Antibacterial Effects of Afzelin Isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, A Leading Cause of Illness in Immunocompromised Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
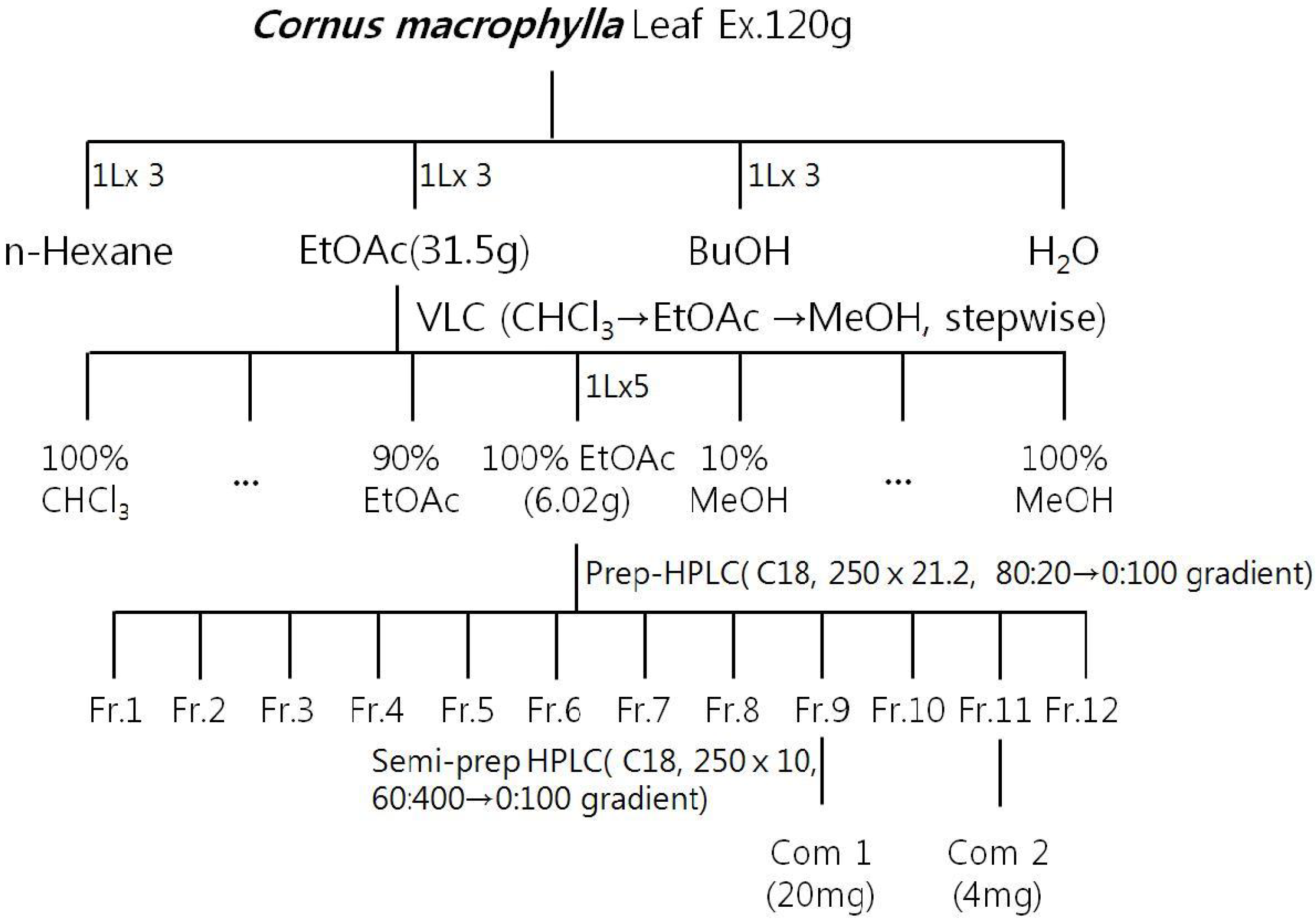
2.1. Isolation of the Active Compound from C. macrophylla and Its Structure Determination
| Fraction | Amount (μg/disc) | Clear Zone (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| n-Hexane layer | 500 | N.A. |
| EtOAc layer | 500 | 15 |
| n-BuOH layer | 500 | 13.1 |
| H2O layer | 500 | N.A. |
| Gentamicin | 10 | 16 |
| Fraction NO. | Amount (μg/disc) | Clear Zone (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 12.5 |
| 2 | 100 | N.A. |
| 3 | 100 | N.A. |
| 4 | 100 | 12 |
| 5 | 100 | N.A. |
| 6 | 100 | 12.5 |
| 7 | 100 | N.A. |
| 8 | 100 | 15 |
| 9 | 100 | N.A. |
| 10 | 100 | N.A. |
| 11 | 100 | 13 |
| 12 | 100 | N.A. |
| Gentamicin | 10 | 16 |

2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Isolated Compound against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
| Compound | Bacteria Tested |
|---|---|
| MIC (μg/mL) | |
| Quercitrin | N.A. |
| Afzelin | ≥31 |
| Kaempferol | ≥59 |
| Gentamicin | ≥5 |
3. Experimental
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Antimicrobial Test
3.5. Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC) Test
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflictts of Interest
References
- Dembry, L.M.; Roberts, J.C.; Schock, K.D.; Marino, S.P.; Farrel, P.A.; Andriole, V.T. Comparison of in vitro activity of trovafloxacin against gram-positive and gram-negative organisms with quinolones and beta-lactam antimicrobial agents. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 31, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.N.; Colón, M.; Bermúdez, R.H.; Ramírez-Ronda, C.H. Unusual presentation of pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A review. Bol. Asoc. Med. Puerto Rico 1991, 83, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack, M.; Koles, N.L.; Preston, M.J.; Brown, B.J.; Pier, G.B. Functional properties of isotype-switched immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG monoclonal antibodies to pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4481–4488. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.; Labbe, R.G. Stimulation of the onset of sporulation of Clostridium perfringens type A by netropsin and distamycin. Curr. Microbiol. 1992, 25, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, D.L. The impact of consumer demands and trends on food processing. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, P.R.; Borlawsky, T.; Kamal, J.; Saltz, J.H. A framework for workflow-based clinical research billing disambiguation. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2007, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Han, J.G.; Ha, J.H.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, M.C.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, H.Y.; Choi, G.P.; Lee, H.Y. Anticancer and immune-modulatory activities of extracts from various parts of cornus macrophylla wall. