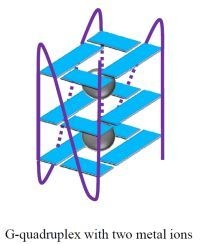
G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
G-Quadruplexes

2. G-Quadruplexes as Detectors
2.1. Detection of Metal Ions
2.1.1. Detection of K+
2.1.2. Detection of Ag+
2.1.3. Detection of Hg2+

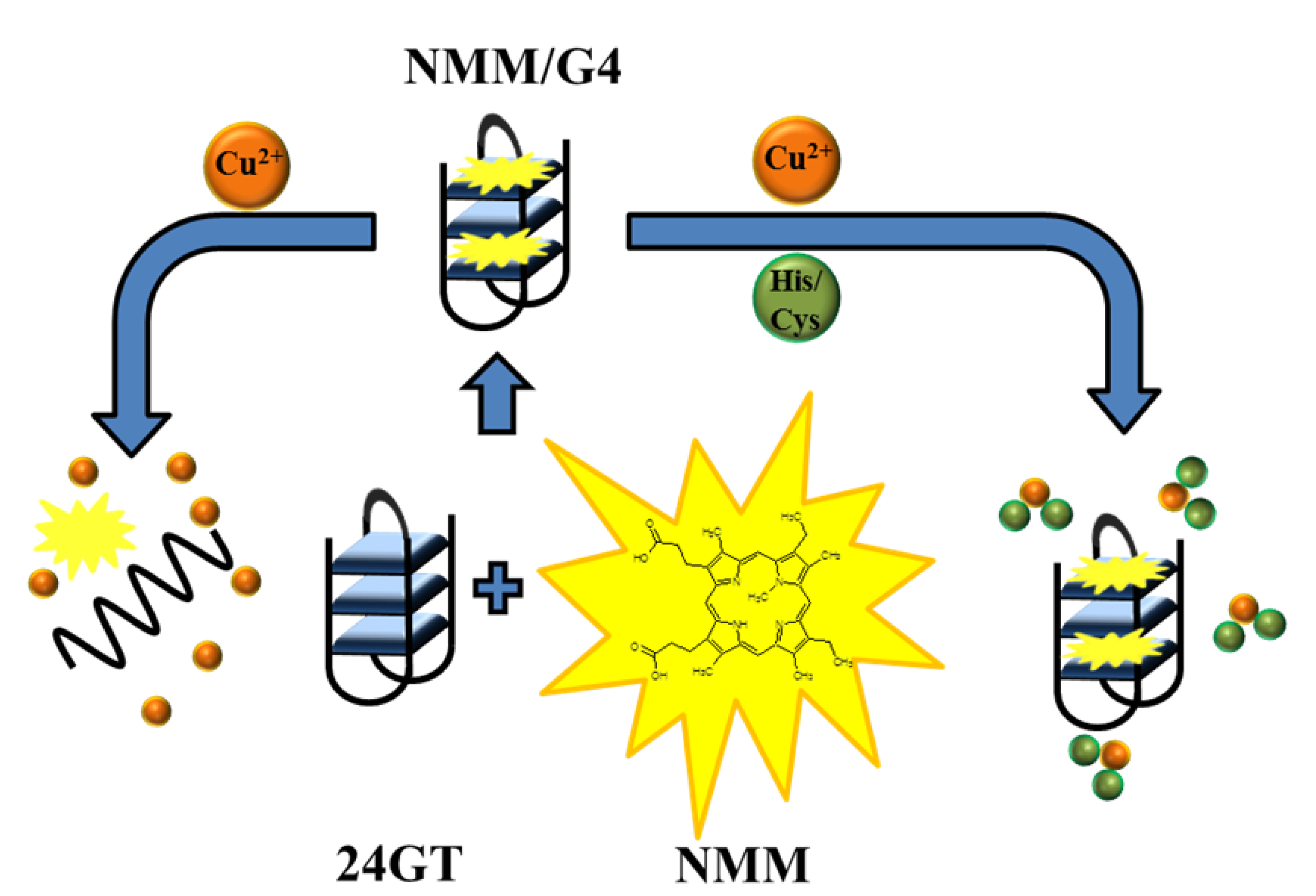
2.1.4. Detection of Cu2+
2.1.5. Detection of Pb2+

2.1.6. Detection of Ca2+
2.1.7. Detection of Sr2+
2.2. Detection of Anions
Detection of I−
2.3. Detection of Organic Molecules
2.3.1. Amino Acid Detection
2.3.2. Glucose Detection
2.3.3. Cholesterol Detection
2.3.4. ATP Detection
2.3.5. Detection of Cocaine
2.4. Detection of Nucleic Acids
2.4.1. MicroRNA Detection

2.4.2. Detection of p53 Gene Sequence
2.4.3. Detection of Gene Deletion
2.4.4. Detection of Genetically Modified Organisms
2.5. Detection of Proteins
2.5.1. Detection of Neutrophil Elastase
2.5.2. RNAse H Detection
2.5.3. Thrombin Detection
2.5.4. Detection of HIV-1 Integrase and Nucleoline
2.5.5. Detection of DNA Polymerase Proofreading Activity
2.6. Detection of Other Analytes
2.6.1. Cisplatin Detection
2.6.2. Detection of Antioxidants
2.7. Performance Characteristics of the G-Quadruplex Based Detection Methods
| Analyte | Type of Detection, Indicator | Detection Limit | Working Range | Selectivity Tested in the Presence of | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | Fluorescence CV | 1 mM | 1–15 mM | Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+ | [28] |
| K+ | Fluorescence Zn-DIGP | 0.8 µM | 0.8–400 µM | Li+, NH4+, Na+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Fe3+ | [29] |
| K+ | Colorimetric TMB | 2 µM | 2–1,000 µM | Li+, NH4+, Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cs2+ | [30] |
| K+ | Fluorescence Berberine | 2 µM | 5–1,000 µM | Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+ | [31] |
| Ag+ | Colorimetric ABTS | 6.3 nM | 5–600 nM | Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ | [25] |
| Ag+ | Colorimetric ABTS | 64 nM | 100–3,000 nM | Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ | [62] |
| Hg2+ | Colorimetric ABTS | 50 nM | 50–2,500 nM | Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ | [23] |
| Hg2+ | Colorimetric ABTS | 9.2 nM | 10–600 nM | Ca2+, Mn2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ | [33] |
| Cu2+ | Fluorescence G-quadruplex–PPIX | 3 nM | 8–2,000 nM | Ca2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, Ni2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ | [27] |
| Pb2+ | Colorimetric ABTS | 32 nM | 32–60,000 nM | Ca2+, Cu2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Fe3+ | [36] |
| Pb2+ | Luminescence Luminol | 1 nM | 1–10,000 nM | Ca2+, Cu2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Fe3+ | [36] |
| Sr2+ | Luminiscence Iridium(III) complex | 13 nM | 13–20,000 nM | K+, Li+, Na+, Ba2+, Ni2+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Mg2+, La3+, Cr3+, Al3+, Ti3+ | [63] |
| Cysteine | Colorimetric ABTS | 5 nM | 5–100,000 nM | Ala, Arg, Asp, Gln, Glu, His, Ile, Gly, Asn, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Thr, Trp, Tyr, Val | [45] |
| Histidine | Fluorescence NMM, Cu2+ | 3 nM | 3–15,000 nM | Ala, Arg, Asp, Cys, Gln, Glu, Ile, Gly, Asn, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Thr, Trp, Tyr, Val | [42] |
| Cisplatin | Electrochemical CV | 20 nM | 50–5,000 nM | Transplatin | [60] |
| Micro RNA 141 | Colorimetric ABTS | 1 fM | 1 fM–100 nM | miR-429, miR-200b, let-7d, miR-21 | [51] |
| p53 DNA | Colorimetric ABTS | 25 fM | 25 fM–500 nM | 2 partly complementary target p53 DNA | [43] |
| Glucose | Colorimetric ADHP | 1 µM | 3–100 µM | Acetaminophen, glycerin, serine, uric acid, ascorbic acid | [46] |
| Cholesterol | Colorimetric ABTS | 0.1 µM | 1–30 µM | Phenol, ascorbic acid, glycerin, glucose, uric acid, serine, cholesterol ester | [47] |
