A PAMPA Assay as Fast Predictive Model of Passive Human Skin Permeability of New Synthesized Corticosteroid C-21 Esters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
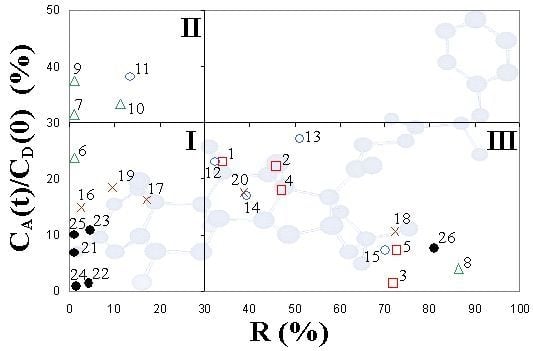
2. Results and Discussion
| Corticosteroids | R (%) | CA(t)/CD(0) (%) | log Pe (cm/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthesized corticosteroid C-21esters | 1 | FA-21-MP | 34.1 ± 3.5 | 23.1 ± 1.4 | −4.64 ± 0.17 |
| 2 | FA-21-EP | 45.8 ± 4.1 | 22.2 ± 1.6 | −4.52 ± 0.19 | |
| 3 | FA-21-PhP | 71.9 ± 2.8 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | −5.68 ± 0.15 | |
| 4 | FA-21-MB | 47.2 ± 3.4 | 18.0 ± 1.3 | −4.65 ± 0.12 | |
| 5 | FA-21-EB | 72.8 ± 2.6 | 7.2 ± 0.9 | −4.82 ± 0.10 | |
| 6 | DEX-21-MP | <1 | 23.8 ± 1.5 | −4.88 ± 0.17 | |
| 7 | DEX-21-EP | <1 | 31.6 ± 0.6 | −4.70 ± 0.11 | |
| 8 | DEX-21-PhP | 86.5 ± 4.2 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | −4.74 ± 0.13 | |
| 9 | DEX-21-MB | <1 | 37.4 ± 1.5 | −4.58 ± 0.15 | |
| 10 | DEX-21-EB | 11.3 ± 3.5 | 33.4 ± 1.2 | −4.58 ± 0.13 | |
| 11 | TA-21-MP | 13.5 ± 4.1 | 38.1 ± 1.6 | −4.45 ± 0.16 | |
| 12 | TA-21-EP | 32.4 ± 1.7 | 23.0 ± 1.8 | −4.66 ± 0.15 | |
| 13 | TA-21-PhP | 51.1 ± 3.8 | 27.1 ± 1.4 | −4.07 ± 0.14 | |
| 14 | TA-21-MB | 39.3 ± 4.1 | 16.9 ± 2.0 | −4.85 ± 0.23 | |
| 15 | TA-21-EB | 70.1 ± 3.4 | 7.3 ± 1.6 | −4.87 ± 0.21 | |
| 16 | H-21-MP | 2.6 ± 1.9 | 14.9 ± 1.8 | −5.11 ± 0.25 | |
| 17 | H-21-EP | 17.2 ± 2.2 | 16.3 ± 1.9 | −4.99 ± 0.19 | |
| 18 | H-21-PhP | 72.2 ± 3.1 | 10.6 ± 1.2 | −4.58 ± 0.15 | |
| 19 | H-21-MB | 9.6 ± 3.2 | 18.5 ± 1.9 | −4.97 ± 0.28 | |
| 20 | H-21-EB | 38.6 ± 1.8 | 17.6 ± 1.4 | −4.77 ± 0.17 | |
| Corticosteroid standards | 21 | FA | <1 | 6.7 ± 1.2 | −5.26 ± 0.15 |
