Curcumin and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Major Mode of Action through Stimulating Endogenous Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Stage | Description | GFR (glomerular filtration rate) mL/min/1.73 m2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR | ≥90 |
| 2 | Kidney damage with mild decreased GFR | 60–89 |
| 3 | Moderate decreased GFR | 30–59 |
| 4 | Severe decreased GFR | 15–29 |
| 5 | Kidney Failure | <15 (or dialysis) |

2. Inflammatory Mediators Playing a Role in CKD
2.1. Eicosanoids
2.2. Cytokines
2.3. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.4. Growth Factors
2.5. Transcription Factors
2.6. Immune System
3. Major Pathologies Affecting CKD
3.1. Hypertension
3.2. Proteinuria
3.3. Cardiovascular System
3.4. Diabetes
4. Curcumin: Action in/on the Gut despite Low Bioavailability
Bioavailability
5. Summary
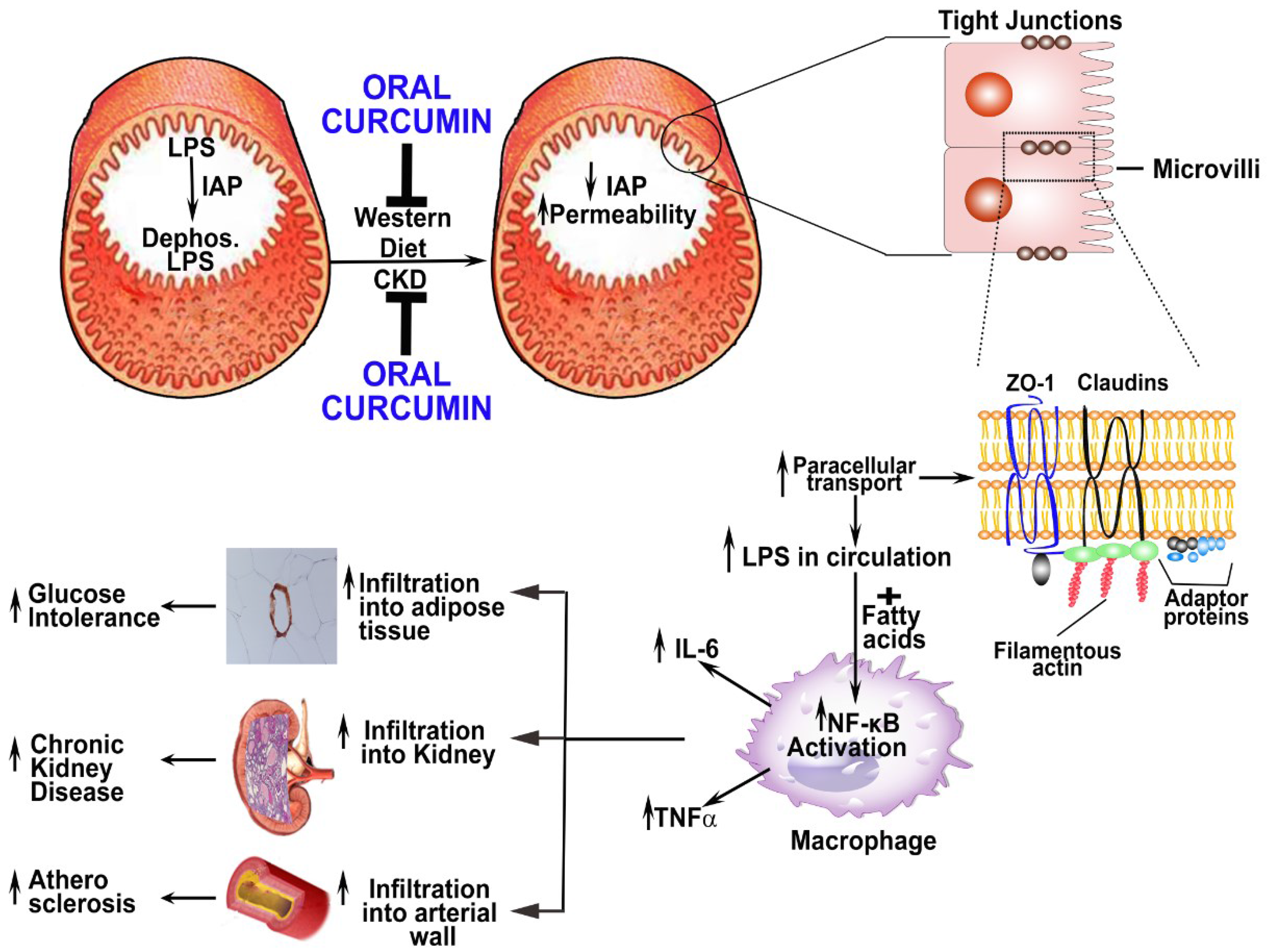
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Himmelfarb, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hakim, R.M. The Elephant in Uremia: Oxidant Stress as a Unifying Concept of Cardiovascular Disease in Uremia. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, H.; Sica, D.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Cardiovascular Burden Associated with Uremic Toxins in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and Regional Mortality from 235 Causes of Death for 20 Age Groups in 1990 and 2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.; Yang, C.W. Chronic Kidney Disease: Global Dimension and Perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Kari, J.A. Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic Roles of Curcumin: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatcher, H.; Planalp, R.; Cho, J.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Curcumin: From Ancient Medicine to Current Clinical Trials. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1631–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Targeting Inflammation-Induced Obesity and Metabolic Diseases by Curcumin and Other Nutraceuticals. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sung, B. Pharmacological Basis for the Role of Curcumin in Chronic Diseases: An Age-Old Spice with Modern Targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a Component of Golden Spice: From Bedside to Bench and Back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Curcumin Action: Gene Expression. Biofactors 2013, 39, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, A.; Vargas-Robles, H.; Gamez-Mendez, A.M.; Escalante, B. Cyclooxygenase-2 and Kidney Failure. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2012, 98, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiba, N.; Kumano, E.; Watanabe, T.; Shinkura, H.; Sugimoto, T.; Inoue, M. Subtotal Nephrectomy Stimulates Cyclooxygenase 2 Expression and Prostacyclin Synthesis in the Rat Remnant Kidney. Nephron 2002, 91, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Krieg, R.; Massey, H.D.; Sica, D.A.; Fakhry, I.; Ghosh, S.; Gehr, T.W. Curcumin and Enalapril Ameliorate Renal Failure by Antagonizing Inflammation in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats: Role of Phospholipase and Cyclooxygenase. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 302, F439–F454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Taccone-Gallucci, M.; Finazzi-Agro, A. 5-Lipoxygenase-Mediated Mitochondrial Damage and Apoptosis of Mononuclear Cells in ESRD Patients. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, S33–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmark, O.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase: Regulation and Possible Involvement in Atherosclerosis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007, 83, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Inflammatory and Atherosclerotic Interactions in the Depleted Uremic Patient. Blood Purif. 2001, 19, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Ketteler, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Lindholm, B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Riella, M.; Heimburger, O.; Cederholm, T.; Girndt, M. IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-Alpha: Central Factors in the Altered Cytokine Network of Uremia—The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1216–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, H.A.; Ishani, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Greer, N.L.; MacDonald, R.; Rossini, D.; Sadiq, S.; Lankireddy, S.; Kane, R.L.; Wilt, T.J. Screening for, Monitoring, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 1 to 3: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 570–581. [Google Scholar]
