui, S.L.; Hallet, R.; Teo, C.G. Natural and iatrogenic variation in hepatitis B virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 1999, 9, 183–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, M.; Liang, T.J. Drug targets and molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Locarnini, S. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Lai, C.L.; Leung, N.; Yao, G.B.; Cui, Z.Y.; Schiff, E.R.; Dienstag, J.L.; Heathcote, E.J.; Little, N.R.; Griffiths, D.A.; Gardner, S.D.; Castiglia, M. Long-term safety of lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.I.; Deslauriers, M.; Andrews, C.W.; Tipples, G.A.; Walters, K.A.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Brown, N.; Condreay, L.D. Identification and characterization of mutations in hepatitis B virus resistant to lamivudine. Lamivudine Clinical Investigation Group. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyver, L.J.; Locarnini, S.A.; Lok, A.; Richman, D.D.; Carman, W.F.; Dienstag, J.L.; Schinazi, R.F. Nomenclature for antiviral-resistant human hepatitis B virus mutations in the polymerase region. Hepatology 2001, 33, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Kuiper, M.; Bartholomeusz, A.; Ayres, A.; Yuen, L.; Shaw, T. The L80I substitution in the reverse transcriptase domain of the hepatitis B virus polymerase is associated with lamivudine resistance and enhanced viral replication in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, W.E., 4th; Yang, H.; Westland, C.E.; Das, K.; Arnold, E.; Gibbs, C.S.; Miller, M.D.; Xiong, S. The hepatitis B virus polymerase mutation rtV173L is selected during lamivudine therapy and enhances viral replication in vitro. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11833–11841. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chopra, R.; Verdine, G.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase transcriptase: Implications for drug resistance. Science 1998, 282, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Xiong, X.; Yang, H.; Westland, C.E.; Gibbs, C.S.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E. Molecular modeling and biochemical characterization reveal the mechanism of hepatitis B virus polymerase resistance to lamivudine (3TC) and emtricitabine (FTC). J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Westland, C.E.; Delaney, W.E.; Heathcote, E.J.; Ho, V.; Fry, J.; Brosgart, C.; Gibbs, C.S.; Miller, M.D.; Xiong, S. Resistance surveillance in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil for up to 60 weeks. Hepatology 2002, 36, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziyannis, S.J.; Tassopoulos, N.C.; Heathcote, E.J.; Chang, T.T.; Kitis, G.; Rizzetto, M.; Marcellin, P.; Lim, S.G.; Goodman, Z.; Ma, J.; Brosgart, C.L.; Borroto-Esoda, K.; Arterburn, S.; Chuck, S.L. Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B for up to 5 years. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, P.; Vaughan, R.; Xiong, S.; Yang, H.; Delaney, W.; Gibbs, C.; Brosgart, C.; Colledge, D.; Edwards, R.; Ayres, A.; Bartholomeusz, A. Locarnini, S. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil therapy associated with the selection of a novel mutation in the HBV polymerase. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, M.N.; Jacquard, A.C.; Pichoud, C.; Durantel, D.; Carrouee-Durantel, S.; Villeneuve, J.P.; Trepo, C.; Zoulim, F. Susceptibility to antivirals of a human HBV strain with mutations conferring resistance to both lamivudine and adefovir. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villet, S.; Pichoud, C.; Billioud, G.; Barraud, L.; Durantel, S.; Trépo, C.; Zoulim, F. Impact of hepatitis B virus rtA181V/T mutants on hepatitis B treatment failure. J Hepatol. 2008, 48, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonno, R.J.; Rose, R.; Baldick, C.J.; Levine, S.; Pokornowski, K.; Yu, C.F.; Walsh, A.; Fang, J.; Hsu, M.; Mazzucco, C.; Eggers, B.; Zhang, S.; Plym, M.; Klesczewski, K.; Tenney, D.J. Entecavir resistance is rare in nucleoside naive patients with hepatitis B. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenney, D.J.; Rose, R.E; Baldick, C.J.; Pokornowski, K.A.; Eggers, B.J.; Fang, J.; Wichroski, M.J.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Wilber, R.B.; Colonno, R.J. Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleosidenaive patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenney, D.J.; Levine, S.M.; Rose, R.E.; Walsh, A.W.; Weinheimer, S.P.; Discotto, L.; Plym, M.; Pokornowski, K.; Yu, C.F.; Angus, P.; Ayres, A.; Bartholomeusz, A.; Sievert, W.; Thompson, G.; Warner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Colonno, R.J. Clinical emergence of entecavir-resistant hepatitis B virus requires additional substitutions in virus already resistant to lamivudine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, K. Telbivudine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Adv. Ther. 2009, 26, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locarnini, S.; Mason, W.S. Cellular and virological mechanisms of HBV drug resistance. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifer, M.; Patty, A.; Serra, I.; Li, B.; Standring, D.N. Telbivudine, a nucleoside analog inhibitor of HBV polymerase, has a different in vitro cross-resistance profile than the nucleotide analog inhibitors adefovir and tenofovir. Antiviral Res. 2009, 81, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Litwin, S.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, Y.; Condreay, L.; Furman, P.; Mason, W.S. Mutations of the woodchuck hepatitis virus polymerase gene that confer resistance to lamivudine and 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta-L-arabinofuranosyluracil. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.K.; Kato, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Kato, J.; Goto, T.; Schinazi, R.F.; Carrilho, F.J.; Omata, M. The polymerase L528M mutation cooperates with nucleotide binding-site mutations, increasing hepatitis B virus replication and drug resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 2001, 107, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, R.; Shaw, T.; Torresi, J.; Sozzi, V.; Trautwein, C.; Bock, T.; Manns, M.; Isom, H.; Furman, P.; Locarnini, S. In vitro susceptibilities of wild-type or drug-resistant hepatitis B virus to (-)-beta-D-2,6-diaminopurine dioxolane and 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta-L-arabinofuranosyluracil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, J.; Camino, N.; Rodés, B.; Bartholomeusz, A.; Kuiper, M.; Tacke, F.; Núñez, M.; Mauss, S.; Lutz, T.; Klausen, G.; Locarnini, S.; Soriano, V. Selection of hepatitis B virus polymerase mutations in HIV-coinfected patients treated with tenofovir. Antivir. Ther. 2005, 10, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Amini-Bavil-Olyaee, S.; Herbers, U.; Sheldon, J.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F. The rtA194T polymerase mutation impacts viral replication and susceptibility to tenofovir in hepatitis B e antigen-positive and hepatitis B e antigen-negative hepatitis B virus strains. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, D.R.; Walsh, A.W.; Baldick, C.J.; Eggers, B.J.; Rose, R.E.; Levine, S.M.; Kapur, A.J.; Colonno, R.J.; Tenney, D.J. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus polymerase by entecavir. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3992–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yuan, Z.H.; Wu, L.; Ding, J.P.; Wen, Y.M. A single amino acid in the reverse transcriptase domain of hepatitis B virus affects virus replication efficiency. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11827–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, A.; Chu, C.K. Understanding the molecular basis of HBV drug resistance by molecular modeling. Antiviral Res. 2008, 80, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeusz, A.; Tehan, B.G.; Chalmers, D.K. Comparisons of the HBV and HIV polymerase, and antiviral resistance mutations. Antivir. Ther. 2004, 9, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Daga, P.R.; Duan, J.; Doerksen, R.J. Computational model of hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase: Molecular dynamics and docking to understand resistant mutations. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Flores, C.; Yang, H.; Toole, J.J.; Gibbs, C.S. Mutations in hepatitis B DNA polymerase associated with resistance to lamivudine do not confer resistance to adefovir in vitro. Hepatology 1998, 28, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloman, C.; Wands, J.R. Resistance of HBV to adefovir dipivoxil: A case for combination antiviral therapy? Hepatology 2003, 38, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, T.; Plosker, G. Adefovir dipivoxil: A review of its use in chronic hepatitis B. Drugs 2003, 63, 2215–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Chu, C.K. Molecular mechanisms of adefovir sensitivity and resistance in HBV polymerase mutants: A molecular dynamics study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4313–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, T.I.; Zhang, H.; Churchill, N.D.; Larsson, T.; Johansson, N.G.; Oberg, B. Profound antiviral effect of oral administration of MIV-210 on chronic hepadnaviral infection in a woodchuck model of hepatitis B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3803–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Dutschman, D.E.; Liu, S.H.; Bridges, E.G.; Cheng, Y.C. Anti-hepatitis B virus activity and metabolism of 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydro-beta-L(-)-5-fluorocytidine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.R.; Cho, D.G.; Roh, K.Y.; Hwang, J.T.; Ahn, S.; Jang, H.S.