Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and Icariside II in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
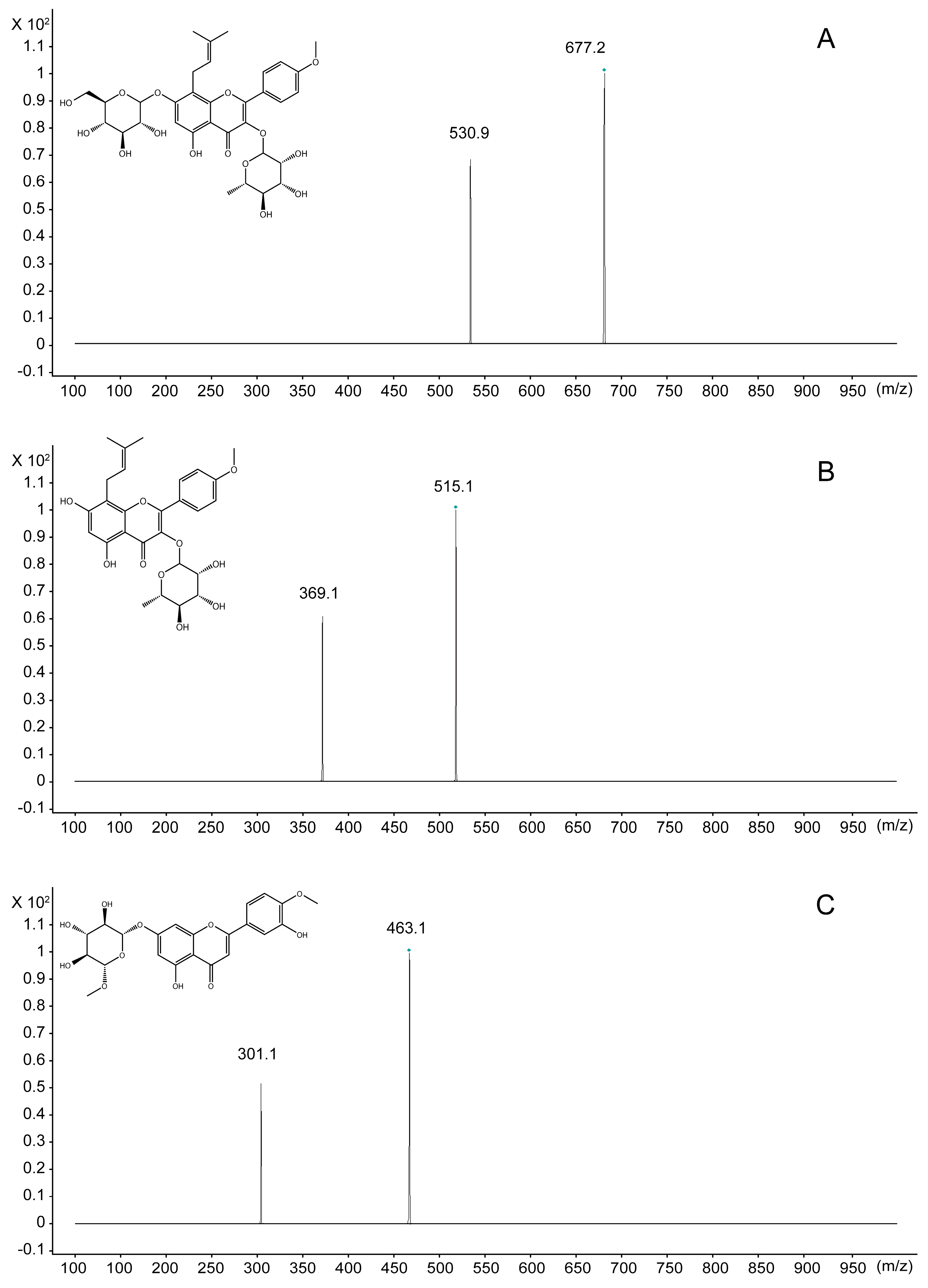
2.2. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Specificity and Selectivity

2.3.2. Calibration and LLOQ
2.3.3. Assay Precision and Accuracy
| Intra-Day (n = 6) | ||||||
| Added (ng/mL) | Founded (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (RE %) | |||
| ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | |
| 5.16 | 5.00 ± 0.16 | 5.27 ± 0.26 | 3.2 | 4.8 | −3.0 | 2.1 |
| 103.2 | 106.4 ± 0.9 | 101.4 ± 4.8 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 3.1 | −1.8 |
| 516.0 | 520.6 ± 2.0 | 521.9 ± 2.8 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| 1032 | 1082 ± 12 | 1052 ± 17 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 4.8 | 2.0 |
| Inter-day (n = 6 Series per day, 6 days) | ||||||
| Added (ng/mL) | Founded (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (RE %) | |||
| ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | |
| 5.16 | 5.02 ± 0.15 | 5.31 ± 0.33 | 3.0 | 6.2 | −2.8 | 3.0 |
| 103.2 | 106.9 ± 2.9 | 102.1 ± 5.9 | 2.7 | 5.8 | 3.6 | −1.1 |
| 516.0 | 513.4 ± 6.0 | 518.6 ± 12.8 | 1.2 | 2.5 | −0.5 | 0.5 |
| 1032 | 1052 ± 24 | 1031 ± 48 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 2.0 | −0.1 |
2.3.4. Recovery and Matrix Effects
| Concentration (ng/mL) | ME (%) | RSD (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | |
| 5.16 | 114.1 | 91.6 | 4.0 | 2.7 |
| 103.2 | 112.6 | 99.0 | 3.4 | 1.3 |
| 516.0 | 114.3 | 101.7 | 3.2 | 3.7 |
| 1032 | 112.4 | 104.9 | 3.1 | 3.7 |
| Concentration (ng/mL) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | ICA II | ICA | ICA II | |
| 5.16 | 86.2 | 89.7 | 14.2 | 14.0 |
| 103.2 | 88.4 | 99.0 | 3.3 | 9.6 |
| 516.0 | 97.5 | 101.7 | 2.4 | 6.9 |
| 1032 | 101.8 | 105.8 | 3.2 | 7.7 |
2.3.5. Stability of ICA and ICA II
| Compound | Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (RE %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Preparative 4 °C, for 24 h | Short-Term 25 °C, for 24 h | Freezing-Thawing −20 °C, 3 cycles | Long-Term −20 °C, 2 month | ||
| ICA | 5.16 | 93.8 | 106.6 | 95.2 | 89.3 |
| 103.2 | 104.2 | 111.6 | 106.8 | 105.5 | |
| 516.0 | 97.5 | 103.7 | 101.5 | 101.0 | |
| 1032 | 104.1 | 102.2 | 108.6 | 96.8 | |
| ICA II | 5.16 | 98.2 | 102.8 | 93.9 | 84.0 |
| 103.2 | 106.1 | 95.4 | 105.4 | 93.7 | |
| 516.0 | 98.7 | 92.0 | 96.6 | 89.7 | |
| 1032 | 103.1 | 87.0 | 100.5 | 88.4 | |
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
| Parameters | Oral Administration of ICA | Oral Administration of ICA II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | ICA II | ICA II | |
| Tmax (min) | 15.0 ± 0.0 | 147.0 ± 17.1 | 24.0 ± 13.4 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 27.2 ± 5.4 | 29.6 ± 6.8 | 103.6 ± 29.3 |
| t1/2z (min) | 73.9 ± 107.4 | 261.7 ± 185.9 | 135.0 ± 127.4 |
| CL (L/min/kg) | 46.2 ± 6.0 | 4.98 ± 1.76 | 3.68 ± 1.02 |
| MRT0-t (min) | 67.9 ± 54.0 | 271.3 ± 43.4 | 153.1 ± 68.6 |
| MRT0-∞ (min) | 83.1 ± 60.8 | 330.5 ± 107.1 | 189.4 ± 99.8 |
| AUC0-t (ng/mL × min) | 642.7 ± 83.2 | 6403 ± 2146 | 8387 ± 2539 |
| AUC0-∞ (ng/mL × min) | 657.8 ± 80.4 | 6601 ± 2067 | 8711 ± 2579 |
| Parameters | Intravenous Injection of ICA | Intravenous Injection of ICA II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | ICA II | ICA II | |
