Abstract
Mesoporous titanium dioxide materials were prepared using a nanocasting technique involving silica SBA-15 as the hard-template. At an optimal loading of titanium precursor, the hexagonal periodic array of pores in SBA-15 was retained. The phases of titanium dioxide could be easily varied by the number of impregnation cycles and the nature of titanium alkoxide employed. Low number of impregnation cycles produced mixed phases of anatase and TiO2(B). The mesoporous TiO2 materials were tested for solar hydrogen production, and the material consisting of 98% anatase and 2% TiO2(B) exhibited the highest yield of hydrogen from the photocatalytic splitting of water. The periodicity of the pores was an important factor that influenced the photocatalytic activity. This study indicates that mixed phases of titania containing ordered array of pores can be prepared by using the nanocasting strategy.
Keywords:
nanocasting; hard-template; titanium dioxide; TiO2; mesoporous; periodic; hexagonal; TiO2(B); hydrogen production; water-splitting 1. Introduction
Titanium dioxide has been extensively studied because of its relative ease of synthesis, benign nature, and photocorrosion stability compared with other semiconductors, such as ZnO, etc. [1,2]. Titania has been employed in various applications, such as solar energy utilization for water splitting, as active material in dye-sensitized solar cells, for environmental remediation of pollutants, elimination of bacteria, bio-medical arenas, and electrochromic applications [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Porous titanium dioxide is favorable in applications involving mass transfer, such as photocatalysis. Many synthetic routes have been attempted for forming mesoporous titanium dioxide, such as room-temperature drying [9,10], low-temperature supercritical drying [11,12,13,14,15], high-temperature supercritical drying [16,17], hydrothermal [18,19,20], Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly (EISA) [21,22,23], microwave [24,25], nanocasting employing soft template [26], and hard template [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The room-temperature drying of titanium dioxide gel to form a xerogel involves long evaporation time period with pores that are non-uniform in nature; therefore, this synthetic method is of little use in forming periodic array of pores [9,10]. The low-temperature supercritical drying (LT-SCD) method forms an aerogel with favorable textural properties compared to the room-temperature prepared xerogel titanium dioxide material [11,12,13,14,15]. The low-temperature supercritical drying method forms titanium dioxide of lower crystallinity in general compared to the high-temperature supercritical drying method [16,17]. However, the challenge with the high-temperature supercritical drying (HT-SCD) process is the use of expensive apparatus and issues concerning safety. In comparison to the HT-SCD method, the hydrothermal or solvothermal method could form mesoporous titanium dioxide in a relatively shorter period of time [18,19,20]. The hydrothermal synthetic method produces titanium dioxide of similar crystallinity as the high-temperature aerogel method, but the pores have random arrangement. The Evaporation-Induced Self Assembly (EISA) synthesis might be an alternative to the synthetic methods discussed thus far [21,22,23]. However, the EISA synthesis method requires removing surfactants or templates using elevated temperatures in air [41]. The result of removing surfactants at high temperatures invariably leads to aperiodic porous structures, especially when cationic surfactants, such as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), are used. The microwave synthesis might be favorable with its short synthesis time period, but the pore structure of titanium dioxide will be random in nature [24,25]. As discussed above, many of these methods do not necessarily lead to the formation of nanomaterials with periodic and regular arrangement of pores. This is particularly difficult when attempting to prepare titanium dioxide with periodic arrangement of pores. This is because the calcination temperature used for removal of the surfactants usually causes crystallization of titanium dioxide particles. During crystallization, the rearrangement of the crystal structure (from an amorphous form) causes restructuring and hence collapse of the pore wall. An alternative method could be the nanocasting strategy using a soft or a hard template. Therefore, the use of soft or hard-template appears to be the avenues for retaining the periodic porous structure after calcination. The major disadvantage of the soft-template using various polymers involves the added expense and care needed in retaining the periodic array of pores using various calcination temperatures [26]. Finally, the hard-template synthesis involves multiple impregnation steps of the titanium precursor with heating time periods to slowly form a periodic arrangement of titanium dioxide under ideal conditions [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40].
Earlier reports have indicated that mixed phases of titanium dioxide exhibit higher activity compared with the pure phase, such as anatase [42,43,44]. The higher photocatalytic activities in many reactions using TiO2 P25 can be attributed to the mixed phases of anatase and rutile. An optimal amount of rutile crystallites on anatase TiO2 has been shown to increase the photocatalytic water splitting outcomes [42]. Another work also notes that having small crystallites of rutile TiO2 on anatase TiO2 favors higher photocatalytic activity from forming “hot spots” [45]. Therefore, it is highly advantageous to identify synthesis methods that produce mixed phases of titanium dioxide in a facile manner. Previous reports preparing TiO2 having mixed phases with surfactants required elevated calcination temperatures in the range of 600 °C to 1200 °C to form the desired phases [46]. In addition, highly reactive TiCl4 or combinations of TiCl4 with Ti(OR)4 were required for forming the mixed phases of titanium dioxide [47]. Hydrothermal synthesis treatment was needed to form the mixed phase TiO2 material under certain conditions [48]. Other synthetic methods used for forming mixed phases of titanium dioxide include microemulsion [49], flame pyrolysis [50], and physical vapor deposition [51]. The EISA synthesis has also been performed to produce mixed phases of titanium dioxide; however, the materials lack periodic porous structure [42]. These former reports provide motivation for developing a relatively simple synthetic method in producing mixed phases of titanium dioxide that has periodic porous structure using the hard-template, mesoporous silica SBA-15.
The formation of mixed phases of anatase, rutile, and TiO2(B) as function of loading and nature of titanium alkoxide precursor were carefully investigated using the hard-template synthetic method. The resulting mixed phase titanium dioxide materials were evaluated for solar hydrogen production. The mixed phase titanium dioxide material with periodic hexagonal phase and having anatase (98%) and TiO2(B) (2%) without platinum co-catalyst exhibited the highest solar hydrogen activity. The results suggest mixed phases of titanium dioxide with periodic porous structure leads to the higher solar evolution compared with previous literature works in preparing mesoporous titanium dioxide having periodic network array of pores. Therefore, the synthetic method employed in this work enables modulation of the phase(s) of titanium dioxide by simply varying the impregnation cycles and nature of the titanium alkoxide precursor. This work suggests that periodic titanium dioxide can be produced as powders having mixed phases in a simple synthetic and controlled manner.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization
2.1.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
A nanocasting strategy was attempted to prepare titania based nanocrystalline materials. Figure 1 shows the high-angle powder XRD data for the titania nanomaterials prepared using titanium isopropoxide and titanium ethoxide as precursors. Three of the titanium dioxide nanomaterials were made using titanium ethoxide (TiO2-10, TiO2-8, and TiO2-3), and the fourth material, TiO2-4, was prepared using titanium isopropoxide as the precursor for titania. The number after the hyphen represents the number of cycles completed in impregnating the hexagonal silica SBA-15 material in the nanocasting process. At low impregnation cycle, with the titanium ethoxide precursor, a mixed phase anatase-TiO2(B) is formed as shown for the TiO2-3 material. Many of the diffraction peaks are typical for TiO2(B) while the remaining peaks belong to anatase TiO2 using the Powder Diffraction File (PDF) cards: TiO2 anatase, 00-21-1272; and TiO2(B), 00-046-1238. The peaks for TiO2(B) seen in TiO2-3 include diffraction planes due to (001), (110), (002), (01), (111), (310), (401), (003), (01), (21), (14), (23), and (621). In addition, the anatase TiO2 peaks are due to diffraction planes of (101), (103), (104), (112), (200), (105), and (211). It should be noted that the diffraction plane (001) of TiO2(B) and anatase TiO2 (101) overlap at approximately 2θ = 25°. The TiO2-3 material was prepared using a molar ratio of 0.60 for TiO2/SiO2 whereas the molar ratio of Ti(OC2H5)4/HCl was kept to be 0.74. Previous research using a different silica host, KIT-6 with a TiO2/SiO2 molar ratio of 0.68, led to the formation of TiO2(B) phase in conjunction with anatase TiO2 using either titanium isopropoxide or titanium butoxide as precursors for titania [32]. The molar ratio of Ti(OCH(CH3)2)4/HCl was maintained at 0.10 by Zhou and coworkers in their study.
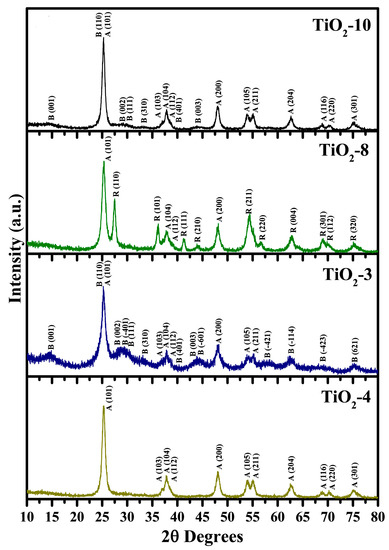
Figure 1.
