Astragaloside IV Stimulates Angiogenesis and Increases Nitric Oxide Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AS-IV Augments Proliferation, Migration, and Tube Formation in HUVECs
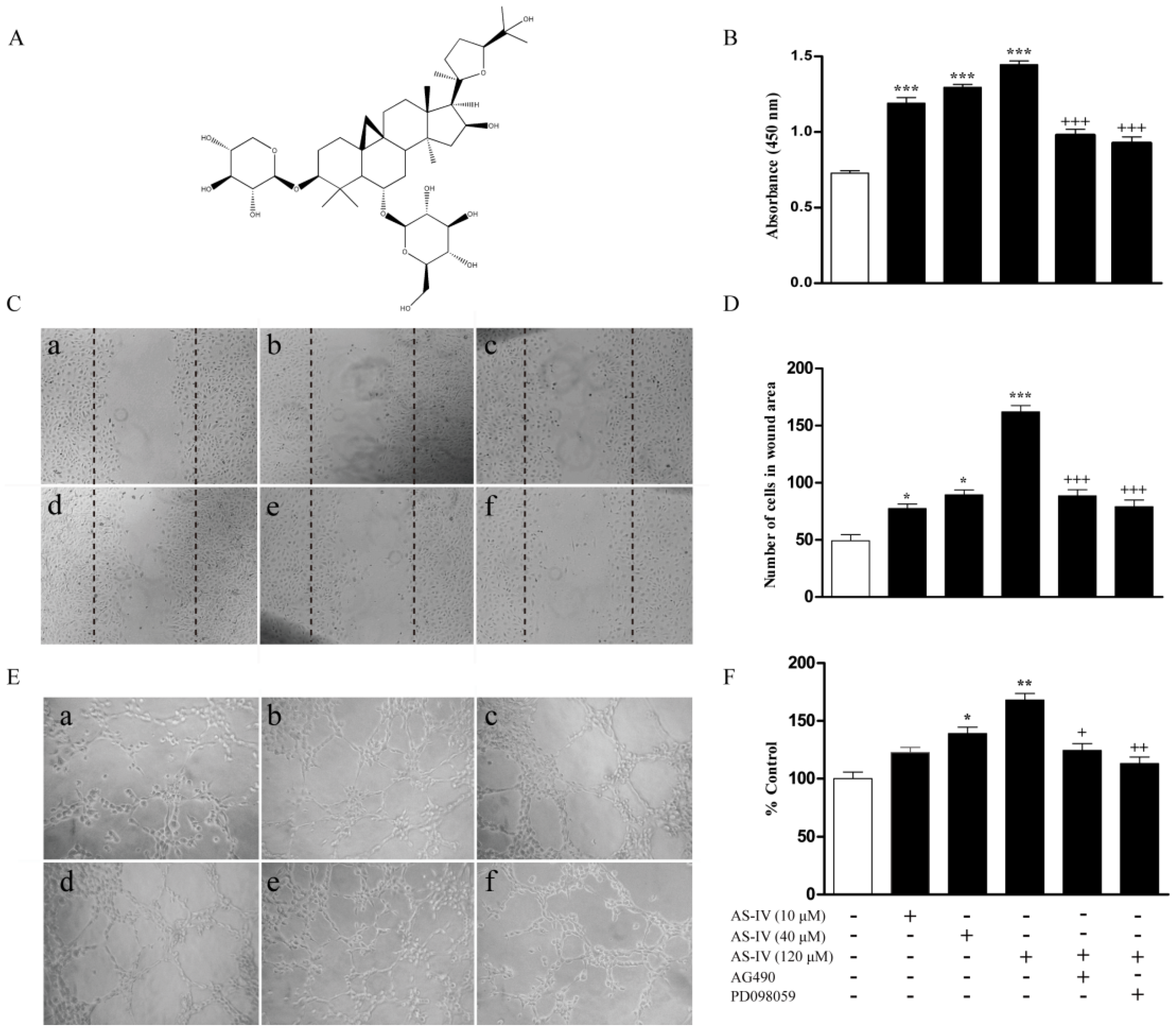
2.2. AS-IV Activates the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway in HUVECs

