Microemulsion System for Topical Delivery of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract: Development, Physicochemical Characterisation and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of Impurity Residues in MSKE
2.1.1. Heavy Metal Residues in MSKE
2.1.2. Pesticide Residues in MSKE
2.1.3. Microorganism Contamination in MSKE
2.2. MSKE Cytotoxicity
2.3. MSKE Solubility
| No. | Solvents | Equilibrium Solubility a,b (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | IPM | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 2. | Water | 26.41 ± 1.60 |
| 3. | PSM | 5.27 ± 1.83 |
| 4. | SM | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 5. | Mixture of PSM and SM (1:1, by weight) | 1.44 ± 0.70 |
| 6. | Absolute EtOH | 1.81 ± 0.31 |
| 7. | 96.3% EtOH | 5.13 ± 0.98 |
| 8. | 1-PA | 0.69 ± 0.21 |
| 9. | 2-PA | 24.98 ± 1.50 |
| 10. | 1,2-PA | 13.22 ± 2.54 |
| 11. | Mixture of water and Absolute EtOH (1:1, by weight) | 26.87 ± 1.16 |
| 12. | Mixture of water and 96.3% EtOH (1:1, by weight) | 24.22 ± 2.79 |
| 13. | Mixture of water and 1-PA (1:1, by weight) | 26.39 ± 2.32 |
| 14. | Mixture of water and 2-PA (1:1, by weight) | 23.39 ± 1.19 |
| 15. | Mixture of water and 1,2-PA (1:1, by weight) | 21.58 ± 4.18 |
2.4. MSKE Partition Coefficient
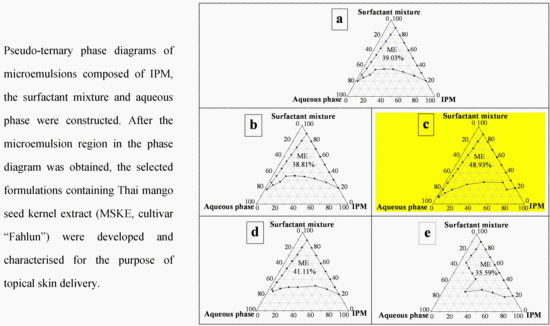
2.5. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagram

2.6. Characterisation of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
| Formulations | σ a,b (μS/cm) | pH a,b | RI a,b | η at 1000 s−1 a,b (mPas) | z-ave a,b (nm) | PDI a,b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unloaded w/o microemulsions | ||||||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 0(0) | 7.31(0.00) | 1.4364(0.0000) | 38.51(0.13) | 17(1) | 0.46(0.08) |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 0(0) | 7.28(0.00) | 1.4353(0.0000) | 40.45(0.27) | 17(0) | 0.41(0.01) |
| 3. 1-PA | 0(0) | 7.32(0.00) | 1.4362(0.0000) | 36.54(0.14) | 10(0) | 0.48(0.06) |
| 4. 2-PA | 0(0) | 7.40(0.00) | 1.4376(0.0000) | 38.02(0.12) | 8(1) | 0.46(0.10) |
| 5. 1,2-PA | 0(0) | 7.14(0.00) | 1.4385(0.0000) | 79.56(0.88) | 9(0) | 0.42(0.10) |
| Unloaded o/w microemulsions | ||||||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 30(0) | 7.07(0.00) | 1.4237(0.0000) | 35.17(0.04) | 23(0) | 0.20(0.00) |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 30(0) | 6.98(0.00) | 1.4248(0.0000) | 37.51(0.11) | 22(0) | 0.22(0.00) |
| 3. 1-PA | 20(0) | 6.99(0.00) | 1.4261(0.0000) | 31.92(0.08) | 21(0) | 0.30(0.01) |
| 4. 2-PA | 20(0) | 7.20(0.00) | 1.4263(0.0000) | 35.07(0.17) | 19(0) | 0.27(0.00) |
| 5. 1,2-PA | 10(0) | 6.92(0.00) | 1.4335(0.0000) | 118.18(0.07) | 29(0) | 0.29(0.01) |