Powder X-ray diffraction of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 as function of impregnation cycles and titanium precursor.
Figure 1.
Powder X-ray diffraction of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 as function of impregnation cycles and titanium precursor.
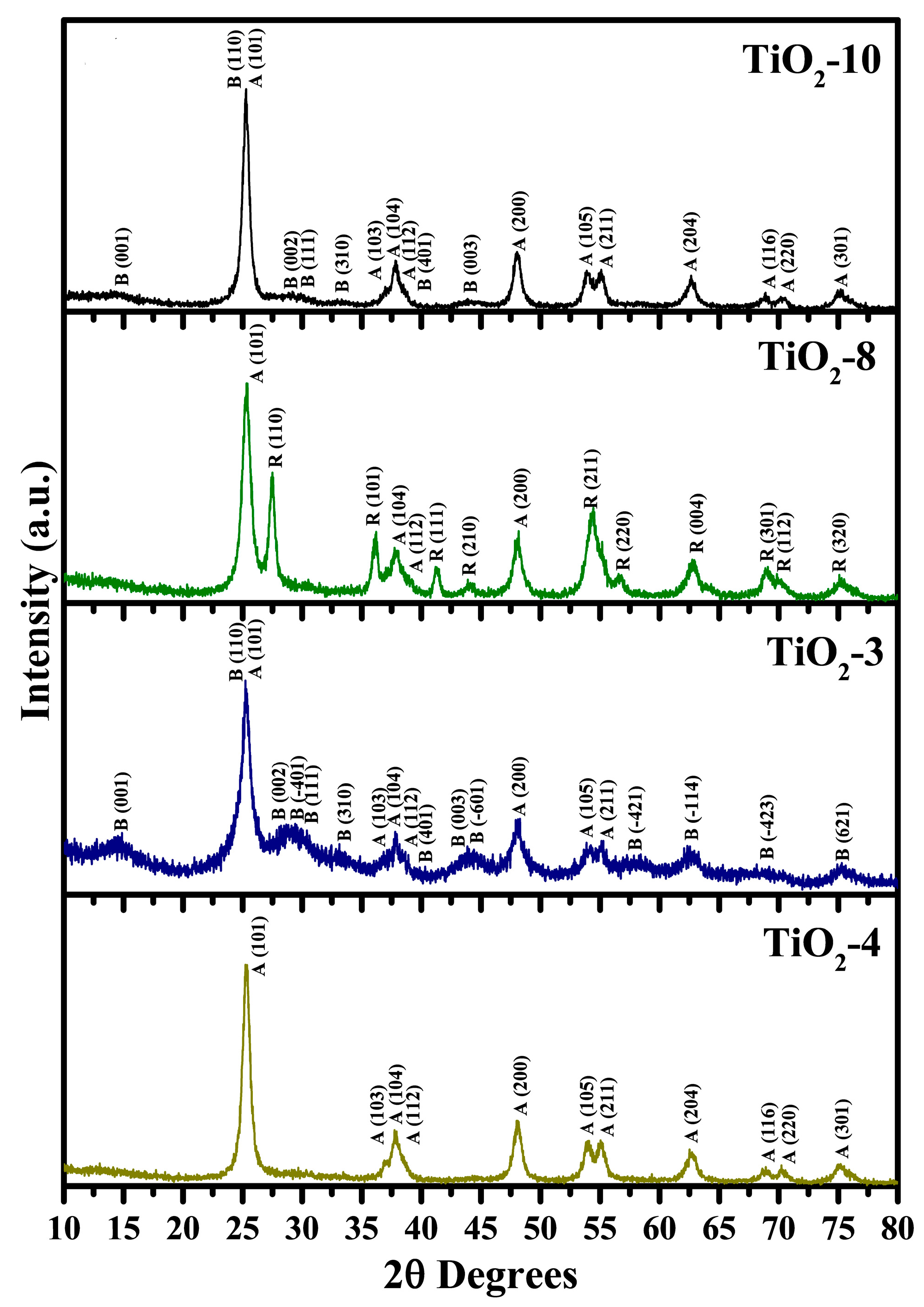
An increase in the number of cycles from three to eight leads to the formation of anatase-rutile mixed phases (TiO2-8) material as shown in Figure 2. The diffraction planes recorded for anatase phase in the TiO2-8 material include (101), (104), (112), and (200). The peaks from the rutile TiO2 phase include (110), (101), (111), (210), (211), (220), (004), (301), (112), and (320) diffraction planes. The Reference Intensity Ratio (RIR) method was used to calculate the percentages of various phases that are indicated in Table 1. The PDF card used for indexing the rutile TiO2 phase was 00-21-1276. Kim and coworkers reported the formation of anatase and rutile phases at similar ratios as ours [29,30]. Correspondingly, lower acidity conditions favor forming an anatase-rutile mixed phase TiO2 material [38] and the results obtained in this work are consistent with previous reports in literature. The additional impregnation cycles led to the formation of a minor amount of TiO2(B) in TiO2-10. The predominant peaks for TiO2(B) and anatase TiO2 are evident in Figure 1 for the TiO2-10 material. The TiO2(B) diffraction planes recorded for the TiO2-10 include (001), (110), (002), (111), (401), and (003). The anatase TiO2 phase peaks observed were due to diffraction planes of (101), (103), (104), (112), (200), (105), (211), (204), (116), (220), and (301). The number of peaks seen for the anatase TiO2 phase suggests that the TiO2-10 material is predominantly anatase, which is supported in RIR percentages in Table 1.
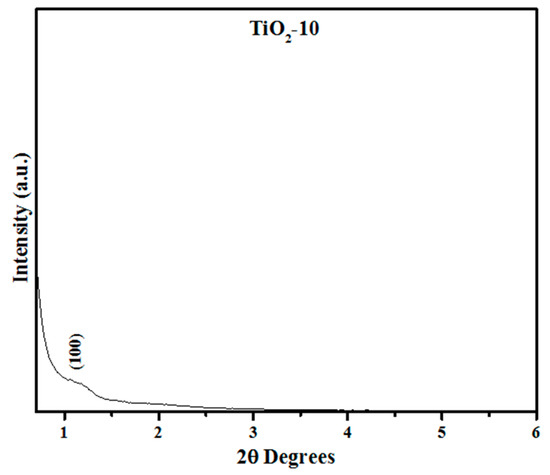
Figure 2.
Powder X-ray diffraction of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 as function of impregnation cycles.
Figure 2.
Powder X-ray diffraction of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 as function of impregnation cycles.
The change of the titanium alkoxide precursor from titanium ethoxide to titanium isopropoxide for impregnating SBA-15 is evident with the TiO2-4 material in Figure 1. This material has only anatase TiO2 phase. The diffraction planes recorded for anatase TiO2 phase include (101), (103), (104, (112), (200), (105), (211), (116), (220), and (301). Previous research suggests that use of titanium isopropoxide in nanocasting using periodic silica host materials leads to anatase TiO2 phase, similar to previous results [29,30,32]. Zhou and coworkers discovered that low calcination temperature of 300 °C led to anatase and TiO2(B) phases [32]. In summary, the powder XRD results shown in Figure 1 and Table 1, collectively, suggest that the loading and nature of the titanium alkoxide precursor affects the phase(s) formed.
In addition, short range powder XRD was completed for the TiO2-10 material as shown in Figure 2. The short range XRD plot indicate a small peak at 2θ near 1.25° due to (100) plane, suggesting some pore ordering. This is supported later in the discussion related to Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) results in Section 2.1.4. The short range powder XRD data of the remaining materials (TiO2-8 TiO2-3, and TiO2-4) are shown in the Supplementary Materials in Figures S1–S3. The results indicate that the periodic arrangement of the pores is destroyed in these materials. Thus, the results suggest that a certain amount of titania loading is required for retention of pores. At an optimal loading amount, the titania particles provide a robust environment for retention of pores. When the loading of titania is relatively low, they do not coat the pore walls of SBA-15 completely and hence on calcination, the pores collapse.

Table 1.
