The Application of Template Selectophores for the Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
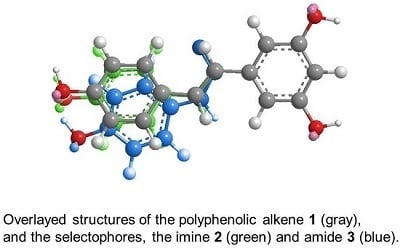
2.1. Selectophore Preparations





2.2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs)


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents and Equipment
3.2. Syntheses of Polyphenolic Selectophores
3.2.1. 3,5-Diacetoxybenzoic Acid
3.2.2. (E)-3,4′,5-Triacetoxystilbene
3.2.3. (E)-Resveratrol, 1
3.2.4. 5-[(4-Hydroxy-phenylimino)-methyl]-benzene-1,3-diol, 2
3.2.5. 3,5-Dihydroxy-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzamide, 3
3.3. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
3.4. Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashim, S.N.N.S.; Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Hearn, M.T.W. A comparison of covalent and non-covalent imprinting strategies for the synthesis of stigmasterol imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hearn, M.T.W.; Langford, S.; Tuck, K.L.; Harris, S.; Boysen, R.I.; Perchyonok, V.T.; Danylec, B.; Schwarz, L.; Chowdhury, J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Patent WO2010085851A1, 5 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition of the bioactive polyphenol, (E)-resveratrol. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Yang, Y.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Enrichment of (E)-resveratrol from peanut byproduct with molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3539–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.E.; Bomser, J.A.; Min, D.B. Bioactivity of resveratrol. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2006, 5, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichenametla, S.N.; Taruscio, T.G.; Barney, D.L.; Exon, J.H. A review of the effects and mechanisms of polyphenolics in cancer. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeandet, P.; Sbaghi, M.; Meunier, P. The potential relationship of stilbene (resveratrol) synthesis to anthocyanin content in grape berry skins. Vitis 1995, 34, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Widstrand, C.; Yilmaz, E.; Boyd, B.; Billing, J.; Rees, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers: A new generation of affinity matrices. Am. Lab. 2006, 38, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, L.I.; Paprica, A.; Arvidsson, T. A highly selective solid-phase extraction sorbent for preconcentration of sameridine made by molecular imprinting. Chromatographia 1997, 46, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, P. Present Status of Chemotherapy. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1909, 42, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Synthetic receptors in bioanalysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Fujiwara, K.; Takeuchi, T. Atrazine-selective polymers prepared by molecular imprinting of trialkylmelamines as dummy template species of atrazine. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, L.I. Efficient sample pre-concentration of bupivacaine from human plasma by solid-phase extraction on molecularly imprinted polymers. Analyst 2000, 125, 1515–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.-F.; Xie, X.-Y.; Shi, Y.-P. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of resveratrol in wine. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1300, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, S.N.N.S.; Schwarz, L.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Yang, Y.; Danylec, B.; Hearn, M.T.W. Rapid solid-phase extraction and analysis of resveratrol and other polyphenols in red wine. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1313, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, L.J.; Potdar, M.K.; Danylec, B.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Microwave-assisted synthesis of resveratrol imprinted polymers with enhanced selectivity. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, M.B.; Liu, J.; Meredith, E.L.; Nartey, E. Synthesis of resveratrol using a direct decarbonylative Heck approach from resorcylic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 4819–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solladie, G.; Pasturel-Jacope, Y.; Maignan, J. A re-investigation of resveratrol synthesis by Perkin reaction. Application to the synthesis of aryl cinnamic acids. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar]
- Andrus, M.; Meredith, E. Synthesis of Resveratrol. Patent WO2001060774A1, 23 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guiso, M.; Marra, C.; Farina, A. A new efficient resveratrol synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, M.B.; Liu, J. Preparation of Resveratrol Ester Analogs as Sirtuin Activators. Patent WO2005069998A2, 4 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Megavand, S.; Fadi, F. Improved Process for the Preparation of Resveratrol via Wittig-Horner Reaction. Patent EP1466884A1, 13 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.; Warner, J. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Kirchhoff, M.M. Origins, current status, and future challenges of green chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossio, F.P.; Aldaba Arevalo, E.; Vara Salazar, Y.I.; Zubia Olascoaga, A.; Vivanco Amato, S.; Mendoza Arteche, M.L.; Salado Pogonza, C.; Gallot Escobal, N.; Vidal Vanaclocha, F. New Nitrogen-Containing Trans-Stilbene Analogs and Their Preparation, Antimetastatic Activity and Their Medical Applications. Patent WO2006108864A2, 19 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Baek, H.S.; Rho, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Chang, I.S.; Lee, O.S.; Shin, H.J. Preparation of Hydroxybenzamides as Antiaging and Antiwrinkle Cosmetic Ingredients. Patent WO2007021067A1, 22 Feburary 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.R.; Voit, B.I.; Mourey, T.H. All-aromatic hyperbranched polyesters with phenol and acetate end groups: Synthesis and characterization. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 4617–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, L.; Holdsworth, C.I.; McCluskey, A.; Bowyer, M.C. Synthesis and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer selective to 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Li, S.; Chowdhury, J.; Hearn, M.T.W. Photolithographic patterning of biomimetic molecularly imprinted polymer thin films onto silicon wafers. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danylec, B.; Schwarz, L.J.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. The Application of Template Selectophores for the Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Molecules 2015, 20, 17601-17613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917601
Danylec B, Schwarz LJ, Harris SJ, Boysen RI, Hearn MTW. The Application of Template Selectophores for the Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Molecules. 2015; 20(9):17601-17613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917601
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanylec, Basil, Lachlan J. Schwarz, Simon J. Harris, Reinhard I. Boysen, and Milton T. W. Hearn. 2015. "The Application of Template Selectophores for the Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers" Molecules 20, no. 9: 17601-17613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917601
APA StyleDanylec, B., Schwarz, L. J., Harris, S. J., Boysen, R. I., & Hearn, M. T. W. (2015). The Application of Template Selectophores for the Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Molecules, 20(9), 17601-17613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917601