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Cho, Y.G.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.Z. A novel class of phosphonate nucleosides. 9-[(1-phosphonomethoxycyclopropyl)-methyl]guanine as a potent and selective anti-HBV agent. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. LB80380: A promising new drug for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2008, 17, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, C.R.; Kim, J.; Ngai, V.; Lai, C.L. Pharmacokinetics of LB80331 and LB80317 following oral administration of LB80380, a new antiviral agent for chronic hepatitis B (CHB), in healthy adult subjects, CHB patients, and mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Han, K.H.; Um, S.H.; Yoon, S.K.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.R.; Lai, C.L. Antiviral activity and safety of LB80380 in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with lamivudine-resistant disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Matelich, M.C.; Ugarkar, B.G.; Gómez-Galeno, J.E.; DaRe, J.; Ollis, K.; Sun, Z.; Craigo, W.; Colby, T.J.; Fujitaki, J.M.; Boyer, S.H.; van Poelje, P.D.; Erion, M.D. Pradefovir: A prodrug that targets adefovir to the liver for the treatment of hepatitis B. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 14, 666–676. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.G.; Lai, C.L.; Myers, M. Final results of a phase I/II dose escalation trial of valtorcitabine in patients with chronic hepatitis B (abstract). J. Hepatol. 2005, 42 Suppl 2, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Luo, J.; Cheng, P.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.J. Anti-HBV agents. Part 1: Synthesis of alisol A derivatives: A new class of hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4647–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.F.; Ma, Y.B.; Guo, R.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.J. Anti-HBV agents. Part 2: Synthesis and in vitro anti-hepatitis B virus activities of alisol A derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2148–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Luo, J.; Ma, Y.B.; Liu, J.F.; Guo, R.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, J.; Niu, W.; Du, F.F.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Chen, J.J. Anti-HBV agents. Part 3: Preliminary structure-activity relationships of tetra-acylalisol A derivatives as potent hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6659–6665. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.S.; Kang, E.H.; Lee, Y.I. A flavonoid from medicinal plants blocks hepatitis B virus-e antigen secretion in HBV-infected hepatocytes. Antiviral Res. 2005, 67, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, A.M.; Guo, H.; Westby, G.; Liu, Y.; Simsek, E.; Guo, J.T.; Mehta, A.; Norton, P.; Gu, B.; Block, T.; Cuconati, A. A substituted tetrahydro-tetrazolo-pyrimidine is a specific and novel inhibitor of hepatitis B virus surface antigen secretion. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4427–4437. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.R.; Yeh, S.F.; Liu, C.M.; Damu, A.G.; Kuo, T.H.; Chiang, P.C.; Bastow, K.F.; Lee, K.H.; Wu, T.S. Anti-HBV and cytotoxic activities of pyranocoumarin derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6137–6143. [Google Scholar]
- Asif-Ullah, M.; Choi, K.J.; Choi, K.I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Yu, Y.G. Identification of compounds that inhibit the interaction between core and surface protein of hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res. 2006, 70, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deres, K.; Schröder, C.H.; Paessens, A.; Goldmann, S.; Hacker, H.J.; Weber, O.; Krämer, T.; Niewöhner, U.; Pleiss, U.; Stoltefuss, J.; Graef, E.; Koletzki, D.; Masantschek, R.N.; Reimann, A.; Jaeger, R.; Gross, R.; Beckermann, B.; Schlemmer, K.H.; Haebich, D.; Rübsamen-Waigmann, H. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by drug-induced depletion of nucleocapsids. Science 2003, 299, 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Delaney, W.E., 4th; Edwards, R.; Colledge, D.; Shaw, T.; Furman, P.; Painter, G.; Locarnini, S. Phenylpropenamide derivatives AT-61 and AT-130 inhibit replication of wild-type and lamivudine-resistant strains of hepatitis B virus in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3057–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.W.; Ladner, S.K.; Miller, T.J.; Zaifert, K.; Perni, R.B.; Conway, S.C.; Otto, M.J. Inhibition of human hepatitis B virus replication by AT-61, a phenylpropenamide derivative, alone and in combination with (-)beta-L-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 3179–31486. [Google Scholar]