Physical properties of mesoporous hard templated TiO2.
| Material | Phase(s) (%) a | Crystallite Size (s) (Å) b | Bandgap (eV) c | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatase | TiO2(B) | Rutile | Anatase | TiO2(B) | Rutile | ||
| TiO2-3 | 48 | 52 | - | 68 | 17 | - | 3.35 |
| TiO2-8 | 75 | - | 25 | 78 | - | 101 | 3.02 |
| TiO2-10 | 98 | 2 | - | 104 | 207 | - | 3.18 |
| TiO2-4 | 100 | - | - | 93 | - | - | 3.20 |
a The percentages of three TiO2 phases (anatase, TiO2(B), and rutile) were calculated using the Reference Intensity Ratio (RIR) method provided in the Integrated Rigaku PDXL software version 2. In the RIR method, RIR values obtained from the Powder Diffraction File (PDF) files and the intensity of the peaks corresponding to the various phases are used to quantify the percentages of the phases; b Crystallite sizes of the mesoporous materials were calculated using the Halder-Wagner method. In the Halder-Wagner (HW) plot, y = (β/tanθ)2 is plotted against x = β/(tanθsinθ). The slope of the resulting straight line gives Kλ/D from which the crystallite size D can be calculated. K is a shape factor (dimensionless), λ = wavelength of Cu Kα radiation, and β = peak area/peak intensity. To be consistent, a standard set of peaks that do not overlap was used. The anatase peaks chosen are: 2θ = 25° (d101), 48° (d200), and 62.8° (d204). The TiO2(B) peaks chosen are: 2θ = 14° (d001), 25° (d110), 29.85° (d111), and 38° (d401). The rutile peaks chosen are: 2θ = 27° (d110), 36° (d101), and 41° (d111); c The bandgap of the mesoporous materials were estimated by extrapolation of the high slope region from the Kubelka-Munk plot (obtained from DRS studies) to the X-axis.
2.1.2. N2 Physisorption
The textural properties of the nanocasted titania materials were evaluated, and the isotherms with their respective Pore Size Distributions (PSDs) are shown in Figure 3A–D. The isotherms are typical type IV characteristic of mesoporous materials with hysteresis loops [52,53]. Figure 3A shows the nitrogen isotherm and the inset shows the PSD of TiO2-10 material. The N2 isotherm for TiO2-10 exhibits monolayer adsorption at low relative pressures (P/P0) of 0.05–0.30 that form the BET region. Following the BET section, an increase in relative pressure leads to formation of multilayers of nitrogen molecules with capillary condensation occurring on increasing the pressure to higher values. Hysteresis loop occur due to differences in the amount of nitrogen adsorbed during adsorption and desorption, and this is seen in the four materials in Figure 3. TiO2-10 material has H3 type hysteresis loop characteristic of materials having plate-like particle structure with pores of slit-like geometry. The TiO2-10 material does not exhibit a leveling off at the saturation vapor pressure at higher relative pressures, which suggests the pore structure is hierarchical in nature. The specific surface area is relatively high with 146 m2/g, but the pore volume is low (0.18 cm3/g) for the TiO2-10 material. The average PSD for the TiO2-10 is 50 Å as indicated in Figure 3A (inset), and this suggests a fairly uniform slit-like pore structure. On decreasing the number of impregnation cycles, the specific surface area reduces from 146 m2/g for TiO2-10 to 83 m2/g in the TiO2-8 material. Figure 3B shows the type IV isotherm for the TiO2-8 material similar to the TiO2-10. However, the PSD (inset in Figure 3B) shows a broader distribution of pores with average pore diameter of 72 Å. The TiO2-8 material has a H3 hysteresis loop typical of materials with slit-like pores. The PSD suggests a hierarchical arrangement of pores in the TiO2-8 material. Further decrease in impregnation cycles of Ti(OC2H5)4 leads to an increase in specific surface area (212 m2/g) and pore volume (0.26 cm3/g) for the TiO2-3 material as shown in Figure 3C. The TiO2-3 material also has type IV isotherm and H3 hysteresis loop is denoted by not leveling off at higher relative pressures corresponding to the saturation vapor pressure. The narrower PSD suggests a greater uniformity of pores for the TiO2-3 material (Figure 3C inset) compared to TiO2-10 and TiO2-8 prepared using titanium ethoxide as the precursor. The final material studied was TiO2-4 nanocasted using titanium isopropoxide with four impregnation cycles. The isotherm is shown in Figure 3D for the TiO2-4 material, which is again type IV characteristic of mesoporous materials. The inset of Figure 3D show the PSD for the TiO2-4 material, and the arrangement of pores for TiO2-4 material is hierarchical in nature similar to the TiO2-8 material. The specific surface area (97 m2/g) and pore volume (0.16 cm3/g) for the TiO2-4 material are in a similar range as the TiO2-8 material. In addition, the average pore diameter is close to 65 Å.
Overall, the nitrogen physisorption results indicate that the textural properties are dependent on the impregnation cycle. Table 2 shows the textural properties of the four nanocasted mesoporous titania materials, which are in a similar range as previous reports [29,30,34,35,37,38,40].
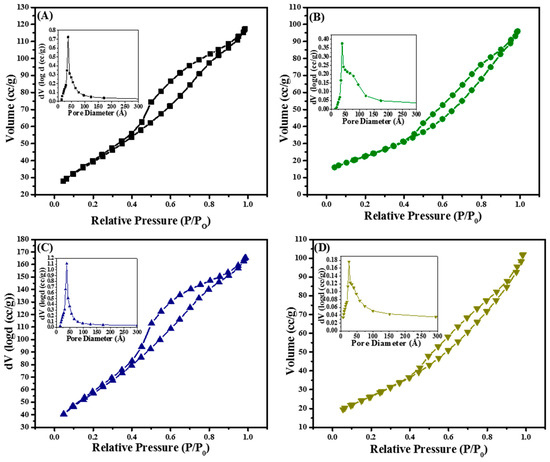
Figure 3.
Nitrogen physisorption isotherms and Pore Size Distributions (insets) of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 (A) TiO2-10; (B) TiO2-8; (C) TiO2-3; and (D) TiO2-4 as function of cycles and titanium precursor.
Figure 3.
Nitrogen physisorption isotherms and Pore Size Distributions (insets) of hard templated mesoporous TiO2 (A) TiO2-10; (B) TiO2-8; (C) TiO2-3; and (D) TiO2-4 as function of cycles and titanium precursor.

Table 2.
Physico-chemical properties of mesoporous hard template TiO2.
| Material | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) a | Pore Volume (cc/g) b | Average Pore Diameter (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2-10 | 146 | 0.18 | 50 |
| TiO2-8 | 83 | 0.15 | 72 |
| TiO2-3 | 212 | 0.26 | 48 |
| TiO2-4 | 97 | 0.16 | 65 |
a Specific surface area was determined by applying the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) equation to the relative pressure range of P/P0 = 0.05–0.30; b The pore volume was determined from the amount of N2 adsorbed at the highest relative pressure (P/P0) of approximately 0.99.
2.1.3. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
The optical response of the mesoporous titanium dioxide materials was evaluated and the Diffuse Reflectance (DR) spectra are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
DRS of hard templated TiO2 mesoporous materials as function of cycle and titanium precursor (A) Absorbance plot and (B) Tauc plot.
Figure 4.
DRS of hard templated TiO2 mesoporous materials as function of cycle and titanium precursor (A) Absorbance plot and (B) Tauc plot.
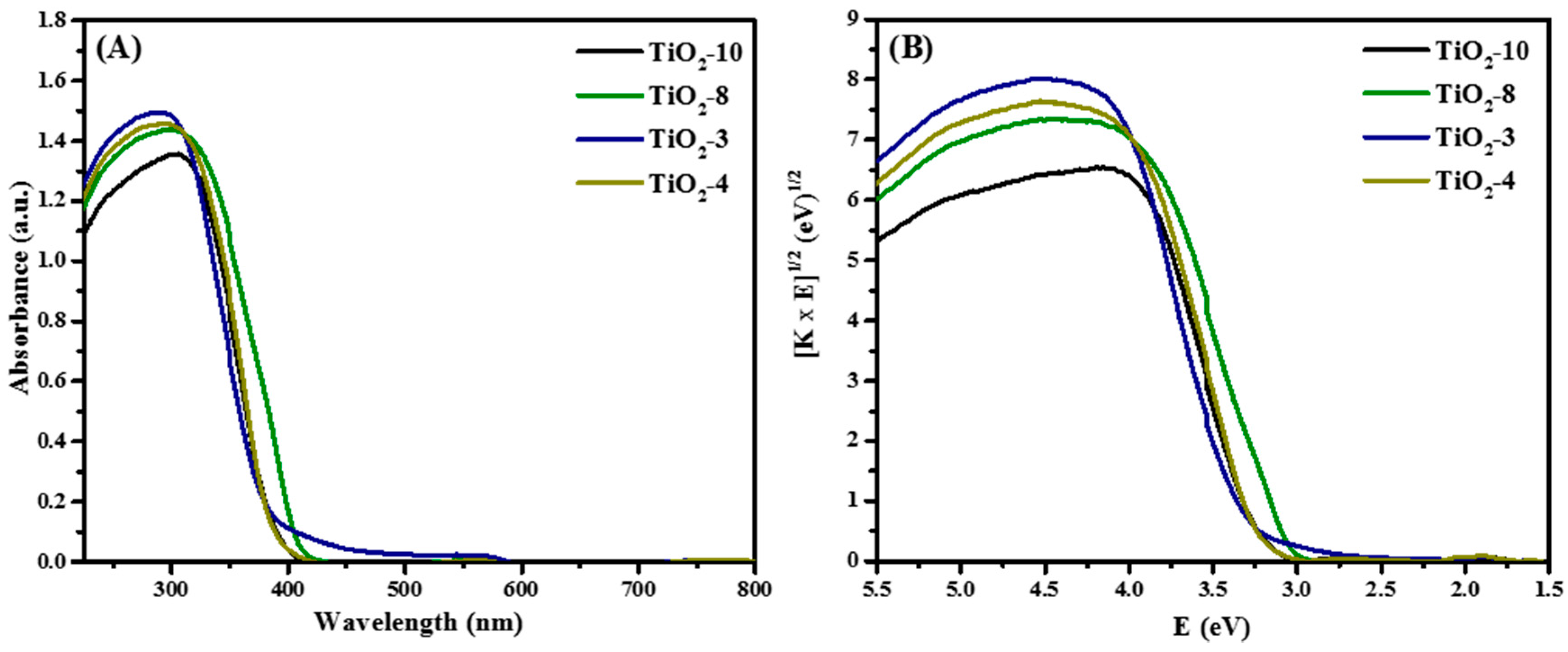
Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy was completed to determine the effects of the various phases on the bandgap. Figure 4A shows the absorbance plot. The corresponding Tauc plot is shown in Figure 4B. The strong absorption in the UV region (< 400 nm) are due to the optical band gap of TiO2, which typically lie in this region. The smallest bandgap was obtained for TiO2-8 material having anatase-rutile mixture, and this is consistent from the smaller bandgap of approximately 3.0 eV for rutile. The TiO2-10 and TiO2-4 had similar bandgap energies because they are composed of mainly anatase or exclusively anatase, with bandgaps of close to 3.2 eV. Greater amounts of TiO2(B) in TiO2-3 material with small crystallite size led to a larger bandgap of 3.35 eV. In addition, the crystallite sizes are consistent with the bandgap energies obtained, as shown in Table 1.
