Herb-Drug Interaction of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analytical Method Validation for Sildenafil

| Nominal concentration (μg/mL) | Observed concentration (μg/mL) | RSD (%) * | Accuracy (%) ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interday | |||
| 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 8.1 | 115.6 |
| 0.1 | 0.10 ± 0.006 | 6.1 | 98.2 |
| 0.5 | 0.50 ± 0.027 | 5.3 | 100.5 |
| 1 | 0.99 ± 0.061 | 6.1 | 99.5 |
| 5 | 4.99 ± 0.240 | 4.8 | 99.9 |
| 10 | 10.00 ± 0.563 | 5.6 | 100.0 |
| Intraday | |||
| 0.05 | 0.05 ± 0.002 | 4.4 | 103.9 |
| 0.1 | 0.10 ± 0.004 | 4.6 | 97.9 |
| 0.5 | 0.50 ± 0.011 | 2.2 | 100.0 |
| 1 | 0.98 ± 0.024 | 2.4 | 97.8 |
| 5 | 5.04 ± 0.074 | 1.5 | 100.8 |
| 10 | 9.98 ± 0.264 | 2.6 | 99.8 |
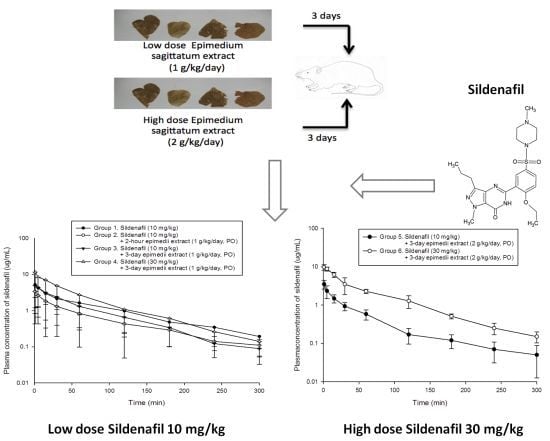
2.2. Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Low Dose Epimedium sagittatum Extract (1 g/kg/day, p.o.)
| Treatment group | Dose of oral Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim extract b | No. of herbal doses | Sildenafil dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 c | None | 0 | 10 mg/kg |
| 2 | 1 g/kg/day, 2h before sildenafil administration | 1 | 10 mg/kg |
| 3 | 1 g/kg/day | 3 | 10 mg/kg |
| 4 | 1 g/kg/day | 3 | 30 mg/kg |
| 5 | 2 g/kg/day | 3 | 10 mg/kg |
| 6 | 2 g/kg/day | 3 | 30 mg/kg |

| Parameters | t1/2 (min) | C0 (μg/mL) | AUC (min μg/mL) | Cl (mL/min/kg) | Vss (L/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 80 ± 34 | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 348 ± 44 | 27 ± 3.6 | 2710 ± 627 |
| Group 2 | 84 ± 17 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 183 ± 15 * | 55 ± 5.0 | 5400 ± 588 |
| Group 3 | 54 ± 3.8 | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 296 ± 24 † | 33 ± 2.8 | 2460 ± 98 † |
| Group 4 | 61 ± 8.5 | 11.6 ± 2.3 *,†,‡ | 536 ± 86 *,†,‡ | 57 ± 8.9 | 3790 ± 552 |
2.3. Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in High Dose Epimedium sagittatum Extract (2 g/kg/day, p.o.)

