Preparative Isolation and Purification of Five Flavonoid Glycosides and One Benzophenone Galloyl Glycoside from Psidium guajava by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Solvent System Selection
| Solvent Ratio | Partition Coefficient (KU/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1:1:1:1 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| 1:2:1:2 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.41 |
| 1:3:1:3 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 1.06 |
| 1:4:1:4 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 1.07 | 1.48 | 2.28 | 3.94 |
| 1:5:1:5 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 1.90 | 3.66 |
| 1:6:1:6 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 1.47 | 2.03 | 3.43 | 6.57 |
| 0.7:4:0.8:4 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 1.28 | 1.68 | 2.64 | 4.40 |
| 0.3:3:0.1:3 | 1.27 | 1.19 | 4.10 | 5.67 | 11.03 | 26.64 |
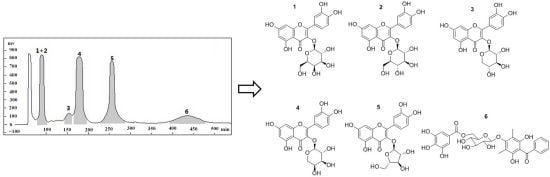
2.2. HSCCC Separation


3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Apparatus

3.3. Preparation of the Crude Sample
3.4. Selection of the Solvent System
3.5. Preparation of the Two-Phase Solvent Systems and Sample Solution
3.6. Separation and Purification by HSCCC
3.7. Separation of Mixture of Compound 1 and Compound 2 by Semi-Preparative HPLC
3.8. HPLC Analysis
3.9. Identification of Target Compounds
| Atom | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 156.2 | 156.1 | 156.1 | 156.2 | 156.3 |
| 3 | 133.5 | 133.3 | 133.1 | 133.7 | 133.4 |
| 4 | 177.5 | 177.4 | 177.3 | 177.5 | 177.7 |
| 5 | 161.2 | 161.2 | 161.1 | 161.2 | 161.2 |
| 6 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.6 |
| 7 | 164.1 | 164.2 | 164.1 | 164.1 | 164.2 |
| 8 | 93.5 | 93.5 | 93.5 | 93.5 | 93.5 |
| 9 | 156.3 | 156.3 | 156.2 | 156.2 | 156.9 |
| 10 | 103.9 | 103.9 | 103.8 | 103.9 | 103.9 |
| 1' | 121.1 | 121.1 | 120.9 | 120.9 | 120.9 |
| 2' | 115.9 | 116.2 | 116.1 | 115.3 | 115.5 |
| 3' | 144.8 | 144.8 | 144.8 | 144.9 | 145.0 |
| 4' | 148.4 | 148.4 | 148.4 | 148.6 | 148.4 |
| 5' | 115.1 | 115.2 | 115.3 | 115.7 | 115.5 |
| 6' | 121.9 | 121.6 | 121.4 | 122.0 | 121.7 |
| 1'' | 101.8 | 100.9 | 101.7 | 101.4 | 107.8 |
| 2'' | 71.2 | 74.1 | 73.5 | 71.6 | 82.1 |
| 3'' | 73.2 | 76.5 | 75.9 | 70.7 | 76.9 |
| 4'' | 67.9 | 69.9 | 69.3 | 66.0 | 85.8 |
| 5'' | 75.8 | 77.5 | 66.0 | 64.2 | 60.6 |
| 6'' | 60.1 | 61.0 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutierrez, R.M.; Mitchell, S.; Solis, R.V. Psidium guajava: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Vazquez Mdel, C.; Carranza-Alvarez, C.; Alonso-Castro, A.J.; Gonzalez-Alcaraz, V.F.; Bravo-Acevedo, E.; Chamarro-Tinajero, F.J.; Solano, E. Ethnobotany of medicinal plants used in Xalpatlahuac, Guerrero, Mexico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCook-Russell, K.P.; Nair, M.G.; Facey, P.C.; Bowen-Forbes, C.S. Nutritional and nutraceutical comparison of Jamaican Psidium cattleianum (strawberry guava) and Psidium guajava (common guava) fruits. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yin, M.C. Renal protective effects of extracts from guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.) in diabetic mice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2012, 67, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, P.L.; Martineau, L.C.; Caves, D.; Haddad, P.S.; Matainaho, T.; Johns, T. Consumption of guava (Psidium guajava L.) and noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) may protect betel quid-chewing Papua New Guineans against diabetes. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 635–643. [Google Scholar]
- Ojewole, J.A.; Awe, E.O.; Chiwororo, W.D. Antidiarrhoeal activity of Psidium guajava Linn. (Myrtaceae) leaf aqueous extract in rodents. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2008, 44, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.C.; Shen, S.C.; Wu, J.S. Effect of guava (Psidium guajava L.) leaf extract on glucose uptake in rat hepatocytes. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H132–H138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.C.; Cheng, F.C.; Wu, N.J. Effect of guava (Psidium guajava L.) leaf soluble solids on glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, S.; Rauf, A.A.; Indira, M.; Rajamanickam, C. Antioxidant and antiglycative potential of ethyl acetate fraction of Psidium guajava leaf extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, S.; Kawai, A.; Kai, K.; Akiyama, K.; Hayashi, H. Inhibitory activity against urease of quercetin glycosides isolated from Allium cepa and Psidium guajava. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, H.G.; Hwang, Y.P.; Han, E.H.; Jin, S.W.; Seo, J.K.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Inhibitory effect of Psidium guajava water extract in the development of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, K.D.; Ker, Y.B.; Chyau, C.C.; Peng, R.Y. Anticancer activity of rhamnoallosan against DU-145 cells is kinetically complementary to coexisting Polyphenolics in Psidium guajava budding leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6114–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston Raja, N.R.; Sundar, K. Psidium guajava Linn confers gastro protective effects on rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rattanachaikunsopon, P.; Phumkhachorn, P. Bacteriostatic effect of flavonoids isolated from leaves of Psidium guajava on fish pathogens. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.C.; Chou, G.X.; Wang, Z.T. One new galloyl glycoside from fresh leaves of Psidium guajava L. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2010, 45, 334–337. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, J.C.; Chou, G.X.; Wang, Z.T. One new diphenylmethane glycoside from the leaves of Psidium guajava L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y.Q.