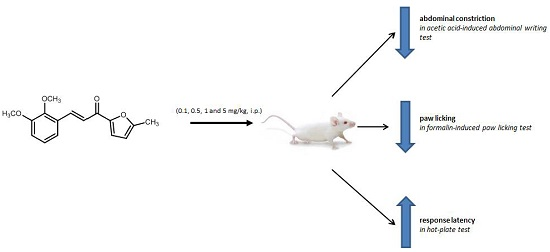
Antinociceptive Effect of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one in Mice Models of Induced Nociception
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antinociceptive Studies
2.1.1. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
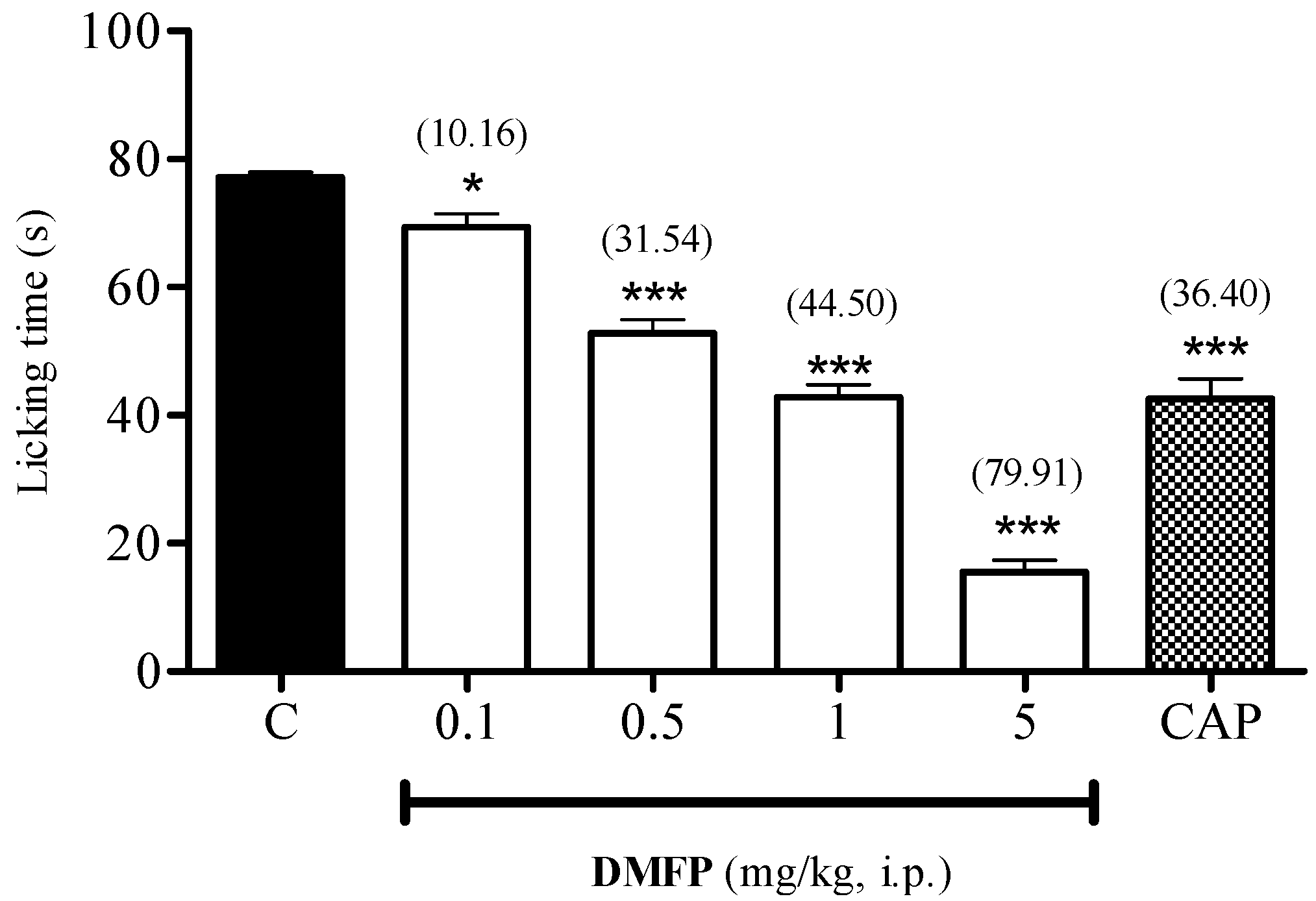
2.1.2. Formalin-Induced Paw-Licking Test
2.1.3. Hot-Plate Test
2.1.4. Capsaicin-Induced Paw-Licking Test
2.1.5. Glutamate-Induced Paw-Licking Test
2.1.6. Involvement of Opioid Receptor
2.2. Motor Performance Study
Rota-Rod Test
2.3. Toxicity Study
Preliminary Acute Toxicity Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Synthesis of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (DMFP)
