Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Purification of Bk and Bk-Related Peptides

| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | M.M. (Da) | I.P. | H.M. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bk | Bradykinin | R | P | P | G | F | S | P | F | R | --- | --- | 1060.7 | 12.0 | 1.195 |
| Bk1 | Val,[T]6-bradykinyl-Val,Asp | V | P | P | G | F | T | P | F | R | V | D | 1231.7 | 5.8 | 1.450 |
| Bk2 | Val,[T]6-bradykinyl-Glu,Ser | V | P | P | G | F | T | P | F | R | Q | S | 1232.7 | 9.7 | 2.443 |
2.2. BTCI and Bk Complex Formation Investigated by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)


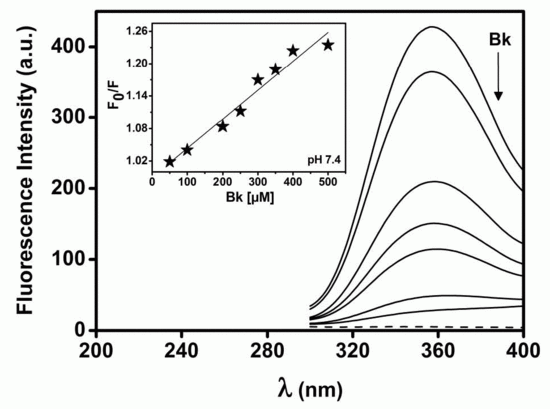
2.3. Structural Analysis of BTCI and BTCI-Bk-Related Peptide Complexes by Fluorescence Spectroscopy

| Peptide | pH | KSV (×102 M−1) | R 2a | S.D. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 5.02 | 0.97 | 0.27 | |
| Bk | 7.4 | 5.53 | 0.97 | 0.30 |
| 9.0 | 4.68 | 0.99 | 0.15 | |
| 5.0 | 5.00 | 0.97 | 0.25 | |
| Bk1 | 7.4 | 4.82 | 0.97 | 0.26 |
| 9.0 | 4.38 | 0.97 | 0.22 | |
| 5.0 | 4.25 | 0.99 | 0.11 | |
| Bk2 | 7.4 | 5.09 | 0.97 | 0.28 |
| 9.0 | 3.84 | 0.98 | 0.17 |

| Peptide | pH | Kb (×103 M−1) | n a | R 2b | S.D. c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.07 | |
| Bk | 7.4 | 9.68 | 1.39 | 0.98 | 0.07 |
| 9.0 | 0.71 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 0.04 | |
| 5.0 | 0.84 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 0.06 | |
| Bk1 | 7.4 | 1.02 | 1.11 | 0.96 | 0.06 |
| 9.0 | 0.23 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.05 | |
| 5.0 | 0.59 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.04 | |
| Bk2 | 7.4 | 0.22 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.06 |
| 9.0 | 1.81 | 1.23 | 0.98 | 0.06 |
2.5. Modulation of Smooth Muscle Contraction Action of Bk Mediated by BTCI


