Development of a New Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis: Synthesis, Small Animal Imaging, and Radiation Dosimetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of 64Cu-Radiolabeled Tracers

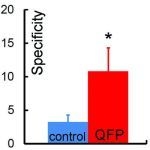
2.2. In Vivo Biodistribution Studies

| Organ | 2 h p.i. | 6 h p.i. | 18 h p.i. | 28 h p.i. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QFP-tracer | ||||
| Tumor | 4.10 ± 1.56 | 7.33 * ± 0.65 | 5.1 * ± 0.57 | 4.03 * ± 1.47 |
| Liver | 94.80 ± 23.19 | 58.77 ± 20.91 | 48.10 ± 15.70 | 38.43 ± 20.88 |
| Lung | 14.05 ± 3.61 | 10.40 ± 3.49 | 8.85 ± 0.21 | 6.20 ± 4.91 |
| Kidney | 19.95 ± 0.07 | 17.67 ± 8.14 | 11.95 ± 2.90 | 7.93 ± 2.22 |
| Heart | 4.55 ± 0.35 | 4.53 ± 0.87 | 4.53 ± 0.87 | 3.10 ± 0.95 |
| Blood | 6.02 ± 3.37 | 5.28 ± 2.15 | 3.97 ± 2.52 | 3.7 ± 0.28 |
| Control-tracer | ||||
| Tumor | 4.65 ± 0.64 | 4.00 ± 2.55 | 2.57 ± 1.40 | 1.53 ± 1.37 |
| Liver | 108.45 ± 16.90 | 82.37 ± 23.29 | 19.23 ± 8.77 | 24.43 ± 1.27 |
| Lung | 10.80 ± 0.14 | 10.20 ± 1.23 | 4.77 ± 2.91 | 6.6 ± 0.49 |
| Kidney | 16.95 ± 2.47 | 14.57 ± 1.46 | 10.73 ± 2.35 | 11.57 ± 0.29 |
| Heart | 3.65 ± 0.49 | 4.43 ± 0.78 | 3.70 ± 0.79 | 4.37 ± 1.20 |
| Blood | 4.83 ± 0.95 | 4.82 ± 1.36 | 3.72 ± 3.23 | 4.75 ± 0.35 |
2.3. Small Animal PET/CT Imaging

2.4. Ex-Vivo Analysis of Intra-Tumoral Tracer Distribution

2.5. Dosimetry Calculations
| Organ | Organ uptake µCi.h/organ.mCi | S-factor Rad/µCi.h | Absorbed dose Rad/mCi (mGy/MBq) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 3375 | 1.90E-04 | 0.641 (0.173) |
| Kidney | 140 | 1.00E-03 | 0.140 (0.038) |
| Lung | 222 | 3.00E-04 | 0.067 (0.018) |
3. Experimental
3.1. Cell Culture, Animals and Tumors
3.2. Radiotracer Synthesis
3.2.1. Phage Propagation and Functionalization with DOTA
3.2.2. Radiolabeling with 64Cu
3.3. Biodistribution Studies of 64Cu-Labeled Tracers in the s.c. LLC Tumor Model
3.4. Small Animal PET/CT Studies
3.4.1. Experimental Protocol
3.4.2. PET Image Analysis
3.5. Autoradiography, Histology and Fluorescence Imaging
3.6. Dosimetry
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rafii, S.; Lyden, D.; Benezra, R.; Hattori, K.; Heissig, B. Vascular and haematopoietic stem cells: Novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 826–835. [Google Scholar]
- Lyden, D.; Hattori, K.; Dias, S.; Costa, C.; Blaikie, P.; Butros, L.; Chadburn, A.; Heissig, B.; Marks, W.; Witte, L.; et al. Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, D.G.; Cohen, K.S.; Kozin, S.V.; Perentes, J.Y.; Fukumura, D.; Scadden, D.T.; Jain, R.K. Evidence for incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells into perfused blood vessels in tumors. Blood 2006, 107, 2774–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Aitsebaomo, J.; Srivastava, S.; Zhang, H.; Jha, S.; Wang, Z.J.; Winnik, S.; Veleva, A.N.; Pi, X.C.; Lockyer, P.; Faber, J.E.; et al. Recombinant human interleukin-11 treatment enhances collateral vessel growth after femoral artery ligation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Lyden, D.; Hattori, K.; Dias, S.; Hajjar, K.; Manova, K.; Moore, M.A.S.; Benezra, R.; Rafii, S. Transplantation of bone marrow derived VEGF-responsive hematopoietic and vasculogenic precursor cells are essential to restore the angiogenic defect in Id1+/-Id3-/- knock out mice. Blood 2000, 96, 529A. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Vakil, V.; Braunstein, M.; Smith, E.L.P.; Maroney, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, K.Z.; Berenson, J.R.; Hussain, M.M.; Klueppelberg, U.; et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells in multiple myeloma: implications and significance. Blood 2005, 105, 3286–3294. [Google Scholar]
- Furstenberger, G.; von Moos, R.; Lucas, R.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Hamacher, J.; Boneberg, E.M. Circulating endothelial cells and angiogenic serum factors during neoadjuvant chemotherapy of primary breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 524–531. [Google Scholar]
- Dome, B.; Timar, J.; Dobos, J.; Meszaros, L.; Raso, E.; Paku, S.; Kenessey, I.; Ostoros, G.; Magyar, M.; Ladanyi, A.; et al. Identification and clinical significance of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7341–7347. [Google Scholar]