2.1.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studied were completed to evaluate the morphology and phase(s) present in these materials. The low magnification TEM image of TiO2-3 shown in Figure 5A indicates that this material has irregular aggregates of particles. High magnification TEM analysis of TiO2-3 (Figure 5B), shows that lattice fringes are present for anatase TiO2 and TiO2(B), and the diffraction planes in the lattice fringes are from anatase (101) and (001) from TiO2(B) with heterojunctions forming between these two phases. Figure 5C shows the low magnification of TiO2-4, and the high magnification of this material is indicated in Figure 5D. Figure 5D shows the lattice fringes from the crystallographic (101) plane of anatase.
Figure 6A,B shows the TEM images of TiO2-8 material. The pore arrangement is random as indicated in Figure 6A. High magnification image indicates lattice fringes due to anatase (101) and rutile (110) with some heterojunction formation between the anatase and rutile phases.
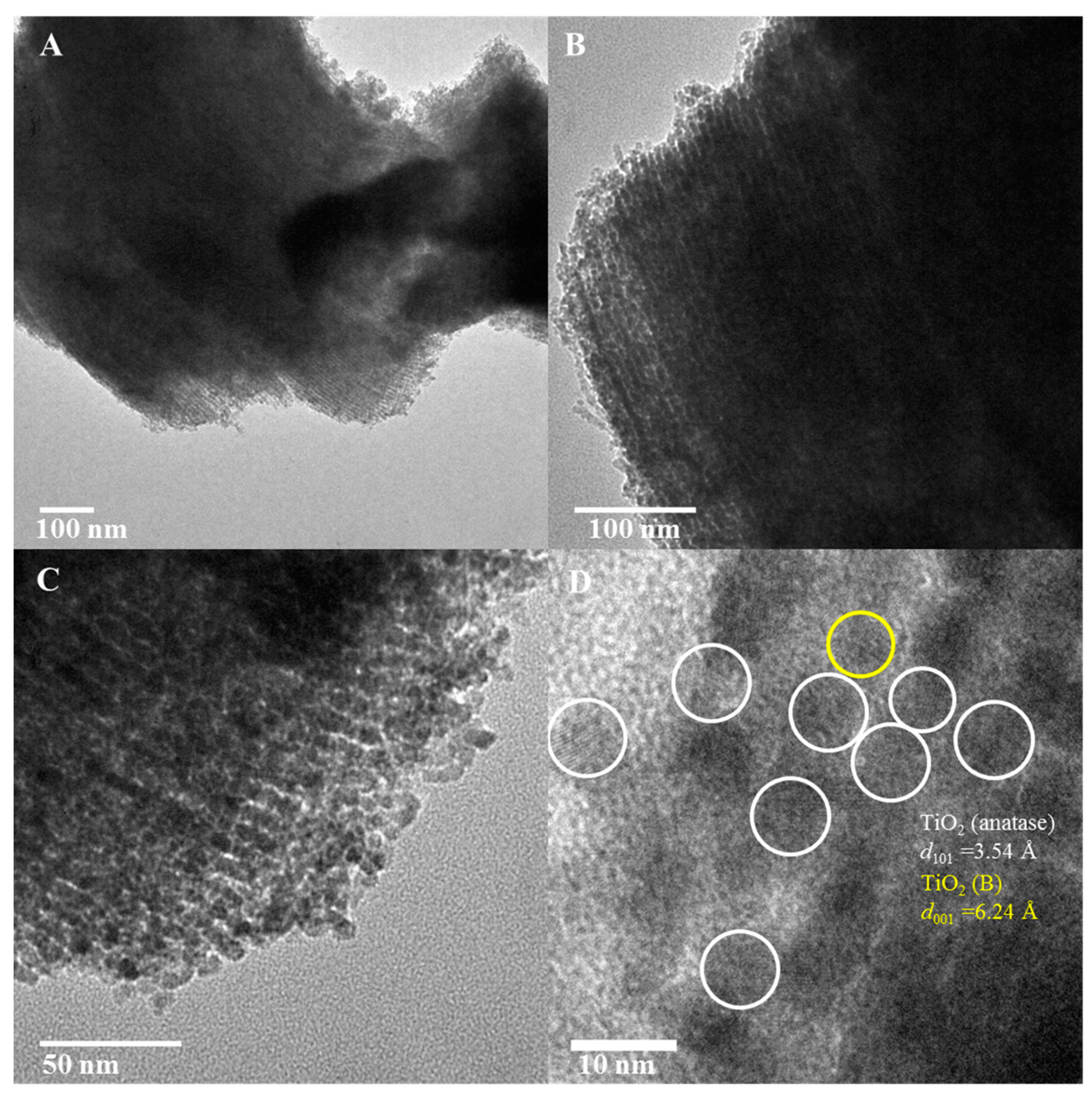
The TEM images in Figure 7A–C show the unidirectional pore channels present in TiO2-10 material. Long unidirectional pore channels, similar to the host periodic mesoporous silica SBA-15 material, are seen in these images. The low magnification TEM results for TiO2-10 are consistent with low-angle powder XRD of this material in Figure 2. An over-focus image of TiO2-10 is shown in Figure 7D. Lattice fringes due to (101) and (001) diffraction planes of anatase and TiO2(B) respectively are observed. Overall, the TEM analysis supports powder XRD results with heterojunctions formed for the three mesoporous materials prepared using titanium ethoxide, and only pure anatase TiO2 phase in TiO2-4 made from titanium isopropoxide.
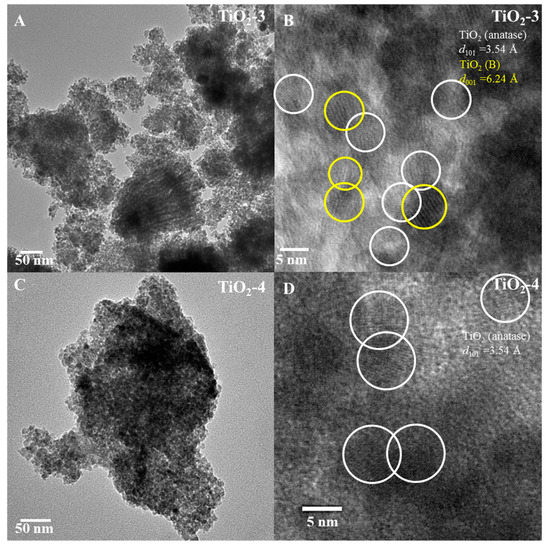
Figure 5.
TEM images. TiO2-3 ((A) low magnification and (B) high magnification) and TiO2-4 ((C) low magnification and (D) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous materials. The yellow and white circles indicate TiO2(B) and anatase phase respectively.
Figure 5.
TEM images. TiO2-3 ((A) low magnification and (B) high magnification) and TiO2-4 ((C) low magnification and (D) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous materials. The yellow and white circles indicate TiO2(B) and anatase phase respectively.