3. G-Quadruplexes and Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamenetskii, F. Biophysics of the DNA molecule. Phys. Rep. Rev. Sect. Phys. Lett. 1997, 288, 13–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, C.E.; Sinden, R.R. Trinucleotide repeat DNA structures: Dynamic mutations from dynamic DNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1998, 8, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doluca, O.; Withers, J.M.; Filichev, V.V. Molecular engineering of guanine-rich sequences: Z-DNA, DNA triplexes, and G-quadruplexes. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3044–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, J.L. Hunting G-quadruplexes. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keniry, M.A. Quadruplex structures in nucleic acids. Biopolymers 2001, 56, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.J.; Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V. Human telomere, oncogenic promoter and 5'-UTR G-quadruplexes: Diverse higher order DNA and RNA targets for cancer therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7429–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, J.L. Structure, location and interactions of G-quadruplexes. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Cohen, G.H.; Davies, D.R. X-ray fiber diffraction and model-building study of polyguanylic acid and polyinosinic acid. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 92, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.; Gilbert, W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of 4-stranded G4-DNA. Nature 1990, 344, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.T. G-quartets 40 years later: From 5'-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 668–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Bourdoncle, A.; Sacca, B.; Lacroix, L.; Mergny, J.L. DNA nanomachines and nanostructures involving quadruplexes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3383–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganesian, L.; Bryan, T.M. Physiological relevance of telomeric G-quadruplex formation: A potential drug target. Bioessays 2007, 29, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bourdoncle, A.; Rosu, F.; Gabelica, V.; Mergny, J.L. Tri-G-quadruplex: Controlled assembly of a G-quadruplex structure from three G-rich strands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 11002–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.T.; Mergny, J.L. Human telomeric DNA: G-quadruplex, i-motif and watson-crick double helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 4618–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Balasubramanian, S. A proton-fuelled DNA nanomachine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 42, 5734–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, D.; Inoue, M.; Sugimoto, N. DNA logic gates based on structural polymorphism of telomere DNA molecules responding to chemical input signals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 7716–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, Y.; Simmel, F.C. Nucleic acid based molecular devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 3124–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Amrane, S.; Korkut, D.N.; Bourdoncle, A.; He, H.Z.; Ma, D.L.; Mergny, J.L. Combination of i-Motif and G-quadruplex structures within the same Strand: Formation and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 7742–7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travascio, P.; Li, Y.F.; Sen, D. DNA-enhanced peroxidase activity of a DNA aptamer-hemin complex. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyahovsky, B.; Li, D.; Katz, E.; Willner, I. Proteins modified with DNAzymes or aptamers act as biosensors or biosensor labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2570–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Z.; Han, J.; Pang, W.S.; Hu, J. G-quadruplex DNAzyme molecular beacon for amplified colorimetric biosensing of pseudostellaria heterophylla. Sensors 2013, 13, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Label-free colorimetric detection of aqueous mercury ion (Hg2+) using Hg2+-modulated G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, Y.; Nie, Z.; Lei, C.; Huang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yao, S. Development of a novel antioxidant assay technique based on G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Kong, D.M.; Shen, H.X. G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzyme-amplified colorimetric detection of Ag+ ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 678, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhao, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Human telomeric G-quadruplex formation and highly selective fluorescence detection of toxic strontium ions. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Ai, J.; Zhou, Z.; Jia, X.; Wang, E. Label-free G-quadruplex-specific fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of copper(II) ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.M.; Guo, J.H.; Yang, W.; Ma, Y.E.; Shen, H.X. Crystal violet-G-quadruplex complexes as fluorescent sensors for homogeneous detection of potassium ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Luedtke, N.W.; Wang, E. G-quadruplex-modulated fluorescence detection of potassium in the presence of a 3500-fold excess of sodium ions. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8356–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, T.; Li, B.L.; Wang, E.K. Potassium-sensitive G-quadruplex DNA for sensitive visible potassium detection. Analyst 2010, 135, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Cheng, D.; Duan, X. Simple and sensitive fluorescence sensor for detection of potassium ion in the presence of high concentration of sodium ion using berberine-G-quadruplex complex as sensing element. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.M.; Cai, L.L.; Shen, H.X. Quantitative detection of Ag+ and cysteine using G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzymes. Analyst 2010, 135, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.M.; Liu, X.F.; Li, P.; Kong, D.M.; Shen, H.X. G-quadruplex DNAzyme-based Hg2+ and cysteine sensors utilizing Hg2+-mediated oligonucleotide switching. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 27, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. Potassium-lead-switched G-quadruplexes: A new class of DNA logic gates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15082–15083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.A.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.R. Spectrophotometric detection of lead(II) ion using unimolecular peroxidase-like deoxyribozyme. Microchim. Acta 2010, 171, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. Lead(II)-induced allosteric G-quadruplex DNAzyme as a colorimetric and chemiluminescence sensor for highly sensitive and selective Pb2+ detection. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Liu, K.-T.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescence detection of lead(II) ions through their induced catalytic activity of DNAzymes. Anal. Chem. 2010, 83, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.Q.; Nie, D.D.; Qiu, C.Y.; Zheng, Q.S.; Wu, H.Y.; Ye, P.R.; Hao, Y.L.; Fu, F.F.; Chen, G.N. A G-quadruplex based label-free fluorescent biosensor for lead ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, X.J.; Guo, S.W.; Wu, N.Q. Detection of lead (II) with a “turn-on” fluorescent biosensor based on energy transfer from CdSe/ZnS quantum dots to graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.-H.; He, H.-Z.; Zhong, H.-J.; Lu, L.; Chan, D.S.-H.; Ma, D.-L.; Leung, C.