4.3. Animals
4.4. Drugs and Chemicals
4.5. Antinociceptive Study
4.5.1 Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
4.5.2. Formalin-Induced Paw-Licking Test
4.5.3. Hot-Plate Test.
4.5.4. Capsaicin-Induced Paw-Licking Test
4.5.5. Glutamate-Induced Paw-Licking Test
4.5.6. Involvement of Opioid Receptors
4.6. Motor Performance Study
Rota-Rod Test
4.7. Toxicity Study
Preliminary Acute Toxicity Test
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kenny, G.N. Potential renal, haematological and allergic adverse effects associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs 1992, 44, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, G.T.; Duong, V.; Ho, S.; Ngo, K.C.; Greer, C.L.; Weeks, D.L. Side effects of commonly prescribed analgesic medications. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candiotti, K.A.; Gitlin, M.C. Review of the effect of opioid-related side effects on the undertreatment of moderate to severe chronic non-cancer pain: Tapentadol, a step toward a solution? Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticha, L.A.; Klaasen, J.A.; Green, I.R.; Naidoo, S.; Baker, B.; Pietersen, R.D. Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Screening of Flavanones and Chalcones from Galenia africana and Dicerothamnus rhinocerotis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, P. Heterocyclic chalcone analogues as potential anticancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sashidhara, K.V.; Avula, S.R.; Mishra, V.; Palnati, G.R.; Singh, L.R.; Singh, N.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Swami, P.; Bhatta, R.S.; Palit, G. Identification of quinoline-chalcone hybrids as potential antiulcer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesello, L.A.; Campos, A.; Wagner, T.; Feliciano, A.S.; de Campos Buzzi, F.; Filho, V.C. Chemical Composition and Antinociceptive Potential of Campomanesia reitziana Fruits. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanage, S.G.; Mohite, P.B.; Pandhare, R.B.; Raju, S.A. Microwave Assisted Synthesis of 1-[5-(Substituted Aryl)-1H-Pyrazol-3-yl]-3,5-diphenyl-1H-1,2,4-Triazole as Antinociceptive and Antimicrobial Agents. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, A.S.; Akhtar, M.N.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Perimal, E.K.; Khalid, S.; Mohd, P.A.; Khalid, M.H.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N.H.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive activity of a synthetic chalcone, flavokawin B on chemical and thermal models of nociception in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 647, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Chowdary, P.V.; Jayashree, B.S. Synthesis, Antiinflammatory and Antibacterial Activity of Novel Indolyl-isoxazoles. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N.H.; Shaari, K.; Mohamed, H.; Wahab, A.A.; Ariffin, K.T.; Hoo, W.Y.; Aziz, N.A.; Kadir, A.A.; et al. Cardamonin, inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators in activated RAW 264.7 cells and whole blood. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 538, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israf, D.A.; Tham, C.L.; Syahida, A.; Lajis, N.H.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Mohamad, A.S.; Zakaria, Z.A. Atrovirinone inhibits proinflammatory mediator synthesis through disruption of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and MAPK phosphorylation in the murine monocytic macrophage RAW 264.7. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaldin, M.N.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Lajis, N.; Perimal, E.K.; Akira, A.; Ming-Tatt, L.; Israf, D.A.; Sulaiman, M.R. Peripheral antinociception of a chalcone, flavokawin B and possible involvement of the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate/potassium channels pathway. Molecules 2013, 18, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.W.; Mohd Faudzi, S.M.; Abas, F.; Mohd Aluwi, M.F.; Rullah, K.; Lam, K.W.; Abdul Bahari, M.N.; Ahmad, S.; Tham, C.L.; Shaari, K.; et al. Nitric oxide inhibitory activity and antioxidant evaluations of 2-benzoyl-6-benzylidenecyclohexanone analogs, a novel series of curcuminoid and diarylpentanoid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3330–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik Mossadeq, W.M.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Tengku Mohamad, T.A.; Chiong, H.S.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Jabit, M.L.; Baharuldin, M.T.; Israf, D.A. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of Mitragyna speciosa Korth methanolic extract. Med. Princ. Pract. 2009, 18, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, M.R.; Mohd Padzil, A.; Shaari, K.; Khalid, S.; Shaik Mossadeq, W.M.; Mohamad, A.S.; Ahmad, S.; Akira, A.; Israf, D.; Lajis, N. Antinociceptive activity of Melicope ptelefolia ethanolic extract in experimental animals. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.M.; Mohamad, A.S.; Makhtar, N.; Khalid, M.H.; Khalid, S.; Perimal, E.K.; Mastuki, S.N.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Lajis, N.; Israf, D.A.; et al. Antinociceptive activity of methanolic extract of Acmella uliginosa (Sw.) Cass. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, M.R.; Tengku Mohamad, T.A.; Shaik Mossadeq, W.M.; Moin, S.; Yusof, M.; Mokhtar, A.F.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N. Antinociceptive activity of the essential oil of Zingiber zerumbet. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming-Tatt, L.; Khalivulla, S.I.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Perimal, E.K.; Khalid, M.H.; Akira, A.; Lajis, N.; Israf, D.A.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive activity of a synthetic curcuminoid analogue, 2,6-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexanone, on nociception-induced models in mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 110, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.W.; Uddin, R.; Liew, C.Y.; Tham, C.L.; Israf, D.A.; Syahida, A.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Lajis, N.H. Synthesis and QSAR analysis of chalcone derivatives as nitric oxide inhibitory agent. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, G.H. Drug discovery and evaluation. In Pharmacological Assays; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1997; p. 716. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars, D.; Gozariu, M.; Cadden, S.W. Animal models of nociception. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 597–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deraedt, R.; Jouquey, S.; Delevallee, F.; Flahaut, M. Release of prostaglandins E and F in an algogenic reaction and its inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 61, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Naraba, H.; Ueno, A.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Murakami, M.; Kudo, I.; Oh-ishi, S. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 causes an enhancement of writhing response in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 352, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Ueno, A.; Naraba, H.; Oh-ishi, S. Involvement of vanilloid receptor VR1 and prostanoids in the acid-induced writhing responses of mice. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Vale, M.L.; Thomazzi, S.M.; Paschoalato, A.B.; Poole, S.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. Involvement of resident macrophages and mast cells in the writhing nociceptive response induced by zymosan and acetic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 387, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.D.; Paiva-Lima, P.; Rezende, R.M.; Dos Reis, W.G.; Ferreira-Alves, D.L.; Bakhle, Y.S.; Francischi, J.N. Peripheral mu-, kappa- and delta-opioid receptors mediate the hypoalgesic effect of celecoxib in a rat model of thermal hyperalgesia. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunskaar, S.; Hole, K. The formalin test in mice: Dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain 1987, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjolsen, A.; Berge, O.G.; Hunskaar, S.; Rosland, J.H.; Hole, K. The formalin test: An evaluation of the method. Pain 1992, 51, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Takahashi, H.; Inoki, R. Modified formalin test: Characteristic biphasic pain response. Pain 1989, 38, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, F.V.; Melzack, R. Brainstem lesions dissociate neural mechanisms of morphine analgesia in different kinds of pain. Brain Res. 1982, 251, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, F.S.; Sirmagul, B.; Yildirim, E.; Oner, S.; Erol, K. Antinociceptive effects of gabapentin & its mechanism of action in experimental animal studies. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Boer, V.C.; Dihal, A.A.; van der Woude, H.; Arts, I.C.; Wolffram, S.; Alink, G.M.; Rietjens, I.M.; Keijer, J.; Hollman, P.C. Tissue distribution of quercetin in rats and pigs. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiekow, C.J.; Figueiro, F.; Dietrich, F.; Vechia, L.D.; Pires, E.N.; Jandrey, E.H.; Gnoatto, S.C.; Salbego, C.G.; Battastini, A.M.; Gosmann, G. Quercetin derivative induces cell death in glioma cells by modulating NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and caspase-3 activation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 84, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Perimal, E.K.; Akira, A.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive effect of the essential oil of Zingiber zerumbet in mice: Possible mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, E.; de Novellis, V.; Marabese, I.; Cuomo, D.; Rossi, F.; Berrino, L.; Maione, S. Interaction between vanilloid and glutamate receptors in the central modulation of nociception. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 439, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Gramsch, C.; Herz, A. Intrinsic mechanisms of antinociception in inflammation: Local opioid receptors and beta-endorphin. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, N.; Mitra, S.; Hines, R.L. Peripheral opioid receptor agonists for analgesia: A comprehensive review. J. Opioid. Manag. 