2.7. Thermodynamic Stability of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
| Formulations | σ a,b (μS/cm) | pH a,b | RI a,b | η at 1000 s−1 a,b (mPas) | z-ave a,b (nm) | PDI a,b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded w/o microemulsions | ||||||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 0(0) | 6.98(0.00) | 1.4385(0.0000) | 50.26(0.49) | 16(0) | 0.43(0.01) |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 0(0) | 6.96(0.00) | 1.4362(0.0000) | 51.23(0.38) | 17(0) | 0.44(0.01) |
| 3. 1-PA | 0(0) | 6.98(0.00) | 1.4378(0.0000) | 41.00(0.15) | 10(0) | 0.43(0.01) |
| 4. 2-PA | 0(0) | 6.98(0.00) | 1.4371(0.0000) | 46.44(0.46) | 9(0) | 0.42(0.01) |
| 5. 1,2-PA * | 0(0) | 6.84(0.00) | 1.4385(0.0000) | 97.87(0.58) | 11(0) | 0.42(0.02) |
| 6. 1,2-PA ** | 0(0) | 6.70(0.00) | 1.4358(0.0000) | 135.75(1.21) | 70(1) | 0.27(0.01) |
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded o/w microemulsions | ||||||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 30(0) | 6.85(0.00) | 1.4256(0.0000) | 41.77(0.13) | 21(0) | 0.30(0.00) |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 30(0) | 6.74(0.00) | 1.4248(0.0000) | 36.71(0.12) | 33(0) | 0.17(0.03) |
| 3. 1-PA | 20(0) | 6.78(0.00) | 1.4283(0.0000) | 34.33(0.09) | 25(0) | 0.29(0.00) |
| 4. 2-PA | 20(0) | 6.68(0.00) | 1.4280(0.0000) | 33.61(0.32) | 36(0) | 0.20(0.01) |
2.8. Stability of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
2.9. Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Study
| Samples | MSKE Content a,c (μg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Epidermis | Dermis | Total | |
| 1% w/w of MSKE solution | 26.78 ± 3.39 | 13.77 ± 2.19 | 40.55 ± 1.23 |
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded w/o microemulsions | |||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 225.42 ± 27.64 | 123.48 ± 6.18 | 348.90 ± 21.54 b |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 161.33 ± 17.00 | 150.79 ± 15.13 | 312.12 ± 9.07 b |
| 3. 1-PA | 1132.50 ± 36.23 | 687.97 ± 19.67 | 1820.47 ± 17.22 b |
| 4. 2-PA | 1075.59 ± 185.97 | 671.00 ± 116.23 | 1746.58 ± 130.00 b |
| 5. 1,2-PA * | 1076.27 ± 184.88 | 610.77 ± 102.78 | 1687.04 ± 84.07 b |
| 6. 1,2-PA ** | 637.38 ± 108.65 | 402.12 ± 66.55 | 1039.50 ± 49.24 b |
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded o/w microemulsions | |||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 327.23 ± 53.04 | 573.07 ± 87.26 | 900.30 ± 34.30 b |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 130.26 ± 19.11 | 613.38 ± 12.33 | 743.64 ± 15.53 b |
| 3. 1-PA | 1070.11 ± 68.72 | 1358.90 ± 234.21 | 2429.01 ± 166.17 b |
| 4. 2-PA | 800.69 ± 138.21 | 1518.43 ± 159.00 | 2319.12 ± 29.05 b |
| Samples | ΔTEWL a,b (g/m2/h) | F a,c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.9 ± 0.3 | − | |