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2008, 16, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Oh, J.H. Screening of Korean forest plants for rat lens aldose reductase inhibition. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Jung, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.G.; Lee, J.; Park, D. Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of afzelin against UVB-induced cell damage. PLoS One 2013, 8, e61971. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, K.I.; Kwon, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.H.; Cho, S.H.; Chung, E.K.; Ha, S.Y.; Lee, M.W. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. BOR. Molecules 2012, 17, 11484–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.S.; Ghimeray, A.K.; Yoo, D.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Kwon, S.S.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, D.H.; Cho, J.Y. Kaempferol and kaempferol rhamnosides with depigmenting and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules 2011, 16, 3338–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, G.L.; Medeiros, A.A. Single-disk diffusion testing (Kirby-Bauer) of susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis to chloramphenicol: Significance of the intermediate category. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Park, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, B.; Jung, K.; Park, E.; Kim, J.; Park, D. In vitro antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of honokiol and magnolol against propionibacterium sp. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 496, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds assayed are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; So, Y.-J.; Shin, M.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J. Antibacterial Effects of Afzelin Isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, A Leading Cause of Illness in Immunocompromised Individuals. Molecules 2014, 19, 3173-3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033173
Lee SY, So Y-J, Shin MS, Cho JY, Lee J. Antibacterial Effects of Afzelin Isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, A Leading Cause of Illness in Immunocompromised Individuals. Molecules. 2014; 19(3):3173-3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033173
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang Yeol, Young-Jin So, Moon Sam Shin, Jae Youl Cho, and Jongsung Lee. 2014. "Antibacterial Effects of Afzelin Isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, A Leading Cause of Illness in Immunocompromised Individuals" Molecules 19, no. 3: 3173-3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033173
APA StyleLee, S. Y., So, Y.-J., Shin, M. S., Cho, J. Y., & Lee, J. (2014). Antibacterial Effects of Afzelin Isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, A Leading Cause of Illness in Immunocompromised Individuals. Molecules, 19(3), 3173-3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033173







