Synthesis and in Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of New N-Heterocyclic Diquaternary Pyridinium Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis


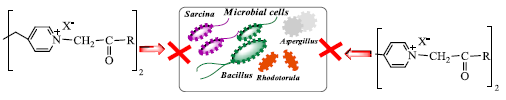
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
| MO | 4a | 4b | 4c | 4d | 5a | 5b | 5c | 5d | H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | 35.00 ± 0.57 | 30.33 ± 0.33 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 40.83 ± 0.44 | 41.33 ± 0.33 | 45.00 ± 0.57 | 19.83 ± 0.44 | 25.33 ± 0.33 | 0 |
| B cereus | 41.66 ± 0.33 | 43.00 ± 0.57 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 37.33 ± 0.33 | 35.50 ± 0.28 | 50.50 ± 0.28 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 21.16 ± 0.16 | 0 |
| S. lutea | 22.33 ± 0.33 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 41.00 ± 0.57 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 46.00 ± 0.57 | 45.33 ± 0.33 | 21.50 ± 0.28 | 41.50 ± 0.28 | 0 |
| S. cerevisiae | 22.00 ± 0.57 | 22.66 ± 0.66 | 19.66 ± 0.66 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 23.16 ± 0.16 | 19.33 ± 0.16 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 0 |
| C. utilis | 22.66 ± 0.66 | 22.50 ± 0.28 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 22.66 ± 0.66 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 0 |
| R. glutinis | 40.33 ± 0.33 | 35.33 ± 0.33 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 19.83 ± 0.44 | 19.66 ± 0.33 | 53.50 ± 0.28 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 19.50 ± 0.50 | 0 |
| A. niger | 19.66 ± 0.66 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.83 ± 0.44 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 32.33 ± 0.33 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 0 |
| P. roqueforti | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.50 ± 0.28 | 0 |
| G. candidum | 20.00 ± 0.57 | 21.66 ± 0.66 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 19.33 ± 0.16 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 33.16 ± 0.16 | 19.16 ± 0.16 | 19.33 ± 0.33 | 0 |
| Compound | mp (°C) | LogP | Polar surface area (Å2) | van der Waals surface area (Å2) | Polarizability | Hydrophobicity (RM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | >250 | −3.4 | 133.5 | 711.4 | 52.5 | 2.091 ± 0.027 |
| 4b | 241–243 | −3.6 | 60.3 | 730.7 | 53.6 | 2.325 ± 0.014 |
| 4c | >300 | −3.0 | 94.5 | 732.4 | 59.5 | 2.122 ± 0.047 |
| 4d | >300 | −3.2 | 68.2 | 707.4 | 57.6 | 1.938 ± 0.023 |
| 5a | 258–259 | −4.3 | 133.5 | 652.1 | 50.3 | 1.739 ± 0.035 |
| 5b | 252–253 | −4.5 | 60.3 | 667.1 | 51.6 | 2.142 ± 0.024 |
| 5c | >300 | −3.9 | 94.5 | 671.0 | 57.3 | 1.917 ± 0.049 |
| 5d | 301–302 | −4.1 | 68.2 | 646.0 | 55.4 | 2.092 ± 0.023 |


3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Determination of Molecular Hydrophobicity
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.H.; Sun, G. Functional finishing of acrylic and cationic dyeable fabrics: Intermolecular interactions. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 1052–056. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Sun, G. Antimicrobial finishing of acrilan fabrics with cetylpyridinium chloride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Son, Y.A.; Sun, G. Durable antimicrobial Nylon 66 fabrics: Ionic interactions with quaternary ammonium salts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Yoshizako, F.; Tsuchido, T. Characterization of a cationic surfactant-resistant mutant isolated spontaneously from Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Whang, H.S.; Ko, S. Synthesis of a quaternary ammonium derivative of chito-oligosaccharide as antimicrobial agent for cellulosic fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Augusta, S.; Gruber, H.F.; Streichsbier, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of immobilized quaternary ammonium salts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 53, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Isquith, A.; Abbot, A.; Walters, P.A. Surface-bonded antimicrobial activity of an organosilicon quaternary ammonium chloride. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 859–863. [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Calas, M.; Bonhoure, A.; Herbute, S.; Vial, H.J. In vivo antimalarial activities of mono-and bis quaternary ammonium salts interfering with Plasmodium phospholipid metabolism. Antimicrob. Agents Ch. 2003, 47, 2598–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanawanno, K.; Chantrapromma, S.; Anantapong, T.; Kanjana-Opas, A.; Fun, H.-K. Synthesis, structure and in vitro antibacterial activities of new hybrid disinfectants quaternary ammonium compounds: Pyridinium and quinolinium stilbene benzenesulfonates. Eur.J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4199–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammeri, H.; Nordmann, P. Extended-spectrum cephalosporinases in Enterobacteriaceae. Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 6, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Obando, D.; Pantarat, N.; Handke, R.; Koda, Y.; Widmer, F.; Djordjevic, J.T.; Ellis, D.H.; Sorrell, T.C.; Jolliffe, K.A. Synthesis, antifungal, haemolytic and cytotoxic activities of a series of bis(alkylpyridinium)alkanes. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6329–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourai, H.; Yabuhara, T.; Shirai, A.; Maeda, T.; Nagamune, H. Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of a series of new bis-quaternary ammonium compounds. Eur.J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.N.; Zhou, X.R.; Xing, X.D.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, Z. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) grafted cellulose fiber: Preparation and antimicrobial function. Acta Polym. Sin. 2004, 14, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchese, A.M.; Marzorati, L. Catálise de transferência de fase. Quim. Nova 2000, 23, 641–652. [Google Scholar]
