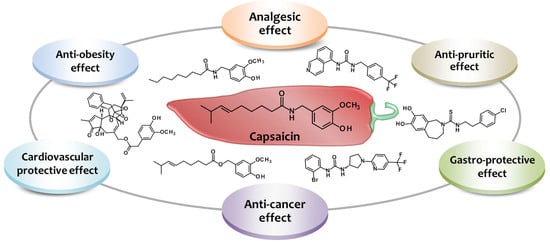
Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases
Abstract
Share and Cite
Basith, S.; Cui, M.; Hong, S.; Choi, S. Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080966
Basith S, Cui M, Hong S, Choi S. Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases. Molecules. 2016; 21(8):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080966
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasith, Shaherin, Minghua Cui, Sunhye Hong, and Sun Choi. 2016. "Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases" Molecules 21, no. 8: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080966
APA StyleBasith, S., Cui, M., Hong, S., & Choi, S. (2016). Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases. Molecules, 21(8), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080966