| Tmax (min) | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.0 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 3.543 × 104. ± 1.026 × 104 | 79.8 ± 22.4 | 4292 ± 1364 |
| T1/2z (min) | 319.8 ± 339.0 | 118.1 ± 57.3 | 281.9 ± 322.0 |
| MRT0-t (min) | 27.4 ± 5.9 | 87.3 ± 47.8 | 98.4 ± 42.1 |
| MRT0-∞ (min) | 33.0 ± 14.3 | 91.5 ± 47.8 | 230.8 ± 314.3 |
| AUC0-t (ng/mL × min) | 6.942 × 105 ± 1.700 × 105 | 2997 ± 1000 | 1.962 × 105 ± 6.328 × 105 |
| AUC0-∞ (ng/mL × min) | 6.954 × 105 ± 1.687 × 105 | 3013 ± 1002 | 2.111 × 105 ± 4.906 × 104 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Apparatus and Analytical Condition
3.3. Preparation of Standard and Quality Control (QC) Samples
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.5. Assay Validation
3.5.1. Specificity and Selectivity
3.5.2. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.5.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.5.4. Recovery and Matrix Effects
3.5.5. Stability
3.6. Animal Protocol and Pharmacokinetic Study
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Xing, W.W.; Li, Y.S.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.; Qin, L.P. Effects of a traditional chinese herbal preparation on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Maturitas 2008, 61, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, R.H.; Wang, X.J. Study on effect of combination of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus on osteoporosis rats induced by retinoic acid. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2013, 38, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.K.; Guo, X.; Pan, Y.L.; Niu, Y.B.; Li, C.R.; Wu, X.L.; Mel, Q.B. A systematic review of the efficacy and pharmacological profile of Herba Epimedii in osteoporosis therapy. Pharmazie 2013, 68, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Mun, Y.J.; Im, S.J.; Han, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Woo, W.H. Effects of the aqueous extract of epimedii herba on the antibody responses in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.K.; Yeun, J.M.; Sook, J.I.; Seung, Y.L.; Sung, W.L.; Won, H.W. Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Epimedii Herba on the Induction of Oral Tolerance in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Gong, Y.; Xie, G.Y.; Liu, H.R.; Qi, M.Y. Protective effect of total flavonoids of herba epimedii on testis degeneration in diabetic mice. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2013, 29, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xin, H.; Liu, T.; Li, G.Y.; Gao, Z.Z.; Liu, J.; Li, W.R.; Cui, W.S.; Bai, G.Y.; Park, N.C.; et al. Effects of icariside II on improving erectile function in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J. Androl. 2012, 33, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.Y.; Kai, C.; Liu, H.R.; Su, Y.H.; Yu, S.Q. Protective effect of Icariin on the early stage of experimental diabetic nephropathy induced by streptozotocin via modulating transforming growth factor β1 and type IV collagen expression in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, P.; Gao, A.; Wang, L.; Ji, L. The Cardioprotective Effect of Icariin on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart: Potential Involvement of the PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 33, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China. Part 1; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 306–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, K.; Yan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L. Effects and mechanisms of icariin on atherosclerosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jung, H.W.; Park, Y.K. Effects of Icariin on insulin resistance via the activation of AMPK pathway in C2C12 mouse muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 758, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, K.; Zhao, F. Icariin regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells through microRNA-21 by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xu, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, F.; Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Tao, J.; Dong, J. Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation. Neuroscience 2015, 294, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Luo, X.Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Wu, W.; Liu, C.M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, S.Y. The antioxidative effect of icariin in human erythrocytes against free-radical-induced haemolysis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, P.; Huang, Y. Icariside II promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells in beagle canine. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4367–4377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Shu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, X.; Sun, E.; Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Jia, X. Reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway is involved in baohuoside I-induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 199, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Jeong, S.J.; Kwon, T.R.; Jung, J.H.; Yun, S.M.; Han, I.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, D.K.; Kang, M.; et al. Janus activated kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway mediates icariside II-induced apoptosis in u266 multiple myeloma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, B. Baohuoside I suppresses invasion of cervical and breast cancer cells through the downregulation of cxcr4 chemokine receptor expression. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 7562–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Ping, G.; Geng, L.; Seow, W.K.; Thong, Y.H. Immunopharmacology and toxicology of the plant flavonoid baohuoside-1 in mice. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1994, 16, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qin, X.C.; Li, W.R.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.Y.; Xin, H.; Gong, Y.Q.; Xin, Z.C. Effects of icariin and icariside II on enos expression and nos activity in porcine aorta endothelial cells. Journal of Peking University. Health Sci. 2011, 43, 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, H.; Lan, Y.; Xi, W.; Tian, L.Z.; Kui, W. Icaritin and its glycosides enhance osteoblastic, but suppress osteoclastic, differentiation and activity in vitro. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 832–840. [Google Scholar]
