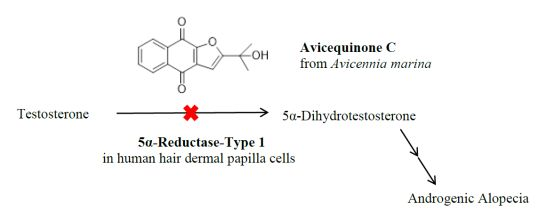
Avicequinone C Isolated from Avicennia marina Exhibits 5α-Reductase-Type 1 Inhibitory Activity Using an Androgenic Alopecia Relevant Cell-Based Assay System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Expression of 5α-R1 in HHDPCs

2.2. AM as 5α-R1 Inhibitor

2.3. TLC Profile and Activity-Guided Fraction of AM




| Position | G1 | Avicequinone C [32,33] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H(mult., J in Hz) | 13C | 1H(mult., J in Hz) | 13C | |
| 1 | - | 173.4 | - | 173.3 |
| 2 | - | 151.8 | - | 151.6 |
| 3 | - | 131.3 | - | 131.2 |
| 4 | - | 180.8 | - | 180.7 |
| 5 | 8.16 (m) | 126.9 | 8.14 (m) | 126.8 |
| 6 | 7.75 (m) | 133.9 | 7.73 (m) | 133.9 |
| 7 | 7.75 (m) | 133.7 | 7.73 (m) | 133.7 |
| 8 | 8.21 (m) | 126.8 | 8.18 (m) | 126.8 |
| 9 | - | 132.5 | - | 132.4 |
| 10 | - | 133.1 | - | |
| 1' | 6.82 (s) | 102.6 | 6.80 (s) | 102.6 |
| 2' | - | 167.9 | - | 168.1 |
| 3' | - | 69.4 | - | 69.3 |
| 4' | 1.69 (s) | 28.8 | 1.67 (s) | 28.7 |
| 5' | 1.69 (s) | 28.8 | 1.67 (s) | 28.7 |
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals, Enzymes and Reagents
3.2. Plant Material and Extraction
3.3. Culturing of HHDPCs
3.4. Checking for the Presence of 5α-R in the HHDPCs
| Name | Primer pair  | Expected size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| 5α-reductase type 1 (5α-R1) GenBank: NM_001047.2 | F:5' ACTGCATCCTCCTGGCCATGTTC 3' R:5' GGCATAGCCACACCACTCCATGA 3' | 380 |
| 5α-reductase type 2 (5α-R2) GenBank: NM_000348.3 | F:5' AAGCACACGGAGAGCCTGAA 3' R:5' GCCACCTTGTGGAATCCTGTAGC 3' | 450 |
| β-actin (internal control) GenBank: NM_001101.3 | F:5' ATGATGATATCGCCGCGCTC 3' R:5' GCGCTCGGTGAGGATCTTCA 3' | 584 |
3.5. Cytotoxicity of AM on HHDPC
3.7. TLC Profile of AM
3.8. Isolation and Structural Analysis of Bioactive Compound(s) within AM
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, F.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, H.; Xiang, W. The chemical investigations of the mangrove plant Avicennia marina and its endophytes. Open Nat. Prod. J. 2009, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liebezeit, G.; Rau, M.T. New Guinean mangroves—Traditional usage and chemistry of natural products. Senckenb. Maritima 2006, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bandaranayake, W. Traditional and medicinal uses of mangroves. Mangroves Salt Marshes 1998, 2, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod Prabhu, V.; Guruvayoorappan, C. Phytochemical screening of methanolic extract of mangrove Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. Pharm. Sin. 2012, 3, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhramani, P.S.; Vidyasagar, G.; Patel, P.M. Biological screening of Avicennia marina for anticancer activity. Pharm. Sin. 2013, 4, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Khafagi, I.; Gab-Alla, A.; Salama, W.; Fouda, M. Biological activities and phytochemical constituents of the gray mangrove Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. Egypt. J. Biol. 2003, 5, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, J.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Metabolic diversity and bioactivity screening of mangrove plants: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, A.; Wang, C.; Erickson, G. Direct inhibitory effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormone upon follicle-stimulating hormone induction of luteinizing hormone receptor and aromatase activity in rat granulosa cells. Endocrinology 1980, 106, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Dimattina, M.; Albertson, B.; Seyler, D.E.; Loriaux, D.L.; Falk, R.J. Effect of the antiprogestin RU486 on progesterone production by cultured human granulosa cells: Inhibition of the ovarian 3B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Contraception 1986, 34, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouni, F.; Godoy, A.; Li, Y.; Mohler, J. The 5 alpha-reductase isozyme family: A review of basic biology and their role in human diseases. Adv. Urol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.J. The biogenesis and growth of human hair. In Hair Toxicology—An Important Bio-Monitor; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Price, V.H. Androgenetic alopecia in women. In Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings; Nature Publishing Group: London, UK, 2003; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, Q.Q.; Sinclair, R. Female pattern hair loss: Current treatment concepts. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Stough, D.; Stenn, K.; Haber, R.; Parsley, W.M.; Vogel, J.E.; Whiting, D.A.; Washenik, K. Psychological effect, pathophysiology, and management of androgenetic alopecia in men. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Itami, S.; Inui, S. Role of androgen in mesenchymal epithelial interactions in human hair follicle. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Orfanos, C. The 5α-reductase system and its inhibitors. Dermatology 1996, 193, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bayne, E.; Flanagan, J.; Einstein, M.; Ayala, J.; Chang, B.; Azzolina, B.; Whiting, D.; Mumford, R.; Thiboutot, D.; Singer, I. Immunohistochemical localization of types 1 and 2 5-reductase in human scalp. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 141, 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Messenger, A.G. The control of hair growth: An overview. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 4S–9S. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, S.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Hwang, S.-L.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, I.-H.; Chang, S.-Y.; Rang, M.-J. The hair growth promoting effect of Asiasari radix extract and its molecular regulation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2005, 38, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, K.; Noguchi, K.; Kondo, M.; Onishi, M.; Watanabe, N.; Okamura, K.; Matsuda, H. Inhibitory activities of Puerariae Flos against testosterone 5α-reductase and its hair growth promotion activities. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 66, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud, J.-P.; Cousse, H.; Martin, P.-M. Inhibition of type 1 and type 2 5α-reductase activity by free fatty acids, active ingredients of Permixon®. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 82, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Pais, P. Potency of a novel saw palmetto ethanol extract, SPET-085, for inhibition of 5α-reductase II. Adv. Ther. 2010, 27, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.A.; Sinclair, R.; Harrap, S.B. Androgenetic alopecia: Pathogenesis and potential for therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Eicheler, W.; Dreher, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Happle, R.; Aumüller, G. Immunohistochemical evidence for differential distribution of 5α-reductase isoenzymes in human skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 133, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Hiipakka, R.A.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Dai, W.; Dai, Q.; Liao, S. Structure-activity relationships for inhibition of human 5α-reductases by polyphenols. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Naruto, S.; Asanuma, Y.; Kubo, M. Anti-androgenic and hair growth promoting activities of Lygodii Spora (Spore of Lygodium japonicum) I. Active constituents inhibiting testosterone 5alpha-reductase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 622–626. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kurashiki, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, R. Structure-activity relationship for inhibition of 5α-reductase by triterpenoids isolated from Ganoderma lucidum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8654–8660. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Rungseevijitprapa, W.; Narkkhong, N.-A.; Suttajit, M.; Chaiyasut, C. 5α-reductase inhibition and hair growth promotion of some Thai plants traditionally used for hair treatment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.; Chaiyasut, C.; Rungseevijitprapa, W.; Suttajit, M. Screening of steroid 5α-reductase inhibitory activity and total phenolic content of Thai plants. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, S.-S.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, M.-H.; Hwang, S.-L.; Rang, M.-J.; Yoon, Y.-K. The hair growth promoting effect of Sophora flavescens extract and its molecular regulation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, S.; Chauhan, N.S.; Dixit, V. Effect of Cuscuta reflexa Roxb on androgen—Induced alopecia. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, C.; Katsuno, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tan, H.; Furukawa, H. Chemical consituents of avicennia alba. isolation and structural elucidation of new naphthoquinones and their analogues. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, J.; Yuewei, G.; Huixin, H. Studies on the chemical constituents from leaves of Avicennia marina. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2004, 2, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Huang, X.; Dahse, H.-M.; Moellmann, U.; Fu, H.; Grabley, S.; Sattler, I.; Lin, W. Unusual naphthoquinone derivatives from the twigs of Avicennia marina. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 923–927. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Fukuda, M.; Kondo, R.; Sakai, K. The 5α-reductase inhibitory components from heartwood of Artocarpus incisus: Structure-activity investigations. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.-H.; Bae, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-U. 5α-reductase inhibitory components as antiandrogens from herbal medicine. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2010, 3, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.S.; Son, E.D.; Nam, G.W.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, M.S.; Lee, B.G.; Jang, I.S.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, C.H. Torilin from Torilis japonica, as a new inhibitor of testosterone 5α-reductase. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 459–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-U.; Son, H.K.; Song, H.K.; Ahn, M.-J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.K. Inhibition of 5α-reductase activity by diarylheptanoids from Alpinia officinarum. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, N.; Tokunaga, M.; Naruto, S.; Iinuma, M.; Matsuda, H. Testosterone 5α-reductase inhibitory active constituents of Piper nigrum leaf. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 2402–2405. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Sample of the compound avicequinone C is available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, R.; Monthakantirat, O.; Tengamnuay, P.; De-Eknamkul, W. Avicequinone C Isolated from Avicennia marina Exhibits 5α-Reductase-Type 1 Inhibitory Activity Using an Androgenic Alopecia Relevant Cell-Based Assay System. Molecules 2014, 19, 6809-6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056809
Jain R, Monthakantirat O, Tengamnuay P, De-Eknamkul W. Avicequinone C Isolated from Avicennia marina Exhibits 5α-Reductase-Type 1 Inhibitory Activity Using an Androgenic Alopecia Relevant Cell-Based Assay System. Molecules. 2014; 19(5):6809-6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056809
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Ruchy, Orawan Monthakantirat, Parkpoom Tengamnuay, and Wanchai De-Eknamkul. 2014. "Avicequinone C Isolated from Avicennia marina Exhibits 5α-Reductase-Type 1 Inhibitory Activity Using an Androgenic Alopecia Relevant Cell-Based Assay System" Molecules 19, no. 5: 6809-6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056809
APA StyleJain, R., Monthakantirat, O., Tengamnuay, P., & De-Eknamkul, W. (2014). Avicequinone C Isolated from Avicennia marina Exhibits 5α-Reductase-Type 1 Inhibitory Activity Using an Androgenic Alopecia Relevant Cell-Based Assay System. Molecules, 19(5), 6809-6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056809