3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a Citrus Flavonoid, Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-like Behavior and Restores Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression, Neurogenesis, and Neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus
Abstract
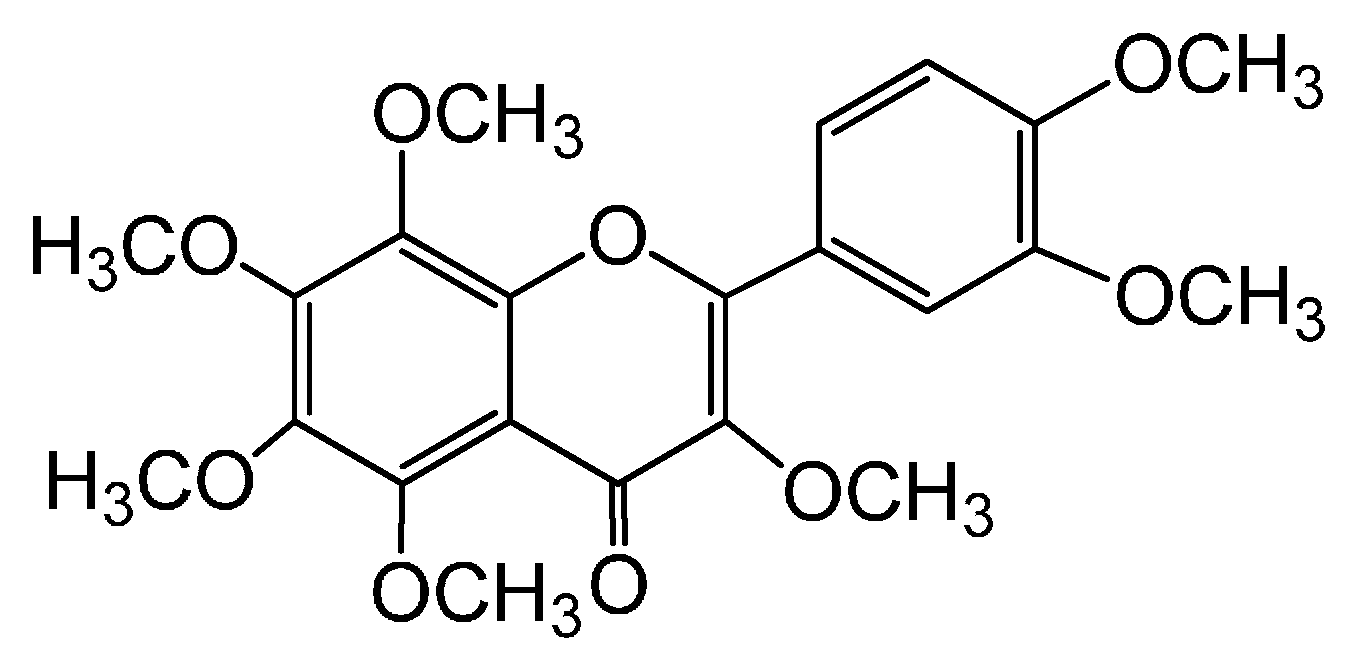
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on Body Weight Changes
2.2. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on Depressive-Like Behavior
2.3. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on the Expression of BDNF in the Hippocampus
2.4. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus
2.5. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on the Neuronal Network in the Hippocampus
2.6. Effects of Corticosterone and HMF on ERK1/2-Phosphorylation in the Hippocampus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Administration of Corticosterone and Test Drugs
4.3. Forced Swim Test
4.4. Tail Suspension Test
4.5. Immunofluorescence for Confocal Microscopy
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. Life stress, genes, and depression: Multiple pathways lead to increased risk and new opportunities for intervention. Sci. STKE 2004, 225, re5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariante, C.M.; Lightman, S.L. The HPA axis in major depression: Classical theories and new developments. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G. Glucocorticoids and the genesis of depressive illness. A psychobiological model. Br. J. Psychiatry 1994, 164, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.; Monteggia, I. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) infusion restored astrocytic plasticity in the hippocampus of a rat model of depression. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 503, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paizanis, E.; Hamon, M.; Lanfumey, L. Hippocampal neurogenesis, depressive disorders, and antidepressant therapy. Neural Plast. 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinowich, K.; Manji, H.; Lu, B. New insights into BDNF function in depression and anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, S.; Morita, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Nishigawa, Y.; Kaji, M.; Sawamoto, A.; Terugo, T.; Toyoda, N.; Makihata, N.; Amakura, Y.; et al. 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a citrus flavonoid, on protection against memory impairment and neuronal cell death in a global cerebral ischemia mouse model. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 70, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, S.; Shimada, N.; Kaji, M.; Morita, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Minami, S.; Amakura, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Heptamethoxyflavone, a citrus flavonoid, enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor production and neurogenesis in the hippocampus following cerebral global ischemia in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 528, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonijevic, I.A.; Steiger, A. Depression-like change of the sleep-EEG during high dose corticosteroid treatment in patients with multiple sclerosis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2003, 28, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Iinuma, M.; Soumiya, H.; Fukumitsu, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Furukawa, S. A novel 2-decenoic acid thioester ameliorates corticosterone-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors and normalizes reduced hippocampal signal transduction in treated mice. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, J.P.; Mørk, A. Chronic corticosterone decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA and protein in the hippocampus, but not in the frontal cortex, of the rat. Brain Res. 2006, 1110, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, Y.; Rizavi, H.S.; Pandey, G.N. Antidepressants reverse corticosterone-mediated decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression: Differential regulation of specific exons by antidepressants and corticosterone. Neuroscience 2006, 139, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostert, J.P.; Koch, M.W.; Heerings, M.; Heersema, D.J.; de Keyser, J. Therapeutic potential of fluoxetine in neurological disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.D.; Ma, L.G.; Hu, C.Y.; Pei, Y.Y.; Jin, S.L.; Fang, X.Y.; Li, Y.C. Berberine up-regulates the BDNF expression in hippocampus and attenuates corticosterone-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 614, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, R.; Shen, J.; Su, H.; Xing, D.; Du, L. A mouse model of depression induced by repeated corticosterone injections. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 581, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Valentino, R.J.; Lucki, I. Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimpton, J. The brain derived neurotrophic factor and influences of stress in depression. Psychiatr. Danub. 2012, 24, 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, J.L.; Klumpers, L.; Maslam, S.; de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M.; Lucassen, P.J. Brief treatment with the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist mifepristone normalises the corticosterone-induced reduction of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2006, 18, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, C.A.; Mayer, J.L.; de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M.; Lucassen, P.J. Brief treatment with the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist mifepristone normalizes the reduction in neurogenesis after chronic stress. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 3395–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, V.; Greif, G.J.; Kennedy, M.B. Detailed State Model of CaMKII Activation and Autophosphorylation. Eur. Biophys. J. 2008, 38, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourley, S.L.; Wu, F.J.; Taylor, J.R. Corticosterone regulates pERK1/2 map kinase in a choronic depression model. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourley, S.L.; Wu, F.J.; Kiraly, D.D.; Ploski, J.E.; Kedves, A.T.; Duman, R.S.; Taylor, J.R. Regionally specific regulation of ERK MAP kinase in a model of antidepressant-sensitive chronic depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.; Okuyama, S.; Amakura, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Fukata, T.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Yoshida, T. Isolation and characterization of activators of ERK/MAPK from citrus plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C. In search of a depressed mouse: Utility of models for studying depression-related behavior in genetically modified mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 326–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrén, E. Is mood chemistry? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya Vetencourt, J.F.; Sale, A.; Viegi, A.; Baroncelli, L.; De Pasquale, R.; O’Leary, O.F.; Castrén, E.; Maffei, L. The antidepressant fluoxetine restores plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 2008, 320, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, J.; Brown, E. Integrating the monoamine, neurotrophin and cytokine hypotheses of depression--a central role for the serotonin transporter? Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, C.L.; Miller, A.H.; Tansey, M.G.; Neigh, G.N. Inflammatory mechanisms contribute to microembolism-induced anxiety-like and depressive-like behaviors. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 303, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, C.; Duman, R.S. Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: A convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sairanen, M.; Lucas, G.; Ernfors, P.; Castrén, M.; Castrén, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, A.; Djordjevic, J.; Elaković, I.; Adzic, M.; Matić, G.; Radojcic, M.B. Effects of fluoxetine on plasticity and apoptosis evoked by chronic stress in rat prefrontal cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 693, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.E.; Machado, D.G.; Budni, J.; Neis, V.B.; Balen, G.O.; Lopes, M.W.; de Souza, L.F.; Dafre, A.L.; Leal, R.B.; Rodrigues, A.L. Fluoxetine modulates hippocampal cell signaling pathways implicated in neuroplasticity in olfactory bulbectomized mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 237, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czéh, B; di Benedetto, B. Antidepressants act directly on astrocytes: Evidences and functional consequences. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, J.A.; Simpson, J.; Mahajan, G.J.; Overholser, J.C.; Jurjus, G.J.; Dieter, L.; Herbst, N.; May, W.; Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A. Hippocampal volume and total cell numbers in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheline, Y.I.; Gado, M.H.; Kraemer, H.C. Untreated depression and hippocampal volume loss. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1516–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Chronic corticosterone exposure reduces hippocampal astrocyte structural plasticity and induces hippocampal atrophy in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 592, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rial, D.; Lemos, C.; Pinheiro, H.; Duarte, J.M.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Real, J.I.; Prediger, R.D.; Gonçalves, N.; Gomes, C.A.; Canas, P.M.; et al. Depression as a Glial-Based Synaptic Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 1997, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Steru, L.; Chermat, R.; Thierry, B.; Simon, P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Xu, J.; Okuyama, S.; Martinez, L.B.; Walsh, S.M.; Jacobsen, M.T.; Swan, R.J.; Schlautman, J.D.; Ciborowski, P.; Ikezu, T. Spatial learning impairment, enhanced CDK5/p35 activity, and downregulation of NMDA receptor expression in transgenic mice expressing tau-tubulin kinase 1. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14511–14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples are not available from the authors.







© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawamoto, A.; Okuyama, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Amakura, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Nakajima, M.; Furukawa, Y. 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a Citrus Flavonoid, Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-like Behavior and Restores Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression, Neurogenesis, and Neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus. Molecules 2016, 21, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040541
Sawamoto A, Okuyama S, Yamamoto K, Amakura Y, Yoshimura M, Nakajima M, Furukawa Y. 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a Citrus Flavonoid, Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-like Behavior and Restores Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression, Neurogenesis, and Neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040541
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawamoto, Atsushi, Satoshi Okuyama, Kana Yamamoto, Yoshiaki Amakura, Morio Yoshimura, Mitsunari Nakajima, and Yoshiko Furukawa. 2016. "3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a Citrus Flavonoid, Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-like Behavior and Restores Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression, Neurogenesis, and Neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus" Molecules 21, no. 4: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040541
APA StyleSawamoto, A., Okuyama, S., Yamamoto, K., Amakura, Y., Yoshimura, M., Nakajima, M., & Furukawa, Y. (2016). 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a Citrus Flavonoid, Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-like Behavior and Restores Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression, Neurogenesis, and Neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus. Molecules, 21(4), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040541