- Rafat, N.; Beck, G.C.; Schulte, J.; Tuettenberg, J.; Vajkoczy, P. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells in malignant gliomas Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Roodhart, J.M.; Langenberg, M.H.; Vermaat, J.S.; Lolkema, M.P.; Baars, A.; Giles, R.H.; Witteveen, E.O.; Voest, E.E. Late release of circulating endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells after chemotherapy predicts response and survival in cancer patients. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, D.G.; Cohen, K.S.; di Tomaso, E.; Au, A.P.; Klein, R.J.; Scadden, D.T.; Willett, C.G.; Jain, R.K. Differential CD 146 expression on circulating versus tissue endothelial cells in rectal cancer patients: Implications for circulating endothelial and progenitor cells as biomarkers for antiangiogenic therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini, R.; Ruoslahti, E. Organ targeting in vivo using phage display peptide libraries. Nature 1996, 380, 364–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, J.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Seo, J.W.; Agemy, L.; Fogal, V.; Mahakian, L.M.; Peters, D.; Roth, L.; Gagnon, M.K.J.; Ferrara, K.W.; et al. Specific penetration and accumulation of a homing peptide within atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7154–7159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Ma, W.H.; Li, G.Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.D.; Yap, L.P.; Hughes, L.D.; Park, R.; Conti, P.S. Synthesis and evaluation of Cu-64-labeled monomeric and dimeric NGR peptides for MicroPET imaging of CD13 receptor expression. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Sun, X.L.; Niu, G.; Ma, Y.; Yap, L.P.; Hui, X.L.; Wu, K.C.; Fan, D.M.; Conti, P.S.; Chen, X.Y. Evaluation of Cu-64 labeled GX1: A phage display peptide probe for PET imaging of tumor vasculature. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gronwall, C.; Stahl, S. Engineered affinity proteins-Generation and applications. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 140, 254–269. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, F.Y.; Tolmachev, V. Affibody (R) molecules: New protein domains for molecular imaging and targeted tumor therapy. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2007, 10, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Sweeney, C.J.; Papadopoulos, K.; Patnaik, A.; Chiorean, E.G.; Mita, A.C.; Sankhala, K.; Furfine, E.; Gokemeijer, J.; Iacono, L.; et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of CT-322 (BMS-844203), a targeted adnectin inhibitor of VEGFR-2 based on a domain of human fibronectin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Skerra, A. Alternative binding proteins: Anticalins-harnessing the structural plasticity of the lipocalin ligand pocket to engineer novel binding activities. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2677–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Klevenz, B.; Butz, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Peptide aptamers: Exchange of the thioredoxin-A scaffold by alternative platform proteins and its influence on target protein binding. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.; Lu, Q.; Bakker, A.; To, W.; Duguay, A.; Alba, B.M.; Smith, R.; Rivas, A.; Li, P.; Le, H.; et al. Multivalent avimer proteins evolved by exon shuffling of a family of human receptor domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, D.; Forrer, P.; Pluckthun, A. Efficient selection of DARPins with sub-nanomolar affinities using SRP phage display. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 1211–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Haubner, R.; Beer, A.J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.Y. Positron emission tomography tracers for imaging angiogenesis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, S86–S103. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, T.K.; Brechbiel, M.W. Radioimmunoimaging with longer-lived positron-emitting radionuclides: Potentials and challenges. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 825–841. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.J.; Jones, L.A.; Bass, L.A.; Sherman, E.L.C.; McCarthy, D.W.; Cutler, P.D.; Lanahan, M.V.; Cristel, M.E.; Lewis, J.S.; Schwarz, S.W. Radiotherapy, toxicity and dosimetry of copper-64-TETA-octreotide in tumor-bearing rats. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.S.; Lewis, M.R.; Cutler, P.D.; Srinivasan, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Schwarz, S.W.; Morris, M.M.; Miller, J.P.; Anderson, C.J. Radiotherapy and dosimetry of Cu-64-TETA-Tyr(3)-octreotate in a somatostatin receptor-positive, tumor-bearing rat model. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, B.E.; Bigott, H.M.; McCarthy, D.W.; Della Manna, D.; Kim, J.; Sharp, T.L.; Welch, M.J. MicroPET imaging of a gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-positive tumor in a mouse model of human prostate cancer using a Cu-64-labeled bombesin analogue. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 756–763. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanphanich, A.F.; Nanda, P.K.; Rold, T.L.; Ma, L.X.; Lewis, M.R.; Garrison, J.C.; Hoffman, T.J.; Sieckman, G.L.; Figueroa, S.D.; Smith, C.J. Cu-64-NOTA-8-Aoc-BBN(7–14)NH2 targeting vector for positron-emission tomography imaging of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-expressing tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12462–12467. [Google Scholar]
