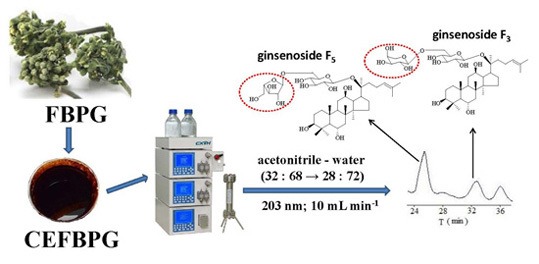
Isolation, Purification and Quantification of Ginsenoside F5 and F3 Isomeric Compounds from Crude Extracts of Flower Buds of Panax ginseng
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Analytical Method
2.1.1. Influence of Mobile Phase Composition
2.1.2. Influence of Volume Ratios of Mobile Phase
2.2. Optimization of Semi-Preparative Method
2.2.1. Optimization of Composition of Mobile Phase
2.2.2. Optimization of Flow Rate
2.2.3. Optimization of Volume Ratios of Mobile Phase
2.2.4. Optimization of Sample Load
2.3. Elucidation of Chemical Structures
2.4. Method Validation
2.4.1. Range and Linearity
2.4.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.4.3. Sensitivity
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of Ginsnoside F5 and F3 in FBPG
2.6. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents, Materials and Preparation of CEFBPG
3.2. Chromatographic Analysis
3.3. Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Separation
3.4. Structure Characterization of Ginsenosides
3.5. Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.H. A review on the medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Song, H.H.; Hong, E.H.; Lee, B.R.; Oh, S.R.; Choi, K.; Yeo, S.G.; Lee, Y.P.; Cho, S.; et al. Antiviral activity of ginsenosides against coxsackievirus B3, enterovirus 71, and human rhinovirus 3. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Gong, X.J. A review on the medicinal potentials of Panax ginseng saponins in diabetes mellitus. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47353–47366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.S.T.; Che, C.M.; Leung, K.W. Recent advances in ginseng as cancer therapeutics: A functional and mechanistic. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.D.; Rhee, D.K.; Lee, Y.H. Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, B.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, E.H.; Chung, B.C. The antistress effect of ginseng total saponin and ginsenoside Rg3 and Rb1 evaluated by brain polyamine level under immobilization stress. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 54, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Yao, C.M.; Yang, X.W. New dammarane-type triterpene saponins from the stems and leaves of Panax ginseng and their cytotoxicity on HL-60 cells. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Yang, X.B.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, J.X.; Gong, X.J. New triterpenoids from the stems and leaves of Panax ginseng. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, D.A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Sugimoto, S.; Nakamura, S.; Sakumae, H.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal flowers. XVI. New dammarane-type triterpene tetraglycosides and gastroprotective principles from flower buds of Panax ginseng. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Song, G.Y.; Nhiem, N.X.; Ding, Y.; Tai, B.H.; Jin, L.G.; Lim, C.M.; Hyun, J.W.; Park, C.J.; Kang, H.K.; et al. Dammarane-type saponins from the flower buds of Panax ginseng and their intracellular radical scavenging capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Song, G.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Hyun, J.H.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, Y.H. Dammarane-type saponins from the flower buds of Panax ginseng and their effects on human leukemia cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Song, S.B.; Tung, N.H.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, Y.H. Inhibition of TNF-a-mediated NF-kB transcriptional activity by dammarane-type ginsenosides from steamed flower buds of Panax ginseng in HepG2 and SK-Hep1 cells. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, S.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Kitagawa, N.; Yoshikawa, M. Chemical constituents from seeds of Panax ginseng: Structure of new dammarane-type triterpene ketone, panaxadione, and HPLC comparisons of seeds and flesh. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.K.; Cho, O.S.; Bae, H.M.; Im, B.O.; Lee, O.H.; Lee, B.Y. Quantitative analysis of ginsenosides composition in flower buds of various ginseng plants. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.L.; Kim, Y.R.; Yang, J.L.; Oh, D.R.; Dao, T.T.; Oh, W.K. Dammarane triterpenes from the leaves of Panax ginseng enhance cellular immunity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.L.; Dou, D.Q.; Chen, X.H.; Yang, H.Z.; Guo, N.; Cheng, G.F. Immunoenhancing activity of protopanaxatriol-type ginsenoside-F3 in murine spleen cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Zhou, H.Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, N.; Gui, M.Y.; Jin, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Li, X.W. Determination of saponins in leaf of Panax ginseng C.A. Mey. by high performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2009, 25, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.N.; Ha, Y.W.; Shin, H.; Son, S.H.; Wu, S.J.; Kim, Y.S. Simultaneous quantification of 14 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer (Korean red ginseng) by HPLC-ELSD and its application to quality control. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuzzati, N.; Gabetta, B.; Jayakar, K.; Pace, R.; Peterlongo, F. Liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometric identification of ginsenosides in Panax giseng roots. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 854, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.S.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Hao, C.; March, R.E. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of ginsenosides. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Ma, Z.Z.; Wen, Y.; Weng, M.H.; Pei, Y.P.; Wang, Z.X.; Kawai, H.; Fukushima, H.; Murakami, Y. A novel minor saponin from the leaves of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 5, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, D.Q.; Wen, Y.; Pei, Y.P.; Chen, Y.J.; Ma, Z.Z. Studies on the minor saponins from leaves of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1997, 22, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshizaki, K.; Devkota, H.P.; Yahara, S. Four new triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Panax japonicus grown in southern Miyazaki Prefecture (4). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.W.; Han, S.B.; Park, I.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, M.K.; Park, J.H. Liquid chromatographic determination of less polar ginsenosides in processed ginseng. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 921, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, J.; Xie, H.; Jia, Y. Development of a sensitive LC-ESI-MS assay for 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh2 and its pharmacokinetic application in dogs: A case for the influence of micronization on traditional Chinese medicine. Intern. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 252, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, P.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Q.; Liang, H. Separation and purification of ginsenoside Re from ginseng bud by selective adsorption of active carbon and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.S.; Gu, L.J.; Fang, Z.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.; Lee, M.R.; Li, Z.; Li, J.J.; Sung, C.K. Simultaneous quantification of 19 ginsenosides in black ginseng developed from Panax ginseng by HPLC-ELSD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Wu, J.A.; McEntee, E.; Yuan, C.S. Saponins composition in American ginseng leaf and berry assayed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Yi, T.; Qin, M.; Liang, Z. Chemical differentiation and quality evaluation of commercial Asian and American ginsengs based on a UHPLC-QTOF/MS/MS metabolomics approach. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 26, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.M.; Li, L.; Bai, H.L. Isolation of four high-purity dammarane saponins from extract of Panax notoginseng by centrifugal partition chromatography coupled with evaporative light scattering detection in one operation. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Han, J.; Duan, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, H. Purification and quantification of ginsenoside Rb3 and Rc from crude extracts of caudexes and leaves of Panax notoginseng. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds ginsenoside F5 and F3 are available from the authors.









