Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Synthesis

| Bile Acid | Abbreviation | R1(C-3) | R2(C-6) | R3(C-7) | R4(C-12) | R5(C-24) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycocholate | GC | OH (α) | H | OH (α) | OH (α) | NHCH2COO− |
| Taurocholate | TC | OH (α) | H | OH (α) | OH (α) | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Glycolithocholate | GLC | OH (α) | H | H | H | NHCH2COO− |
| Glycohyocholate | GHC | OH (α) | OH (α) | OH (α) | H | NHCH2COO− |
| Tauroursodeoxycholate | TUDC | OH (α) | H | OH (β) | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Taurohyodeoxycholate | THDC | OH (α) | OH (α) | H | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Glycohyodeoxycholate | GHDC | OH (α) | OH (α) | H | H | NHCH2COO− |
| Glycochenodeoxycholate | GCDC | OH (α) | H | OH (α) | H | NHCH2COO− |
| Glyco-7-oxo-lithocholate | G-7-oxo-LC | OH (α) | H | =O | OH (α) | NHCH2COO− |
| Taurodeoxycholate | TDC | OH (α) | H | H | OH (α) | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Taurochenodeoxycholate | TCDC | OH (α) | H | OH (α) | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Glycodeoxychoate | GDC | OH (α) | H | H | OH (α) | NHCH2COO− |
| Glycoursodeoxycholate | GUDC | OH (α) | H | OH (β) | H | NHCH2COO− |
| Taurolithocholate | TLC | OH (α) | H | H | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Taurohyocholate | THC | OH (α) | OH (α) | OH (α) | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Glycol-3α-6-keto-5β-cholate | Glycol3α6keto-5β-cholate | OH (α) | =O | H | OH (α) | NHCH2COO− |
| Tauro-α-hyocholate | T-α-MC | OH (α) | OH (α) | OH (α) | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Tauro-β-hyocholate | T-β-MC | OH (α) | OH (α) | OH (β) | H | NHCH2CH2SO−3 |
| Compartment | Concentration |
|---|---|
| Gall bladder | 10–50 mmol/L |
| Gut | ~4–20 mmol/L |
| Liver Canaliculi | ~5 mmol/L |
| Portal vein blood | 0.1 mmol/L |
| Peripheral blood | 5–20 μmol/L |
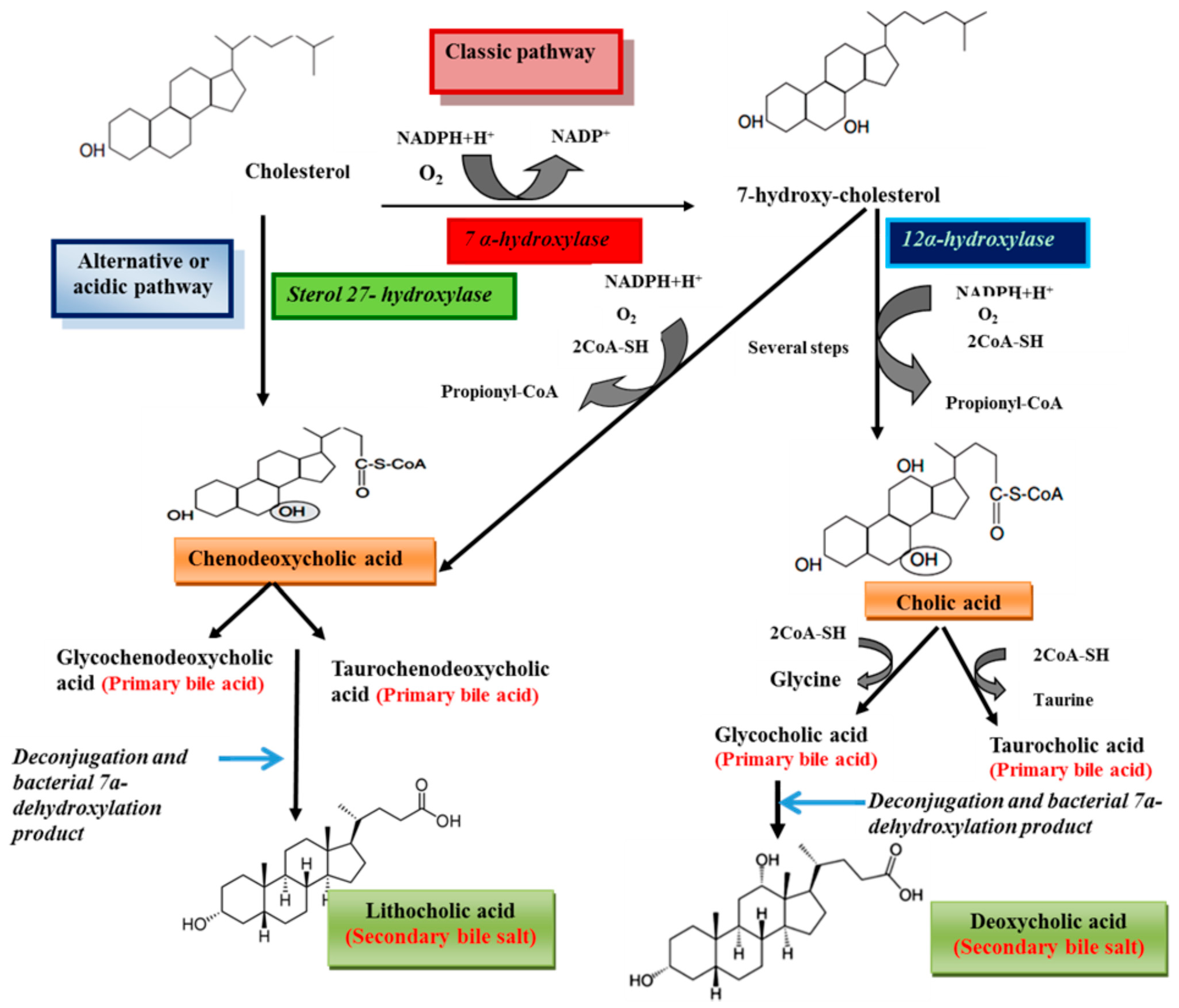
3. Physiological Functions
4. Physico-Chemical Properties

5. Bile Salts as Absorption Enhancer
5.1. Oral Drug Delivery

5.2. Transdermal Delivery
5.3. Nasal Delivery
| Bile Salts | Animals | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium deoxycholate | Rat | Blood glucose levels dropped to 60% of initial levels after 30 min | [75] |
| Sodium glycocholate | Rat | Increases insulin efficacy | [76] |
| Sodium taurocholate | Rabbit | Microcrystalline cellulose suspension containing insulin and sodium taurocholate (1% w/w) sprayed into the nasal cavity provided a bioavailability of 8.36% | [77] |
| Sodium glycocholate | Dog | Increases absorption of insulin | [78] |
| Sodium cholate | Rabbit | Reduces blood glucose (60.06%) | [79] |
5.4. Buccaland Mucosal Drug Delivery
5.5. Rectal Drug Delivery


5.6. Ocular Drug Delivery
6. Mechanism of Action of Bile Salts as Absorption Enhancers

7. Toxicity


8. Novel Approaches
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NavasDiaz, A.; GarciaSa’nchez, F.; GarciaPareja, A. Cholic acid behavior in water and organic solvent: Study of normal and inverted aggregates. Colloids Surf. A 1998, 142, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunness, P.; Flanagan, B.M.; Shelat, K.; Gilbert, R.G.; Gidley, M.J. Kinetic analysis of bile salt passage across a dialysis membrane in the presence of cereal soluble dietary fiber polymers. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Paul Fawcett, J.; Mikov, M.; Tucker, I.G. Effect of bile salts on the transport of morphine-6-glucuronide in rat brain endothelial cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagey, L.R.; Vidal, N.; Hofmann, A.F.; Krasowski, M.D. Evolutionary diversity of bile salts in reptiles and mammals, including analysis of ancient human and extinct giant ground sloth coprolites. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Tucker, I.G.; Østergaard, J. Effects of bile salts on propranolol distribution into liposomes studied by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senel, S.; Hincal, A.A. Drug permeation enhancement via buccal route: Possibilities and limitations. J. Control. Release 2001, 72, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarwani, K.; Gupta, R. Bioavailability enhancers of herbal origin: An overview. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coufalová, L.; Mrózek, L.; Rárová, L.; Placek, L.; Opatrilová, R.; Dohnal, J.; Králová, K.; Paleta, O.; Král, V.; Drašar, P.; et al. New propanoyloxy derivatives of 5β-cholan-24-oic acid as drug absorption modifiers. Steroids 2013, 78, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, R.; Müllertz, A.; Mu, H. Bile salts and their importance for drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snigdha Mishra, S.; Subuddhi, U. Spectroscopic investigation of interaction of nile blue A, a potent photosensitizer, with bile salts in aqueous medium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 141, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poša, M.; Sebenji, A. Determination of number-average aggregation numbers of bile salts micelles with a special emphasis on their oxo derivatives-The effect of the steroid skeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Hofmann, A.F.; Mysels, K.J. The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 6362–6370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stamp, D.; Jenkins, G. An overview of bile-Acid synthesis, chemistry and function. In Bile Acids, Toxicology and Bioactivity; Royal Society of Chemistry; Jenkins, G., Hardie, L.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- AguiarVallim, T.Q.; Tarling, E.J.; Edwards, P.A. Pleiotropic roles of bile acids in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchia, E.C.; Stolz, A.; Agellon, L.B. Differential modulation of cellular death and survival pathways by conjugated bile acids. BMC Biochem. 2001, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, M.J.; Marin, J.J.G.; Antelo, A.; Vazquez-Tato, J. Bile acids: Chemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KullakUblick, G.A.; Stieger, B.; Meier, P.J. Enterohepatic bile salt transporters in normal physiology and liver disease. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 322–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Maitra, U. Chemistry and biology of bile acids. Curr. Sci. 2004, 87, 1666–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Merkus, F.W.H.M.; Schipper, N.G.M.; Verhoef, J.C. The influence of absorption enhancers on intranasal insulin absorption in normal and diabetic subjects. J. Control. Release 1996, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.D.; Im, E.K.; Hyun Choi, Y.; Hyun Yoo, Y. Synthetic bile acids: Novel mediators of apoptosis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 35, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dial, E.J.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Darling, R.L.; Romero, J.J.; Lichtenberger, L.M. Role of phosphatidylcholine saturation in preventing bile salt toxicity to gastrointestinal epithelia and membranes. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garidel, P.; Hildebrand, A.; Knauf, K.; Blume, A. Membranolytic activity of bile salts: Influence of biological membrane properties and composition. Molecules 2007, 12, 2292–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zughaid, H.; Forbes, B.; Martin, G.P.; Patel, N. Bile salt composition is secondary to bile salt concentration in determining hydrocortisone and progesterone solubility in intestinal mimetic fluids. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmann, T.S.; Kamel, L. Examination of the solubilization of drugs by bile salt micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1743–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, D.M.; Admirand, W. Solubility of bile salts. Nature 1969, 221, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W. Fifty years of advances in bile acid synthesis and metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2009, S120–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Mysels, K.J. Bile salts as biological surfactants. Colloid Surf. 1987, 30, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, G.; Gopinath, D. Ultrasonic relaxation studies on micelle formation in aqueous solutions of some bile salts. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 198, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrasa, J.I.; Olmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Turnay, J. Bile acids in the colon, from healthy to cytotoxic molecules. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claro da Silva, T.; Polli, J.E.; Swaan, P.W. The solute carrier family 10 (SLC10): Beyond bile acid transport. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, J.; Krausz, K.W.; Li, T.; Ferrell, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acid signaling in lipid metabolism: Metabolomic and lipidomic analysis of lipid and bile acid markers linked to anti-obesity and anti-diabetes in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, C.M.; Knoefler, D.; Vitvitsky, V.; Banerjee, R.; Jakob, U. Bile salts act as effective protein-unfolding agents and instigators of disulfide stress in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 4, E1610–E1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, G.; An, H.; Luo, Y.; Hao, Y. A novel vector for lactic acid bacteria that uses a bile salt hydrolase gene as apotential food-grade selection marker. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauch, E.D.; Yamaguchi, J.; Bass, B.L.; Wang, J.Y. Bile salts regulate intestinal epithelial cell migration by nuclear factor-K β-induced expression of transforming growth factor-β. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2003, 197, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, N.; Keely, S.J. Bile acids in regulation of intestinal physiology. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2009, 11, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroka, C.J.; Boyer, J.L. Biosynthesis and trafficking of the bile salt export pump, BSEP: Therapeutic implications of BSEP mutations. Mol. Asp. Med. 2014, 37, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.P.; Rajagopal, S.; Mahavadi, S.; Mirshahi, F.; Grider, J.R.; Murthy, K.S.; Sanyal, A.J. Activation of transmembrane bile acid receptor TGR5 stimulates insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 427, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torcello-Gómez, A.; Foster, T.J. Interactions between cellulose ethers and a bile salt in the control of lipid digestion of lipid-based systems. Carbohydr. Polymers 2014, 113, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, Y.S. Multifaceted applications of bile salts in pharmacy: An emphasis on nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3955–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, A.A.; Titorenko, V.I.; Beach, A.; Sanderson, J.T. Bile acids induce apoptosis selectively inandrogen-dependent and -independentprostate cancer cells. Peer J. 2013, 1, e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Arnold, J.J.; Khan, M.A.; Ahsan, F. Absorption enhancers in pulmonary protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 94, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Holzinger, F.; Hagey, L.R.; Cerrè, C.; Ton-Nu, H.T.; Schteingart, C.D.; Steinbach, J.H.; Shneider, B.L.; Hofmann, A.F. Physicochemical and physiological properties of 5α-cyprinol sulfate the toxic bile salt of cyprinid fish. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Goddard, E.D.; Turro, N.J.; Kuo, P.L. Fluorescence probes for critical micelle concentration. Langmuir 1985, 1, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Charman, W.N.; Porter, C.J.H.; Mithani, S.; Dressman, J.B. Physicochemical and physiological mechanisms for the effects of food on drug absorption: The role of lipids and pH. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Rods, A. Physicochemical properties of bile acids and their relationship to biological properties: An overview of the problem. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.O.; Martin, G.H.; Elias, E. The effect of tyrosine conjugation on the critical micellar concentration of free and glycine-conjugated bile salts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 876, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaneya, C.M.; O’Driscoll, C.M. A comparison of the permeation enhancement potential of simple bile salt and mixed bile salt: Fatty acid micellar systems using the CaCo-2 cell culture model. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 207, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, S.; Duchene, D.; Hıncal, A.A.; Capan, Y.; Ponchel, G. In vitro studies on enhancing effect of sodium glycocholate on transbuccal permeation of morphine hydrochloride. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spivak, W.; Morrison, C.; Devinuto, D.; Yuey, W. Spectrophotometric determination of the critical micellar concentration of bile salts using bilirubin monoglucuronide as a micellar probe. Biochem. J. 1988, 252, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, R.; Ravivarapu, H.; Redkar, S.; Li, X.; Jasti, B.R. Transbuccal delivery of 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine: Effects of drug concentration, buffer solution, and bile salts on permeation. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 8, E1–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, R.; Sakhare, S.; Mali, K. In vitro absorption studies of mucoadhesive tablets of Acyclovir. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2010, 44, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, N.N.; Eddington, N.D.; Fasano, A. Tight junction modulation and its relationship to drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.H.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K. Enhanced intestinal absorption of salmon calcitonin (sCT) from proliposomes containing bile salts. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin1, M.; SinanAktas, M.; Vural, I.; Ozturk, M. Salmon calcitonin-loaded Eudragit® and Eudragit®-PLGAnanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2012, 29, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimipour, E.; Jalali, A.; SajjadiTabassi, S.A.; Löbenberg, R. The enhancing effect of sodium glycocholate and sodium salicylate on rats gastro-intestinal permeability to insulin. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2004, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, A.; Moghimipour, E.; Akhgari, A. Enhancing effect of bile salts on gastrointestinal absorption of insulin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, K.; More, R.M.; Patel, D.M.; Sandeep, D.S.; Ganesh, N.S. Chemical permeation enhancers for transdermal drug delivery: A brief review. Der Pharm. Lett. 2010, 2, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Shembale, A.I.; Borole, D.K.; Lohiya, R.T. Useful permeation enhancers for transdermal drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2010, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, H. Effect of penetration enhancer on in vitro release of diclofenac sodium gel formulation. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2011, 2, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Valenta, C.; Nowack, E.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Deoxycholate-hydrogels: Novel drug carrier systems for topical use. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 185, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyigit, T.; Tekmen, I.; Sönmez, Ü.; Santi, P.; Özer, Ö. Deoxycholate hydrogels of betamethasone-17-valerate intended for topical use: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchak, M.; Handali, S. Effects of various penetration enhancers on penetration of aminophylline through shed snake skin. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2014, 9, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moghimipour, E.; SajjadiTabassi, S.A.; Kouchak, M.; Varghaei, H. Combination strategies for enhancing transdermal absorption of theophylline through shed snake skin. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, H.A. Transdermal drug delivery: Penetration enhancement techniques. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamman, J.H.; Stander, M.; Kotze, A.F. Effect of the degree of quaternisation of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride on absorption enhancement: In vivo evaluation in rat nasal epithelia. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 232, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkus, F.W.H.M.; Schipper, N.G.M.; Hermens, W.A.J.J.; Romeijn, S.G.; Verhoef, J.C. Absorption enhancers in nasal drug delivery: Efficacy and safety. J. Control. Release 1993, 24, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, S.K.S.; Kumar Keshari, R.; Rai, A.K. Advances in nasal trans-mucosal drug delivery. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ozsoy, Y.; Gungor, S.; Cevher, E. Nasal delivery of high molecular weight drugs. Molecules 2009, 14, 3754–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillion, D.J.; Amsden, J.A.; Kensil, C.R.; Recchia, J. Structure-function relationship among Quillaja saponins serving as excipients for nasal and ocular delivery of Insulin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, S.; Yashiki, T.; Mima, H. Mechanisms for the enhancement of the nasal absorption of insulin by surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 1981, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, G.S.; Moses, A.C.; Silver, R.D.; Flier, J.S.; Carey, M.C. Nasal absorption of insulin: Enhancement by hydrophobic bile salts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7419–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türker, S.; Onur, E.; Özer, Y. Nasal route and drug delivery systems. Pharm. World Sci. 2004, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, N.; Maitani, Y.; Machida, Y.; Nakagaki, M.; Nagai, T. Influence of bile salts on the permeability of insulin through the nasal mucosa of rabbits in comparison with dextran derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 1991, 74, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, M.A.; Wulff Nielsen, H.; Bechgaard, E. Nasal bioavailability of peptide T in rabbits: Absorption enhancement by sodium glycocholate and glycofurol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, C.L.; Mokhtarzadeh, L.; Venkatesan, P.; Babu, S.; Axelrod, H.R.; Sofia, M.J.; Kakarla, R.; Chan, T.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Design of compounds that increase the absorption of polar molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12218–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aungst, B.J.; Rogers, N.J.; Shefter, E. Comparison of nasal, rectal, buccal, sublingual and intramuscular insulin efficacy and the effects of a bile salt absorption promoter. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 244, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dondeti, P.; Zia, H.; Needham, T.E. In vivo evaluation of spray formulations of human insulin for nasal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 122, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harai, S.; Ikenaga, T.; Matsuzawa, T. Nasal absorption ofinsulin in dogs. Diabetes 1978, 27, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SajadiTabassi, S.A.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Ramezani, M.; Moghimipour, E.; Mohajeri, S.A. Isolation, characterization and study of enhancing effects on nasal absorption of insulin in rat of the total saponin from Acanthophyllumsquarrosum. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2007, 39, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodla, S.; Velmurugan, S. Buccal penetration enhancers-an review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hearnden, V.; Sankar, V.; Hull, K.; VidovićJuras, D.; Greenberg, M.; Ross Kerr, A.; Lockhart, P.B.; Patton, L.L.; Porter, S.; Thornhill, M.H. New developments and opportunities in oral mucosal drug delivery for local and systemic disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.H.; Chun, K.H.; Jeon, S.O.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, S. Enhanced transbuccal salmon calcitonin (sCT) delivery: Effect of chemical enhancers and electrical assistance on in vitro sCTbuccal permeation. Eur J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogstraate, A.J.; Senel, S.; Cullander, C.; Verhoef, J.; Junginger, H.E.; Bodd, H.E. Effects of bile salts on transport rates and routes of FITC-labelled compounds across porcine buccal epithelium in vitro. J. Control. Release 1996, 40, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, G. Delivery of insulin to the buccal mucosa utilizing the RapidMistTM system. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, R.; Robinson, J. Mechanisms of penetration enhancement for transbuccal delivery of salicylic acid. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 85, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem-Quintanara, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Falson-Rieg, F.; Buri, P. Mechanisms of oral permeation enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 156, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hayakawa, E.; Kato, Y.; Nishiura, A.; Lee, V.H. A mechanistic study on enhancement of rectal permeability to insulin in albino rabbits. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 263, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim1, D.W.; Ramasamy, T.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O.; Choi, H.G. The influence of bile salt on the chemotherapeutic response of docetaxelloaded thermosensitive nanomicelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3815–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saettone, M.F.; Chetoni, P.; Cerbai, R.; Mazzanti, G.; Braghiroli, L. Evaluation of ocular permeation enhancers: In vitro effects on corneal transport of fourβ-blockers, and in vitro/in vivo toxic activity. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 142, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Luo, A.; Dodda-Kashi, S.; Lee, V. The ocular route for systemic insulin delivery in the albino rabbit. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 249, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicolazzo, J.A.; Reed, B.L.; Finnin, B.C. Buccal penetration enhancers-How do they really work? J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojancevic, M.; Pavlovic, N.; Golocorbin-Kon, S.; Mikov, M. Application of bile acids in drug formulation and delivery. Front. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Chow, M.S.S. HO-1-u-1 model for screening sublingual drug delivery-Influence of pH, osmolarity and permeation enhancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 370, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.S.I.; Derle, N.D.; Bhamber, R. Permeability enhancement techniques for poorly permeable drugs: A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchcliffe, M.; Illum, L. Intranasal insulin delivery and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 35, 199–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gebhardt, M.; Bian, S.; Kwon, K.A.; Shim, C.K.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, D.D. Enhancing effect of surfactants on fexofenadine. HCltransportacross the human nasal epithelial cell monolayer. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 330, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H.L.; Yamamoto, A. Penetration and enzymatic barriers to peptide and protein absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1990, 4, 171–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpar, H.O.; Eyles, J.E.; Williamson, E.D.; Somavarapu, S. Intranasal vaccination against plague, tetanus and diphtheria. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 51, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, C.; Kiran Kumar, Y.; Venkateshwar Rao, P.; Rama Rao, T. Chemical enhancers in buccal and sublingual delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanothecnol. 2011, 4, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hayakawa, E.; Lee, V.H.L. Insulin and proinsulin proteolysis in mucosal homogenates of the albino rabbit: Implications in peptide delivery from nonoral routes. Life Sci. 1990, 47, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, Y.; Awata, C.; Nakamichi, C.; Sugimoto, I. The effectof additives on the oral mucosal absorption of humancalcitonin in rats. J. Pharmacobiol. Dyn. 1988, 11, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchateau, G.S.M.J.E.; Zuidema, J.; Merkus, F.W.H.M. Bile salts and intranasal drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 31, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, M.A.; Dent, J.; Wheeldon, E.B.; Smith, P.L. Nasal drug delivery: An in vitro characterization of transepitehlial electrical properties and fluxes in the presence or absence of enhancers. J. Control. Release 1998, 8, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwana, M.A.