- Gaertner, F.C.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.J.; Schwaiger, M.; Beer, A.J. Radiolabelled RGD peptides for imaging and therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, R.A.; Deininger, F.; Haubner, R.; Maecke, H.R.; Weber, W.A.; Fani, M. Novel Cu-64- and Ga-68-Labeled RGD conjugates show improved PET imaging of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin expression and facile radiosynthesis. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.H.; Kimura, R.H.; Withofs, N.; Tran, P.T.; Miao, Z.; Cochran, J.R.; Cheng, Z.; Felsher, D.; Kjaer, A.; Willmann, J.K.; et al. PET Imaging of tumor neovascularization in a transgenic mouse model with a novel Cu-64-DOTA-knottin peptide. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9022–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.P.; Meyer, L.A.; Capretto, D.A.; Sherman, C.D.; Anderson, C.J. Receptor-binding, biodistribution, and metabolism studies of (64)Cu-DOTA-cetuximab, a PET-imaging agent for epidermal growth-factor receptor-positive tumors. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2008, 23, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, K.; Cao, Q.Z.; Tice, D.A.; Chen, X.Y. In vitro and in vivo characterization of Cu-64-labeled Abegrin (TM) a humanized monoclonal antibody against integrin alpha(v)beta(3). Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9673–9681. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.B.; Ebrahimnejad, A.; Chen, K.; Cao, Q.Z.; Li, Z.B.; Tice, D.A.; Chen, X.Y. Quantitative radioimmunoPET imaging of EphA2 in tumor-bearing mice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 2024–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Philpott, G.W.; Schwarz, S.W.; Anderson, C.J.; Dehdashti, F.; Connett, J.M.; Zinn, K.R.; Meares, C.F.; Cutler, P.D.; Welch, M.J.; Siegel, B.A. RadioimmunoPET: Detection of colorectal carcinoma with positron-emitting copper-64-labeled monoclonal antibody. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Veleva, A.N.; Nepal, D.B.; Frederick, C.B.; Schwab, J.; Lockyer, P.; Yuan, H.; Lalush, D.S.; Patterson, C. Efficient in vivo selection of a novel tumor-associated peptide from a phage display library. Molecules 2011, 16, 900–914. [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher, S.L. Phage display in molecular imaging and diagnosis of cancer. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3196–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Furukawa, T.; Fujieda, S.; Kasamatsu, S.; Yonekura, Y.; Fujibayashi, Y. Double-tracer autoradiography with Cu-ATSM/FDG and immunohistochemical interpretation in four different mouse implanted tumor models. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- MIRD Pamphlet No. 11.; Society of Nuclear Medicine: New York, NY, USA, 1975.
- Veleva, A.N.; Cooper, S.L.; Patterson, C. Selection and initial characterization of novel peptide ligands that bind specifically to human blood outgrowth endothelial cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, M.; Carey, P.C.; Gaehle, G.; Madrid, E.; Voller, T.; Margenau, W.; Welch, M.J.; Lapi, S.E. A semi-automated system for the routine production of copper-64. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Schroeder, T.; Bowsher, J.E.; Hedlund, L.W.; Wong, T.; Dewhirst, M.W. Intertumoral differences in hypoxia selectivity of the PET imaging agent Cu-64(II)-diacetyl-bis(N-4-methylthiosemicarbazone). J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 989–998. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, M.S.; Dyer, L.A.; Ren, R.; Lockyer, P.; Moreno-Miralles, I.; Schisler, J.C.; Patterson, C. BMPER regulates cardiomyocyte size and vessel density in vivo. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2012, 22, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Contact authors for sample availability.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Patterson, C.; Frederick, C.B.; Yuan, H.; Dyer, L.A.; Lockyer, P.; Lalush, D.S.; Veleva, A.N. Development of a New Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis: Synthesis, Small Animal Imaging, and Radiation Dosimetry. Molecules 2013, 18, 5594-5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055594
Patterson C, Frederick CB, Yuan H, Dyer LA, Lockyer P, Lalush DS, Veleva AN. Development of a New Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis: Synthesis, Small Animal Imaging, and Radiation Dosimetry. Molecules. 2013; 18(5):5594-5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055594
Chicago/Turabian StylePatterson, Cam, C. Brandon Frederick, Hong Yuan, Laura A. Dyer, Pamela Lockyer, David S. Lalush, and Anka N. Veleva. 2013. "Development of a New Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis: Synthesis, Small Animal Imaging, and Radiation Dosimetry" Molecules 18, no. 5: 5594-5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055594
APA StylePatterson, C., Frederick, C. B., Yuan, H., Dyer, L. A., Lockyer, P., Lalush, D. S., & Veleva, A. N. (2013). Development of a New Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis: Synthesis, Small Animal Imaging, and Radiation Dosimetry. Molecules, 18(5), 5594-5610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055594