Structure-Based Drug Design of Small Molecule Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors to Treat Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. High-Throughput Virtual Screening
2.2. Design and Synthesis of Derivatives of M7594_0037
2.3. Anticancer Activity of M7594_0037 and Its Derivatives
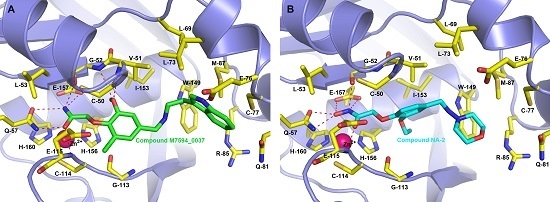
2.4. Binding Modes of M7594_0037 and Its Derivatives
2.5. In Silico Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Predictions of M7594_0037 and Its Derivatives
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. High-Throughput Virtual Screening
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. Synthesis of Ethyl 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-formylphenoxy)acetate (EV-1)
3.2.2. Synthesis of Ethyl 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-((pyridin-3-ylamino)methyl)phenoxy)acetate (3AP-1)
3.2.3. Synthesis of 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-((pyridin-3-ylamino)methyl)phenoxy)-N-hydroxyacetamide (3AP-2)
3.2.4. Synthesis of Ethyl 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-((morpholinoamino)methyl)phenoxy)acetate (NA-1)
3.2.5. Synthesis of 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-((morpholinoamino)methyl)phenoxy)-N-hydroxyacetamide (NA-2)
3.2.6. Synthesis of ethyl 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-(((4-(3-oxomorpholino)phenyl)amino)methyl)phenoxy)acetate (M-1)
3.2.7. Synthesis of 2-(2-Ethoxy-4-(((4-(3-oxomorpholino)phenyl)amino)methyl)phenoxy)-N-hydroxyacetamide (M-2)
3.3. Anticancer Activity Evaluation of M7594_0037 and Its Derivatives
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. In Silico Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Prediction of M7594_0037 and Its Derivatives
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leeds, J.A.; Dean, C.R. Peptide deformylase as an antibacterial target: A critical assessment. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2006, 6, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, P.T.R.; Yu, X.C.; Pei, D. Peptide Deformylase: A New Type of Mononuclear Iron Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 12418–12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinnel, T.; Patiny, L.; Ragusa, S.; Blanquet, S. Design and synthesis of substrate analogue inhibitors of peptide deformylase. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 4287–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Z.; Patel, D.V.; Hackbarth, C.J.; Wang, W.; Dreyer, G.; Young, D.C.; Margolis, P.S.; Wu, C.; Ni, Z.-J.; Trias, J.; et al. Actinonin, a Naturally Occurring Antibacterial Agent, Is a Potent Deformylase Inhibitor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Nguyen, K.T.; Verlinde, C.L.M.J.; Hol, W.G.J.; Pei, D. Structure-Based Design of a Macrocyclic Inhibitor for Peptide Deformylase. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofland, D.; Difuntorum, S.; Waller, A.; Clements, J.M.; Weaver, M.K.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Johnson, K. In vitro antibacterial activity of the peptide deformylase inhibitor BB-83698. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, K.; Hackel, M.; Hightower, S.; Hoban, D.; Bouchillon, S.; Qin, D.; Aubart, K.; Zalacain, M.; Butler, D. Comparative analysis of the antibacterial activity of a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, GSK1322322. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglione, C.; Pierre, M.; Meinnel, T. Peptide deformylase as a target for new generation, broad spectrum antimicrobial agents. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglione, C.; Serero, A.; Pierre, M.; Boisson, B.; Meinnel, T. Identification of eukaryotic peptide deformylases reveals universality of N-terminal protein processing mechanisms. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5916–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinnel, T. Peptide Deformylase of Eukaryotic Protists: A Target for New Antiparasitic Agents? Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Antczak, C.; Li, Y.; Sirotnak, F.M.; Bornmann, W.G.; Scheinberg, D.A. A new human peptide deformylase inhibitable by actinonin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serero, A.; Giglione, C.; Sardini, A.; Martinez-Sanz, J.; Meinnel, T. An unusual peptide deformylase features in the human mitochondrial N-terminal methionine excision pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52953–52963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Alvarez, S.; Gardner, J.; Sheth, A.; Manfredi, G.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Heaney, M.; Scheinberg, D. Inhibition of human peptide deformylase disrupts mitochondrial function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 5099–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, A.C.; Spremulli, L.L. Interaction of mitochondrial initiation factor 2 with mitochondrial fMet-tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5464–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.X.; Spremulli, L.L. Identification and initial characterization of translational initiation factor 2 from bovine mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13618–13622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Castro, I.; Costa, L.T.D.; Amorim, A.; Azevedo, L. Transcriptional regulation of the human mitochondrial peptide deformylase (PDF). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Liu, B.-G.; Yang, Z.-W.; Li, C.-M.; Wang, B.-C.; Yang, C.-P. Genome-Wide Identification and in Silico Analysis of Poplar Peptide Deformylases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5112–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Hu, X.; Colton, C.; Chakrabarti, R.; Zhu, M.X.; Pei, D. Characterization of a human peptide deformylase: Implications for antibacterial drug design. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 9952–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, H.; Chikara, S.; Gehring, D.; Yildirim, T.; Menon, J.; Reindl, K. Overexpression of peptide deformylase in breast, colon, and lung cancers. BMC Cancer 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, W.-J.; Jeon, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, B.-J.; Ryu, K.-S. Codon optimization enhances protein expression of human peptide deformylase in E. coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 70, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Alvarez, S.; Goldgur, Y.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Li, Y.; Scheinberg, D. Structure and activity of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a novel cancer target. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; She, Y.; Soskis, M.J.; Borella, C.P.; Gardner, J.R.; Hayes, P.A.; Dy, B.M.; Heaney, M.L.; Philips, M.R.; Bornmann, W.G.; et al. Human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a new anticancer target of actinonin-based antibiotics. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antczak, C.; Shum, D.; Escobar, S.; Bassit, B.; Kim, E.; Seshan, V.E.; Wu, N.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Li, Y.M.; et al. High-throughput identification of inhibitors of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antczak, C.; Shum, D.; Bassit, B.; Frattini, M.G.; Li, Y.M.; de Stanchina, E.; Scheinberg, D.A.; Djaballah, H. Identification of benzofuran-4,5-diones as novel and selective non-hydroxamic acid, non-peptidomimetic based inhibitors of human peptide deformylase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4528–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangshetti, J.N.; Khan, F.A.; Shinde, D.B. Peptide deformylase: A new target in antibacterial, antimalarial and anticancer drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SYBYL 7.1. Tripos Associates Inc.: S.H. R., St. Louis, USA, 2005.
