Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLC?1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Effect of Hinokitiol on PDGF-BB-Induced Proliferation of VSMCs

2.1.2. G0/G1 Phase Arrest of Hinokitiol in Cell Cycle Progression


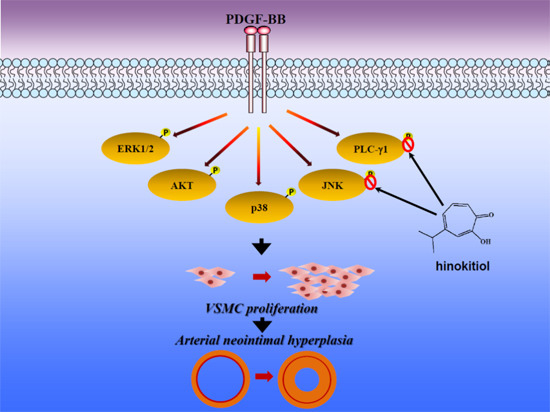
2.1.3. Down-Regulation of Hinokitiol in PDGF-BB Signaling Pathway
2.1.4. Hinokitiol on PDGF-BB Induced p-PLC-γ1, Its Substrate (Ser/Thr) Phosphorylation and p27kip1 Expression


2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Animal Care and Cultivation of Rat Primary VSMCs
3.3. VSMC Viability Test and Proliferation Assay
3.4. Cell Cycle Progression Analysis
3.5. Immunoblotting
3.6. Confocal Microscopy
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions

Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, R. Mechanisms of atherosclerosis—A review. Adv. Nephrol. Necker Hosp. 1990, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dzau, V.J.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Sedding, D.G. Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: New perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature 1993, 62, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzucidlo, E.M.; Martin, K.A.; Powell, R.J. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, A25–A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrae, J.; Gallini, R.; Betsholtz, C. Role of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1276–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, A.A.; Waseem, S.; Riaz, A.M.; Dilawar, B.A.; Mukhtar, S.; Minhaj, S.; Waseem, M.S.; Daniel, S.; Malik, B.A.; Nawaz, A.; et al. PDGF: The nuts and bolts of signalling toolbox. Tumour Biol. 2011, 32, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Jeon, B.H.; Won, K.J.; Lee, C.K.; Park, T.K.; Choi, W.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.K.; Park, S.H.; et al. Gene transfer of redox factor-1 inhibits neointimal formation: Involvement of platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor signaling via the inhibition of the reactive oxygen species-mediated Syk pathway. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, K.; Van Bockstaele, D.R.; Berneman, Z.N. The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003, 36, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueret, O. New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: A function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenn, B.M.; Gaudernak, E.; Holzer, B.; Lanke, K.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Seipelt, J. Antiviral activity of the zinc ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiol against picornavirus infections. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Sata, M. Effect of oral care gel on the quality of life for oral lichen planus in patients with chronic HCV infection. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Kuo, J.R.; Lu, W.J.; Chung, C.L.; Chou, D.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol inhibits platelet activation ex vivo and thrombus formation in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, T.; Hsu, W.H.; Yen, T.L.; Luo, J.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Fong, T.H.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol, a natural tropolone derivative, offers neuroprotection from thromboembolic stroke in vivo. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Lu, S.H.; Chang, C.C.; Thomas, P.A.; Jayakumar, T.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol, a tropolone derivative, inhibits mouse melanoma (B16-F10) cell migration and in vivo tumor formation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J.; Kim, J.W.; Machesky, L.M.; Rhee, S.G.; Pollard, T.D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science 1991, 251, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, Y.; Emori, Y.; Takenawa, T. Purification of recombinant SH2/SH3 proteins of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and -gamma 2 and their inhibitory effect on PIP2-hydrolysis induced by both types of phospholipase C-gamma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 182, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglayan, E.; Vantler, M.; Leppänen, O.; Gerhardt, F.; Mustafov, L.; Ten Freyhaus, H.; Kappert, K.; Odenthal, M.; Zimmermann, W.H.; Tallquist, M.D.; et al. Disruption of platelet-derived growth factor-dependent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phospholipase Cγ1activity abolishes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration and attenuates neointima formation in vivo. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.M. Smooth muscle migration in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, S87–S89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.; Kwon, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S.H.; Park, R.K.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, J.T.; Yoo, H.S.; Kwon, B.M.; Yun, Y.P. Obovatol from Magnolia obovate inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and intimal hyperplasia by inducing p21Cip1. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, F.; Haendeler, J.; Goebel, C.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Growth factor-induced phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase/Akt phosphorylation in smooth muscle cells: Induction of cell proliferation and inhibition of cell death. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 48, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedin, U.; Roy, J.; Tran, P.K. Control of smooth muscle cell proliferation in vascular disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2004, 15, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavezzi, A.M.; Ottaviani, G.; Matturri, L. Biology of the smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerosis. APMIS 2005, 113, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, A.S.; Yu, L.M.; Wu, Q.; Gong, Q.H. Effects of isorhynchophylline on angiotensin II-induced proliferation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.; Bennett, M. Defining the role of vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in atherosclerosis. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslin, A.J. MAPK signalling in cardiovascular health and disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Clin. Sci. 2008, 115, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raines, E.W. PDGF and cardiovascular disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumara, G.; Belwal, M.; Ricci, R. Jnking atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioroi, T.; Yamamori, M.; Yagi, K.; Hirai, M.; Zhan, Y.; Kim, S.; Iwao, H. Dominant negative c-Jun inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-directed migration by vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 91, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Kim, S.; Izumi, Y.; Izumiya, Y.; Nakao, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Iwao, H. Role of JNK, p38, and ERK in platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascularproliferation, migration, and gene expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jin, Y.R.; Park, B.S.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Yoo, H.S.; Yun, Y.P. Luteolin prevents PDGF-BB-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibition of PDGF beta-receptor phosphorylation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.G.; Bae, Y.S. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15045–15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallquist, M.D.; Klinghoffer, R.A.; Heuchel, R.; Mueting-Nelsen, P.F.; Corrin, P.D.; Heldin, C.H.; Johnson, R.J.; Soriano, P. Retention of PDGFR-beta function in mice in the absence of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase and phospholipase Cgamma signaling pathways. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 3179–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.J.; de Los Santos, J.; Carpenter, G. Contrasting role of phospholipase C-γ1 in the expression of immediate early genes induced by epidermal or platelet-derived growth factors. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, E.S.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Moon, H.J.; Bae, Y.C.; Jung, J.S.; Kim, J.H. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine induces proliferation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells via activation of JNK. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.Z.; Liang, H.J.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Zhong, W.B.; Ho, F.M.; Hou, W.C.; Lo, J.L.; Ho, Y.S.; Lin, P.J.; et al. Switch activation of PI-PLC downstream signals in activated macrophages with wortmannin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Uen, Y.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, S.C.; Tseng, S.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Sheu, J.R.; Hsieh, C.Y. Platonin inhibited PDGF-BB-induced proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells via JNK1/2-dependent signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Hsu, M.J.; Jayakumar, T.; Chou, D.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Hsiao, G.; Sheu, J.R. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by the vitamin E derivative pentamethylhydroxychromane in an in vitro and in vivo study: Pivotal role of hydroxyl radical-mediated PLCgamma1 and JAK2 phosphorylation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, M.J.; Hsiao, G.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, C.W.; Chen, S.W.; Jayakumar, T.; Chiu, P.T.; Chiu, Y.H.; Sheu, J.R. Andrographolide enhances NF-{kappa}B subunit p65 Ser536 dephosphorylation through activation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5942–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not avaiable.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.-S.; Wang, M.-J.; Jayakumar, T.; Chou, D.-S.; Ko, C.-Y.; Hsu, M.-J.; Hsieh, C.-Y. Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLC?1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 8198-8212. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058198
Yang P-S, Wang M-J, Jayakumar T, Chou D-S, Ko C-Y, Hsu M-J, Hsieh C-Y. Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLC?1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Molecules. 2015; 20(5):8198-8212. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058198
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Po-Sheng, Meng-Jiy Wang, Thanasekaran Jayakumar, Duen-Suey Chou, Ching-Ya Ko, Ming-Jen Hsu, and Cheng-Ying Hsieh. 2015. "Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLC?1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells" Molecules 20, no. 5: 8198-8212. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058198
APA StyleYang, P.-S., Wang, M.-J., Jayakumar, T., Chou, D.-S., Ko, C.-Y., Hsu, M.-J., & Hsieh, C.-Y. (2015). Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLC?1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Molecules, 20(5), 8198-8212. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058198