- Feld, J.J.; Colledge, D.; Sozzi, V.; Edwards, R.; Littlejohn, M.; Locarnini, S.A. The phenylpropenamide derivative AT-130 blocks HBV replication at the level of viral RNA packaging. Antiviral Res. 2007, 76, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Gong, P. Synthesis and anti-hepatitis B virus evaluation of novel ethyl 6-hydroxyquinoline-3-carboxylates in vitro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6522–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Yeo, H.; Zhu, J.L.; Chou, C.K.; Kou, Y.H.; Yeh, S.F.; Gullen, E.; Austin, D.; Cheng, Y.C. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by helioxanthin and its derivative. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2005, 16, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, C.; Li, Y.; Leung, C.H.; Robek, M.D.; Cheng, Y.C. Unique antiviral mechanism discovered in anti-hepatitis B virus research with a natural product analogue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8526–8531. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, G.F.; He, P.L.; Huang, W.G.; Zhu, F.H.; Gao, H.Y.; Tang, W.; Luo, Y.; Feng, C.L.; Shi, L.P.; Ren, Y.D.; Lu, W.; Zuo, J.P. Synthesis and anti-hepatitis B virus activity of novel benzimidazole derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4790–4794. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, G.F.; Luo, Y.; Huang, W.G.; Tang, W.; Feng, C.L.; Shi, L.P.; Ren, Y.D.; Zuo, J.P.; Lu, W. Identification of 1-isopropylsulfonyl-2-amine benzimidazoles as a new class of inhibitors of hepatitis B virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Sheng, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.; Zhong, H.; Niu, C.; Li, K. Design, synthesis, and antihepatitis B virus activities of novel 2-pyridone derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembower, D.E.; Lin, Y.M.; Flavin, M.T.; Chen, F.C.; Korba, B.E. Robustaflavone, a potential non-nucleoside anti-hepatitis B agent. Antiviral Res. 1998, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.L.; Liu, Z.X.; Liu, X.H.; Li, Z.M.; Zhao, W.G. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new acrylamide derivatives containing 1,2,3-thiadiazole as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus replication. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Cai, Z.; Pan, W.; Cao, P.; Hao, X.; Liang, G. Synthesis and anti-hepatitis B virus activities of Matijing-Su derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korba, B.E.; Montero, A.B.; Farrar, K.; Gaye, K.; Mukerjee, S.; Ayers, M.S. Rossignol, J.F. Nitazoxanide, tizoxanide and other thiazolides are potent inhibitors of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus replication. Antiviral Res. 2008, 77, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, H.; Gong, P. Synthesis and in vitro anti-hepatitis B virus activities of some ethyl 5-hydroxy-1H-indole-3-carboxylates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, L.; You, Q.; Yang, Y.; Gu, H.; Song, G.; Lu, N.; Xin, J. Anti-hepatitis B virus activity of wogonin in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 2007, 74, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.R.; Efferth, T.; Serrano, M.A.; Castaño, B.; Macias, R.I.; Briz, O.; Marin, J.J. Effect of artemisinin/artesunate as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus production in an "in vitro" replicative system. Antiviral Res. 2005, 68, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, N.; Korba, B.E.; Hosmane, R.S. Synthesis and in vitro anti-hepatitis B and C virus activities of ring-expanded ('fat') nucleobase analogues containing the imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,8-dione ring system. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5397–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shim, H.; Park, Y.; Park, S.; Shin, J.; Yang, W.; Lee, H.; Park, W.; Chung, Y.; Lee, S. 2,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid derivatives as non-nucleosidic reverse transcriptase inhibitors of hepatitis B virus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2715–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Pai, S.B.; Liu, S.H.; Grove, K.L.; Jones, B.C.; Simons, C.; Zemlicka, J.; Cheng, Y.C. Inhibition of replication of hepatitis B virus by cytallene in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, N.D.; Seong, B.L. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening: A review of recent applications. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musmuca, I.; Caroli, A.; Mai, A.; Kaushik-Basu, N.; Arora, P.; Ragno, R. Combining 3-D quantitative structure-activity relationship with ligand based and structure based alignment procedures for in silico screening of new hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, S.I.; Han, C.K.; Yoon, J.H.; No, K.T.; Kim, K.H.; Seong, B.L. Identification of novel inhibitors of HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by pharmacophore-based virtual screening and in vitro evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2975–2982. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, D.E.; Chong, Y. Identification of novel HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors using pharmacophore-guided virtual screening. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2008, 72, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustanji, Y.; Al-Masri, I.M.; Qasem, A.; Al-Bakri, A.G.; Taha, M.O. In silico screening for non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors using physicochemical filters and high-throughput docking followed by in vitro evaluation. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2009, 74, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.; Barreca, M.L.; Ferro, S.; Christ, F.; Iraci, N.; Gitto, R.; Monforte, A.M.; Debyser, Z.; Chimirri, A. Pharmacophore-based discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions between HIV-1 integrase and cellular cofactor LEDGF/p75. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, A.; Pérez-Nueno, V.I.; Fano, A.; Pistone, C.; Ritchie, D.W.; Teixidó, J. Biological profiling of anti-HIV agents and insight into CCR5 antagonist binding using in silico techniques. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C. A genetic algorithm for flexible molecular overlay and pharmacophore elucidation. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 1995, 9, 532–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.W.; Langley, D.R.; Colonno, R.J.; Tenney, D.J. Mechanistic characterization and molecular modeling of hepatitis B virus polymerase resistance to entecavir. PLoS One. 2010, 5, e9195. [Google Scholar]
- Belloni, L.; Pollicino, T.; De Nicola, F.; Guerrieri, F.; Raffa, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19975–19979. [Google Scholar]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Mu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Z. Evidence that methylation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in liver tissues of patients with chronic hepatitis B modulates HBV replication. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollicino, T.; Belloni, L.; Raffa, G.; Pediconi, N.; Squadrito, G.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Hepatitis B virus replication is regulated by the acetylation status of hepatitis B virus cccDNA-bound H3 and H4 histones. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 823–837. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Mier, W.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; von Weizsäcker, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Fischer, L.; Pollok, J.M.; Erbes, B.; Seitz, S.; Urban, S. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in vivo by entry inhibitors derived from the large envelope protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, D.V.; Lockridge, J.A.; Shaw, L.; Blanchard, K.; Jensen, K.; Breen, W.; Hartsough, K.; Machemer, L.; Radka, S.; Jadhav, V.; Vaish, N.; Zinnen, S.; Vargeese, C.; Bowman, K.; Shaffer, C.S.; Jeffs, L.B.; Judge, A.; MacLachlan, I.; Polisky, B. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.L.; Huang, L.R.; Huang, C.C.; Lai, H.L.; Liu, C.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsu, Y.W.; Lu, C.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. RNA interference-mediated control of hepatitis B virus and emergence of resistant mutant. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.J.; Wang, L.H.; Schneider, R.J. Calcium signaling by HBx protein in hepatitis B virus DNA replication. Science 2001, 294, 2376–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kennedy, W.D.; Yin, Y.W. Structural insight into processive human mitochondrial DNA synthesis and disease-related polymerase mutations. Cell 2009, 139, 312–324, Erratum in: Cell 2009, 139, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, M.; Larsson, N.G. Structure casts light on mtDNA replication. Cell 2009, 139, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not Available.
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
