The Determination of Food Dyes in Vitamins by RP-HPLC
Abstract
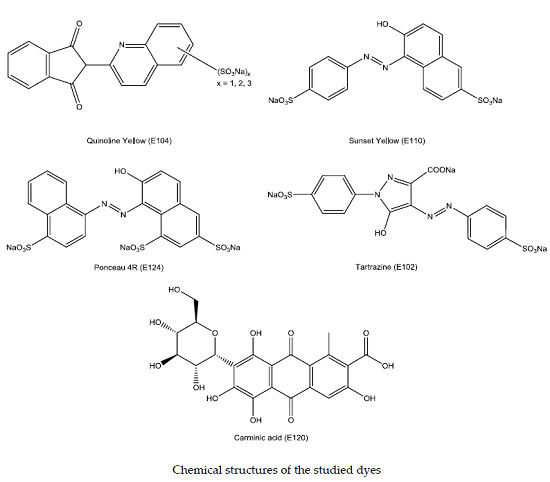
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Solutions
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Instrumentation and HPLC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations World Health Organization; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Concepts, definitions and approaches used to define nutritional needs and recommendations. In Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization, Ed.; SNP Best-set Typesetter Ltd.: Hong Kong, China, 2004; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hurrell, R.F.; Bohn, T.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Reddy, M. 100 Years of Vitamins. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2012, 82, 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, K.V.; Kumar, G.P. Colorants—The cosmetics for the pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwrigh, M. Dyes in the development of drugs and pharmaceuticals. Dyes Pigm. 2008, 76, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, L. Biotechnological production of colorants. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 143, 51–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vlase, L.; Muntean, D.; Cobzac, S.C.; Filip, L. Development and validation of an HPLC-UV method for determination of synthetic food dyes. Revue Roum. Chim. 2014, 59, 719–725. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council Directive. European Parliament and Council Directive 94/36/EC of 30 June 1994 on Colours for Use in Foodstuffs; Official Journal of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council Directive. Directive 2009/35/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on Colouring Matters Which May Be Added to Medicinal Products; Official Journal of the European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Amchová, P.; Kotolova, H.; Rudá, J. Health safety issues of synthetic food colorants. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golka, K.; Kopps, S.; Mysliak, Z.W. Carcinogenity of azo colorants: Influence of solubility and bioavailability. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 151, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Chen, H. Toxicological significance of azo dye metabolism by human intestinal microbiota. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 568–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerlick, R.A.; Campbell, C.F. Medication dyes as a source of drug allergy. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.; Baker, J.R.; Baldwin, J.L.; Chou, A. Identification of carmine allergens among carmine allergy patients. Allergy 2001, 56, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gultekin, F.; Doguc, D.K. Allergic and immunologic reactions to food additives. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 6–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overmeyer, S.; Taylor, E. Annotation: Principles of treatment for hyperkinetic disorder: Practice approaches for the UK. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1999, 40, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downham, A.; Collins, P. Colouring our food in the last and next millennium. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, D.; Barrett, A.; Cooper, A.; Crumpler, D.; Dalen, L.; Grimshaw, K.; Kitchin, E.; Lok, K.; Porteous, L.; Prince, E.; et al. Food additives and hyperactive behaviour in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS). Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of cochineal, carminic acid, carmines (E 120) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.H.; Alshammery, H.M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Alghamdi, A.F. Determination of Carmine Food Dye (E120) in Foodstuffs by Stripping Voltammetry. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chanlon, S.; Joly-Pottuz, L.; Chatelut, M.; Vittori, O.; Cretier, J.L. Determination of Carmoisine, Allura red and Ponceau 4R in sweets and soft drinks by Differential Pulse Polarography. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2005, 18, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, P.; Yarnitzky, C.; Cais, M. Determination of synthetic food colours by means of a novel sample preparations system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 248, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, S.; Őzdemir, Y. Determination of Ponceau 4R and Tartrazine in Various Samples by Derivative Spectrophotometric Methods. Turk. J. Chem. 1997, 2, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.C.; Mou, S.F.; Hou, X.P.; Riviello, J.M.; Ni, Z.M. Determination of eight synthetic food dyes in drinks by high-performance ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 827, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, N.; Ichihashi, K. Determination of 40 synthetic food colors in drinks and candies by high-performance liquid chromatography using a short column with photodiode array detection. Talanta 2008, 74, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschbaum, J.; Krause, C.; Pfalzgraf, S.; Brückner, H. Development and Evaluion of an HPLC-DAD. Method for Determination of Synthetic Food Dyes. Chromatographia 2003, 57, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Minioti, K.S.; Sakellariou, C.F.; Thomaidis, N.S. Determination of 13 synthetic food dyes in water-soluble foods by reversed-phase high-performance liuid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 583, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Choi, J.C.; Song, S.B.; Kim, M. Quntitative determination of carmine in foods by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, M.; Szulińska, Z.; Wilk, M.; Anuszewska, E. Separation of synthetic food colourants in the mixed micellar system. Application to pharmaceutical analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1081, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.P.; Brum, D.M.; Branco de Andrade, E.C.; Netto, A.D.P. Determination of synthetic dyes in selected foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography with UV-DAD detection. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the appropriateness of the food azo-colours Tartrazine (E 102), Sunset Yellow FCF (E 110), Carmoisine (E 122), Amaranth (E 123), Ponceau 4R (E 124), Allura Red AC (E 129), Brilliant Black BN (E 151), Brown FK (E 154), Brown HT (E 155) and Litholrubine BK (E 180) for inclusion in the list of food ingredients set up in Annex IIIa of Directive 2000/13/EC. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants; WHO Technical Report Series No. 901; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.



| Sample | Retention Time (min) | Concentration of Colorant (μg·mL−1) | Content of Colorant (μg/Capsule) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E (Generica) | 1.830 | 49.50 (E120) | 495 ± 0.02 |
| Vitamin E (Noventis) | 1.870 | 31.48 (E120) | 314.8 ± 0.02 |
| Vitamin E (Zentiva) | 2.420 | 7.95 (E124) | 79.5 ± 0.01 |
| Vitamin AD (Slovakofarma) | 2.463 | 52.40 (E102) | 524.0 ± 0.01 |
| Celaskon long effect (Zentiva) body | 4.337 | 4.00 (E110) | 40.0 ± 0.01 |
| Celaskon long effect (Zentiva) cap | 4.340 | 11.90 (E110) | 119.0 ± 0.01 |
| Colorant | Wavelength (nm) | Calibration Equation | LOD (μg·mL−1) | LOQ (μg·mL−1) | Correlation Coefficient (n = 3) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinoline Yellow (E104) | 425 | y = 465.0856x − 0.1182 | 1.00 | 3.32 | 0.9994 | 0.464 |
| Sunset Yellow (E110) | 480 | y = 562.5234x − 0.0315 | 0.40 | 1.33 | 0.9995 | 1.088 |
| Ponceau 4R (E124) | 510 | y = 154.5389x + 0.2086 | 0.70 | 2.33 | 0.9991 | 1.784 |
| Tartrazine (E102) | 425 | y = 580.9923x − 0.2535 | 3.72 | 12.38 | 0.9993 | 1.663 |
| Carmine (E120) | 520 | y = 86.1634x − 0.0242 | 2.40 | 7.99 | 0.9989 | 2.421 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šuleková, M.; Hudák, A.; Smrčová, M. The Determination of Food Dyes in Vitamins by RP-HPLC. Molecules 2016, 21, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101368
Šuleková M, Hudák A, Smrčová M. The Determination of Food Dyes in Vitamins by RP-HPLC. Molecules. 2016; 21(10):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101368
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠuleková, Monika, Alexander Hudák, and Miroslava Smrčová. 2016. "The Determination of Food Dyes in Vitamins by RP-HPLC" Molecules 21, no. 10: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101368
APA StyleŠuleková, M., Hudák, A., & Smrčová, M. (2016). The Determination of Food Dyes in Vitamins by RP-HPLC. Molecules, 21(10), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101368