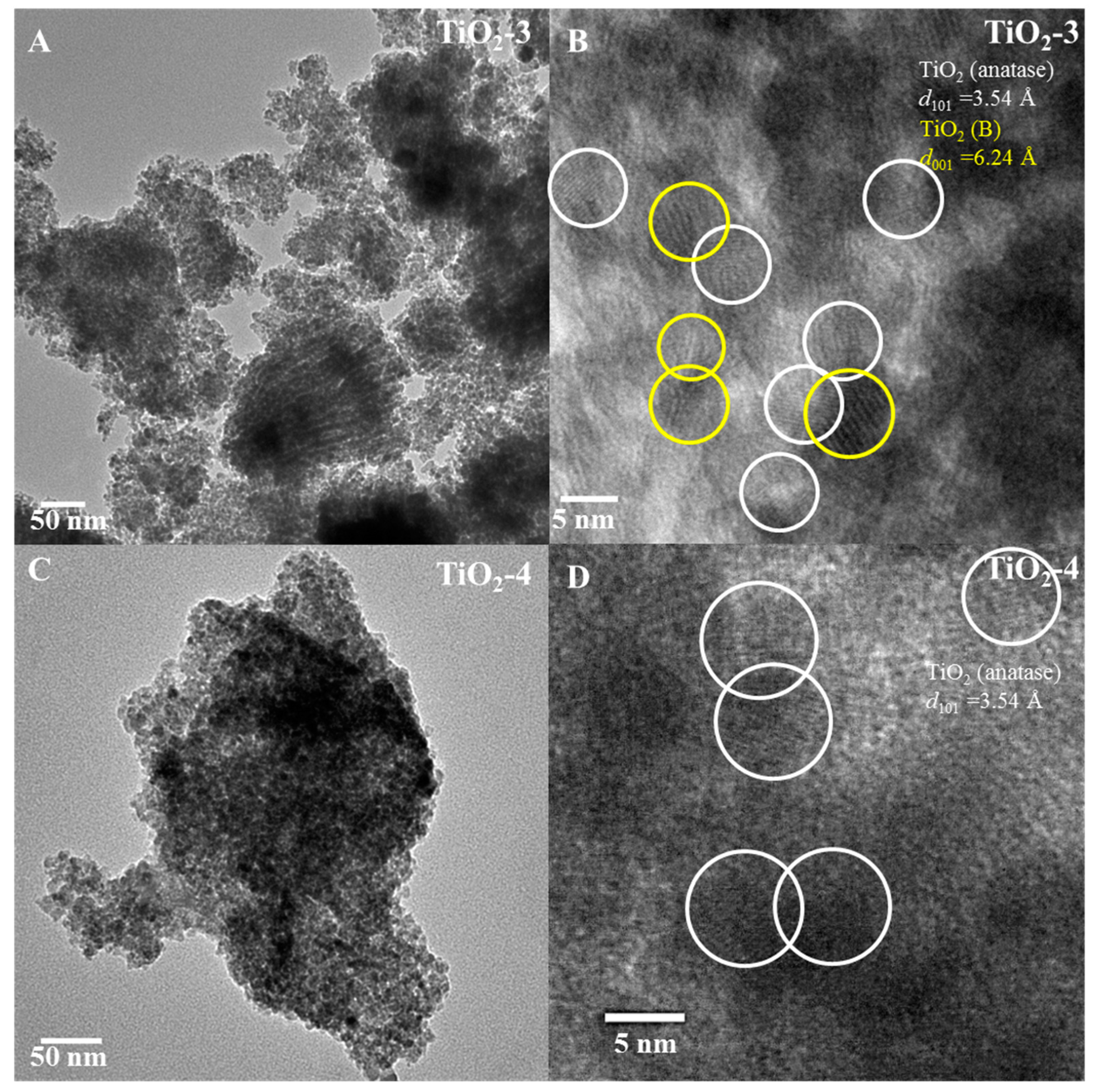
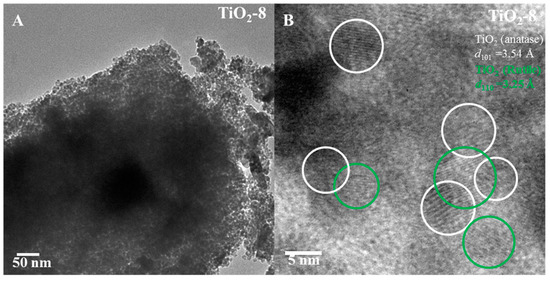
Figure 6.
TEM images of TiO2-8 ((A) low magnification and (B) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous material. The green and white circles denote rutile and anatase phase respectively.
Figure 6.
TEM images of TiO2-8 ((A) low magnification and (B) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous material. The green and white circles denote rutile and anatase phase respectively.
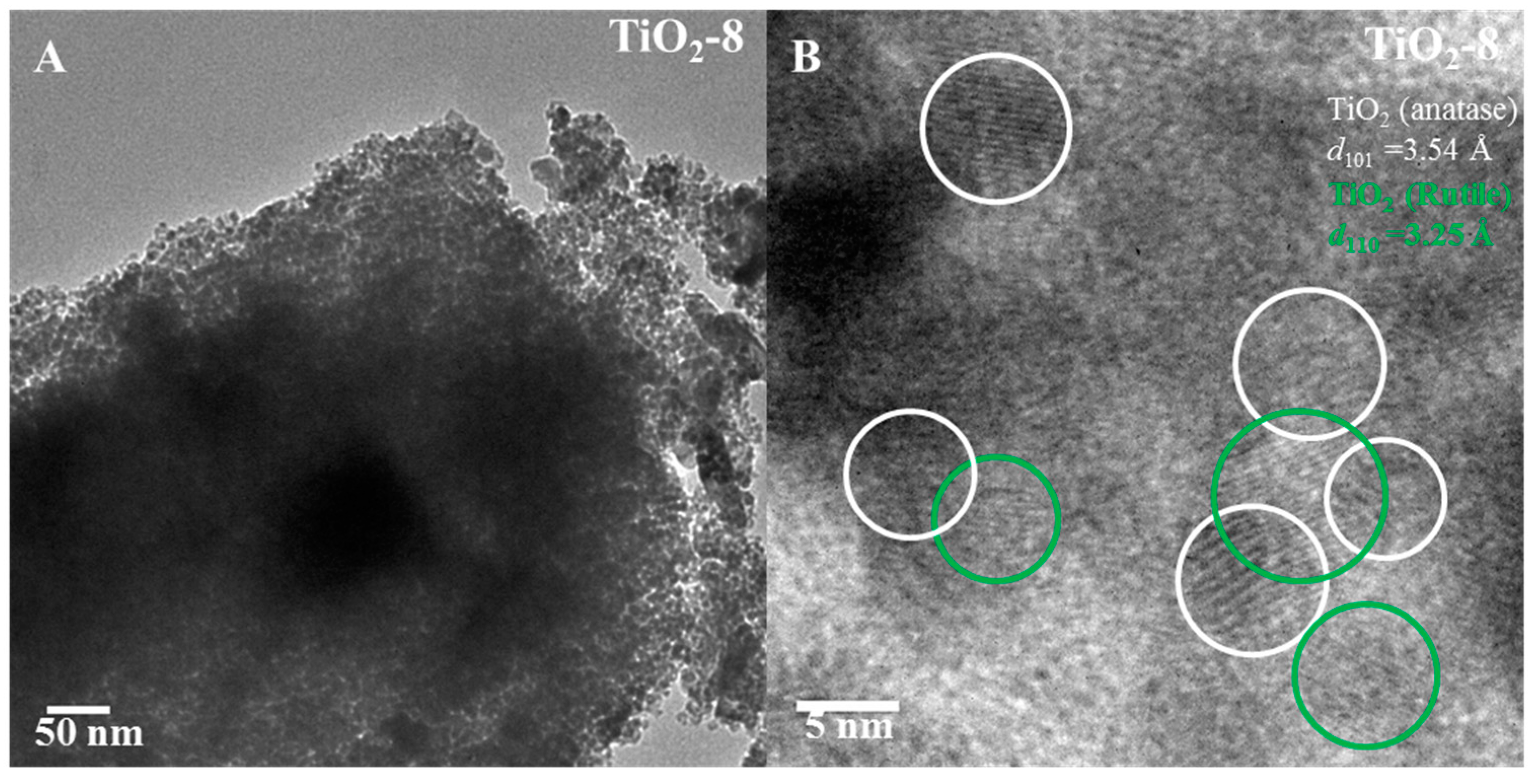
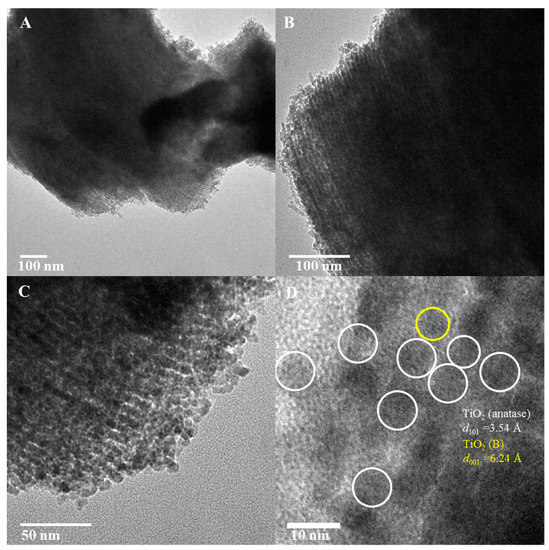
Figure 7.
