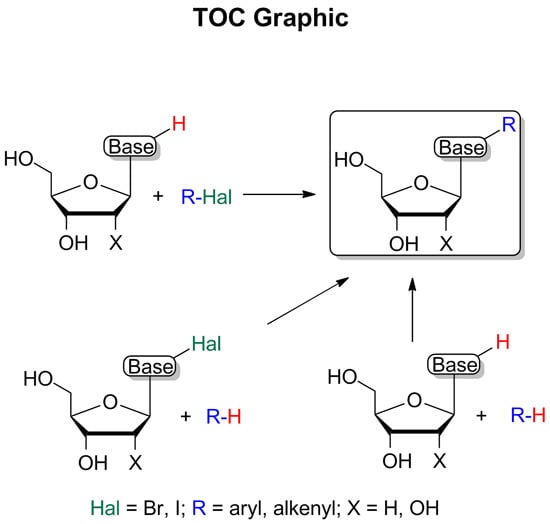
Modification of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleosides by Direct C-H Bond Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Direct Activation of C8-H Bond in Purine and Purine Nucleosides
2.1. Cross-Coupling of Adenine Nucleosides with Aryl Halides

| Entry | Base/Ligand | Substrates | Ar | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | Products | Yield (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Piperidine | 7 | 4-Tol-I | 150 | 5 | 9 | 68 | [23] |
| 2 | Piperidine | 8 | 4-Tol-I | 125 | 5 | 10 | 31 | [23] |
| 3 | Cs2CO3 | 8 | Ph-I | 80 | 13 | 10 | 84 | [27] |
| 4 | Cs2CO3/Pyridine | 7 | Ph-I | 120 | 13 | 9 | 30–95 a | [27] |
| 5 | Cs2CO3/Piperidine | 8 | 4-Tol-I | 80 | 15 | 10 | 85 | [26] |




2.2. Cross-Coupling of Inosine and Guanine Nucleosides with Aryl Halides



2.3. Synthesis of Fused Purines via Inter- or Intramolecular Direct C8-H Arylation



2.4. Miscellaneous Direct C8-H Functionalizations



3. N1-Directed Modifications of C6-Substituted Purine Nucleosides via ortho C-H Bond Activation






4. Direct Activation of C5-H or C6-H Bond in Uracils and Uracil Nucleosides
4.1. Cross-Coupling with Aryl Halides



4.2. Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling with Arenes and Heteroarenes at C5 Position