2.3. AS-IV Promotes the Phosphorylation of ERK1/2, but not JNK and p38 in HUVECs

2.4. AS-IV Upregulates NO via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway

3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Cell Migration Scratch Assay
4.5. Tube Formation Assay
4.6. NO Assays
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Kawamoto, A.; Tjwa, M.; Horii, M.; Hayashi, S.; Oyamada, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Suehiro, S.; Carmeliet, P.; Asahara, T. PlGF repairs myocardial ischemia through mechanisms of angiogenesis, cardioprotection and recruitment of myo-angiogenic competent marrow progenitors. PLoS One 2011, 6, e24872. [Google Scholar]
- Zachary, I.; Morgan, R.D. Therapeutic angiogenesis for cardiovascular disease: Biological context, challenges, prospects. Heart 2011, 97, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikol, S.; Baumgartner, I.; van Belle, E.; Diehm, C.; Visona, A.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Ferreira-Maldent, N.; Gallino, A.; Wyatt, M.G.; Wijesinghe, L.D.; et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis with intramuscular NV1FGF improves amputation-free survival in patients with critical limb ischemia. Mol. Ther 2008, 16, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.D.; Annex, B.H.; McKendall, G.R.; Azrin, M.A.; Lopez, J.J.; Giordano, F.J.; Shah, P.K.; Willerson, J.T.; Benza, R.L.; Berman, D.S.; et al. The VIVA trial: Vascular endothelial growth factor in Ischemia for Vascular Angiogenesis. Circulation 2003, 107, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, R.H.; Li, H.L.; Chen, H.Z. Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus shows cardioprotection during myocardial ischemia in vivo and in vitro. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qin, Z.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, D.; Fu, J.H.; Zhang, W.D.; Chen, J. Astragaloside IV protects against ischemic brain injury in a murine model of transient focal ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 363, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Meng, D.; Feng, L.; Bian, Y.Y.; Li, P.; Yang, D.; Cao, K.J.; Zhang, J.N. Protective effect of astragalosides on myocardial injury by isoproterenol in SD rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Wu, S.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Gao, L.; Gao, G.D. Astragaloside IV protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Hufnagl, P.; Binder, B.R.; Wojta, J. Antiinflammatory activity of astragaloside IV is mediated by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 904–914. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Lu, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. Astragaloside IV stimulates angiogenesis and increases hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha accumulation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, S.; Lachambre, M.P.; Lord-Dufour, S.; Beliveau, R. Propranolol suppresses angiogenesis in vitro: Inhibition of proliferation, migration, and differentiation of endothelial cells. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2010, 53, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, Z.C. STAT3: A critical transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Platt, D.; Lemtalsi, T.; Gu, X.; Brooks, S.E.; Marrero, M.B.; Caldwell, R.B. VEGF differentially activates STAT3 in microvascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1562–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, J.; Adya, R.; Tan, B.K.; Chen, J.; Randeva, H.S. Identification of chemerin receptor (ChemR23) in human endothelial cells: chemerin-induced endothelial angiogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hao, H.; Elton, T.S.; Liu, Z.; Ou, H. Intronic microRNA suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression and endothelial cell proliferation via inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 357, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliers, D.; Chen, X.; Akis, N.; Choudhury, G.G.; Madaio, M.; Kasinath, B.S. VEGF regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in glomerular endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Li, S.; Li, Z.H.; Lam, C.O.; Hong, S.J.; Kwan, Y.W.; Chan, S.W.; Leung, G.P.; Lee, S.M. Pro-angiogenic activity of astragaloside IV in HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 805–811. [Google Scholar]
- Murohara, T.; Asahara, T.; Silver, M.; Bauters, C.; Masuda, H.; Kalka, C.; Kearney, M.; Chen, D.; Symes, J.F.; Fishman, M.C.; et al. Nitric oxide synthase modulates angiogenesis in response to tissue ischemia. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 101, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; deMuinck, E.D.; Zhuang, Z.; Drinane, M.; Kauser, K.; Rubanyi, G.M.; Qian, H.S.; Murata, T.; Escalante, B.; Sessa, W.C. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is critical for ischemic remodeling, mural cell recruitment, and blood flow reserve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10999–11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chopp, M. Nitric oxide enhances angiogenesis via the synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor and cGMP after stroke in the rat. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zacharek, A.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Roberts, C.; Lu, M.; Kapke, A.; Chopp, M. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and neurogenesis after stroke in mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.L. In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchan, J.R.; Chan, B.; Kale, S.; Schnipper, L.E.; Sukhatme, V.P. In vitro and in vivo induction of antiangiogenic activity by plasminogen activators and captopril. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the Astragaloside IV is available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-G.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.-D.; Yang, C.-H.; Chen, X.-H. Astragaloside IV Stimulates Angiogenesis and Increases Nitric Oxide Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway. Molecules 2013, 18, 12809-12819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012809
Wang S-G, Xu Y, Chen J-D, Yang C-H, Chen X-H. Astragaloside IV Stimulates Angiogenesis and Increases Nitric Oxide Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway. Molecules. 2013; 18(10):12809-12819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012809
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shi-Guang, Yan Xu, Jian-Dong Chen, Chuan-Hua Yang, and Xiao-Hu Chen. 2013. "Astragaloside IV Stimulates Angiogenesis and Increases Nitric Oxide Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway" Molecules 18, no. 10: 12809-12819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012809
APA StyleWang, S. -G., Xu, Y., Chen, J. -D., Yang, C. -H., & Chen, X. -H. (2013). Astragaloside IV Stimulates Angiogenesis and Increases Nitric Oxide Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 Pathway. Molecules, 18(10), 12809-12819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012809