-H. A highly sensitive G-quadruplex-based luminescent switch-on probe for the detection of polymerase 3'–5' proofreading activity. Methods 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liang, G.; Li, X. Chemiluminescence assay for the sensitive detection of iodide based on extracting Hg2+ from a T-Hg2+-T complex. Analyst 2013, 138, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Fang, Y.X.; Qin, Y.A.; Xu, S.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, E.K. G-quadruplex-based ultrasensitive and selective detection of histidine and cysteine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Ultrasensitive label-free amplified colorimetric detection of p53 based on G-quadruplex MBzymes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Chen, C.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. A Hg2+-mediated label-free fluorescent sensing strategy based on G-quadruplex formation for selective detection of glutathione and cysteine. Analyst 2013, 138, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.C.; Qiao, F.M.; Duan, R.H.; Chen, L.J.; Ai, S.Y. A novel label-free optical cysteine sensor based on the competitive oxidation reaction catalyzed by G-quadruplex halves. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Qi, H.; Zhang, C. Selective, colorimetric assay of glucose in urine using G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes and 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxy phenoxazine. Talanta 2013, 108, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiong, C.; Xiao, Z.; Ling, L. Colorimetric detection of cholesterol with G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes and ABTS(2−). Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 724, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.A.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.L.; Deng, L. Highly effective colorimetric and visual detection of ATP by a DNAzyme-aptamer sensor. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, Z.Q.; Li, Y.J. Label free, highly sensitive and selective recognition of small molecule using gold surface confined aptamers. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, B.L.; Guo, S.J.; Zhou, Z.X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. G-Quadruplex-based DNAzyme for colorimetric detection of cocaine: Using magnetic nanoparticles as the separation and amplification element. Analyst 2011, 136, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Yin, B.C.; Wang, P.; Ye, B.C. Highly sensitive detection of microRNAs based on isothermal exponential amplification-assisted generation of catalytic G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Z.; Chan, D.S.H.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. A highly selective G-quadruplex-based luminescent switch-on probe for the detection of gene deletion. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9462–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Lin, Y.B.; Lu, Y.J.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Chen, G.N. A novel fluorescent biosensor for detection of target DNA fragment from the transgene cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.H.; He, H.Z.; Ma, V.P.Y.; Yang, H.; Chan, D.S.H.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. A G-quadruplex-selective luminescent switch-on probe for the detection of sub-nanomolar human neutrophil elastase. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Pu, F.; Huang, Z.Z.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. A Quadruplex-based, label-free, and real-time fluorescence assay for RNase H activity and inhibition. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. G-quadruplex-based DNAzyme for facile colorimetric detection of thrombin. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2008, 3654–3656. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, E.; Dong, S.J. Chemiluminescence thrombin aptasensor using high-activity DNAzyme as catalytic label. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2008, 5520–5522. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Xie, J. Label-free and amplified aptasensor for thrombin detection based on background reduction and direct electron transfer of hemin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, L.L.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. Multifunctional G-quadruplex aptamers and their application to protein detection. Chemistry 2009, 15, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Conformational switch for cisplatin with hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme supersandwich structure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.M.; Liu, X.F.; Kong, D.M.; Shen, H.X. A simple, post-additional antioxidant capacity assay using adenosine triphosphate-stabilized 2,2'-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline)-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) radical cation in a G-quadruplex DNAzyme catalyzed ABTS-H2O2 system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Kong, D.M.; Shen, H.X. Ag+ and cysteine quantitation based on G-quadruplex-Hemin DNAzymes disruption by Ag+. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.H.; Ma, V.P.Y.; He, H.Z.; Chan, D.S.H.; Yang, H.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. A highly selective G-quadruplex-based luminescent switch-on probe for the detection of nanomolar strontium(II) ions in sea water. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8273–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.E.; Zhao, C.Q.; Yang, X.J.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Enzymatic manipulation of DNA-modified gold nanoparticles for screening G-quadruplex ligands and evaluating selectivities. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, H.F.; Doudt, A.; Zerbe, C.; Basu, S. Detection of quadruplex DNA by gold nanoparticles. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Meng, X.M.; Yin, H.S.; Ai, S.Y. Amplified electrochemical microRNA biosensor using a hemin-G-quadruplex complex as the sensing element. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7140–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, Z. Highly selective resonance scattering detection of trace thrombin using aptamer-modified AuRe nanoprobe. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.L. Monitoring human telomere DNA hybridization and G-quadruplex formation using gold nanorods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 668, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jin, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y. Colorimetric assay of lead using unmodified gold nanorods. Gold Bull. 2012, 45, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, X.X.; Zhou, T.; Ma, H.; Qiang, H.; Liu, Y.F. Colorimetric detection of potassium ions using aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not Available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Kudr, J.; Nejdl, L.; Maskova, D.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes. Molecules 2013, 18, 14760-14779. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181214760
Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Kudr J, Nejdl L, Maskova D, Kizek R, Adam V. G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes. Molecules. 2013; 18(12):14760-14779. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181214760
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuttkay-Nedecky, Branislav, Jiri Kudr, Lukas Nejdl, Darina Maskova, Rene Kizek, and Vojtech Adam. 2013. "G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes" Molecules 18, no. 12: 14760-14779. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181214760
APA StyleRuttkay-Nedecky, B., Kudr, J., Nejdl, L., Maskova, D., Kizek, R., & Adam, V. (2013). G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes. Molecules, 18(12), 14760-14779. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181214760