- Dawei, Z.; Jin, C.Z.; Chi, C.F.; Xin, S.Y.; Meng, S.Y. Herba epimedii flavonoids suppress osteoclastic differentiation and bone resorption by inducing G2/M arrest and apoptosis. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.C.; Peng, F.T.; Yong, J.; Yi, T.W.; Shao, P.L. Effect of stability of internal standard on quantification of 15 flavonoids in Epimedium using CZE. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Chena, X.J.; Guo, B.L.; Li, S.P.; Zhang, Q.W.; Tu, P.F.; Wang, Y.T. Simultaneous determination of 15 flavonoids in Epimedium using pressurized liquid extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, S.; Shih, P.W.; Jun, L.; Yong, E.L. Simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for simultaneous measurement of five Epimedium prenylflavonoids in rat sera. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.W.; Jin, L.Z.; Tong, H.Z.; Bao, L.G.; Yi, L.W.; Jin, F.H. Simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in dog plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a bioequivalence study of bioactive components in Herba Epimedii and Er-Xian Decoction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Ya, P.Z.; Ming, Y.; Zi, Y.S.; Xin, M.Z.; Wei, D.Z.; Hai, Y.L. LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of icariin and its major metabolites in rat plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.; Yi, H.M.; Zhong, Z.; Yan, C.; Ying, W.; Xia, G. Intestinal absorption and metabolism of Epimedium Flavonoids in Osteoporosis Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, X.; Tan, X.; Hu, M. Role of intestinal hydrolase in the absorption of prenylated flavonoids present in Yinyanghuo. Molecules 2011, 16, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Fan, M.; Fan, L.; Sun, J.; Guo, D. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of metabolites in rats after administration of prenylflavonoids from Epimediums. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, D.; Ming, P.; Tong, Z.; Jian, S.T.; Zhen, Z.C.; Yong, Z. Quantification of conjugated metabolites of drugs in biological matrices after the hydrolysis with β-glucuronidase and sufatase: A review of bio-analytical methods. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds icariin and icariside II are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lu, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y. Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and Icariside II in Rats. Molecules 2015, 20, 21274-21286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219763
Cheng T, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Lu L, Ding Y, Zhao Y. Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and Icariside II in Rats. Molecules. 2015; 20(12):21274-21286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219763
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Tao, Yong Zhang, Tong Zhang, Lu Lu, Yue Ding, and Yuan Zhao. 2015. "Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and Icariside II in Rats" Molecules 20, no. 12: 21274-21286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219763
APA StyleCheng, T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., Lu, L., Ding, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2015). Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and Icariside II in Rats. Molecules, 20(12), 21274-21286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219763