| 22 | DEX | 4.2 ± 2.0 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | −5.99 ± 0.10 | |
| 23 | TA | 4.7 ± 2.3 | 10.8 ± 1.5 | −5.01 ± 0.17 | |
| 24 | H | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 0.8 ± 0.5 | −6.23 ± 0.09 | |
| 25 | H-21-Ac | <1 | 10.0 ± 1.7 | −5.07 ± 0.19 | |
| 26 | MF | 81.0 ± 2.9 | 7.7 ± 1.5 | −4.10 ± 0.15 |


3. Experimental
3.1. General
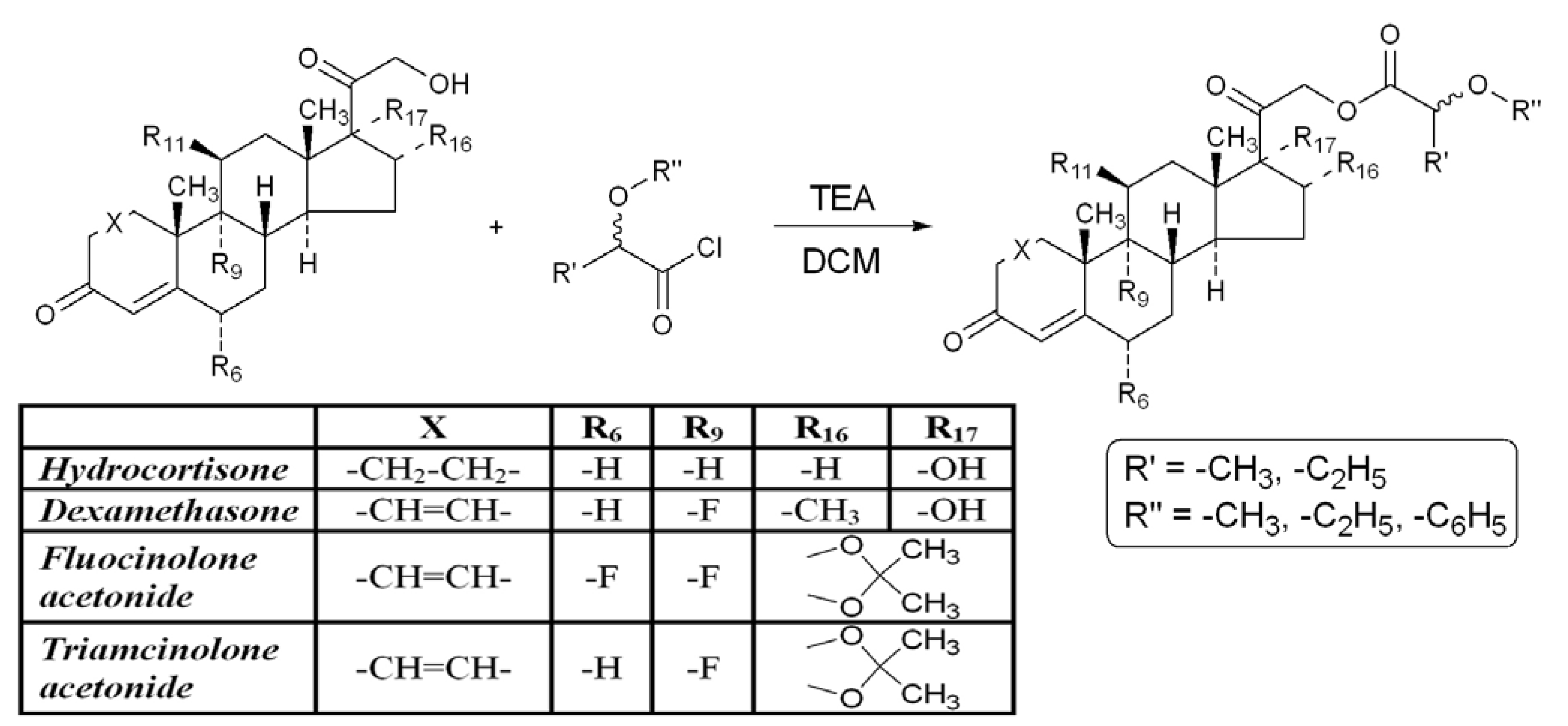
3.2. Permeability Measurements Using the PAMPA Technique
3.2.1. Chemicals
3.2.2. PAMPA Test
3.3. Permeability Calculations


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 36th ed; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa, J.M.; Vanaclocha, F.; Borrego, L.; Fernandez-Lopez, E.; Fuertes, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez-Freire, L.; Zulaica, A.; Tuneu, A.; Caballe, G.; Colome, E.; et al. Update of the topical treatment of psoriasis. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009, 100, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedersberg, S.; Leopold, C.S.; Gay, R.H. Bioavailability and bioequivalence of topical glucocorticoids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershing, L.K.; Corlett, J.L.; Lambert, L.D.; Poncelet, C.E. Circadian activity of topical 0.05% betamethasone dipropionate in human skin in vivo. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Topical Steroids Potency Chart. National Psoriasis Foundation, Portland, OR, USA; 1998. Available online: http://www.psoriasis.org/page.aspx?pid=469 accessed on 9 December 2011.
- British National Formulary; British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain: London, UK, 2004.