| 20% w/v of SDS solution | 24.6 ± 2.2 d | − | |
| 0.9% w/v of NaCl solution | − | 0.00 ± 0.00 | |
| 37% v/v of HNO3 solution | − | −0.50 ± 0.03 | |
| 1% w/w of MSKE solution | 1.5 ± 0.9 e | 4.82 ± 0.42 | |
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded w/o microemulsions | |||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 3.2 ± 1.0 f | 4.12 ± 0.47 g | |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 4.0 ± 2.0 f | 7.47 ± 0.27 g | |
| 3. 1-PA | 3.1 ± 1.9 f | 11.32 ± 0.83 g | |
| 4. 2-PA | 4.1 ± 2.4 f | 6.59 ± 0.21 g | |
| 5. 1,2-PA * | 4.8 ± 0.8 f | 7.00 ± 1.07 g | |
| 6. 1,2-PA ** | 4.7 ± 1.8 f | 6.99 ± 1.05 g | |
| 1% w/w MSKE-loaded o/w microemulsions | |||
| 1. Absolute EtOH | 5.1 ± 0.8 f | 8.05 ± 0.47 g | |
| 2. 96.3% EtOH | 5.6 ± 2.0 f | 7.85 ± 0.35 g | |
| 3. 1-PA | 5.4 ± 1.5 f | 6.56 ± 0.25 g | |
| 4. 2-PA | 5.9 ± 1.6 f | 9.56 ± 0.96 g | |
2.10. The Non-Perfused Pig Ear Test for Skin Irritance
2.11. Ex Vivo Skin Corrosion Study
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. MSKE Preparation

3.3. Analysis of PGG Content in MSKE
3.4. Determination of Impurity Residues in MSKE
3.4.1. Heavy Metal Residues Analysis
3.4.2. Pesticide Residues Analysis
3.4.3. Microorganism Contamination Analysis
3.5. MSKE Cytotoxicity Test
3.6. MSKE Solubility Determination
3.7. MSKE Partition Coefficient Determination
3.8. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagram Construction
3.9. Preparation of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
| Component | Unloaded Microemulsions | MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o (% w/w) | o/w (% w/w) | w/o (% w/w) | o/w (% w/w) | |
| MSKE | - | - | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PSM:SM (1:1, by weight) | 40 | 40 | 39.60 | 39.60 |
| IPM | 45 | 30 | 44.55 | 29.70 |
| Water:Cosurfactant a (1:1, by weight) | 15 | 30 | 14.85 | 29.70 |
3.10. Characterisation of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
3.10.1. Macroscopic Observation
3.10.2. Conductivity Measurement
3.10.3. pH Measurement
3.10.4. Refractive Index Measurement
3.10.5. Viscosity and Rheological Behaviour Determination
3.10.6. Particle Size Measurement
3.11. Thermodynamic Stability of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
3.11.1. Centrifuge Stress Test
3.11.2. Freeze-Thaw Stress Test
3.12. Stability Study of Unloaded and MSKE-Loaded Microemulsions
3.13. Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Study
3.14. The Non-Perfused Pig Ear Test for Skin Irritance
3.15. Ex Vivo Skin Corrosion Study
3.16. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Database Collections, Agricultural Data; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/ (accessed on 21 April 2014).