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. The effect of absorption enhancers on the initialdegradation kinetics of insulin by α-chymotrypsin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 217, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Uehara, Y.; Iwanaga, K.; Kakemi, M.; Ohashi, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Nakai, Y. Influence of absorption enhancers (bile salts) and the preservative (benzalkonium chloride) on mucociliary function and permeation barrier function in rabbit tracheas. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.; Adu, J.; Davey, A.J.; Abbott, N.J.; Bradbury, M.W.B. The effect of bile salts on the permeability and ultrastructure of the perfused, energy-depleted, rat blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1991, 11, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, J.M.; Lichtenberger, L.M. Role of biliary phosphatidylcholine in bile acid protection and NSAID injury of the ileal mucosa in rats. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Qi, J.; Lu, Y.; Hu, F.; Yin, Z.; Wu, W. Lecithin in mixed micelles attenuates the cytotoxicity of bile salts in Caco-2 cells. Toxicol. in Vitro 2013, 27, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.G.; Yao, J. Nasal absorption enhancement of insulin by sodium deoxycholate in combination with cyclodextrins. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2001, 22, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muheem, A.; Shakeel, F.; Jahangir, M.A.; Anwara, M.; Mallick, N.; Kumar Jain, G.; Husain Warsia, M.; Jalees Ahmad, F. A review on the strategies for oral delivery of proteins and peptides and their clinical perspectives. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J. Liposomal formulations for enhanced lymphatic drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niua, M.; Lu, Y.; Hovgaard, L.; Guan, P.; Tan, Y.; Lian, R.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. Hypoglycemic activity and oral bioavailability of insulin-loaded liposomes containing bile salts in rats: The effect of cholate type, particle size and administered dose. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.; Ferro, V.A.; Mullen, A.B.; Tetley, L.; Mullen, M.; Carter, K.C.; Alexander, J.; Stimson, W.H. Optimisation of a lipid based oral delivery system containing A/Panama influenza haemagglutinin. Vaccine 2004, 22, 2425–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Niu, M.; Lian, R.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Enhanced oral bioavailability of cyclosporine A by liposomes containing a bile salt. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Conacher, M.; Alexander, J.; Brewer, J.M. Oral immunisation with peptide and protein antigens by formulation in lipid vesicles incorporating bile salts (bilosomes). Vaccine 2001, 19, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.; Scales, H.E.; Shakir, E.; Alexander, J.; Carter, K.C.; Mullen, A.B.; Ferro, V.A. Oral delivery of tetanus toxoid using vesicles containing bile salts (bilosomes) induces significant systemic and mucosal immunity. Methods 2006, 38, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Khatri, K.; Gupta, P.N.; Goyal, A.K.; Mehta, A.; Vyas, S.P. Oral immunization against hepatitis B using bile salt stabilized vesicles (bilosomes). J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moghimipour, E.; Ameri, A.; Handali, S. Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts. Molecules 2015, 20, 14451-14473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814451
Moghimipour E, Ameri A, Handali S. Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts. Molecules. 2015; 20(8):14451-14473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814451
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoghimipour, Eskandar, Abdulghani Ameri, and Somayeh Handali. 2015. "Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts" Molecules 20, no. 8: 14451-14473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814451
APA StyleMoghimipour, E., Ameri, A., & Handali, S. (2015). Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts. Molecules, 20(8), 14451-14473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200814451