- Shing, C.M.; Adams, M.J.; Fassett, R.G.; Coombes, J.S. Nutritional Compounds Influence Tissue Factor Expression and Inflammation of Chronic Kidney Disease Patients in Vitro. Nutrition 2011, 27, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreillon, J.J.; Bowden, R.G.; Deike, E.; Griggs, J.; Wilson, R.; Shelmadine, B.; Cooke, M.; Beaujean, A. The use of an Anti-Inflammatory Supplement in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2013, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H.; Kang, K.S.; Kwak, M.K. Effect of Redox Modulating NRF2 Activators on Chronic Kidney Disease. Molecules 2014, 19, 12727–12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soetikno, V.; Watanabe, K.; Sari, F.R.; Harima, M.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Veeraveedu, P.T.; Arozal, W.; Sukumaran, V.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Arumugam, S; et al. Curcumin Attenuates Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting PKC-Alpha and PKC-beta1 Activity in Streptozotocin-Induced Type I Diabetic Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Tapia, E.; Soto, V.; Avila-Casado, C.; Franco, M.; Wessale, J.L.; Zhao, L.; Johnson, R.J. Effect of Febuxostat on the Progression of Renal Disease in 5/6 Nephrectomy Rats with and without Hyperuricemia. Nephron Physiol. 2008, 108, p69–p78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Krieg, R.; Sica, D.A.; Fakhry, I.; Mirshahi, S.; Gehr, T.W.B. Role of Pla2 and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism in Inflammation during Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 852. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D.M.; Coombes, J.S.; Bennett, N.; Johnson, D.W.; Gobe, G.C. Oxidative Stress, Anti-Oxidant Therapies and Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrology 2012, 17, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulsky, A.V. Growth Factor Pathways in Proliferative Glomerulonephritis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2000, 9, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Hernandez, F.J.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M. Role of TGF-Beta in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Integration of Tubular, Glomerular and Vascular Effects. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajehdehi, P.; Pakfetrat, M.; Javidnia, K.; Azad, F.; Malekmakan, L.; Nasab, M.H.; Dehghanzadeh, G. Oral Supplementation of Turmeric Attenuates Proteinuria, Transforming Growth Factor-Beta and Interleukin-8 Levels in Patients with Overt Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind and Placebo-Controlled Study. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2011, 45, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Gehr, T.W.; Ghosh, S.; Fakhry, I.; Sica, D.A.; Lyall, V.; Schoolwerth, A.C. PPARgamma Ligand Attenuates PDGF-Induced Mesangial Cell Proliferation: Role of MAP Kinase. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Sato, W.; Kosugi, T.; Johnson, R.J. Uncoupling of VEGF with Endothelial NO as a Potential Mechanism for Abnormal Angiogenesis in the Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 184539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Kong, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, S. Curcumin Attenuates Angiogenesis in Liver Fibrosis and Inhibits Angiogenic Properties of Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Salloum, F.N.; Abbate, A.; Krieg, R.; Sica, D.A.; Gehr, T.W.; Kukreja, R.C. Curcumin Prevents Cardiac Remodeling Secondary to Chronic Renal Failure through Deactivation of Hypertrophic Signaling in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H975–H984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J. Regulation of PPARgamma Function by TNF-Alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Massey, H.D.; Krieg, R.; Fazelbhoy, Z.A.; Ghosh, S.; Sica, D.A.; Fakhry, I.; Gehr, T.W. Curcumin Ameliorates Renal Failure in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats: The Role of Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwe, S. Anti-Inflammatory Interventions of NF-kappaB Signaling: Potential Applications and Risks. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijarro, C.; Egido, J. Transcription Factor-Kappa B (NF-Kappa B) and Renal Disease. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedruzzi, L.M.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Leite, M., Jr.; Mafra, D. Nrf2-keap1 System Versus NF-kappaB: The Good and the Evil in Chronic Kidney Disease? Biochimie 2012, 94, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, C.K.; Antunes, G.R.; Mattar, A.L.; Malheiros, D.M.; Vieira, J.M., Jr.; Zatz, R. Chronic Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Attenuates Renal Injury in the 5/6 Renal Ablation Model. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F92–F99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoja, C.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. The Nrf2 Pathway in the Progression of Renal Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Vaziri, N.D. Contribution of Impaired Nrf2-Keap1 Pathway to Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Chronic Renal Failure. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010, 298, F662–F671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoja, C.; Abbate, M.; Remuzzi, G. Progression of Renal Injury toward Interstitial Inflammation and Glomerular Sclerosis is Dependent on Abnormal Protein Filtration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Massiah, M.A.; Bozak, R.E.; Hicks, R.J.; Talalay, P. Potency of Michael Reaction Acceptors as Inducers of Enzymes that Protect Against Carcinogenesis Depends on their Reactivity with Sulfhydryl Groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. Relation of Structure of Curcumin Analogs to their Potencies as Inducers of Phase 2 Detoxification Enzymes. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soetikno, V.; Sari, F.R.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Arumugam, S.; Harima, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kawachi, H.; Watanabe, K. Curcumin Alleviates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Renal Fibrosis in Remnant Kidney through the Nrf2-keap1 Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, V.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: The Role of Macrophages. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Chaves, L.; Eadon, M.T.; Chang, A.; Quigg, R.J.; Alexander, J.J. Curcumin Alleviates Immune-Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis in Factor-H-Deficient Mice. Immunology 2013, 139, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.L.; Townsend, R.R. Hypertension and Kidney Disease: What do the Data really show? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garimella, P.S.; Uhlig, K. Current Issues in the Management and Monitoring of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia, E.; Soto, V.; Ortiz-Vega, K.M.; Zarco-Marquez, G.; Molina-Jijon, E.; Cristobal-Garcia, M.; Santamaria, J.; Garcia-Nino, W.R.; Correa, F.; Zazueta, C.; et al. Curcumin Induces Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation and Prevents Glomerular Hypertension, Hyperfiltration, Oxidant Stress, and the Decrease in Antioxidant Enzymes in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, E.; Zatarain-Barron, Z.L.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Zarco-Marquez, G.; Molina-Jijon, E.; Cristobal-Garcia, M.; Santamaria, J.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Curcumin Reverses Glomerular Hemodynamic Alterations and Oxidant Stress in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, M.; Zoja, C.; Remuzzi, G. How does Proteinuria Cause Progressive Renal Damage? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2974–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajehdehi, P.; Zanjaninejad, B.; Aflaki, E.; Nazarinia, M.; Azad, F.; Malekmakan, L.; Dehghanzadeh, G.R. Oral Supplementation of Turmeric Decreases Proteinuria, Hematuria, and Systolic Blood Pressure in Patients Suffering from Relapsing Or Refractory Lupus Nephritis: A Randomized and Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Cohen, G.; Glorieux, G.; Jankowski, J. European Uremic Toxin Work Group. A Bench to Bedside View of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Glorieux, G.; de Smet, R.; Lameire, N. European Uremic Toxin Work Group. New Insights in Uremic Toxins. Kidney Int. 2003, 84, S6–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; de Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A.; European Uremic Toxin Work Group. Normal and Pathologic Concentrations of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, M.; Ishii, H.; Murakami, R.; Isobe, S.; Hayashi, M.; Amano, T.; Arai, K.; Yoshikawa, D.; Ohashi, T.; Uetani, T.; et al. Impact of Renal Function on Coronary Plaque Composition. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Pelisek, J.; Hahntow, I.N.; Eckstein, H.H.; Ockert, S.; Reeps, C.; Heider, P.; Luppa, P.B.; Frank, H. Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Carotid Plaque Vulnerability. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 54, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tousoulis, D.; Psarros, C.; Demosthenous, M.; Patel, R.; Antoniades, C.; Stefanadis, C. Innate and Adaptive Inflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Vascular Disease: The Emerging Role of Statins. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.K.; Ha, T.Y.; McGregor, R.A.; Choi, M.S. Long-Term Curcumin Administration Protects Against Atherosclerosis Via Hepatic Regulation of Lipoprotein Cholesterol Metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Luo, T.; Tan, Y.; Tian, D.; Guo, Z. Curcumin Inhibits Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Expression and Enhances Cholesterol Efflux by Suppressing the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Pathway in Macrophage. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S.T.; Zingg, J.M.; Kwan, P.; Noble, T.; Smith, D.; Meydani, M. Curcumin Modulation of High Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis and Steatohepatosis in LDL Receptor Deficient Mice. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Bie, J.; Wang, J.; Ghosh, S. Oral Supplementation with Non-Absorbable Antibiotics Or Curcumin Attenuates Western Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis and Glucose Intolerance in LDLR-/- Mice—Role of Intestinal Permeability and Macrophage Activation. PLoS One 2014, 9, e108577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Sunagawa, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Takaya, T.; Wada, H.; Nagasawa, A.; Komeda, M.; Fujita, M.; Shimatsu, A.; Kita, T.; et al. The Dietary Compound Curcumin Inhibits p300 Histone Acetyltransferase Activity and Prevents Heart Failure in Rats. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 868–878. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, D.N.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Vescovo, G.; House, A.A.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A. Pathophysiology of Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 2 in Stable Chronic Heart Failure: Workgroup Statements from the Eleventh Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 182, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gullestad, L.; Aukrust, P. Review of Trials in Chronic Heart Failure Showing Broad-Spectrum Anti-Inflammatory Approaches. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Ruilope, L.M. Insulin Resistance, Hyperinsulinemia, and Renal Injury: Mechanisms and Implications. Am. J. Nephrol. 2006, 26, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.P.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Jaber, B.L. Endotoxin-Binding Affinity of Sevelamer: A Potential Novel Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, S20–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Yuan, J.; Rahimi, A.; Ni, Z.; Said, H.; Subramanian, V.S. Disintegration of Colonic Epithelial Tight Junction in Uremia: A Likely Cause of CKD-Associated Inflammation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.J.; Andersen, K.; Stecher, B. The Intestinal Microbiota, a Leaky Gut, and Abnormal Immunity in Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.A.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Curcumin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metzler, M.; Pfeiffer, E.; Schulz, S.I.; Dempe, J.S. Curcumin Uptake and Metabolism. Biofactors 2013, 39, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, J.; Schulte, K.L.; Lenz, T. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors in Renal Failure. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1993, 24, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachter, M. Chemical, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties of Statins: An Update. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, A.; Raj, D.S. The Gut Microbiome, Kidney Disease, and Targeted Interventions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Yuan, J.; Nazertehrani, S.; Ni, Z.; Liu, S. Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Disruption of Gastric and Small Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. CKD Impairs Barrier Function and Alters Microbial Flora of the Intestine: A Major Link to Inflammation and Uremic Toxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B.M.; Guadagnini, D.; Tsukumo, D.M.; Schenka, A.A.; Latuf-Filho, P.; Vassallo, J.; Dias, J.C.; Kubota, L.T.; Carvalheira, J.B.; Saad, M.J. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Antibiotics Improves Insulin Signalling in High-Fat Fed Mice. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesso, S.; Popolo, A.; Bianco, G.; Sorrentino, R.; Pinto, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S. The Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulphate Enhances Macrophage Response to LPS. PLoS One 2013, 8, e76778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.T.; Niu, K.C.; Chang, C.K.; Lin, M.T.; Chang, C.P. Curcumin Inhibits the Increase of Glutamate, Hydroxyl Radicals and PGE2 in the Hypothalamus and Reduces Fever during LPS-Induced Systemic Inflammation in Rabbits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 593, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalambous, B.M.; Stephens, R.C.; Feavers, I.M.; Montgomery, H.E. Role of Bacterial Endotoxin in Chronic Heart Failure: The Gut of the Matter. Shock 2007, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Turner, J.R. The Tight Junction in Inflammatory Disease: Communication Breakdown. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentala, H.; Verweij, W.R.; Huizinga-Van der Vlag, A.; van Loenen-Weemaes, A.M.; Meijer, D.K.; Poelstra, K. Removal of Phosphate from Lipid A as a Strategy to Detoxify Lipopolysaccharide. Shock 2002, 18, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalles, J.P. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase: Novel Functions and Protective Effects. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wu, H.; Lv, F. Study on the Antibiotic Activity of Microcapsule Curcumin against Foodborne Pathogens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 136, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Recent Developments in Delivery, Bioavailability, Absorption and Metabolism of Curcumin: The Golden Pigment from Golden Spice. Cancer. Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongfa, L.; Chiu, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Yen, W.; Fan-Havard, P.; Yee, L.D.; Chan, K.K. Enhancement of Curcumin Oral Absorption and Pharmacokinetics of Curcuminoids and Curcumin Metabolites in Mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Global Issue of Kidney Disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 101.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, S.S.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Ghosh, S. Curcumin and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Major Mode of Action through Stimulating Endogenous Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Molecules 2014, 19, 20139-20156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220139
Ghosh SS, Gehr TWB, Ghosh S. Curcumin and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Major Mode of Action through Stimulating Endogenous Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Molecules. 2014; 19(12):20139-20156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220139
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Siddhartha S., Todd W. B. Gehr, and Shobha Ghosh. 2014. "Curcumin and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Major Mode of Action through Stimulating Endogenous Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase" Molecules 19, no. 12: 20139-20156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220139
APA StyleGhosh, S. S., Gehr, T. W. B., & Ghosh, S. (2014). Curcumin and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Major Mode of Action through Stimulating Endogenous Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Molecules, 19(12), 20139-20156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220139