4.3. Cross-Dehydrogenative Alkenylation at C5 Position



4.4. Miscellaneous Direct C-H Functionalizations




5. Coupling of 5-Halouracil Nucleosides with Arenes and Heteroarenes


6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meijere, A.D.; Diederich, F. Metal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kambe, N.; Iwasaki, T.; Terao, J. Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of alkyl halides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4937–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry Announcement. Available online: http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2010/# (accessed on 12 March 2015).
- Ackermann, L.; Vicente, R.; Kapdi, A.R. Transition-metal-catalyzed direct arylation of (hetero)arenes by C-H bond cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 9792–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagnou, K. Mechanistic considerations in the development and use of azine, diazine and azole N-oxides in palladium-catalyzed direct arylation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2010, 292, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.X.; Sun, L.P. Recent progress towards transition-metal-catalyzed direct arylation of heteroarenes. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2012, 9, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafrance, M.; Fagnou, K. Palladium-catalyzed benzene arylation: incorporation of catalytic pivalic acid as a proton shuttle and a key element in catalyst design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16496–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liégault, B.; Lapointe, D.; Caron, L.; Vlassova, A.; Fagnou, K. Establishment of broadly applicable reaction conditions for the Palladium-catalyzed direct arylation of heteroatom-containing aromatic compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, J.M.; Touré, B.B.; Sames, D. C−H Bonds as ubiquitous functionality: A general approach to complex arylated imidazoles via regioselective sequential arylation of all three C−H bonds and regioselective N-alkylation enabled by SEM-group transposition. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrofoglio, L.A.; Gillaizeau, I.; Saito, Y. Palladium-assisted routes to nucleosides. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1875–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ornellas, S.; Williams, T.J.; Baumann, C.G.; Fairlamb, I.J.S. (Eds.) Catalytic C-H/C-X bond functionalisation of nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids, amino acids, peptides and proteins. In C-H and C-X Bond Functionalization: Transition Metal Mediation; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2013.
- Shaughnessy, K. Palladium-catalyzed functionalization of unprotected nucleosides in aqueous media. Molecules 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq, E.; Descamps, J.; de Somer, P.; Barr, P.J.; Jones, A.S.; Walker, R.T. (E)-5-(2-Bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine: A potent and selective anti-herpes agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 2947–2951. [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan, C.; Barucki, H.; Blewett, S.; Carangio, A.; Erichsen, J.T.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; de Clercq, E.; Balzarini, J. Highly potent and selective inhibition of varicella-zoster virus by bicyclic furopyrimidine nucleosides bearing an aryl side chain. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4993–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, N.J.; Tor, Y. Simple fluorescent pyrimidine analogues detect the presence of DNA abasic sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10784–10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivatsan, S.G.; Tor, Y. Using an emissive uridine analogue for assembling fluorescent HIV-1 TAR constructs. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 3601–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noé, M.S.; Ríos, A.C.; Tor, Y. Design, synthesis, and spectroscopic properties of extended and fused pyrrolo-dC and pyrrolo-C analogs. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3150–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicke, L.; Engels, J.W. Postsynthetic on column RNA labeling via Stille coupling. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valis, L.; Mayer-Enthart, E.; Wagenknecht, H.A. 8-(Pyren-1-yl)-2′-deoxyguanosine as an optical probe for DNA hybridization and for charge transfer with small peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3184–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninger-Weiß, C.; Valis, L.; Wagenknecht, H.A. Pyrene-modified guanosine as fluorescent probe for DNA modulated by charge transfer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Bazzanini, R.; Marangoni, M.; Simoni, D.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of 6-vinyl- and 6-ethynyluridine and 8-vinyl- and 8-ethynyladenosine. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.X.; Krawczyk, S.H.; Swaminathan, S.; Shea, R.G.; Dougherty, J.P.; Terhorst, T.; Law, V.S.; Griffin, L.C.; Coutré, S.; Bischofberger, N. N2- and C8-Substituted oligodeoxynucleotides with enhanced thrombin inhibitory activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerna, I.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. The first direct C-H arylation of purine nucleosides. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4729–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čerňa, I.; Pohl, R.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Direct C−H arylation of purines: Development of methodology and its use in regioselective synthesis of 2,6,8-trisubstituted purines. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5389–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čerňa, I.; Pohl, R.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of 6,8,9-tri- and 2,6,8,9-tetrasubstituted purines by a combination of the Suzuki cross-coupling, N-arylation, and direct C−H arylation reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9048–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storr, T.E.; Baumann, C.G.; Thatcher, R.J.; De Ornellas, S.; Whitwood, A.C.; Fairlamb, I.J. S. Pd(0)/Cu(I)-mediated direct arylation of 2′-deoxyadenosines: Mechanistic role of Cu(I) and reactivity comparisons with related purine nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5810–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storr, T.E.; Firth, A.G.; Wilson, K.; Darley, K.; Baumann, C.G.; Fairlamb, I.J. S. Site-selective direct arylation of unprotected adenine nucleosides mediated by palladium and copper: Insights into the reaction mechanism. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 6125–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.G.; De Ornellas, S.; Reeds, J.P.; Storr, T.E.; Williams, T.J.; Fairlamb, I.J.S. Formation and propagation of well-defined Pd nanoparticles (PdNPs) during C–H bond functionalization of heteroarenes: are nanoparticles a moribund form of Pd or an active catalytic species? Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6174–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storr, T.E.; Strohmeier, J.A.; Baumann, C.G.; Fairlamb, I.J. S. A sequential direct arylation/Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling transformation of unprotected 2'-deoxyadenosine affords a novel class of fluorescent analogues. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6470–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ornellas, S.D.; Storr, T.E.; Williams, T.J.; Baumann, C.G.; Fairlamb, I.J. S. Direct C-H/C-X coupling methodologies mediated by Pd/Cu or Cu: An examination of the synthetic applications and mechanistic findings. Curr. Org. Synth. 2011, 8, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaňková, B.; Krchňák, V.; Soural, M.; Hlaváč, J. Direct C–H arylation of purine on solid phase and its use for chemical libraries synthesis. ACS Comb. Sci. 2011, 13, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahnoun, S.; Messaoudi, S.; Peyrat, J.F.; Brion, J.D.; Alami, M. Microwave-assisted Pd(OH)2-catalyzed direct C−H arylation of free-(NH2) adenines with aryl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 7279–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, S.; Messaoudi, S.; Brion, J.D.; Alami, M. A site selective C-H arylation of free-(NH2) adenines with aryl chlorides: Application to the synthesis of 6,8-disubstituted adenines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4271–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngassa, F.N.; DeKorver, K.A.; Melistas, T.S.; Yeh, E.A.H.; Lakshman, M.K. Pd−Xantphos-Catalyzed Direct Arylation of Nucleosides. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4613–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellina, F.; Cauteruccio, S.; Rossi, R. Palladium- and copper-mediated direct C-2 arylation of azoles—including free (NH)-imidazole, -benzimidazole and -indole—Under base-free and ligandless conditions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2006, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, E.C.; Shaughnessy, K.H. Inhibitory effects of the guanine moiety on Suzuki couplings of unprotected halonucleosides in aqueous media. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 6378–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.; Priego, E.M.; Sánchez-Carrasco, P.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; Vande Voorde, J.; Camarasa, M.J.; Balzarini, J.; González-Pacanowska, D.; Pérez-Pérez, M.J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of C-8 aryl and heteroaryl inosines and determination of their inhibitory activities against Plasmodium falciparum purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 82, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čerňa, I.; Pohl, R.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. Intramolecular direct C-H arylation approach to fused purines. Synthesis of purino[8,9-f]phenanthridines and 5,6-dihydropurino[8,9-a]isoquinolines. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campeau, L.C.; Parisien, M.; Jean, A.; Fagnou, K. Catalytic direct arylation with aryl chlorides, bromides, and iodides: Intramolecular studies leading to new intermolecular reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 128, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaroshenko, V.O.; Ostrovskyi, D.; Miliutina, M.; Maalik, A.; Villinger, A.; Tolmachev, A.; Volochnyuk, D.M.; Langer, P. Design and synthesis of polycyclic imidazole-containing N-heterocycles based on C-H activation/cyclization reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, N.; SanMartin, R.; Dominguez, E. Ligand-free copper(I)-catalysed intramolecular direct C-H functionalization of azoles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Niu, H.Y.; Qu, G.R.; Fossey, J.S.; Li, J.P.; Guo, H.M. Synthesis of fused N-heterocycles via tandem C-H activation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9601–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, P.; Yang, F.; Qin, S.; Zhao, D.; Lan, J.; Gao, G.; Hu, C.; You, J. Palladium(II)-catalyzed oxidative C−H/C−H cross-coupling of heteroarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1822–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, D.R.; Fagnou, K. The catalytic cross-coupling of unactivated arenes. Science 2007, 316, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vabre, R.; Chevot, F.; Legraverend, M.; Piguel, S. Microwave-Assisted Pd/Cu-Catalyzed C-8 Direct Alkenylation of Purines and Related Azoles: An Alternative Access to 6,8,9-Trisubstituted Purines. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 9542–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahnoun, S.; Messaoudi, S.; Brion, J.D.; Alami, M. Pd/Cu-catalyzed direct alkenylation of azole heterocycles with alkenyl halides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 6097–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagisetty, P.; Zhang, L.; Lakshman, M.K. Simple methodology for Heck arylation at C-8 of adenine nucleosides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klecka, M.; Pohl, R.; Klepetarova, B.; Hocek, M. Direct C-H borylation and C-H arylation of pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines: synthesis of 6,8-disubstituted 7-deazapurines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, N.; Klecka, M.; Slavetinska, L.; Klepetarova, B.; Hocek, M. Direct C-H amination and C-H chloroamination of 7-deazapurines. RSC Advances 2014, 4, 62140–62143. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovs, I.; Lubriks, D.; Suna, E. Copper-catalyzed intermolecular C–H amination of (hetero)arenes via transient unsymmetrical λ3-iodanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6920–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klecka, M.; Pohl, R.; Cejka, J.; Hocek, M. Direct C-H sulfenylation of purines and deazapurines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5189–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, G.R.; Liang, L.; Niu, H.Y.; Rao, W.H.; Guo, H.M.; Fossey, J.S. Copper-catalyzed synthesis of purine-fused polycyclics. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.M.; Jiang, L.L.; Niu, H.Y.; Rao, W.H.; Liang, L.; Mao, R.Z.; Li, D.Y.; Qu, G.R. Pd(II)-catalyzed ortho arylation of 6-arylpurines with aryl iodides via purine-directed C−H activation: A new strategy for modification of 6-arylpurine derivatives. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2008–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, M.K.; Deb, A.C.; Chamala, R.R.; Pradhan, P.; Pratap, R. Direct arylation of 6-phenylpurine and 6-arylpurine nucleosides by Ruthenium-catalyzed C-H bond activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11400–11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamala, R.R.; Parrish, D.; Pradhan, P.; Lakshman, M.K. Purinyl N1-directed aromatic C–H oxidation in 6-arylpurines and 6-arylpurine nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7423–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Ryu, J.