- Brazzini, B.; Pimpinelli, N. New and established topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuder-Gilabert, L.; Martínez-Pla, J.J.; Sagrado, S.; Villanueva-Camañas, R.M.; Medina-Hernández, M.J. Biopartitioning micellar separation methods: Modelling drug absorption. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 797, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchoz, Y.; Bard, B.; Guillarme, D.; Carrupt, P.A.; Veuthey, J.L.; Martel, S. Analytical tools for the physicochemical profiling of drug candidates to predict absorption/distribution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 707–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yourick, J.J.; Jung, C.T.; Bronaugh, R.L. In vitro and in vivo percutaneous absorption of retinol from cosmetic formulations: Significance of the skin reservoir and prediction of systemic absorption. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 231, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Transdermal skin delivery: Predictions for humans from in vivo, ex vivo and animal models. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, D.R. In vitro skin permeation techniques. J. Control. Release 1992, 18, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgraft, J. Skin deep. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, W.J.; Berge, W.F.; Banton, M.I.; Heneweer, M.; Moore, N.P. Dermal penetration of propylene glycols: Measured absorption across human abdominal skin in vitro and comparison with a QSAR model. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, G.P.; Dearden, J.C.; Patel, H.; Cronin, M.T.D. Quantitative structure-permeability relationships (QSPRs) for percutaneous absorption. Toxicol. In Vitro 2002, 16, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, F.; Cappello, B.; Miro, A.; La Rotonda, M.I.; Quaglia, F. Chromatographic indexes on immobilized artificial membranes for the prediction of transdermal transport of drugs. Il Farmaco 1998, 53, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansy, M.; Senner, F.; Gubernator, K. Physicochemical high-throughput screening: Parallel artificial membrane permeation assay in the description of passive absorption processes. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensch, J.; Melis, A.; Mackie, C.; Verreck, G.; Brewster, E. Evaluation of various PAMPA models to identify the most discriminating method for the prediction of BBB permeability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High throughput artificial membrane permeability assay for blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, P.S.; Soppimath, K.S.; Betageri, G.V. Proliposomes of exemestane for improved oral delivery: Formulation and in vitro evaluation using PAMPA, Caco-2 and rat intestine. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 380, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviani, G.; Martel, S.; Carrupt, P.-A. Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay: A new membrane for the fast prediction of passive human skin permeability. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3948–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, G.; Martel, S.; Carrupt, P.-A. In silico and in vitro filters for the fast estimation of skin permeation and distribution of new chemical entities. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkó, B.; Kökösi, J.; Avdeef, A.; Takács-Novák, K. A PAMPA study of the permeability-enhancing effect of a new ceramide analogues. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruell, J. Membrane-based drug assays. Mod. Drug Discov. 2003, 6, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, E.H. High throughput physicochemical profiling for drug discovery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1838–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sabus, C.; Carter, G.T.; Du, C.; Avdeef, A.; Tischler, M. In vitro permeability of poorly aqueous soluble compounds using different solubilizers in the PAMPA assay with liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry detection. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, S.; Reali, V.; Misiano, P.; Dondio, G.; Bigogno, C. Evaluation of in vitro brain penetration: Optimized PAMPA and MDCKII-MDR1 assay comparison. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 345, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensch, J.; Noppe, M.; Adriaensen, J.; Melis, A.; Mackie, C.; Augustijns, P.; Brewster, M.E. Novel generic UPLC/MS/MS method for high throughput analysis applied to permeability assessment in early Drug Discovery. J. Chromatogr.B 2007, 847, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, B.D.; Dobricic, V.D.; Vladimirov, S.M.; Cudina, O.A.; Savic, V.M.; Karljikovic-Rajic, K.D. An investigation of solvolysis kinetics of new synthesized fluocinolone acetonide C-21 esters–In vitro model for prodrug activation. Molecules 2011, 16, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, B.; Vladimirov, S.; Pitic, D.; Savic, V.; Jacevic, V.; Dobric, S. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of new α-oxyalcanoyl esters of fluocinolone acetonide. In Proceedings of Hungarian-Austrian-Czech-German-Greek-Italian-Polish-Slovak Joint Meeting on Medicinal Chemistry, Budapest, Hungary, 24–27 June 2009; Medimond S.r.l.—Monduzzi Editore International Proceedings Division: Bologna, Italy, 2009. pp. 41–44.
- Benninger, M.S.; Ahmad, N.; Marple, B.F. The safety of intranasal steroids. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 739–750. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, M.; Gans, E.H. Topical Corticosteroids, Structure-activity and the glucocorticoid receptor: Discovery and development—A process of “planned serendipity”. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2936–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipps, G.H.; Bailey, E.J.; Bain, B.M.; Borella, R.A.; Buckton, J.B.; Clark, J.C.; Doherty, A.E.; English, A.F.; Fazakerley, H.; Laing, S.B.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships in a series of anti-inflammatory corticosteroid analogues, halomethyl androstane-17β-carbothioates and -17β-carboselenoates. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3717–3729. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Markovic, B.D.; Vladimirov, S.M.; Cudina, O.A.; Odovic, J.V.; Karljikovic-Rajic, K.D. A PAMPA Assay as Fast Predictive Model of Passive Human Skin Permeability of New Synthesized Corticosteroid C-21 Esters. Molecules 2012, 17, 480-491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010480
Markovic BD, Vladimirov SM, Cudina OA, Odovic JV, Karljikovic-Rajic KD. A PAMPA Assay as Fast Predictive Model of Passive Human Skin Permeability of New Synthesized Corticosteroid C-21 Esters. Molecules. 2012; 17(1):480-491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010480
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkovic, Bojan D., Sote M. Vladimirov, Olivera A. Cudina, Jadranka V. Odovic, and Katarina D. Karljikovic-Rajic. 2012. "A PAMPA Assay as Fast Predictive Model of Passive Human Skin Permeability of New Synthesized Corticosteroid C-21 Esters" Molecules 17, no. 1: 480-491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010480
APA StyleMarkovic, B. D., Vladimirov, S. M., Cudina, O. A., Odovic, J. V., & Karljikovic-Rajic, K. D. (2012). A PAMPA Assay as Fast Predictive Model of Passive Human Skin Permeability of New Synthesized Corticosteroid C-21 Esters. Molecules, 17(1), 480-491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010480