Antibacterial Activity of Neat Chitosan Powder and Flakes
Abstract
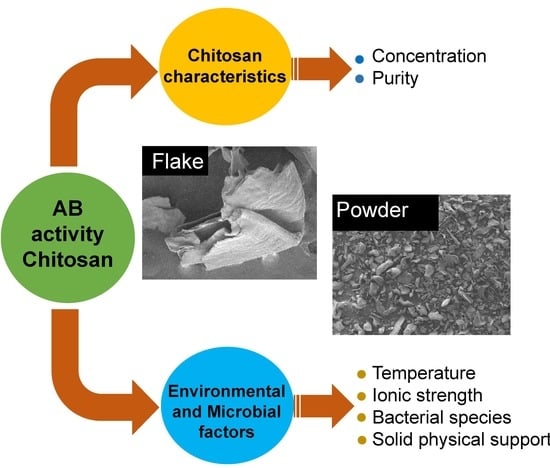
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SEM
2.1.1. Elemental Analysis
2.1.2. Particle Size, Thickness, Shape and Particle Size Distribution
2.2. Antibacterial Assays
2.2.1. Effect of Chitosan Concentration
2.2.2. Identification of Proteins
2.2.3. Effect of Temperature
2.2.4. Effect of Salt Concentration and Ionic Strength
2.2.5. Influence of Bacterial Species
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Bacteria Strains and Culture
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2.2. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
3.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Moisture Content
Ash Content
Protein Content
3.2.4. Deproteinization and Identification of Proteins
3.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Particle Size
3.2.6. Elemental Analysis
3.2.7. Attenuated Total Reflectance Spectroscopy (ATR)
3.2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.2.9. Antibacterial (AB) Assays
3.2.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goosen, M.F. Applications of Chitin and Chitosan; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.; Cordi, L.; Duran, N.; Mei, L. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan Solutions for Wound Dressing. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 245–246, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y. Antibacterial characteristics and activity of acid-soluble chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Zhu, J.F. Study on antimicrobial activity of chitosan with different molecular weights. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 54, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, T.; Snow, G. Biochemistry of Antimicrobial Action; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Devlieghere, F.; Vermeulen, A.; Debevere, J. Chitosan: Antimicrobial activity, interactions with food components and applicability as a coating on fruit and vegetables. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhale, S.; No, H.K.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Farr, A.; Nadarajah, K.; Meyers, S.P. Chitosan coating improves shelf life of eggs. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, B.; Simard, R.E.; Piette, G.; Bégin, A.; Holley, R.A. Inhibition of surface spoilage bacteria in processed meats by application of antimicrobial films prepared with chitosan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 62, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingyuad, S.; Ruamsin, S.; Reekprkhon, D.; Douglas, S.; Pongamphai, S.; Siripatrawan, U. Effect of chitosan coating and vacuum packaging on the quality of refrigerated grilled pork. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2006, 19, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.K.; Meyers, S.P.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Xu, Z. Applications of chitosan for improvement of quality and shelf life of foods: A review. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R87–R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Chen, X.G.; Park, H.J.; Liu, C.G.; Liu, C.S.; Meng, X.H.; Yu, L.J. Effect of MW and concentration of chitosan on antibacterial activity of Escherichia coli. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.K.; Park, N.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Meyers, S.P. Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, N.Y.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Stability and antibacterial activity of chitosan solutions affected by storage temperature and time. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, I.; Nurmiaho-Lassila, E.L.; Ahvenainen, R.; Rhoades, J.; Roller, S. Chitosan disrupts the barrier properties of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 71, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chung, Y.C.; Woan Wang, L.; Chen, K.T.; Li, S.Y. Antibacterial properties of chitosan in waterborne pathogen. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2002, 37, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Tripathi, S.; Mehrotra, G.; Dutta, J. Perspectives for chitosan based antimicrobial films in food applications. J. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverlya, R.L.; Janes, M.E.; Prinyawiwatkula, W.; No, H.K. Edible chitosan films on ready-to-eat roast beef for the control of listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-González, L.; Cháfer, M.; Hernández, M.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Antimicrobial activity of polysaccharide films containing essential oils. Food Control 2011, 22, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Camacho, A.P.; Cortez-Rocha, M.O.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan nanofibers obtained by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Ocio, M.; Lagaron, J. Development of active antimicrobial fiber-based chitosan polysaccharide nanostructures using electrospinning. J. Eng. Life Sci. 2008, 8, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Starbova, K.; Markova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun nano-fibre mats with antibacterial properties from quaternised chitosan and poly (vinyl alcohol). Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila, N.; Medina, N.; Arkoun, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A.; Panchal, C.J. Chitosan-bacterial nanocellulose nanofibrous structures for potential wound dressing applications. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3089–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, N.; Daigle, F.; Heuzey, M.C.; Ajji, A. Effect of chitosan physical form on its antibacterial activity against pathogenic bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2017. Article accepted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Zou, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, C.G.; Meng, X.H.; Yu, L.J. Antibacterial mechanism of chitosan microspheres in a solid dispersing system against E. coli. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 65, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.-G.; Xue, Y.-P.; Liu, C.-S.; Yu, L.-J.; Ji, Q.-X.; Cha, D.S.; Park, H.J. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan microshperes in a solid dispersing system. Front. Mater. Sci. China 2008, 2, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yien, L.; Zin, N.M.; Sarwar, A.; Katas, H. Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles and correlation with their physical properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 632698. [Google Scholar]
- Lertsutthiwong, P.; How, N.C.; Chandrkrachang, S.; Stevens, W.F. Effect of chemical treatment on the characteristics of shrimp chitosan. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2002, 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sini, T.K.; Santhosh, S.; Mathew, P.T. Study on the production of chitin and chitosan from shrimp shell by using bacillus subtilis fermentation. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Raith, G.; Tubertini, O. Separation of trace elements from see water, brine and sodium and magnesium salt solutions by chromatography on chitosan. J. Chromatogr. 1970, 47, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.I.; No, H.K.; Meyers, S.P. Physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of various commercial chitin and chitosan products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3839–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Czerwicka, M.; Kaczyński, Z.; Bychowska, A.; Brzozowski, K.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Application of spectroscopic methods for structural analysis of chitin and chitosan. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1567–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.T.; Simionato, J.I.; Garcia, J.C.; Nozaki, J. Characterization of chitosan and chitin produced from silkworm crysalides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Li, J.; Yao, F.; Yin, Y. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Functions and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Xu, W. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiecki, J.; Al-Khateeb, N.A. Production, properties, and some new applications of chitin and its derivatives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, G.J.; Su, W.H. Antibacterial activity of shrimp chitosan against Escherichia coli. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Chou, C.-C. Factors affecting the susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus CCRC 12657 to water soluble lactose chitosan derivative. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Bégin, A.; Carreau, P.J. Physical gelation of chitosan in the presence of β-glycerophosphate: The effect of temperature. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, N.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, C.S.; Meng, X.H.; Liu, C.G. Protonation constants of chitosan with different molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-J.; Park, P.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Antimicrobial effect of chitooligosaccharides produced by bioreactor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Wang, H.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, S.L. Effect of abiotic factors on the antibacterial activity of chitosan against waterborne pathogens. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 88, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Sahl, H.G. Chitosan and its antimicrobial potential–a critical literature survey. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, D.R. Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Guibal, E. Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R.; Hernandez-Zapata, E.; Chen, N.; Pincus, P.; Israelachvili, J.N. Debye length and double-layer forces in polyelectrolyte solutions. Macromol. 2002, 35, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Lee, A.A.; Perkin, S. The electrostatic screening length in concentrated electrolytes increases with concentration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrou, C.; Fabry, P.; Poignet, J.