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, S. Rhodium-catalyzed intermolecular amidation of arenes with sulfonyl azides via chelation-assisted C–H bond activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9110–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čerňová, M.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Switching the regioselectivity of direct C–H arylation of 1,3-dimethyluracil. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 22, 3698–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čerňová, M.; Čerňá, I.; Pohl, R.; Hocek, M. Regioselective direct C–H arylations of protected uracils. Synthesis of 5- and 6-aryluracil bases. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 5309–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.N. Palladium-catalyzed direct 5-arylation of 1,3-dimethyluracil with aryl bromides: An electrophilic metalation–deprotonation with electrophilic arylpalladium intermediate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 6228–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.N. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of benzo[c]pyrimido[1,6-a]azepine scaffold from Morita–Baylis–Hillman adducts: Intramolecular 6-arylation of uracil nucleus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shih, Y.C.; Chen, H.T.; Chien, T.C. Regioselective arylation of uracil and 4-pyridone derivatives via copper(I) bromide mediated C–H bond activation. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelsky, S.I.; Lapointe, D.; Fagnou, K. Analysis of the palladium-catalyzed (aromatic) C–H bond metalation–deprotonation mechanism spanning the entire spectrum of arenes. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 77, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellina, F.; Cauteruccio, S.; Rossi, R. Efficient and practical synthesis of 4(5)-aryl-1H-imidazoles and 2,4(5)-diaryl-1H-imidazoles via highly selective palladium-catalyzed arylation reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8543–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, A.; Wolfenden, R. Equilibrium of formation of the 6-carbanion of UMP, a potential intermediate in the action of OMP decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13986–13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, F.Y.; Cuasito, R.R.; Capule, C.C.; Wong, F.M.; Wu, W. Carbanions from decarboxylation of orotate analogs: Stability and mechanistic implications. Bioorg. Chem. 2007, 35, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amyes, T.L.; Wood, B.M.; Chan, K.; Gerlt, J.A.; Richard, J.P. Formation and stability of a vinyl carbanion at the active site of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: pKa of the C-6 proton of enzyme-bound UMP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1574–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.Q.; Daugulis, O. A general method for Copper-catalyzed arene cross-dimerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13577–13586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, B.; Hazra, S.; Roy, B. Pd(II)-catalyzed regioselective direct arylation of uracil via oxidative Heck reaction using arylboronic acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.N. Palladium(II)-catalyzed oxidative homo-coupling of 1,3-dimethyluracil derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianmehr, E.; Rezaeefard, M.; Rezazadeh Khalkhali, M.; Khan, K.M. Pd-catalyzed dehydrogenative cross-coupling of pyridine-N-oxides with uracils. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 13764–13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.S.; Verhelst, G.; Walker, R.T. The synthesis of the potent anti-herpes virus agent, E-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2′-deoxyuridine and related compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 4415–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Jones, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Sayers, J.R.; Walker, R.T.; Sakuma, T.; de Clercq, E. The synthesis and antiviral properties of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine-related compounds. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 4601–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahara, T. Oxidative coupling of uracil derivatives with maleimides by Palladium acetate. Chem. Lett. 1986, 15, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Isobe, Y.; Kitade, Y.; Maki, Y. A simple synthesis of 5-(1-alkenyl)uracil derivatives by Palladium-catalyzed oxidative coupling of uracils with olefins. Synthesis 1987, 1987, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Georg, G.I. Dehydrogenative alkenylation of uracils via palladium-catalyzed regioselective C-H activation. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3694–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bras, J.; Muzart, J. Intermolecular dehydrogenative Heck reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1170–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.N. Pd(II)-Catalyzed acetoxylation of uracil via electrophilic palladation. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Hazra, S.; Mondal, B.; Majumdar, K.C. Cu(OTf)2-catalyzed dehydrogenative C–H activation under atmospheric oxygen: An expedient approach to pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4570–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćerňová, M.; Pohl, R.; Klepetářová, B.; Hocek, M. C-H trifluoromethylations of 1,3-dimethyluracil and reactivity of the products in C-H arylations. Heterocycles 2014, 89, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gloudeman, J.; Wnuk, S.F. Palladium-catalyzed direct arylation of 5-halouracils and 5-halouracil nucleosides with arenes and heteroarenes promoted by TBAF. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 4094–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafrance, M.; Rowley, C.N.; Woo, T.K.; Fagnou, K. Catalytic intermolecular direct arylation of perfluorobenzenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8754–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Wnuk, S.F. Modification of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleosides by Direct C-H Bond Activation. Molecules 2015, 20, 4874-4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034874
Liang Y, Wnuk SF. Modification of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleosides by Direct C-H Bond Activation. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):4874-4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034874
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yong, and Stanislaw F. Wnuk. 2015. "Modification of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleosides by Direct C-H Bond Activation" Molecules 20, no. 3: 4874-4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034874
APA StyleLiang, Y., & Wnuk, S. F. (2015). Modification of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleosides by Direct C-H Bond Activation. Molecules, 20(3), 4874-4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034874