TEM of TiO2-10 ((A–C) low magnification and (D) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous materials. The yellow and white circles represent TiO2(B) and anatase phase respectively.
Figure 7.
TEM of TiO2-10 ((A–C) low magnification and (D) high magnification) nanocasted titania mesoporous materials. The yellow and white circles represent TiO2(B) and anatase phase respectively.
2.1.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Figure 8 shows the scanning electron microscopy image of TiO2-10 with accompanying Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping of this sample. The SEM image shows irregular morphology for the TiO2-10 material, and EDX mapping suggests a small amount of silica from the SBA-15 template after removing with NaOH aqueous solution. The retention of a small amount of silica is fairly common using the nanocasting method. Overall, the TEM and SEM analyses suggest TiO2-10 periodic unidirectional pore channels with globular morphology. The SEM of TiO2-3, -4, and -8 are shown in Figures S4–S6.
2.2. Solar Hydrogen Evolution
The photocatalytic activity for solar hydrogen production was evaluated for the nanocasted titania mesoporous materials and are shown in Figure 9. The photocatalytic activity was noted to be in the following order of TiO2-10 > TiO2-8 > TiO2-3 > TiO2-4. The materials made with titanium ethoxide had mixed phases, and the TiO2-4 material synthesized using titanium isopropoxide had only anatase phase. Therefore, the mixed phases may impart enhanced charge separation resulting in increased photocatalytic activity. Within the materials prepared using titanium ethoxide, TiO2-3 had 48% anatase and 52% TiO2(B) and TiO2-8 was found to have 75% anatase and 25% rutile content as indicated in Table 1. The TiO2-10 material was noted to have 98% anatase TiO2 and 2% TiO2(B).
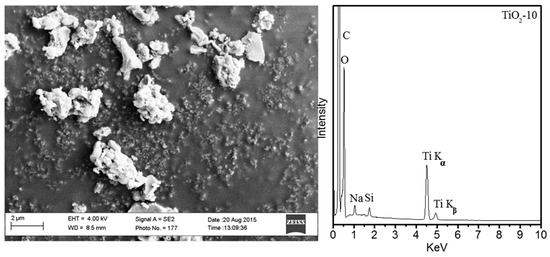
Figure 8.
SEM image of TiO2-10 hard templated-TiO2 mesoporous material and EDX mapping of this material.
Figure 8.
SEM image of TiO2-10 hard templated-TiO2 mesoporous material and EDX mapping of this material.
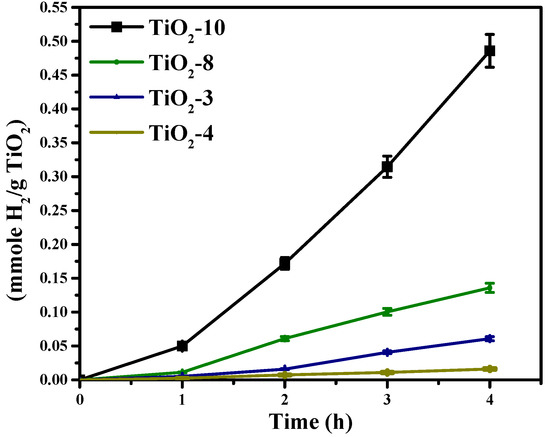
Figure 9.
Hydrogen evolution from the hard templated mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts.
Figure 9.
Hydrogen evolution from the hard templated mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts.
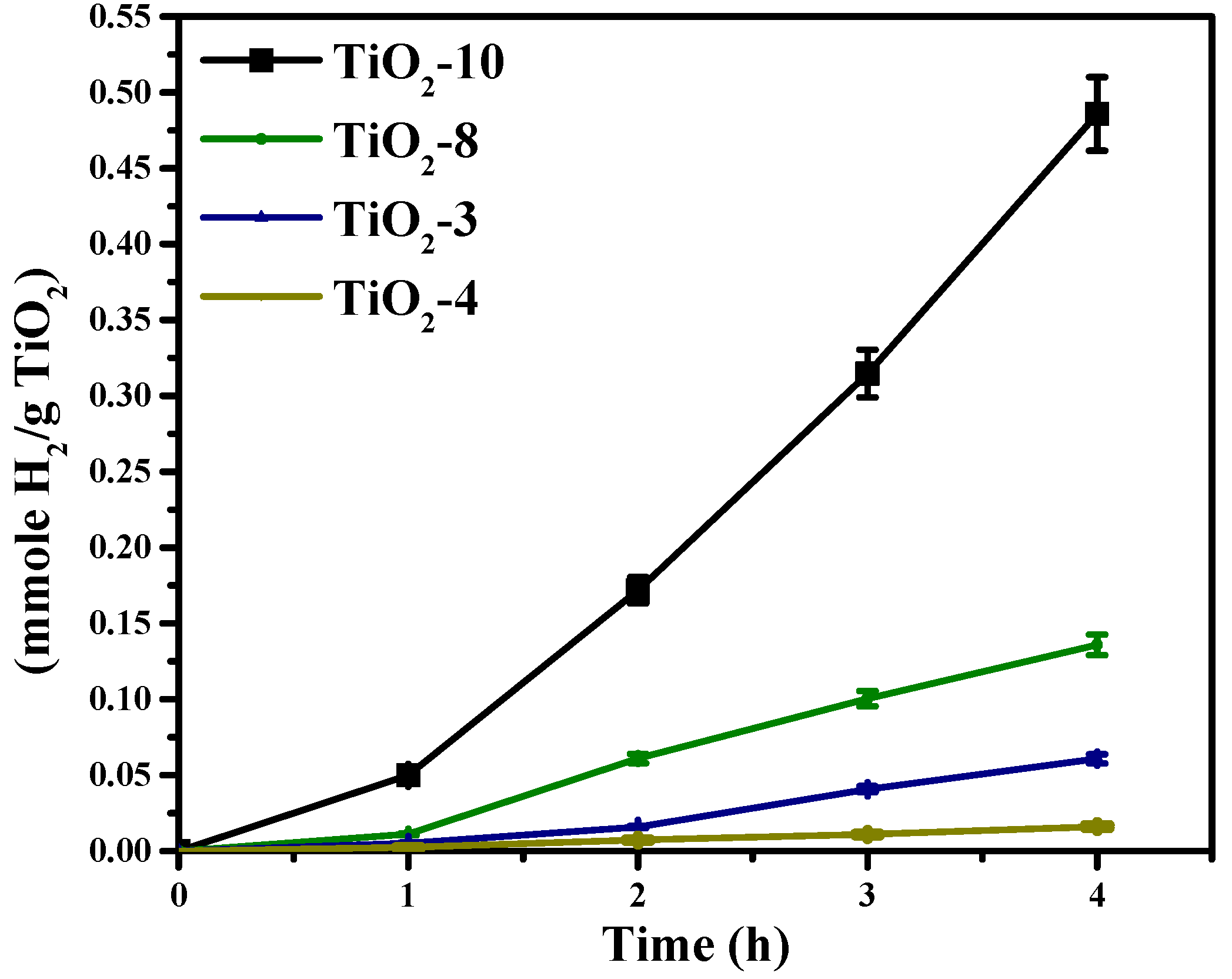
The photocatalytic activity of titania is a function of several factors, such as crystallinity, crystallite size, phase(s), surface area, porosity, etc. The crystallinity trend is TiO2-10 ≈ TiO2-4 > TiO2-8 > TiO2-4. However, crystallinity alone may not be the only factor responsible for the relative high activity of TiO2-10. This is because TiO2-10 produces much greater hydrogen than TiO2-4. TiO2-8 and TiO2-3 have similar photocatalytic activity, so differences in crystallinity may not fully explain the trends obtained in production of hydrogen. The crystallite sizes vary, as shown in Table 1. However, TiO2-10 and TiO2-4 anatase crystallite sizes vary little, but the TiO2(B) crystallite size significantly varies for TiO2-10 and TiO2-3. Therefore, the crystallite size and crystallinity appear to have a modest influence on the photocatalytic activity. Table 2 shows the porosity of these four materials, and the specific surface area is the highest for TiO2-3. If specific surface area was an important factor, then, the solar hydrogen evolution should be the largest for TiO2-3. However, this is not the case. Furthermore, the average pore diameter for TiO2-10 and TiO2-3 are similar, so the porosity (specific surface area and pore size) does not seem to be a major factor. As illustrated in the TEM images (Figure 7A–D), the periodic arrangement of pores seems to have been retained in TiO2-10 in comparison to the rest of the three mesoporous materials. The photocatalytic activity of TiO2-10 was found to be the highest in this study. Previously, we have observed that the pore architecture is an important factor for hydrogen evolution [54]. We reported that the photocatalytic activity was higher when a periodic mesoporous silica support was used to disperse titania and Pd nanoparticles in comparison to an aperiodic mesoporous silica support. The results from this study also indicate that the presence of such periodic pores (albeit not highly uniform), leads to effective hydrogen evolution. In addition to the critical role of the support, the phase(s) formed and their relative percentages may also play a role as well. The TiO2-10 material has perhaps an optimal amount of anatase and TiO2(B), which minimizes electron-hole recombination. The present outcome is consistent with prior observations with mixed phase titania for solar hydrogen evolution [43]. In order to understand this better, photoluminescence studies were carried out.