2011, 7, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Gan, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Song, Q.; Xu, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel tetrahydroisoquinoline quaternary derivatives as peripheral kappa-opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 2964–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, R.; Jacobson, J.; Bain, G.; Kornetsky, C. Naloxone blockade of morphine analgesia: A dose-effect study of duration and magnitude. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 199, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Julius, D. TRP channels and pain. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 355–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurada, T.; Matsumura, T.; Moriyama, T.; Sakurada, C.; Ueno, S.; Sakurada, S. Differential effects of intraplantar capsazepine and ruthenium red on capsaicin-induced desensitization in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, S.M. Peripheral excitatory amino acids. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Komak, S.; Du, J.; Carlton, S.M. Metabotropic glutamate 1alpha receptors on peripheral primary afferent fibers: Their role in nociception. Brain Res. 2001, 913, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, V. Metabotropic glutamate receptors--important modulators of nociception and pain behavior. Pain 2002, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.; Rupsingh, R.; Smith, M.; Wells, J.L.; Borrie, M.J.; Bartha, R. Increased glutamate in the hippocampus after galantamine treatment for Alzheimer disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.; Santos, A.R.; Calixto, J.B. The role of systemic, spinal and supraspinal l-arginine-nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in thermal hyperalgesia caused by intrathecal injection of glutamate in mice. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Neugebauer, V. Block of NMDA and non-NMDA receptor activation results in reduced background and evoked activity of central amygdala neurons in a model of arthritic pain. Pain 2004, 110, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirith, A.; Santos, A.R.; Calixto, J.B. Mechanisms underlying the nociception and paw oedema caused by injection of glutamate into the mouse paw. Brain Res. 2002, 924, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirith, A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Bonetti, V.R.; Konzen, M.; Seifriz, I.; Paula, M.S.; Franco, C.V.; Calixto, J.B. Antinociceptive properties and nitric oxide synthase inhibitory action of new ruthenium complexes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 369, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, J.S.; Beirith, A.; Calixto, J.B. Evidence for the involvement of metabotropic glutamatergic, neurokinin 1 receptor pathways and protein kinase C in the antinociceptive effect of dipyrone in mice. Brain Res. 2004, 1003, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perimal, E.K.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Khalid, M.H.; Ming, O.H.; Khalid, S.; Tatt, L.M.; Kamaldin, M.N.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Israf, D.A.; et al. Zerumbone-induced antinociception: Involvement of the l-arginine-nitric oxide-cGMP -PKC-K+ ATP channel pathways. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 108, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosland, J.H.; Hunskaar, S.; Hole, K. Diazepam attenuates morphine antinociception test-dependently in mice. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1990, 66, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorke, D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Arch. Toxicol. 1983, 54, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compound, 3-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (DMFP), is available from Mohd Roslan Sulaiman.








© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, N.I.; Ming-Tatt, L.; Lajis, N.; Akhtar, M.N.; Akira, A.; Perimal, E.K.; Israf, D.A.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive Effect of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one in Mice Models of Induced Nociception. Molecules 2016, 21, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081077
Ismail NI, Ming-Tatt L, Lajis N, Akhtar MN, Akira A, Perimal EK, Israf DA, Sulaiman MR. Antinociceptive Effect of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one in Mice Models of Induced Nociception. Molecules. 2016; 21(8):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081077
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Nur Izzati, Lee Ming-Tatt, Nordin Lajis, Muhammad Nadeem Akhtar, Ahmad Akira, Enoch Kumar Perimal, Daud Ahmad Israf, and Mohd Roslan Sulaiman. 2016. "Antinociceptive Effect of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one in Mice Models of Induced Nociception" Molecules 21, no. 8: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081077
APA StyleIsmail, N. I., Ming-Tatt, L., Lajis, N., Akhtar, M. N., Akira, A., Perimal, E. K., Israf, D. A., & Sulaiman, M. R. (2016). Antinociceptive Effect of 3-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one in Mice Models of Induced Nociception. Molecules, 21(8), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081077