- Collet, A. ChemInform Abstract: Cyclotriveratrylene and Related Hosts. Cheminform 1997, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F.; Carson, K.G.; Harris, B.D.; Maryanoff, C.A.; Shah, R.D. Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones with Sodium Triacetoxyborohydride. Studies on Direct and Indirect Reductive Amination Procedures. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogza, Y.P.; Katsiel’, A.L.; Sharypova, A.N.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Fisyuk, A.S. Synthesis and Biological Activity of 4H-Thieno[3,2-c]Chromene Derivatives. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2015, 50, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSIRIS Property Explorer. Available online: http://www.organic-chemistry.org/prog/peo/ (accessed on 29 January 2016).
- Vyas, V.K.; Goel, A.; Ghate, M.; Patel, P. Ligand and structure-based approaches for the identification of SIRT1 activators. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 228, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not available.





| Compounds | A549 (μM) | MCF7 (μM) | HeLa (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M7594_0037 | 29.49 ± 2.09 | 24.63 ± 2.19 | 35.26 ± 3.17 |
| 3AP-2 | 45.37 ± 2.08 | 13.62 ± 3.42 | 96.57 ± 3.73 |
| NA-2 | 67.85 ± 2.22 | 22.89 ±3.41 | 9.60 ± 3.04 |
| M-2 | 119.95 ± 3.71 | 48.02 ± 2.32 | 36.39 ± 3.90 |
| Parameters | M7594_0037 | 3AP-2 | NA-2 | M-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicity risk management | ||||
| (a) Mutagenicity a | No | No | No | Yes |
| (b) Tumorigenicity b | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| (c) Irritant c | No | No | Yes | No |
| (d) Reproductive effective d | No | No | No | No |
| Solubility e | −4.08 | −2.59 | −1.68 | −3.47 |
| cLogP | 2.1 | 0.61 | −1.29 | 0.71 |
| Drug likeness f | 3.69 | 0.3 | 1.07 | −1.2 |
| Molecular weight | 387.0 | 317.0 | 325.0 | 415.0 |
| Drug score g | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 0.17 |
| Parameters | M7594_0037 | 3AP-2 | NA-2 | M-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score from cLoP | 0.947 | 0.987/1.0 | 0.998/1.0 | 0.986/1.0 |
| Score from logS | 0.716 | 0.917/1.0 | 0.965/1.0 | 0.822/1.0 |
| Score from molecular weight | 0.795/1.0 | 0.899/1.0 | 0.89/1.0 | 0.734/1.0 |
| Score from drug likeness | 0.975/1.0 | 0.575/1.0 | 0.744/1.0 | 0.23/1.0 |
| No risk of mutagenicity | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 0.6/1.0 |
| No risk of tumorigenicity | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 0.6/1.0 | 0.6/1.0 |
| Risk of irritating effect | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 0.8/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 |
| No risk of reproductive effect | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 | 1.0/1.0 |
| Average total drug score | 0.740 | 0.712 | 0.388 | 0.173 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Qiu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, L.; Zheng, Y. Structure-Based Drug Design of Small Molecule Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors to Treat Cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040396
Gao J, Wang T, Qiu S, Zhu Y, Liang L, Zheng Y. Structure-Based Drug Design of Small Molecule Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors to Treat Cancer. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040396
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jian, Tao Wang, Shengzhi Qiu, Yasheng Zhu, Li Liang, and Youguang Zheng. 2016. "Structure-Based Drug Design of Small Molecule Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors to Treat Cancer" Molecules 21, no. 4: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040396
APA StyleGao, J., Wang, T., Qiu, S., Zhu, Y., Liang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2016). Structure-Based Drug Design of Small Molecule Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors to Treat Cancer. Molecules, 21(4), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040396