-C. Electrochemistry: The Basics, with Examples; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 3; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Hajmeer, M.; Ceylan, E.; Marsden, J.L.; Fung, D.Y. Impact of sodium chloride on Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus analysed using transmission electron microscopy. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, P.; Fernandes, J.C.; Pereira, E.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Atomic force microscopy study of the antibacterial effects of chitosans on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, L.; Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Jellouli, K.; Younes, I.; Nasri, M. Extraction and characterization of chitin, chitosan, and protein hydrolysates prepared from shrimp waste by treatment with crude protease from bacillus cereus SV1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-C.; Kung, S.-K.; Chen, H.-H.; Lin, S.-B. Evaluation of zeta potential difference as an indicator for antibacterial strength of low molecular weight chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Su, Y.P.; Chen, C.C.; Jia, G.; Wang, H.L.; Wu, J.G.; Lin, J.G. Relationship between antibacterial activity of chitosan and surface characteristics of cell wall. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dickson, J.S.; Koohmaraie, M. Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goy, R.C.; Morais, S.T.; Assis, O.B. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan and its quaternized derivative on E. coli and S. aureus growth. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, G.J.; Su, W.H.; Chen, H.C.; Pan, C.L. Antimicrobial activity of shrimp chitin and chitosan from different treatments and applications of fish preservation. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B. Adsorption of residue oil from palm oil mill effluent using powder and flake chitosan: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z. Lead sorption from aqueous solutions on chitosan nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2004, 251, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. Cytotoxic activities of chitosan nanoparticles and copper-loaded nanoparticles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1397–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkoun, M.; Daigle, F.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. Antibacterial electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers: A bacterial membrane perforator. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017. Article under revision process. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Khor, E.; Lim, L.-Y. Uptake and cytotoxicity of chitosan molecules and nanoparticles: Effects of molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaih, M.L.; Chen, R.H. Molecular weight determination of 83% degree of decetylation chitosan with non-gaussian and wide range distribution by high-performance size exclusion chromatography and capillary viscometry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavertu, M.; Darras, V.; Buschmann, M.D. Kinetics and efficiency of chitosan reacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytic Chemist (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytic Chemist: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Some samples of the compounds could be available from the authors upon request.










| CS Grade a | DDA (%) | MW (KDa) | PDI- | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | mg Protein/g Chitosan | Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-90-207 b | 90 | 207 | 1.7 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 8.8 ± 0.2 | 0.67 ± 0.40 mm |
| P-95-57 c | 95 | 57 | 2.2 | 9.8 ± 0.1 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 175.7 ± 0.3 | 55.09 ± 43.73 μm |
| Chitosan | Element | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Na | Ca | Mg | S | Si | Co | Al | Cl | |
| F-90-207 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| P-95-57 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Chitosan Type | Survival Bacteria (log CFU/mL) | Reduction * (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram− | Gram+ | Gram− | Gram+ | |||
| E. coli | L. innocua | S. aureus | E. coli | L. innocua | S. aureus | |
| Control | 6.5 ± 0.6 a | 6.6 ± 0.5 a | 7.5 ± 0.8 a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| F-90-207 | 4.2 ± 0.4 b | 5.4 ± 0.7 b | 6.6 ± 0.9 a | 99.5 | 93.1 | 88.2 |
| P-95-57 | 0.0 c | 0.0 c | 6.1 ± 0.6 a | 100 | 100 | 96.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ardila, N.; Daigle, F.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. Antibacterial Activity of Neat Chitosan Powder and Flakes. Molecules 2017, 22, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010100
Ardila N, Daigle F, Heuzey M-C, Ajji A. Antibacterial Activity of Neat Chitosan Powder and Flakes. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleArdila, Nury, France Daigle, Marie-Claude Heuzey, and Abdellah Ajji. 2017. "Antibacterial Activity of Neat Chitosan Powder and Flakes" Molecules 22, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010100
APA StyleArdila, N., Daigle, F., Heuzey, M.-C., & Ajji, A. (2017). Antibacterial Activity of Neat Chitosan Powder and Flakes. Molecules, 22(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010100