| Parameters | t1/2 (min) | C0 (μg/mL) | AUC (min μg/mL) | Cl (mL/min/kg) | Vss (L/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 5 | 55 ± 17 | 3.3 ± 1.3 | 108 ± 34 | 111 ± 70 | 6540 ± 3760 |
| Group 6 | 69 ± 17 | 9.4 ± 1.9 ** | 440 ± 106 ** | 73 ± 23 | 4790 ± 510 |
2.4. Effects of Epimedium sagittatum Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil (10 mg/kg, i.v.)
| Parameters | t1/2 (min) | C0 (μg/mL) | AUC (min μg/mL) | Cl (mL/min/kg) | Vss (L/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 80 ± 34 | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 348 ± 44 | 27 ± 3.6 | 2710 ± 627 |
| Group 2 | 84 ± 17 | 3.4 ± 0.8 * | 183 ± 15* | 55 ± 5.0 | 5400 ± 588 |
| Group 3 | 54 ± 3.8 | 5.3 ± 0.9 † | 296 ± 24 † | 33 ± 2.8 | 2460 ± 98 |
| Group 4a | 61 ± 8.5 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 178 ± 29 *,‡ | 57 ± 8.9 | 3790 ± 552 |
| Group 5 | 55 ± 17 | 3.3 ± 1.3 *,‡ | 108 ± 34 *,†,‡,§ | 111 ± 70 *,‡ | 6540 ± 3760 *,‡ |
| Group 6a | 69 ± 17 | 3.1 ± 0.6 *,‡ | 147 ± 35 *,‡ | 73 ± 23 | 4790 ± 510 |
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract
3.3. Liquid Chromatography
3.4. Plasma Preparation of Sildenafil Extraction
3.5. Study Protocol
3.6. Surgical Procedures
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, K.K.; Chiang, H.S.; Jiann, B.P.; Lin, J.S.; Liu, W.J.; Wu, C.J.; Hsieh, J.T.; Wang, C.J.; Hwang, T.I.; Lee, S.S. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and impacts on sexual activity and self-reported intercourse satisfaction in men older than 40 years in Taiwan. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jønler, M.; Moon, T.; Brannan, W.; Stone, N.N.; Heisey, D.; Bruskewitz, R.C. The effect of age, Ethnicity and geographical location on impotence and quality of life. Br. J. Urol. 1995, 75, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althof, S.E. Quality of life and erectile dysfunction. Urology 2002, 59, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, F.; Di Palo, C.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; D’Andrea, F.; D’Armiento, M.; Giugliano, D. Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004, 291, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVary, K.T. Clinical practice. Erectile dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsertsvadze, A.; Fink, H.A.; Yazdi, F.; MacDonald, R.; Bella, A.J.; Ansari, M.T.; Garritty, C.; Soares-Weiser, K.; Daniel, R.; Sampson, M.; et al. Oral phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and hormonal treatments for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eardley, I.; Donatucci, C.; Corbin, J.; El-Meliegy, A.; Hatzimouratidis, K.; McVary, K.; Munarriz, R.; Lee, S.W. Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 524–540. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, D.J.; Muirhead, G.J.; Harness, J.A. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after single oral doses in healthy male subjects: Absolute bioavailability, food effects and dose proportionality. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53 Suppl. 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.K.; Ackland, M.J.; James, G.C.; Muirhead, G.J.; Rance, D.J.; Wastall, P.; Wright, P.A. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sildenafil in mouse, rat, rabbit, dog and man. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, R.; Roe, E.G.; Jones, B.C.; Smith, D.A. Identification of the cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the N-demethylation of sildenafil. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; He, S. Species and geographic distribution of large-flowered taxa of Epimedium in China. Zhong Yao Cai 2005, 28, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Weng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Fan, W.; Dai, R.; Hu, Z. Angiogenesis and anti-angiogenesis activity of Chinese medicineal herbal extracts. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.H.; Kim, M.J.; Jeon, B.H.; Shon, J.H.; Cha, I.J.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Shin, J.G. Inhibition of human cytochrome P450 isoforms and NADPH-CYP reductase in vitro by 15 herbal medicines, including Epimedii herba. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2006, 31, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Yang, G.; Tao, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Duan, X.; Cao, Y.; Dong, J. Neuroprotective effects of icariin on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1375, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, J.H.; Chen, K.K.; Chien, T.M.; Chiou, W.F.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Lui, W.Y.; Wu, C.W. Epimedium brevicornum Maxim extract relaxes rabbit corpus cavernosum through multitargets on nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006, 18, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, M.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Tesakova, S.V.; Makarov, V.G.; Tikhonov, V.P. Effect of lipid-based suspension of Epimedium koreanum Nakai extract on sexual behavior in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xin, H.; Li, W.R.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.Y.; Gong, Y.Q.; Gao, Z.Z.; Qin, X.C.; Cui, W.S.; Shindel, A.W.; et al. Effects of icariin on improving erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, D.; Jia, Z. The genus Epimedium: an ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Qiu, F.; Wang, S.; He, J. HPLC analysis and pharmacokinetics of icariin in rats. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Wong, S.P.; Li, J.; Yong, E.L. Simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for simultaneous measurement of five Epimedium prenylflavonoids in rat sera. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.D.; Yao, H.J.; Gu, L.; Wang, S.P.; Liu, G.L. Effect of total flavonoids of epimedium on liver microsomal CYP1A2, CYP3A4 and CYP2E1 activities in rats. JCPS 2008, 17, 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Lin, C.W.; Lin, L.C.; Chiu, A.W.; Chen, K.K.; Tsai, T.H. Analysis of biliary excretion of icariin in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9905–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.F.; Stember, D.S.; Nagler, H.M. Sexual medicine disparities between Asia and North America: commentary on male sexual dysfunction in Asia. Asian J. Androl. 2011, 13, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.Y. Switching between traditional chinese medicine and viagra: cosmopolitanism and medical pluralism today. Med. Anthropol. 2007, 26, 53–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Bae, S.K.; Lee, M.G. Pharmacokinetics ofsildenafilafter intravenous and oral administration in rats: hepatic and intestinal first-pass effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 320, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.B. Transporters and xenobiotic disposition. Toxicology 2002, 181-182, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.B. Drugs as P-glycoprotein substrates, Inhibitors, and inducers. Drug Metab. Rev. 2002, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindel, A.W.; Xin, Z.C.; Lin, G.; Fandel, T.M.; Huang, Y.C.; Banie, L.; Breyer, B.N.; Garcia, M.M.; Lin, C.S.; Lue, T.F. Erectogenic and neurotrophic effects of icariin, a purified extract of horny goat weed (Epimedium spp.) in vitro and in vivo. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, D.C.; Lin, H.R.; Lu, H.W. Zhong Kuo Zhong Yao Tsai Chen Wei Chien Pei Tu Dian” (Verified Illustrations of Chinese Materia Medica); Guangdong Science & Technology Publisher: Guangzhou, China, 1999; Volume 4, p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim extract are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsueh, T.Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Lin, L.-C.; Chiu, A.W.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-H. Herb-Drug Interaction of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Rats. Molecules 2013, 18, 7323-7335. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067323
Hsueh TY, Wu Y-T, Lin L-C, Chiu AW, Lin C-H, Tsai T-H. Herb-Drug Interaction of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Rats. Molecules. 2013; 18(6):7323-7335. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067323
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsueh, Thomas Y., Yu-Tse Wu, Lie-Chwen Lin, Allen W. Chiu, Chi-Hung Lin, and Tung-Hu Tsai. 2013. "Herb-Drug Interaction of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Rats" Molecules 18, no. 6: 7323-7335. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067323
APA StyleHsueh, T. Y., Wu, Y.-T., Lin, L.-C., Chiu, A. W., Lin, C.-H., & Tsai, T.-H. (2013). Herb-Drug Interaction of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil in Rats. Molecules, 18(6), 7323-7335. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067323