2.3. Photoluminescence
The phase(s) of titania appear to play a role in the solar hydrogen production photocatalytic activity. We endeavored to further understand the trends in photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Therefore, photoluminescence studies were conducted on the four mesoporous materials as shown in Figure 10. All the samples show an intense peak that appears near 430 nm that is attributed to electron-hole recombination due to self-trapped excitons from all phase(s) of titania. In addition, small peaks can be seen near 467, 482, and 492 nm. The presence of oxygen defects can be inferred from the small peaks seen at approximately 467 nm, whereas the peaks at 482 and 492 nm may be attributed to surface states. These trap states will facilitate trapping charge carriers. The PL results supports the trends in photocatalytic activity previously shown in Figure 9. TiO2-4 material comprised solely of anatase and has the largest photoluminescence from increased electron-hole recombination, and correspondingly, the amount of hydrogen produced from this material is the lowest. The photoluminescence from TiO2-8 and TiO2-3 are similar. In comparing the photocatalytic activities, one notices that the amount of hydrogen produced is similar after 1 h of irradiation. On irradiation for longer durations of time, some difference is observed in the yield of hydrogen in these two materials. The photoluminescence signal from TiO2-10 was significantly lower in comparison to the rest of the mesoporous materials, and this suggests significantly reduced electron-hole recombination. This is consistent with the relatively high photocatalytic activity obtained for this material. In summary, the photoluminescence studies validate the trends observed in photocatalytic production of hydrogen.
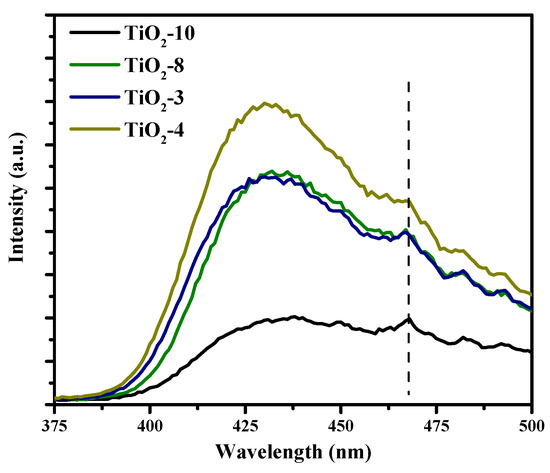
Figure 10.
Photoluminescence of hard templated mesoporous TiO2.
Figure 10.
Photoluminescence of hard templated mesoporous TiO2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Titanium ethoxide, Ti(OC2H5)4, (Acros Organics, Pittsburg, PA, USA), titanium isopropoxide, Ti(OCH(CH3)2)4, (Acros Organics, 98+%), conc. HCl (Fisher-Scientific, ACS grade, 37 wt %), and sodium hydroxide, NaOH, (Acros Organics, analysis grade) were used for the synthesis of the titanium dioxide. Deionized water of 18.2 MΩ cm water was employed throughout the synthesis.
3.2. Synthesis
The hard template synthetic or nanocasting method was employed for preparing mesoporous titanium dioxide materials [30]. In a typical hard template synthesis, various microliters of titanium ethoxide or titanium isopropoxide were added to a known amount of deionized (DI) water. This solution was stirred for 30 min to form an amorphous titania precipitate. The total amount of titanium precursor added was dependent on the number of cycles completed. After the initial step of forming the amorphous titania precipitate, the aqueous suspension was centrifuged for 30 min, and the white solid was dissolved in concentrated HCl. This solution was added to the periodic silica SBA-15 host under stirring for 30 min. Then, the mixture was heated to 160 °C for 10 min, which concluded 1 cycle. These steps were repeated to obtain the desired number of impregnation cycles. Finally, the mixture was heated for 24 h at 100 °C and then ground to a fine powder. The dry and finely grounded composite was subjected to calcination at 450 °C for 3 h at a heating rate of 3 °C/minute. The final step involved etching the calcined composite with 17 mL of 1M NaOH for 12 h under stirring followed by centrifugation and washing with deionized water resulting in a white material.
The periodic SBA-15 material was prepared according to a previous report published by us [55].
3.3. Characterization and Photocatalytic Studies
The hard template TiO2 mesoporous materials were extensively characterized by many techniques. Powder X-ray diffraction analysis of the mesostructured materials were recorded under ambient conditions using a Rigaku Ultima IV instrument (Akishima-shi, Tokyo, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5408 Å). The accelerating voltage used was 40 kV, and the emission current employed was 44 mA. In addition, the powder XRD analysis was completed by scanning from 2θ = 10° to 80° for evaluating the phase and crystallinity of the titania materials. The materials were scanned at 0.02° step width and the scan rate was 1°/min. The samples were scanned from 2θ = 0.6° to 6° for determining the periodic nature. The percentages of various phases of TiO2 were determined using Reference Intensity Ratio (RIR) method with the Rigaku PDXL version 2 software. The textural properties such as specific surface area, pore volume, and pore diameter distribution, were delineated with N2 physisorption measurements. The materials were dried overnight at 80 °C and extensively degassed at 110 °C for 7.5 h. The N2 isotherms were collected at 77 K (−196 °C, liquid nitrogen temperature) using at NOVA 2200e (Quantachrome Instruments) surface area and pore volume analyzer. The specific surface areas were calculated using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) equation from the relative pressure range (P/P0) of 0.05–30. The pore volumes were determined from the amount of nitrogen adsorbed at the highest relative pressure (P/P0) of ~0.99. The average pore diameter was calculated using the equation, average pore diameter = 4 (pore volume)/(specific surface area). The UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra were completed using a Cary 5000 UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Santa Clara CA, USA) equipped with a Harrick Scientific praying mantis accessory. The bandgaps of the samples were evaluated by extrapolating the highest slope region to the X-axis in the Tauc plot, and this was completed by transforming the absorbance plot using the Kubelka–Munk function. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were recorded using a Tecnai G2 instrument (Hillsboro, OR, USA) operating at 120 kV. Before the TEM analysis, the TiO2 samples were dispersed in ethanol, and the suspensions were subjected to centrifugation for 30 min. Then, one drop of the suspension was placed onto the copper grid coated with carbon film followed by overnight drying under ambient conditions. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was completed using Zeiss Sigma instrument. An Oxford X-max detector was used for EDX mapping. The acceleration voltage used was 12 kV. Photoluminescence measurements were completed with a Horiba Jobin Yvon-Fluoromax 4 instrument (Edison, NJ, USA). The excitation wavelength was 275 nm, and the emission spectra were monitored in the range of 375 to 500 nm.
The photocatalytic water splitting experiments were completed as follows. A known ratio of 1 g of photocatalyst per Liter of solution was placed in the photoreactor, and suspension contained water-methanol mixture with molar ratio of [H2O]/[CH3OH] = 8. The resulting mixture was degassed with ultrahigh purity Ar before irradiation. The suspensions were stirred extensively over the course of the experiment. A 300 W Xe Oriel lamp with appropriate filter (Oriel Filter 57396, Franklin, MA, USA) was employed as the UV light source. The concentration of hydrogen was determined by gas chromatography using a SRI 8610 C instrument (Torrance, CA, USA) that had a molecular sieve column coupled to a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). The amount of hydrogen formed was calculated from a calibration curve made previously.
4. Conclusions
A nanocasting method using silica SBA-15 as hard-template was explored for forming mesoporous titanium dioxide. This synthetic method afforded mixed phases of titania by simply varying the number of impregnation cycles and nature of the titanium alkoxide precursor. Depending on the experimental conditions, phases of anatase, rutile, or TiO2(B) phases were formed. The mesoporous material TiO2-10, formed after ten impregnation cycles, exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity. The periodic nature of the pores in the TiO2-10 material was an important factor that contributed to enhanced solar hydrogen production. The synthesis method provides an avenue for fabricating periodic mesoporous titanium dioxide for various other applications such as photocatalytic degradation of organics and dyes and dye-sensitized solar cells.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/20/12/19812/s1.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to NSF-CHE-0722632, NSF-EPS-0903804, NSF-DGE-0903685, DE-EE0000270, and SD NASA-EPSCOR NNX12AB17G. We are thankful to Aravind Baride for assistance with SEM-EDX studies.
