MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for the Simultaneous Location of Resveratrol, Pterostilbene and Viniferins on Grapevine Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Stilbene Analyses by MALDI-TOFMS
2.1.1. Matrix Selection for Stilbene Analyses by MALDI-TOFMS
| Ion mode | Matrix | S/N ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| trans-Resveratrol | Pterostilbene | trans-δ-Viniferin | ||
| Negative | without | 307 | 166 | / |
| 9-AA | 68 | 114 | 11 | |
| DAN | 349 | 230 | N/A | |
| CHCA | / | / | / | |
| THAP | / | / | / | |
| DHB | / | / | / | |
| Positive | without | 91 | 451 | / |
| DAN | / | / | / | |
| DAN+TFA | / | / | / | |
| DHB | 25 | 55 | 139/145 * | |
| DHB+TFA | 259 | 358 | 231/239 * | |
| CHCA | N/A | 246 | 146 * | |
| CHCA+TFA | N/A | 708 | 501 * | |
| THAP | / | / | / | |
| THAP+TFA | 38 | / | 44 | |
| 9-AA | / | / | / | |
2.1.2. MALDI-TOFMS Analysis of Stressed Leaf Extract
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | [M-H]− | Precursor Ion | MS/MS (CID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-piceid | 13.01 | C16H15O3− | 389 | 228(100) |
| trans-piceid | 13.68 | C16H15O3− | 389 | 228(100) |
| cis-ε-viniferin | 17.02 | C28H21O6− | 453 | 435(20); 411(10); 369(12); 359(42); 347(100); 333(44) |
| trans-ε-viniferin | 18.07 | C28H21O6− | 453 | 435(24); 411(14); 359(100); 347(58); 333(18) |
| trans-δ-viniferin | 21.60 | C28H21O6− | 453 | 435(22); 411(15); 359(100); 347(40); 333(8) |
| cis-δ-viniferin | 22.65 | C28H21O6− | 453 | 435(100); 411(68); 369(62); 359(38); 347(40) ; 333(50); 317(14); 307(20); 267(12); 251(13) |
| trans-resveratrol | 42.72 | C14H11O3− | 227 | 185(100); 183(38); 159(32); 157(29); 143(11) |
| trans-pterostilbene | 47.94 | C14H11O3- | 255 | 240(100); 239(5) |


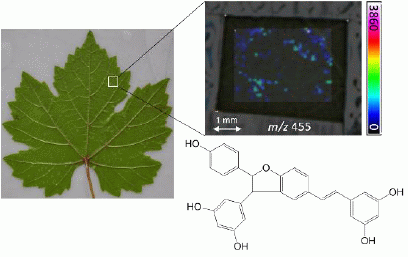
2.2. In-Situ MALDI-MSI of Stilbenes on Stressed Leaves



3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Material and Leaf Sample Preparation
3.2. Leaf Extraction
3.3. Standard and Solvents
3.4. LC-MS and MS/MS
3.5. MALDI Mass Spectrometer
3.6. Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glinski, M.; Weckwerth, W. The role of mass spectrometry in plant systems biology. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 173–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, R.M.; Farmer, T.B.; Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: Localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, L.A.; Heeren, R.M.A. Imaging mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 606–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurand, P. Imaging mass spectrometry of thin tissue sections: A decade of collective efforts. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 4883–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.M.; Caprioli, R.M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization imaging mass spectrometry: In situ molecular mapping. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2013, 52, 3818–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassl, J.; Taylor, N.L.; Millar, A.H. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging and its development for plant protein imaging. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 21–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquenazi, E.; Yang, Y.-L.; Watrous, J.; Gerwick, W.H.; Dorrestein, P.C. Imaging mass spectrometry of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Perdian, D.C.; Song, Z.; Yeung, E.S.; Nikolau, B.J. Use of mass spectrometry for imaging metabolites in plants. Plant J. 2012, 70, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnholt, N.; Li, B.; D’Alvise, J.; Janfelt, C. Mass spectrometry imaging of plant metabolites – principles and possibilities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 818–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, C.; Hanley, L. Ion sources for mass spectrometric identification and imaging of molecular species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matros, A.; Mock, H.-P. Mass spectrometry based imaging techniques for spatially resolved analysis of molecules. Front. Plant Sic. 2013, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, G.; Carré, V.; Poutaraud, A.; Maunit, B.; Frache, G.; Merdinoglu, D.; Muller, J.-F. Determination and imaging of metabolites from Vitis vinifera leaves by laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Douillet-Breuil, A.-C.; Bessis, R.; Debord, S.; Sbaghi, M.; Adrian, M. Phytoalexins from the Vitaceae: Biosynthesis, phytoalexin gene expression in transgenic plants, antifungal activity, and metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Poutaraud, A.; Hugueney, P. Metabolism and roles of stilbenes in plants. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Villaverde, V.; Voinesco, F.; Viret, O.; Spring, J.-L.; Gindro, K. The effectiveness of stilbenes in resistant Vitaceae: Ultrastructural and biochemical events during Plasmopara viticola infection process. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Delaunois, B.; Conreux, A.; Donnez, D.; Nuzzo, V.; Cordelier, S.; Clément, C.; Courot, E. Biosynthesis, metabolism, molecular engineering, and biological functions of stilbene phytoalexins in plants. BioFactors 2010, 36, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Delaunois, B.; Aziz, A.; Donnez, D.; Vasserot, Y.; Cordelier, S.; Courot, E. Metabolic engineering of yeast and plants for the production of the biologically active hydroxystilbene, resveratrol. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Clément, C.; Courot, E.; Cordelier, S. Modulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis in engineered plants for disease resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14136–14170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langcake, P.; Pryce, R.J. A new class of phytoalexins from grapevines. Experientia 1977, 33, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langcake, P.; Pryce, R.J. The production of resveratrol and the viniferins by grapevines in response to ultraviolet irradiation. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Breuil, A.C.; Adrian, M.; Weston, L.A.; Debord, S.; Meunier, P.; Maume, G.; Bessis, R. HPLC analysis of grapevine phytoalexins coupling photodiode array detection and fluorometry. Anal Chem. 1997, 69, 5172–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezet, R.; Gindro, K.; Viret, O.; Spring, J.-L. Glycosylation and oxidative dimerization of resveratrol are respectively associated to sensitivity and resistance of grapevine cultivars to downy mildew. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 65, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnee, S.; Viret, O.; Gindro, K. Role of stilbenes in the resistance of grapevine to powdery mildew. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 72, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattivi, F.; Vrhovsek, U.; Malacarne, G.; Masuero, D.; Zulini, L.; Stefanini, M.; Moser, C.; Velasco, R.; Guella, G. Profiling of resveratrol oligomers, important stress metabolites, accumulating in the leaves of hybrid vitis vinifera (merzling × teroldego) genotypes infected with plasmopara viticola. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5364–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezet, R.; Perret, C.; Jean-Denis, J.B.; Tabacchi, R.; Gindro, K.; Viret, O. δ-Viniferin, a Resveratrol dehydrodimer: One of the major stilbenes synthesized by stressed grapevine leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5488–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezet, R.; Gindro, K.; Viret, O.; Richter, H. Effects of resveratrol, viniferins and pterostilbene on Plasmopara viticola zoospore mobility and disease development. Vitis 2004, 43, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, M.; Jeandet, P. Effects of resveratrol on the ultrastructure of Botrytis cinerea conidia and biological significance in plant/pathogen interactions. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, S.; Peukert, M.; Svatos, A.; Matros, A.; Mock, H.-P. MALDI-imaging mass spectrometry — An emerging technique in plant biology. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrkoslav, V.; Muck, A.; Cvačka, J.; Svatoš, A. MALDI imaging of neutral cuticular lipids in insects and plants. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Gemperline, E.; Venkateshwaran, M.; Chen, R.; Delaux, P.-M.; Howes-Podoll, M.; Ané, J.-M.; Li, L. MALDI mass spectrometry-assisted molecular imaging of metabolites during nitrogen fixation in the Medicago truncatula–Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiosis. Plant J. 2013, 75, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Zee, O.P. Direct analysis for the distribution of toxic glycoalkaloids in potato tuber tissue using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Warburton, K.; Seymour, M.; Clench, M.; Thomas-Oates, J. Localization of water-soluble carbohydrates in wheat stems using imaging matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, M.M.; Earnshaw, C.J.; Clench, M.R. Imaging matrix assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry: A technique to map plant metabolites within tissues at high spatial resolution. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Zhang, H.; Ilarslan, H.I.; Wurtele, E.S.; Brachova, L.; Nikolau, B.J.; Yeung, E.S. Direct profiling and imaging of plant metabolites in intact tissues by using colloidal graphite-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Plant J. 2008, 55, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, L.; de Rosso, M.; Panighel, A.; Vedova, A.D.; Flamini, R.; Traldi, P. Collisionally induced fragmentation of [M–H]− species of resveratrol and piceatannol investigated by deuterium labelling and accurate mass measurements. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, F.; di Donna, L.; Benabdelkamel, H.; Gabriele, B.; Napoli, A.; Sindona, G. The assay of pterostilbene in spiked matrices by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and isotope dilution method. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 358–363. [Google Scholar]
- Poutaraud, A.; Latouche, G.; Martins, S.; Meyer, S.; Merdinoglu, D.; Cerovic, Z.G. Fast and local assessment of stilbene content in grapevine leaf by in vivo fluorometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Denis, J.B.; Pezet, R.; Tabacchi, R. Rapid analysis of stilbenes and derivatives from downy mildew-infected grapevine leaves by liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure photoionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1112, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, L.; Carré, V.; Poutaraud, A.; Merdinoglu, D.; Chaimbault, P. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for the Simultaneous Location of Resveratrol, Pterostilbene and Viniferins on Grapevine Leaves. Molecules 2014, 19, 10587-10600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710587
Becker L, Carré V, Poutaraud A, Merdinoglu D, Chaimbault P. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for the Simultaneous Location of Resveratrol, Pterostilbene and Viniferins on Grapevine Leaves. Molecules. 2014; 19(7):10587-10600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710587
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Loïc, Vincent Carré, Anne Poutaraud, Didier Merdinoglu, and Patrick Chaimbault. 2014. "MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for the Simultaneous Location of Resveratrol, Pterostilbene and Viniferins on Grapevine Leaves" Molecules 19, no. 7: 10587-10600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710587
APA StyleBecker, L., Carré, V., Poutaraud, A., Merdinoglu, D., & Chaimbault, P. (2014). MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for the Simultaneous Location of Resveratrol, Pterostilbene and Viniferins on Grapevine Leaves. Molecules, 19(7), 10587-10600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710587