| Test No. | Volume Ratios of Moble Phase (Acetonitrile–Water) (n = 3) | Peak Purity of Ginsenoside F5 (%) a,b | RSD (%) (Ginsenoside F5) | Peak Purity of Ginsenoside F3 (%) a,b | RSD (%) (Ginsenoside F3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28:72 | 96.55 ± 1.18 | 1.22 | 94.69 ± 1.25 | 1.32 |
| 2 | 32:68 | 96.19 ± 1.35 | 1.41 | 90.47 ± 2.45 | 2.71 |
| 3 | 32:68 → 28:72 (15 min) | 95.87 ± 0.87 | 0.91 | 94.09 ± 1.02 | 1.08 |
| 4 | 32:68 → 28:72 (10 min) | 96.96 ± 1.04 | 1.08 | 97.18 ± 1.27 | 1.30 |
| Sample Load (mg) | Peak Purity of Ginsenoside F5 (%) a,b | RSD (%) (Ginsenoside F5) | Peak Purity of Ginsenoside F3 (%) a,b | RSD (%) (Ginsenoside F3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.2 | 97.18 ± 1.64 | 1.68 | 97.55 ± 2.11 | 2.16 |
| 15.6 | 96.50 ± 1.22 | 1.27 | 98.20 ± 1.38 | 1.40 |
| 18.4 | 97.21 ± 0.85 | 0.87 | 97.42 ± 1.94 | 1.99 |
| 21.1 | 96.88 ± 1.79 | 1.85 | 97.29 ± 0.92 | 0.95 |
| 28.8 | 97.43 ± 2.15 | 2.21 | 97.12 ± 0.89 | 0.92 |
| 30.5 | 96.14 ± 1.81 | 1.89 | 96.88 ± 1.55 | 1.59 |
| 32.8 | 95.26 ± 2.84 | 2.98 | 94.84 ± 1.05 | 1.11 |
| 43.5 | 93.17 ± 1.36 | 1.46 | 92.90 ± 1.56 | 1.68 |
| No. | Ginsenoside F5 | Ginsenoside F3 | No. | Ginsenoside F5 | Ginsenoside F3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.4 | 39.5 | 22 | 36.2 | 36.3 |
| 2 | 28.2 | 28.2 | 23 | 23.2 | 23.3 |
| 3 | 78.6 | 78.6 | 24 | 126.1 | 126.0 |
| 4 | 40.4 | 40.4 | 25 | 131.1 | 131.3 |
| 5 | 61.8 | 61.8 | 26 | 25.8 | 25.9 |
| 6 | 67.8 | 67.9 | 27 | 17.9 | 18.0 |
| 7 | 47.5 | 47.5 | 28 | 32.0 | 32.1 |
| 8 | 41.3 | 41.3 | 29 | 16.5 | 16.6 |
| 9 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 30 | 17.5 | 17.7 |
| 10 | 39.4 | 39.5 | 1′ | 98.1 | 98.2 |
| 11 | 30.8 | 30.9 | 2′ | 75.1 | 75.0 |
| 12 | 70.3 | 70.4 | 3′ | 79.3 | 79.2 |
| 13 | 49.1 | 49.2 | 4′ | 72.2 | 72.2 |
| 14 | 51.4 | 51.5 | 5′ | 76.6 | 76.8 |
| 15 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 6′ | 68.6 | 69.3 |
| 16 | 26.7 | 26.8 | 1′′ | 110.2 | 104.7 |
| 17 | 51.7 | 51.8 | 2′′ | 83.4 | 71.9 |
| 18 | 17.7 | 18.0 | 3′′ | 78.9 | 74.2 |
| 19 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 4′′ | 86.1 | 68.6 |
| 20 | 83.3 | 83.6 | 5′′ | 62.7 | 65.7 |
| 21 | 22.4 | 22.4 |
| Ginsenosides | Original (μg) | Spiked (μg) | Found (μg) (Mean ± SD) | Recovery (%) a | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F5 | 210.6 | 200 | 405.9 ± 3.70 | 97.10 | 1.04 |
| 400 | 596.6 ± 3.36 | 96.58 | 0.84 | ||
| F3 | 252.4 | 200 | 452.2 ± 4.46 | 99.91 | 2.23 |
| 400 | 657.6 ± 4.38 | 101.32 | 1.09 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.-K.; Xu, F.; Gong, X.-J. Isolation, Purification and Quantification of Ginsenoside F5 and F3 Isomeric Compounds from Crude Extracts of Flower Buds of Panax ginseng. Molecules 2016, 21, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030315
Li K-K, Xu F, Gong X-J. Isolation, Purification and Quantification of Ginsenoside F5 and F3 Isomeric Compounds from Crude Extracts of Flower Buds of Panax ginseng. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ke-Ke, Fei Xu, and Xiao-Jie Gong. 2016. "Isolation, Purification and Quantification of Ginsenoside F5 and F3 Isomeric Compounds from Crude Extracts of Flower Buds of Panax ginseng" Molecules 21, no. 3: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030315
APA StyleLi, K.-K., Xu, F., & Gong, X.-J. (2016). Isolation, Purification and Quantification of Ginsenoside F5 and F3 Isomeric Compounds from Crude Extracts of Flower Buds of Panax ginseng. Molecules, 21(3), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030315