2.6. Cardiovascular Effects of the Infusion of BTCI or Vehicle
2.8. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.2. Spectroscopic Measurements
3.2.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Assays
3.2.2. Circular Dichroism (CD) Assays
3.2.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Assays
3.3. Enzymatic Assay
3.4. Smooth Muscle Constriction Force Assay using Mammalian Bk and Its Analogues Associated with BTCI
3.5. Evaluation of the Cardiovascular Effect of Intravenous Infusion of Bk, Bk1, Bk2 and BTCI
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobo, J.; Major, B.; Kekesi, K.A.; Szabo, I.; Megyeri, M.; Hajela, K.; Závodszky, P.; Gál, P. Cleavage of kininogen and subsequent Bradykinin release by the complement component: Mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease (MASP)-1. PLoS One 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mamenko, M.; Zaika, O.; Doris, P.A.; Pochynyuk, O. Salt-dependent inhibition of epithelial Na+ channel—Mediated Sodium reabsorption in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron by bradykinin. Hypertens 2012, 60, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola, K.D.; Figueroa, C.D.; Worthy, K. Bioregulation of kinins: Kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992, 44, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Regoli, D.; Gobeil, F.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Jukic, D.; Seoane, P.R.; Salvino, J.M.; Sawutz, D.G. Bradykinin receptor types and B2 subtypes. Life Sci. 1994, 55, 735–749. [Google Scholar]
- Regoli, D.; Jukic, D.; Gobeil, F.; Rhaleb, N.E. Receptors for bradykinin and related kinins: A critical analysis. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993, 71, 556–567. [Google Scholar]
- Carretero, O.A.; Scicli, A.G. Local hormonal factors (intracrine, autocrine, and paracrine) in hypertension. Hypertension 1991, 18, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- McGiff, J.C.; Carroll, M.A.; Escalante, B. Arachidonate metabolites and kinins in blood pressure regulation. Hypertension 1991, 18, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Duka, A.; Duka, I.; Gao, G.; Shenouda, S.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Role of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors in normal blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Golias, C.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Stagikas, D.; Charalabopoulos, K.; Batistatou, A. The kinin system—Bradykinin: Biological effects and clinical implications. Multiple role of the kinin system—Bradykinin. Hippokratia 2007, 3, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Potthast, R.; Ehler, R.; Scheving, L.A.; Sindic, A.; Schlatter, E.; Kuhn, M. High salt intake increase uroguanylin expression in mouse kidney. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar]
- Carrithers, S.L.; Taylor, B.; Cai, W.Y.; Johnson, B.R.; Otto, C.E.; Gremberg, R.N.; Jackson, B.A. Guanylyl cyclase-C receptor mRNA distribution along the rat nephron. Regul. Pep. 2000, 95, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Erdös, E.G.; Fulong, T.F.; Skidgel, R.A. Angiotensin I-Converting enzyme inhibitors are allosteric enhancers of kinin B1 and B2 receptor function. Hypertension 2010, 55, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Yong, Q.C.; Thomas, C.M.; Baker, K.M. Intracardiac intracellular angiotensin system in diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski, M.; Qasim, M.A. What can the structures of enzyme-inhibitor complexes tell us about the structures of enzyme substrate complexes? Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1477, 324–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.A. Proteinase inhibitors in plants: Genes for improving defenses against insects and pathogens. Ann. Rev. Phytol. 1991, 28, 425–449. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, O.L.; Santos, R.C.; Batista, J.A.N.; Mendes, A.C.M.; Araújo, M.A.M.; Monnerat, R.G.; Grossi-de-Sá, R.F.; Freitas, S.M. Effects of black-eyed pea trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor on proteolytic activity and on development of Anthonomus grandis. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Benedetti, B.; Kamoun, S. A second kazal-like protease inhibitor from Phytophthora infestans inhibits and interacts with the apoplastic pathogenesis-related protease P69B of tomato. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Itoh, H.; Koono, M. Emerging multifunctional aspects of cellular serine proteinase inhibitors in tumor progression and tissue regeneration. Pathol. Int. 2002, 52, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Esse, H.P.; Klooster, J.W.; Bolton, M.D.; Yadeta, K.A.; Baarlen, P.; Boeren, S.; Vervoort, J.; de Wit, P.J.G.M.; Thommas, B.P.H.J. The Cladosporium fulvum virulence protein Avr2 inhibits host proteases required for basal defense. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1948–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.R. Chemopreventive agents: Protease inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 78, 167–209. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, W.B.; Kennedy, A.R.; Wan, X.S.; Taylor, T.H.; Nguyen, T.A.; Jensen, J.; Thompsom, W.; Lagerberg, W.; Meyskens, F.L. Clinical modulation of oral leukoplakia and protease activity by Bowman-Birk inhibitor concentrate in a phase IIa chemoprevention trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4684–4691. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Wan, X.S. Effects of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor on growth, invasion, and clonogenic survival of human prostate epithelial cells and prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2002, 50, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.W.; Huang, S.C.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Bowman-Birk inhibitor abates proteasome function and suppresses the proliferation of MCF7 breast cancer cells through accumulation of MAP kinase phosphatase-1. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Sato, H.; Virgona, N.; Hagiwara, H.; Kashiwagi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Asano, R.; Yano, T. Negative growth control of osteosarcoma cell by Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor from soybean; involvement of connexin. Cancer Lett. 2007, 43, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Joanitti, G.A.; Azevedo, R.B.; Freitas, S.M. Apoptosis and lysosome membrane permeabilization induction on breast cancer cells by an anticarcinogenic Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata seeds. Cancer Lett. 2010, 293, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Morhy, L.; Ventura, M.M. The complete amino acid sequence of the Vigna unguiculata (L.) WaLP seed trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1987, 59, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, M.M.; Martin, C.O.; Morhy, L. A trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor form black-eyed pea (Vigna sinensis L.). VI. Isolation and properties of complexes with trypsin and chymotrypsin. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1975, 47, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, S.M.; Mello, L.V.; Silva, M.C.; Vriend, G.; Neshich, G.; Ventura, M.M. Analysis of the black-eyed pea trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor-α-chymotrypsin complex. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.A.R.G.; Silva, L.P.; Teles, R.C.L.; Esteves, G.F.; Azevedo, R.B.; Ventura, M.M.; Freitas, S.M. Crystal structure of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata seeds in complex with β-Trypsin at 1.55 Å resolution and its structural properties in association with proteinases. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Santos-Neto, M.S.; Monteiro, H.S.A.; Freitas, S.M.; Morhy, L.; Nascimento, N.R.F.; Fonteles, M.C. BTCI enhances guanylin-induced natriuresis and promotes renal glomerular and tubular effects. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Borgstahl, G.E.O. How to use Dynamic Light Scattering to improve the likelihood of growing macromolecular crystals. In Macromolecular Crystallography Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology; Doublié, S., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 363, pp. 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, M.M.; Mizuta, K.; Ikemoto, H. Self-association of the black-eyed pea trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor in solution. A study by light scattering. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1981, 53, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.P.; Azevedo, R.B.; Morais, P.C.; Ventura, M.M.; Freitas, S.M. Oligomerization states of Bowman-Birk inhibitor by atomic force microscopy and computational approaches. Prot. Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 61, 642–648. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, M.M.; Mizuta, K.; Ikemoto, H. Solvent perturbation and surface accessibility of the tryptophyl and tyrosyl groups in black-eyed pea trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1984, 56, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, A.H.; Ryan, J.W. Circular Dichroism of Bradykinin and Related Peptides. Biochem. J. 1971, 121, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Cann, J.R.; Stewart, J.M.; Matsuedai, G.R. A circular dichroism study of the secondary structure of Bradykinin. Biochemistry 1973, 19, 3780–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Kotovych, G.; Cann, J.R.; Stewart, J.M.; Yamamoto, H. NMR and CD conformational studies of bradykinin and its agonists and antagonists: Application to receptor binding. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 76, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Fachetti, H.C.S.; Mizuta, K.; Ventura, M.M. Thermodynamics of the black-eyed pea trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1984, 56, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, S.M.; Ikemoto, H.; Ventura, M.M. Thermodynamics of the binding of chymotrypsin with the black-eyed pea trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor (BTCI). J. Protein Chem. 1999, 18, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, G.; Muhr, R.; Jaenicke, R. Quantitative analysis of protein far UV circular dichroism spectra. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Chapter 8; p. 698. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, G.D.; Krause, F.C.; Silva, L.P.; Leite, J.R.S.A.; Melo, J.A.T.; Prates, M.V.; Pesquero, J.B.; Santos, E.L.; Nakaie, C.R.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; et al. Bradykinin-related peptides from Phyllomedusa hypochondrials. Peptides 2006, 27, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Regoli, D.; Barabé, J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol. Rev. 1980, 32, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, E.; Colescott, R.L.; Bossinger, C.D.; Cook, P. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid phase synthesis of peptides. Anal. Biochem. 1970, 34, 595–598. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.B.; Kies, M.W. A note on spectrophotometric determination of proteins in dilute solution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1960, 45, 382–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, M.M.; Xavier-Filho, J. A trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor from black-eyed pea (Vigna sinensis). I. Purification and partial characterization. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1996, 38, 553–566. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, A.X.; Zhao, R.M.; Qu, X.S.; Qu, S.S. Studies on the interaction between rare-earth salts of heteropoly EuHSiMo10-W2O40·25H2O and bovine serum albumin. Acta Chim. Sin. 2004, 62, 1519–1523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger, B.F.; Kokowsky, N.; Cohen, W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 95, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, M.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvares, A.D.C.M.; Schwartz, E.F.; Amaral, N.O.; Trindade, N.R.; Pedrino, G.R.; Silva, L.P.; De Freitas, S.M. Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides. Molecules 2014, 19, 17536-17558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117536
Álvares ADCM, Schwartz EF, Amaral NO, Trindade NR, Pedrino GR, Silva LP, De Freitas SM. Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides. Molecules. 2014; 19(11):17536-17558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117536
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvares, Alice Da Cunha M., Elisabeth Ferroni Schwartz, Nathalia Oda Amaral, Neidiane Rosa Trindade, Gustavo Rodrigues Pedrino, Luciano Paulino Silva, and Sonia Maria De Freitas. 2014. "Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides" Molecules 19, no. 11: 17536-17558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117536
APA StyleÁlvares, A. D. C. M., Schwartz, E. F., Amaral, N. O., Trindade, N. R., Pedrino, G. R., Silva, L. P., & De Freitas, S. M. (2014). Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides. Molecules, 19(11), 17536-17558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117536