- Hemavathy, J.; Prabhakar, J.V.; Sen, D.P. Drying and storage behaviour of mango (Mangifera indica) seeds and composition of kernel fat. ASEAN Food J. 1988, 4, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Arogba, S.S. Physical, chemical and functional properties of Nigerian mango (Mangifera indica) kernel and its processed flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 73, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, E. Natural polyphenols (vegetable tannins) as drugs: Possible modes of action. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soong, Y.Y.; Barlow, P.J. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of selected fruit seeds. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithitanakool, S.; Pithayanukul, P.; Bavovada, R. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Thai mango seed kernel extract. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leanpolchareanchai, J.; Pithayanukul, P.; Bavovada, R.; Saparpakorn, P. Molecular docking studies and anti-enzymatic activities of Thai mango seed kernel extract against snake venoms. Molecules 2009, 14, 1404–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithitanakool, S.; Pithayanukul, P.; Bavovada, R.; Saparpakorn, P. Molecular docking studies and anti-tyrosinase activity of Thai mango seed kernel extract. Molecules 2009, 14, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pithayanukul, P.; Leanpolchareanchai, J.; Saparpakorn, P. Molecular docking studies and anti-snake venom metalloproteinase activity of Thai mango seed kernel extract. Molecules 2009, 14, 3198–3213. [Google Scholar]
- Jiamboonsri, P.; Pithayanukul, P.; Bavovada, R.; Chomnawang, M.T. The inhibitory potential of Thai mango seed kernel extract against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2011, 16, 6255–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Kim, S.H.; Hagerman, A.E.; Lü, J. Anti-cancer, anti-diabetic and other pharmacologic and biological activities of penta-galloyl-glucose. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Ju, H.Q.; Komatsu, M.; Ji, Y.H.; Liu, G.; Guo, C.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, C.R.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. Autophagy is involved in anti-viral activity of pentagalloylglucose (PGG) against Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulik, S.P.; Paul, B.K. Structure, dynamics and transport properties of microemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 78, 99–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špiclin, P.; Homar, M.; Zupančič-Valant, A.; Gašperlin, M. Sodium ascorbyl phosphate in topical microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 256, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.B.; Lin, Y.H.; Lu, T.M.; Wang, R.J.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wu, P.C. Transdermal delivery of capsaicin derivative-sodium nonivamide acetate using microemulsions as vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M. Self-microemulsifying and microemulsion systems for transdermal delivery of indomethacin: Effect of phase transition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M. Transdermal delivery of hydrocortisone from eucalyptus oil microemulsion: Effects of cosurfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.J.; Rees, G.D. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 45, 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozman, B.; Gasperlin, M.; Tinois-Tessoneaud, E.; Pirot, F.; Falson, F. Simultaneous absorption of vitamins C and E from topical microemulsions using reconstructed human epidermis as a skin model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.M.; Abdel Malak, N.S.; El-Gazayerly, O.N.; Abdel Rehim, A.A. Formulation of microemulsion gel systems for transdermal delivery of celecoxib: In vitro permeation, anti-inflammatory activity and skin irritation tests. Drug Discov. Ther. 2010, 4, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malakar, J.; Sen, S.O.; Nayak, A.K.; Sen, K.K. Development and evaluation of microemulsions for transdermal delivery of insulin. ISRN Pharm. 2011. Available online: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn.pharmaceutics/2011/780150/ (accessed on 21 April 2014). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Lipid nanoemulsions loaded with doxorubicin-oleic acid ionic complex: Characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 496–505. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, E.H.; Vaishali, B.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Tricaprylin microemulsion for oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin conjugates. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Bhasin, K.K. Tween-embedded microemulsions-Physicochemical and spectroscopic analysis for antitubercular drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg-Cettina, M.; Liu, P.; Nightingale, J.; Kurihara-Bergstrom, T. Enhanced transdermal delivery of estradiol in vitro using binary vehicles of isopropyl myristate and short-chain alkanols. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 114, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.; Gallarate, M.; Pattarino, F.; Carlotti, M.E. Investigation of the phase behaviour of systems containing lecithin and 2-acyl lysolecithin derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 190, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ramachandran, C.; Weiner, N.D.; Roessler, B.J. Topical transport of hydrophilic compounds using water-in-oil nanoemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 220, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, S.E. Micelles, microemulsions, liquid crystals, and the structure of stratum corneum lipids. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1990, 41, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Alany, R.G.; Tucker, I.G.; Davies, N.M.; Rades, T. Characterizing colloidal structures of pseudoternary phase diagrams formed by oil/water/amphiphile systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, K.; Lindman, B. Organized surfactant systems: Microemulsions. Langmuir 1987, 3, 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Baboota, S.; Alam, M.; Sharma, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Ali, J. Nanocarrier-based hydrogel of betamethasone dipropionate and salicylic acid for treatment of psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wester, R.; Maibach, H. Individual and regional variation with in vitro percutaneous absorption. In In Vitro Percutaneous Absorption: Principles, Fundamentals, and Applications; Bronaugh, R., Maibach, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, T.; Mak, V.H.W.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Mechanism of percutaneous penetration enhancement: Effect of n-alkanols on the permeability barrier of hairless mouse skin. J. Control. Release 1990, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantasart, D.; Li, S.K.; He, N.; Warner, K.S.; Prakongpan, S.; Higuchi, W.I. Mechanistic studies of branched-chain alkanols as skin permeation enhancers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 762–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fentem, J.H.; Briggs, D.; Chesné, C.; Elliott, G.R.; Harbell, J.W.; Heylings, J.R.; Portes, P.; Roguet, R.; van de Sandt, J.J.; Botham, P.A. A prevalidation study on in vitro tests for acute skin irritation: Results and evaluation by the Management Team. Toxicol. In Vitro 2001, 15, 57–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuang, V.; Balls, M.; Botham, P.A.; Coquette, A.; Corsini, E.; Curren, R.D.; Elliott, G.R.; Fentem, J.H.; Heylings, J.R.; Liebsch, M.; et al. Follow-up to the ECVAM prevalidation study on in vitro tests for acute skin irritation. The ECVAM skin irritation task force report 2. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2002, 30, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padois, K.; Cantiéni, C.; Bertholle, V.; Bardel, C.; Pirot, F.; Falson, F. Solid lipid nanoparticles suspension versus commercial solutions for dermal delivery of minoxidil. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holak, W. Analysis of foods for lead, cadmium, copper, zinc, arsenic, and selenium, using closed system sample digestion: Collaborative study. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1980, 63, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jorhem, L.; Engman, J. Determination of lead, cadmium, zinc, copper, and iron in foods by atomic absorption spectrometry after microwave digestion: NMKL1 collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Papathakis, M.L.; Feng, H.M.C.; Hunter, G.F.; Carr, J.E. Multipesticide residue method for fruits and vegetables: California Department of Food and Agriculture. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1991, 339, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, J.A.; Milroy, R.; Kaye, S.B. Effect of the pH dependence of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide-formazan absorption on chemosensitivity determined by a novel tetrazolium based assay. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kale, N.J.; Allen, L.V. Studies on microemulsions using Brij 96 as surfactant and glycerin, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol as cosurfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumberger, J.P.; Suntzeff, V.; Cowdry, E.V. Methods for the separation of epidermis from dermis and some physiologic and chemical properties of isolated epidermis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1942, 2, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Stobbe, J.L.; Drake, K.D.; Maier, K.J. Comparison of in vivo (Draize method) and in vitro (Corrositex assay) dermal corrosion values for selected industrial chemicals. Int. J. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leanpolchareanchai, J.; Padois, K.; Falson, F.; Bavovada, R.; Pithayanukul, P. Microemulsion System for Topical Delivery of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract: Development, Physicochemical Characterisation and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies. Molecules 2014, 19, 17107-17129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117107
Leanpolchareanchai J, Padois K, Falson F, Bavovada R, Pithayanukul P. Microemulsion System for Topical Delivery of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract: Development, Physicochemical Characterisation and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies. Molecules. 2014; 19(11):17107-17129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeanpolchareanchai, Jiraporn, Karine Padois, Françoise Falson, Rapepol Bavovada, and Pimolpan Pithayanukul. 2014. "Microemulsion System for Topical Delivery of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract: Development, Physicochemical Characterisation and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies" Molecules 19, no. 11: 17107-17129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117107
APA StyleLeanpolchareanchai, J., Padois, K., Falson, F., Bavovada, R., & Pithayanukul, P. (2014). Microemulsion System for Topical Delivery of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract: Development, Physicochemical Characterisation and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies. Molecules, 19(11), 17107-17129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117107