- Tehfe, M.-A.; Zein-Fakiha, A.; Lalevée, J.; Dumur, F.; Gigmes, D.; Graff, B.; Morlet-Savarya, F.; Hamieh, T.; Fouassier, J.-P. New pyridinium salts as versatile compounds for dye sensitized photopolymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Pernak, J.; Rogoza, J. Synthesis of 3-substituted pyridinium salts. ARKIVOC 2000, 1, 889–904. [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier, H. Asymmetric 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 3235–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Causin, V.; Saielli, G. Effect of a structural modification of the bipyridinium core on the phase behaviour of, viologen-based bistriflimide salts. J. Mol. Liq. 2009, 145, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rowley, N.M.; Mortimer, R.J. New electrochromic materials. Sci. Progr. London 2002, 85, 243–262. [Google Scholar]
- Pisarenko, S.V.; Demidov, O.P.; Aksenov, A.V.; Borovlev, I.V. Synthesis and hydroxylation of 1-alkyl- and 7-alkyl- 1,3,7-triazapyrenium salts. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2009, 45, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- Furdui, B.; Dinica, R.M.; Tabacaru, A.; Pettinari, C. Synthesis and physico-chemical properties of a novel series of aromatic electron acceptors based on N-heterocycles. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 6164–6168. [Google Scholar]
- Dinica, R.; Furdui, B.; Bahrim, G.; Demeunynck, M. Precurseurs de nouveaux heterocycles d’intéret biologique. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2008, 53, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shuchismita, D.; Adhikary, K.K.; Kim, C.K.; Lee, B.-S.; Lee, H.W. Nucleophilic substitution reactions of α-chloroacetanilides with pyridines in dimethyl sulfoxide. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, 26, 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Furdui, B.; Bahrim, G; Dinica, R.; Druţă, I.; Demeunynck, M. In vitro antimicrobial activity of new nitrogen heterocycles derivates from 4,4'-bipyridine. Rom. Biotech. Lett. 2007, 12, 3073–3078. [Google Scholar]
- Furdui, B.; Constantin, O.; Tabacaru, A.; Dinica, R. New bis-pyridinium diquaternary salts with antimicrobial properties. Rev. Chim. 2012, 63, 667–671. [Google Scholar]
- Piddoc, L.-J.V. Techniques used for the determination of antimicrobial resistance and sensitivity in bacteria. J. Appl. Bactriol. 1990, 68, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Englera, A.C.; Wiradharmab, N.; Ongb, Z.Y.; Coadya, D.J.; Hedricka, J.L.; Yang, Y.-Y. Emerging trends in macromolecular antimicrobials to fight multi-drug-resistant infections. Nano Today 2012, 7, 201–222. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wan, H. Studies on mechanism of action of anticancer peptides by modulation of hydrophobicity within a defined structural framework. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, R. Theoretical Drug Design Method; Elsevier Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 30–79. [Google Scholar]
- Calculator Plugins were used for structure property prediction and calculation, Marvin 6.0.2, 2013, ChemAxon. Available online: http://www.chemaxon.com accessed (accessed on 13 June 2014).
- Furdui, B.; Constantin, O.; Dinica, R.; Bahrim, G.; University “Dunarea de Jos” of GalaÅ£i, GalaÅ£i, Romania. Unpublished work. 2012.
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Furdui, B.; Parfene, G.; Ghinea, I.O.; Dinica, R.M.; Bahrim, G.; Demeunynck, M. Synthesis and in Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of New N-Heterocyclic Diquaternary Pyridinium Compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 11572-11585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811572
Furdui B, Parfene G, Ghinea IO, Dinica RM, Bahrim G, Demeunynck M. Synthesis and in Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of New N-Heterocyclic Diquaternary Pyridinium Compounds. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11572-11585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811572
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurdui, Bianca, Georgiana Parfene, Ioana Otilia Ghinea, Rodica Mihaela Dinica, Gabriela Bahrim, and Martine Demeunynck. 2014. "Synthesis and in Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of New N-Heterocyclic Diquaternary Pyridinium Compounds" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11572-11585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811572
APA StyleFurdui, B., Parfene, G., Ghinea, I. O., Dinica, R. M., Bahrim, G., & Demeunynck, M. (2014). Synthesis and in Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of New N-Heterocyclic Diquaternary Pyridinium Compounds. Molecules, 19(8), 11572-11585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811572