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, D.M.; Tang, Q.F.; Jiang, R.W.; Sun, X.G.; Lv, Z.P.; Zhang, X.Q.; et al. Guadial A and psiguadials C and D, three unusual meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Wei, K.; Hai, P.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.K. Isolation and biomimetic synthesis of (+/−)-guajadial B, a novel meroterpenoid from Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5936–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Hassan, S.I.; Ali, S.N.; Siddiqui, B.S. Chemical constituents from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 18, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenberger, T.; Selg, M.; Krennhuber, K. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase activity by flavonol glycosides of guava (Psidium guajava L.): A key to the beneficial effects of guava in type II diabetes mellitus. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.F.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.O.; Cai, G.P. Suppressive effects of quercetin-3-O-(6''-Feruloyl)-beta-d-galactopyranoside on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through down-regulation of PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha expression. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 438–444. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Xiong, Q.J.; Shu, Q.; Wu, W.N.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.G.; Hu, Z.L. Hyperoside protects cortical neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-reperfusion induced injury via nitric oxide signal pathway. Brain Res. 2012, 1469, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kimura, M.; Ishii, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Morita, R.; Hayashi, S.M.; Suzuki, K.; Shibutani, M. Effect of enzymatically modified isoquercitrin on preneoplastic liver cell lesions induced by thioacetamide promotion in a two-stage hepatocarcinogenesis model using rats. Toxicology 2013, 305, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.S.; Lauridsen, M.B.; Dragsted, L.O.; Nielsen, J.; Staerk, D. Development of a bioassay-coupled HPLC-SPE-ttNMR platform for identification of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in apple peel (Malus xdomestica Borkh.). Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.M.; Omar, A.A.; Harraz, F.M.; El Sohafy, S.M. Phytochemical investigation and antimicrobial activity of Psidium guajava L. leaves. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Ishii, R.; Kobiyama, K.; Kitanaka, S. New benzophenone and quercetin galloyl glycosides from Psidium guajava L. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ji, L.; Boakye-Yiadom, M.; Li, W.; Song, X.; Gao, X. Preparative isolation and purification of four compounds from Cistanches deserticola Y.C. Ma by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Molecules 2012, 17, 8276–8284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, K.; Bouju, E.; Suchet, P.; Berthod, A. Use of limonene in countercurrent chromatography: A green alkane substitute. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, D. Excellent combination of counter-current chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography to separate galactolipids from pumpkin. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4176–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.L. HSCCC Technology and Application; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.K.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. A new flavonol glycoside from Hylomecon vernalis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguelefack, T.B.; Mbakam, F.H.; Tapondjou, L.A.; Watcho, P.; Nguelefack-Mbuyo, E.P.; Ponou, B.K.; Kamanyi, A.; Park, H.J. A dimeric triterpenoid glycoside and flavonoid glycosides with free radical-scavenging activity isolated from Rubus rigidus var. camerunensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.M.D.M.; Férézoub, J.-P.; Tinoco, L.W.; Kaiser, C.R.; Costa, S.S. Flavonoids from Mimosa xanthocentra (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae) and molecular modeling studies for isovitexin-2"-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside rotamers. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, T. Preparative Isolation and Purification of Five Flavonoid Glycosides and One Benzophenone Galloyl Glycoside from Psidium guajava by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC). Molecules 2013, 18, 15648-15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215648
Zhu Y, Liu Y, Zhan Y, Liu L, Xu Y, Xu T, Liu T. Preparative Isolation and Purification of Five Flavonoid Glycosides and One Benzophenone Galloyl Glycoside from Psidium guajava by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC). Molecules. 2013; 18(12):15648-15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215648
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yindi, Yue Liu, Ying Zhan, Lin Liu, Yajuan Xu, Tunhai Xu, and Tonghua Liu. 2013. "Preparative Isolation and Purification of Five Flavonoid Glycosides and One Benzophenone Galloyl Glycoside from Psidium guajava by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC)" Molecules 18, no. 12: 15648-15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215648
APA StyleZhu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhan, Y., Liu, L., Xu, Y., Xu, T., & Liu, T. (2013). Preparative Isolation and Purification of Five Flavonoid Glycosides and One Benzophenone Galloyl Glycoside from Psidium guajava by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC). Molecules, 18(12), 15648-15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215648