Author Contributions
All authors in this study were involved in the design of the experiments. L.M. was primarily involved in the synthesis and photocatalytic studies; and S.R. and C.-M.W. were involved in the characterization and analysis of data. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Burda, C. TiO2 nanoparticles as functional building blocks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9283–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhou, B. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials for sensor applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10131–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Mora-Seró, I.; de Angelis, F.; Bisquert, J.; Wang, P. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials for photovoltaic applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10095–10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, H.; Li, C. Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9987–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Yao, D.; Field, M.R.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Ou, J.Z. Electrochromic properties of TiO2 nanotubes coated with electrodeposited MoO3. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10353–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, A.; Jani, H.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Bhargava, S.K.; Bansal, V. Gold nanoparticle-decorated keggin ions/TiO2 photococatalyst for improved solar light photocatalysis. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6661–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjo, M.T.; Ricardi, N.C.; Arenas, L.T.; Benvenutti, E.V.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Santos, M.J.L.; Costa, T.M.H. TiO2 and TiO2/SiO2 nanoparticles obtained by sol-gel method and applied on dye sensitized solar cells. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2014, 72, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-Y.; Deka, J.R.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Rogeau, A.; Lu, S.-Y. One-step, surfactant-free hydrothermal method for syntheses of mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates and their applications in high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietron, J.J.; Rolison, D.R. Improving the efficiency of titania aerogel-based photovoltaic electrodes by electrochemically grafting isopropyl moieties on the titania surface. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 350, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietron, J.J.; Stux, A.M.; Compton, R.S.; Rolison, D.R. Dye-sensitized titania aerogels as photovoltaic electrodes for electrochemical solar cells. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C 2007, 91, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-C.; Cheng, W.-Y.; Lu, S.-Y. Titania aerogels as a superior mesoporous structure for photoanodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 6910–6919. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Yonezawa, S. Preparation of dye sensitized solar cell by using supercritical carbon dioxide drying. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 77, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.-Y.; Gao, X.-D.; Li, X.-M.; Jiang, Z.-W.; Huang, Y.-D. Nanoporous TiO2 aerogel blocking layer with enhanced efficiency for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 590, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Parayil, S.K.; Psota, R.J.; Koodali, R.T. Modulating the textural properties and photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of TiO2 by high temperature supercritical drying. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 10215–10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Shen, X.-D.; Cui, S. Direct synthesis of anatase TiO2 aerogel resistant to high temperature under supercritical ethanol. Mater. Lett. 2014, 117, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasalingam, S.; Wu, C.-M.; Koodali, R.T. Modulation of pore sizes of titanium dioxide photocatalysts by a facile template free hydrothermal synthesis method: Implications for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine b. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, A.; Zai, J.; Elbohy, H.; Poudel, P.; Adhikari, N.; Qian, X.; Qiao, Q. TiO2 coated urchin-like SnO2 microspheres for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.P.; Zhang, Q.; Russo, B.; Fryxell, G.E.; Cao, G. Titania particle size effect on the overall performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6296–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Sanchez, C.; Lebeau, B.; Patarin, J. Chemical strategies to design textured materials: From microporous and mesoporous oxides to nanonetworks and hierarchical structures. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4093–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Louis, A.; Sanchez, C. Synthesis and characterization of mesostructured titania-based materials through evaporation-induced self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, D.; Cagnol, F.; Soler-Illia, G.; Crepaldi, E.; Amenitsch, H.; Brunet-Bruneau, A.; Bourgeois, A.; Sanchez, C. Fundamentals of mesostructuring through evaporation-induced self-assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.-S.; Tai, Y.-C.; Chen, P.; Wu, Y.-C. Clean and time-effective synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystalline by microwave-assisted solvothermal method for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Fei, C.; Lv, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, G. Rapid construction of TiO2 aggregates using microwave assisted synthesis and its application for dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8622–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Fei, C.; Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Cao, G. Dye-sensitized solar cells based on hierarchically structured porous TiO2 filled with nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11320–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, J. Controlled synthesis of highly dispersed TiO2 nanoparticles using SBA-15 as hard template. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-W.; Park, S.-J.; Ihm, S.-K.; Lee, K.-H. Synthesis of bimodal mesoporous titania with high thermal stability via replication of citric acid-templated mesoporous silica. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Lee, H.I.; Shon, J.K.; Hur, J.Y.; Kang, M.S.; Park, S.S.; Kong, S.S.; Yu, J.A.; Seo, M.; Li, D.; et al. Preparation of highly ordered mesoporous TiO2 materials with crystalline framework from different mesostructured silica templates via nanoreplication. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-J.; Yoo, S.-J.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, J.-M.; Shim, W.-G.; Kim, S.-I.; Lee, J.-W. Photovoltaic performance of nanoporous TiO2 replicas synthesized from mesoporous materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 4976–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.; Xu, X.; Irvine, J.T.S.; Attidekou, P.S.; Liu, C.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, W. Mesoporous monocrystalline TiO2 and its solid-state electrochemical properties. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Randorn, C.; Attidekou, P.S.; Su, Z.; Irvine, J.T.S.; Zhou, W. Syntheses, Li insertion, and photoactivity of mesoporous crystalline TiO2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2826–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hardwick, L.J.; Bruce, P.G. Lithium intercalation into mesoporous anatase with an ordered 3D pore structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2570–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zuo, F.; Feng, P. Hard template synthesis of crystalline mesoporous anatase TiO2 for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-J.; Shim, W.-G.; Jung, S.-H.; Yoo, S.-J.; Lee, J.-W. Analysis of adsorption properties of N719 dye molecules on nanoporous TiO2 surface for dye-sensitized solar cell. Appl. Surface Sci. 2010, 256, 5428–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K.E.; Stahl, A.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Hard templating of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide with chiral nematic ordering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6886–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Park, J.-N.; Shon, J.; Li, Z.; Lee, E.; Kim, J. Highly ordered crystalline mesoporous metal oxides for hydrogen peroxide decomposition. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, D.P.; Calleja, G.; Pizarro, P.; Gálvez, P. Enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production by improving the Pt dispersion over mesostructured TiO2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 4812–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusior, A.; Warchal, A.; Komornicki, S.; Radecka, M. Hard-template synthesis of titanium dioxide hollow spheres. Micro Nano Lett. 2014, 9, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Bak, W.; Kim, J.-J.; Snyder, M.A.; Yoo, W.C.; Sung, Y.-E. How pore parameters affect Li ion depletion in mesoporous materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 7604–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, L.; Koodali, R. Versatility of evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) method for preparation of mesoporous TiO2 for energy and environmental applications. Materials 2014, 7, 2697–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, M.; Shivatharsiny, R.; Chia-Ming, W.; Rui, P.; Ranjit, T.K. Aging dependent phase transformation of mesostructured titanium dioxide nanomaterials prepared by evaporation-induced self-assembly process: Implications for solar hydrogen production. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2015, 2, 230–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kho, Y.K.; Iwase, A.; Teoh, W.Y.; Mӓdler, L.; Kudo, A.; Amal, R. Photocatalytic H2 evolution over TiO2 nanoparticles. The synergistic effect of anatase and rutile. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronic, L.; Perniu, D.; Duta, A. Synergistic effect between TiO2 sol-gel and Degussa P25 in dye photodegradation. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2013, 66, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Chen, L.; Nichols, J.M.; Rajh, T.; Gray, K.A. The important role of tetrahedral ti4+ sites in the phase transformation and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5402–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J. Effects of calcination on the physical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 powders prepared by sol–gel template method. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2005, 34, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yao, B.; Cao, Y.; Fan, K. Synthesis of well-ordered mesoporous titania with tunable phase content and high photoactivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11849–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wu, Y.; Sakai, T.; Du, Z.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M. Preparation of highly crystalline TiO2 nanostructures by acid-assisted hydrothermal treatment of hexagonal-structured nanocrystalline titania/cetyltrimethyammonium bromide nanoskeleton. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Anpo, M. Preparation of controllable crystalline titania and study on the photocatalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 8673–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleki, A.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Gouma, P.I. Sensing of organic vapors by flame-made TiO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 119, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Gorges, R.; Kreisel, G. Preparation and characterisation of titanium dioxide films for catalytic applications generated by anodic spark deposition. Thin Solid Films 2004, 450, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems—With special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Wu, C.M.; Koodali, R.T. Pd-Ti-MCM-48 cubic mesoporous materials for solar simulated hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Rathi, M.; Ahrenkiel, S.P.; Koodali, R.T.; Wang, Z.Q. Facile synthesis of MOF-5 confined in SBA-15 hybrid material with enhanced hydrostability. Chem. Comm. 2013, 49, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the mesoporous materials are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
