Recent Progress in the Molecular Recognition and Therapeutic Importance of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Functional Role of IRAK4
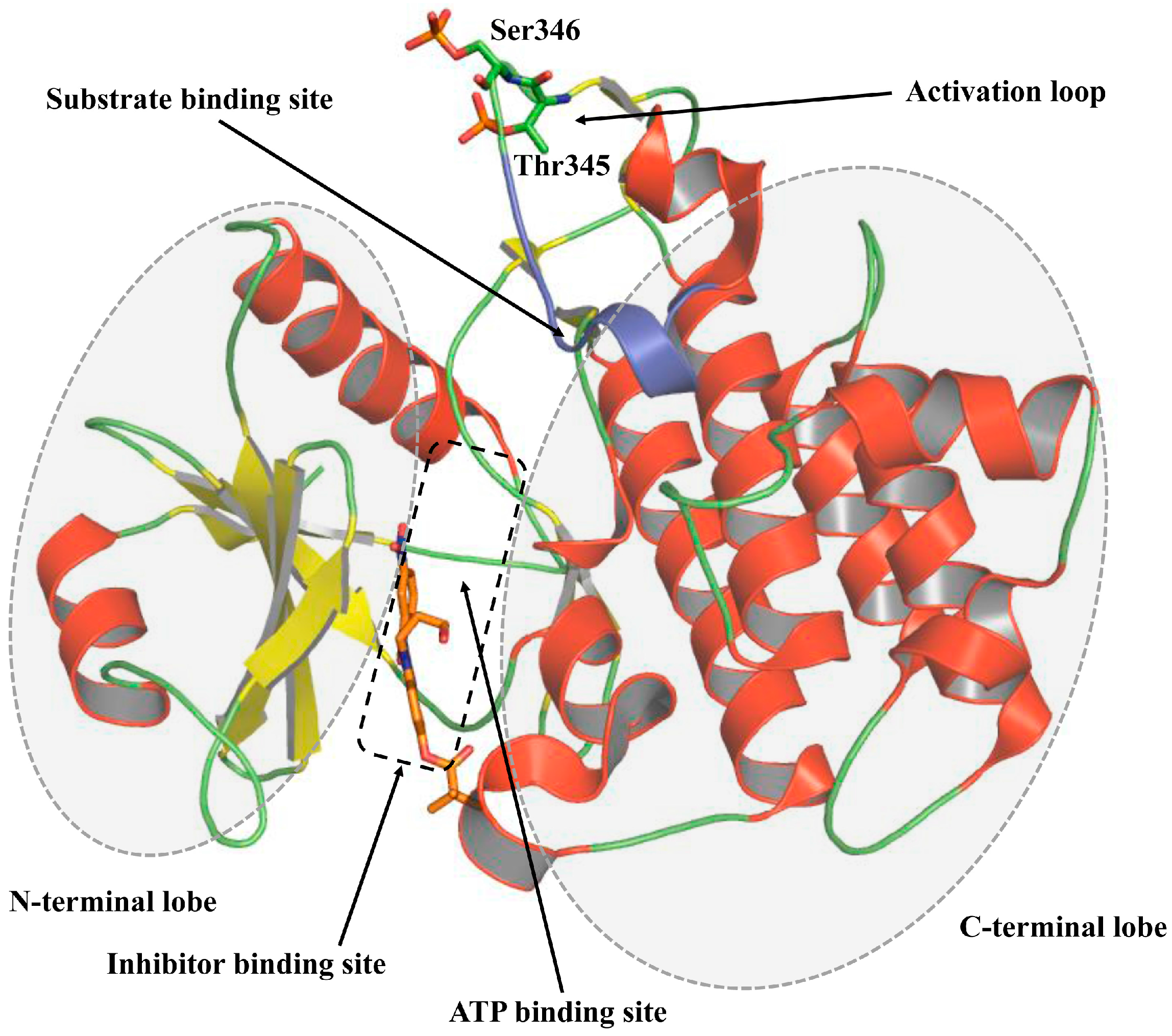
3. Structure of Kinase Domain of IRAK4
4. Structure of IRAK4 with Bound Inhibitors
5. Development of IRAK4 Inhibitor (Non-Crystallographic Study)
6. Selective Kinase Inhibitor Development Targeting Inactive or Allosteric Sites of IRAK4
7. Therapeutic Importance of IRAK4
8. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Strelow, A.; Fontana, E.J.; Wesche, H. IRAK-4: A novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5567–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Wijmenga, C.; O’Neill, L.A. Genetic variation in toll-like receptors and disease susceptibility. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrao, R.; Li, J.; Bergamin, E.; Wu, H. Structural insights into the assembly of large oligomeric signalosomes in the toll-like receptor-interleukin-1 receptor superfamily. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.C.; Lo, Y.C.; Wu, H. Helical assembly in the MYD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature 2010, 465, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Addona, T.; Keshishian, H.; Dahlstrand, E.; Lu, C.; Dorsch, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, A.; Ocain, T.D.; Li, P.; et al. Regulation of IRAK-4 kinase activity via autophosphorylation within its activation loop. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 352, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hernandez, L.D.; Galan, J.E.; Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, M.; Fukuda, K.; Im, J.; Yao, P.; Cui, W.; Bulek, K.; Zepp, J.; Wan, Y.; Kim, T.W.; et al. IRAK-M mediates toll-like receptor/IL-1R-induced nfkappab activation and cytokine production. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollewe, C.; Mackensen, A.C.; Neumann, D.; Knop, J.; Cao, P.; Li, S.; Wesche, H.; Martin, M.U. Sequential autophosphorylation steps in the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 regulate its availability as an adapter in interleukin-1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5227–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, C.; Puel, A.; Bonnet, M.; Ku, C.L.; Bustamante, J.; Yang, K.; Soudais, C.; Dupuis, S.; Feinberg, J.; Fieschi, C.; et al. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK-4 deficiency. Science 2003, 299, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treon, S.P.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Sheehy, P.; Manning, R.J.; Patterson, C.J.; Tripsas, C.; et al. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bernuth, H.; Picard, C.; Jin, Z.; Pankla, R.; Xiao, H.; Ku, C.L.; Chrabieh, M.; Mustapha, I.B.; Ghandil, P.; Camcioglu, Y.; et al. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with myd88 deficiency. Science 2008, 321, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Thomas, K.; Awomoyi, A.; Kuhns, D.B.; Gallin, J.I.; Li, X.; Vogel, S.N. Cutting edge: Expression of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4) proteins with mutations identified in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections alters normal IRAK-4 interaction with components of the IL-1 receptor complex. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6587–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, S.; Duncan, G.S.; Millar, D.G.; Wada, T.; Mirtsos, C.; Takada, H.; Wakeham, A.; Itie, A.; Li, S.; et al. Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature 2002, 416, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziczak-Holbro, M.; Gluck, A.; Tschopp, C.; Mathison, J.C.; Gram, H. IRAK-4 kinase activity-dependent and -independent regulation of lipopolysaccharide-inducible genes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, N.; Tangsinmankong, N.; Ochs, H.; Rucker, R.; Picard, C.; Casanova, J.L.; Haraguchi, S.; Good, R. Interleukin receptor-associated kinase (IRAK-4) deficiency associated with bacterial infections and failure to sustain antibody responses. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Staschke, K.; Bulek, K.; Yao, J.; Peters, K.; Oh, K.H.; Vandenburg, Y.; Xiao, H.; Qian, W.; Hamilton, T.; et al. A critical role for IRAK4 kinase activity in toll-like receptor-mediated innate immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Lan, J.L.; Hung, W.T.; Chen, H.H.; Lai, K.L.; Hsieh, C.W. Involvement of TLR7 MYD88-dependent signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of adult-onset still’s disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X. IRAK4 in TLR/IL-1R signaling: Possible clinical applications. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. TLR2 and TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 47, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Netea, M.G. New insights in the immunobiology of IL-1 family members. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, L.; Stochaj, W.; Siegel, M.; Czerwinski, R.; Dower, K.; Wright, Q.; Hirschfield, M.; Casanova, J.L.; Picard, C.; Puel, A.; et al. Interleukin 1/toll-like receptor-induced autophosphorylation activates interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 4 and controls cytokine induction in a cell type-specific manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10865–10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrao, R.; Zhou, H.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Shaw, D.E.; Li, X.; Wu, H. IRAK4 dimerization and trans-autophosphorylation are induced by myddosome assembly. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasker, M.V.; Gajjar, M.M.; Nair, S.K. Cutting edge: Molecular structure of the IL-1R-associated kinase-4 death domain and its implications for TLR signaling. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4175–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sudom, A.; Ayres, M.; Li, S.; Wesche, H.; Powers, J.P.; Walker, N.P. Crystal structures of IRAK-4 kinase in complex with inhibitors: A serine/threonine kinase with tyrosine as a gatekeeper. Structure 2006, 14, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuglstatter, A.; Villasenor, A.G.; Shaw, D.; Lee, S.W.; Tsing, S.; Niu, L.; Song, K.W.; Barnett, J.W.; Browner, M.F. Cutting edge: IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 structures reveal novel features and multiple conformations. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2641–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wesche, H.; Stevens, T.; Walker, N.; Yeh, W.C. IRAK-4 inhibitors for inflammation. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.P.; Li, S.; Jaen, J.C.; Liu, J.; Walker, N.P.; Wang, Z.; Wesche, H. Discovery and initial sar of inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2842–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahia, M.S.; Kaur, M.; Silakari, P.; Silakari, O. Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase inhibitors: Potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory- and immune-related disorders. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, W.T.; Michael Seganish, W.; Jason Herr, R.; Harding, J.; Yang, J.; Yet, L.; Komanduri, V.; Prakash, K.C.; Lavey, B.; Tulshian, D.; et al. Discovery and hit-to-lead optimization of 2,6-diaminopyrimidine inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, W.T.; Tan, Z.; Ho, G.; Paliwal, S.; Li, G.; Seganish, W.M.; Tulshian, D.; Tata, J.; Fischmann, T.O.; Sondey, C.; et al. Potent and selective amidopyrazole inhibitors of IRAK4 that are efficacious in a rodent model of inflammation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seganish, W.M.; McElroy, W.T.; Herr, R.J.; Brumfield, S.; Greenlee, W.J.; Harding, J.; Komanduri, V.; Matasi, J.; Prakash, K.C.; Tulshian, D.; et al. Initial optimization and series evolution of diaminopyrimidine inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3203–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Altman, M.D.; Baker, J.; Brubaker, J.D.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Fischmann, T.; Gibeau, C.; Kleinschek, M.A.; Leccese, E.; et al. Discovery of 5-Amino-N-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide inhibitors of IRAK4. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisak, J.; Seganish, W.M.; McElroy, W.T.; Tang, H.; Zhang, R.; Tsui, H.C.; Fischmann, T.; Tulshian, D.; Tata, J.; Sondey, C.; et al. Efforts towards the optimization of a bi-aryl class of potent IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4250–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, D.; Robinson, S.; Romero, D.L. Recent advances in the discovery of small molecule inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) as a therapeutic target for inflammation and oncology disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, G.M.; Ceska, T.A.; Fraser, J.L.; Gowers, L.; Groom, C.R.; Higueruelo, A.P.; Jenkins, K.; Mack, S.R.; Morgan, T.; Parry, D.M.; et al. IRAK-4 inhibitors. Part II: A structure-based assessment of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3291–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, G.M.; Fosbeary, R.; Fraser, J.L.; Gowers, L.; Higueruelo, A.P.; James, L.A.; Jenkins, K.; Mack, S.R.; Morgan, T.; Parry, D.M.; et al. IRAK-4 inhibitors. Part III: A series of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3656–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, G.M.; Gowers, L.; Higueruelo, A.P.; Jenkins, K.; Mack, S.R.; Morgan, T.; Parry, D.M.; Pitt, W.R.; Rausch, O.; Richard, M.D.; et al. IRAK-4 inhibitors. Part 1: A series of amides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3211–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.N.; Romero, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Chaudhary, D.; Robinson, S.; Miao, W.; Rui, L.; Westlin, W.F.; Kapeller, R.; et al. Selective interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune disorders and lymphoid malignancy. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppers, R. IRAK4 inhibition to shut down TLR signaling in autoimmunity and MYD88-dependent lymphomas. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Jiang, N.; Chen, D.; Li, E.; Tan, R.; Hou, Y. A novel benzenediamine derivate rescued mice from experimental sepsis by attenuating proinflammatory mediators via IRAK4. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tumey, L.N.; Boschelli, D.H.; Bhagirath, N.; Shim, J.; Murphy, E.A.; Goodwin, D.; Bennett, E.M.; Wang, M.; Lin, L.L.; Press, B.; et al. Identification and optimization of indolo[2,3-c]quinoline inhibitors of IRAK4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yu, L.; Wan, B.; Yu, L.; Huang, Q. Predicting inactive conformations of protein kinases using active structures: Conformational selection of type-ii inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gray, N.S. Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Knapp, S.; Liu, Q.; Gray, N.S. Exploration of type ii binding mode: A privileged approach for kinase inhibitor focused drug discovery? ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, L.A.; Piao, W.; Ru, L.W.; Vogel, S.N.; Toshchakov, V.Y. Targeting toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling by toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adapter protein/MyD88 adapter-like (TIRAP/Mal)-derived decoy peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24641–24648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, W.; Shirey, K.A.; Ru, L.W.; Lai, W.; Szmacinski, H.; Snyder, G.A.; Sundberg, E.J.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Vogel, S.N.; Toshchakov, V.Y. A decoy peptide that disrupts tirap recruitment to TLRs is protective in a murine model of influenza. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, W.; Vogel, S.N.; Toshchakov, V.Y. Inhibition of TLR4 signaling by tram-derived decoy peptides in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.I.; Hunt, J.P.; Herrgard, S.; Ciceri, P.; Wodicka, L.M.; Pallares, G.; Hocker, M.; Treiber, D.K.; Zarrinkar, P.P. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H. Endogenous tlr ligands and autoimmunity. Adv. Immunol. 2006, 91, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraczek, J.; Kim, T.W.; Xiao, H.; Yao, J.; Wen, Q.; Li, Y.; Casanova, J.L.; Pryjma, J.; Li, X. The kinase activity of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 is required for interleukin-1 receptor/toll-like receptor-induced TAK1-dependent NFkappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31697–31705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagoe, T.; Sato, S.; Jung, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Kato, H.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Essential role of IRAK-4 protein and its kinase activity in toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses but not in tcr signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziczak-Holbro, M.; Littlewood-Evans, A.; Pollinger, B.; Kovarik, J.; Dawson, J.; Zenke, G.; Burkhart, C.; Muller, M.; Gram, H. The critical role of kinase activity of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 in animal models of joint inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.; Bastian, J.F. Immunodeficiency in childhood. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2006, 6, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavine, E.; Somech, R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Puel, A.; Bossuyt, X.; Picard, C.; Casanova, J.L.; Roifman, C.M. Cellular and humoral aberrations in a kindred with IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhter, M.; Staschke, K.; Estridge, T.; Rutherford, P.; Jackson, N.; Gifford-Moore, D.; Foxworthy, P.; Reidy, C.; Huang, X.D.; Kalbfleisch, M.; et al. Genetic ablation of IRAK4 kinase activity inhibits vascular lesion formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Kang, S.; Anderson, C.; Sagara, J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Alnemri, E.S. Cutting edge: TLR signaling licenses IRAK1 for rapid activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.M.; Hu, W.; Troutman, T.D.; Jennings, M.; Brewer, T.; Li, X.; Nanda, S.; Cohen, P.; Thomas, J.A.; Pasare, C. IRAK-1 bypasses priming and directly links tlrs to rapid nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.L.; Zhang, D.M.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Jia, K.K.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, R.; Kong, L.D. Cinnamaldehyde and allopurinol reduce fructose-induced cardiac inflammation and fibrosis by attenuating CD36-mediated TLR4/6-IRAK4/1 signaling to suppress nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Kaczanowska, S.; Davila, E. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase signaling and its role in inflammation, cancer progression, and therapy resistance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhyasen, G.W.; Starczynowski, D.T. IRAK signalling in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.; Geng, D.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Z.; Joseph, M.A.; McKenna, C.; Bansal, N.; Ochoa, A.; Davila, E. Augmentation of therapeutic responses in melanoma by inhibition of IRAK-1,-4. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6209–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y.; Manning, R.J.; Patterson, C.J.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Gray, N.; Tai, Y.T.; et al. A mutation in MYD88 (L265P) supports the survival of lymphoplasmacytic cells by activation of bruton tyrosine kinase in waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood 2013, 122, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Pan, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, T.; Li, W.; Wu, W. Relation between anti-atherosclerotic effects of IRAK4 and modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in diabetic rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, J.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1/4 as a novel target for inhibiting neointimal formation after carotid balloon injury. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 1317–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Younger, K.; Gartenhaus, R.; Joseph, A.M.; Hu, F.; Baer, M.R.; Brown, P.; Davila, E. Inhibition of IRAK1/4 sensitizes T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to chemotherapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Yang, P.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Ye, J. The role of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases in vogt-koyanagi-harada disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seganish, W.M. Inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4): A patent review (2012–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patra, M.C.; Choi, S. Recent Progress in the Molecular Recognition and Therapeutic Importance of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4. Molecules 2016, 21, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111529
Patra MC, Choi S. Recent Progress in the Molecular Recognition and Therapeutic Importance of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4. Molecules. 2016; 21(11):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111529
Chicago/Turabian StylePatra, Mahesh Chandra, and Sangdun Choi. 2016. "Recent Progress in the Molecular Recognition and Therapeutic Importance of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4" Molecules 21, no. 11: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111529
APA StylePatra, M. C., & Choi, S. (2016). Recent Progress in the Molecular Recognition and Therapeutic Importance of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4. Molecules, 21(11), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111529




