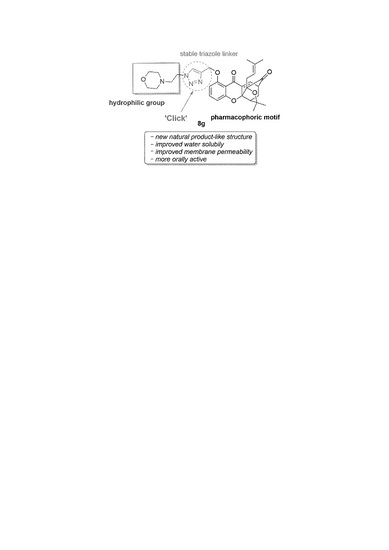
‘Click Chemistry’ Synthesis of Novel Natural Product-Like Caged Xanthones Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Moiety with Improved Druglike Properties as Orally Active Antitumor Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. In Vitro Cytotoxic Effects
2.3. Drug-Like Property Evaluation
2.4. In Vivo Antitumor Evaluations of Compound 8h
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of Compound 3
3.3. Synthesis of Compound 5
3.4. Synthesis of Compounds 8a–8j
3.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.6. Determination of the Druglike Properties
3.7. In Vivo Tumor Growth Inhibition Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural product as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.S. The role of natural product chemistry in drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhen, C.; Wu, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhou, C.; Guo, Q. General pharmacological properties, developmental toxicity, and analgesic activity of gambogic acid, a novel natural anticancer agent. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 33, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantarasriwong, O.; Batova, A.; Chavasiri, W.; Theodorakis, E. A Chemistry and biology of the caged Garcinia xanthones. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 6, 9944–9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.B.; Xu, H.X. Caged Garcina xanthones: Development since 1937. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3775–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, Q.-L.; You, Q.-D.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Gu, H.-Y. Gambogic acid induces apoptosis and regulates expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; Sung, B.; Ahh, K.S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwall, B.B. Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potential TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Blood 2007, 110, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Yang, Y.; You, Q.-D.; Ma, Y.-J.; Yang, L.; Nie, F.-F.; Gu, H.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Lu, N.; Qi, Q.; et al. Inhibition of glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis by gambogic acid: An in vivro and in vivo study. Biochem. Pharmcol. 2008, 75, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, N.; Zhao, C.; Liao, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, S.; et al. Gambogic acid is a tissue-specific proteasome inhibitor in vitro and in vivo. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, K.H.; Preince, T.L.; Qu, S.; Bai, F.; Jennings, P.A.; Onuchic, J.N.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Neckers, L. Gambogic acid identifies an isoform-specific druggable pocket in the middle domain of Hsp90β. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4801–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Y. Global profiling of cellular targets of gambogic acid by quantitative chemical proteomics. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 14035–14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Song, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; You, Q.; Lu, N. Gambogic acid suppresses cancer invasion and migration by inhibiting TGFβ1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27120–27136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Garcina xanthones as orally active antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Yang, Q.; Gong, D.; Lin, C.; Zhang, S.; Xi, M.; Gao, Y.; Wei, L.; Guo, Q.; et al. Studies on chemical modification and biology of a natural product, gambogic acid (III): Determination of the essential pharmacophore for biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, L.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Q.; You, Q. Synthesis and evaluation of novel aza-caged Garcina xanthones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 3288–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yang, Y.-R.; Sun, H.-P.; You, Q.-D. Progress in research of the structural optimization of natural product-like Garcinia caged xanthones. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2014, 49, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Bian, J.; Jiang, F.; Sun, H.; You, Q.; Zhang, X. Novel natural-product-like caged xanthones with improved druglike properties and in vivo antitumor potency. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2584–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Bao, Q.; Bian, J.; You, Q.; Zhang, X. Novel natural product-like caged xanthones bearing a carbamate moiety exhibit antitumor potency and anti-angiogenesis activity in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 35771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Gu, C.; You, Q.; Zhang, X. Structure-activity relationship of Garcina xanthones analogues: Potent Hsp90 inhibitors with cytotoxicity and antiangiogenesis actitvity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4626–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghani, N.M.; Amin, H.; Lee, B.J. Mechanistic applications of click chemistry for pharmaceutical drug discovery and drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheer, D.; Singh, V.; Shankar, R. Medicinal attributes of 1,2,3-triazoles: Current developments. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 71, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, J.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y.; You, Q. 2-Substituted 3,7,8-trimethylnaphtho[1,2-b]furan-4,5-diones as specific L-shaped NQO1-mediated redox modulators for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 8a–8j are available from the authors. |





| Cpd | -NRR | n | IC50 (μM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | A549/Taxol | A549/Cisplatin | HepG2 | HCT116 | U2OS | |||
| 8a |  | 2 | 1.95 ± 0.40 | 1.22 ± 0.21 | 1.48 ± 0.10 | 2.12 ± 0.41 | 1.64 ± 0.26 | 2.22 ± 0.09 |
| 8b |  | 3 | 2.62 ± 0.20 | 1.30 ± 0.08 | 1.66 ± 0.11 | 1.36 ± 0.16 | 2.27 ± 0.05 | 2.73 ± 0.05 |
| 8c |  | 2 | 2.58 ± 0.39 | 1.29 ± 0.07 | 1.34 ± 0.09 | 1.19 ± 0.31 | 0.98 ± 0.31 | 2.01 ± 0.20 |
| 8d |  | 3 | 2.62 ± 0.04 | 1.70 ± 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.24 | 4.48 ± 0.29 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | 3.05 ± 0.07 |
| 8e |  | 2 | 2.17 ± 0.12 | 2.03 ± 0.11 | 1.29 ± 0.48 | 4.85 ± 0.39 | 2.14 ± 0.18 | 4.66 ± 0.03 |
| 8f |  | 3 | 1.07 ± 0.28 | 1.29 ± 0.08 | 1.32 ± 0.12 | 6.30 ± 0.48 | 1.39 ± 0.04 | 2.07 ± 0.11 |
| 8g |  | 2 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 3.79 ± 0.43 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.21 |
| 8h |  | 3 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 0.55 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 3.07 ± 0.13 | 0.95 ± 0.12 | 0.73 ± 0.07 |
| 8i |  | 2 | 3.33 ± 0.49 | 2.12 ± 0.09 | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 5.35 ± 0.23 | 6.15 ± 0.86 | 9.51 ± 1.52 |
| 8j |  | 3 | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.82 ± 0.08 | 1.29 ± 0.11 | 2.91 ± 0.03 | 1.09 ± 0.21 | 5.86 ± 0.21 |
| DDO-6101 | — | 2.59 ± 0.17 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 2.11 ± 0.10 | 2.04 ± 0.08 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | 5.35 ± 0.08 | |
| GA | — | 2.02 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 2.50 ± 0.06 | 2.08 ± 0.07 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 4.67 ± 0.11 | |
| Cpd | PSA_2D (Å2) a | Log D 7.4 b | Absorption_Level c | S (mM) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8a | 92.614 | 2.1 | 0 | 1.12 |
| 8b | 92.614 | 1.8 | 0 | 1.54 |
| 8c | 92.614 | 2.2 | 0 | 1.40 |
| 8d | 92.614 | 1.6 | 0 | 1.92 |
| 8e | 92.614 | 2.9 | 0 | 0.56 |
| 8f | 92.614 | 2.7 | 1 | 0.88 |
| 8g | 101.544 | 1.3 | 0 | 3.02 |
| 8h | 101.544 | 0.9 | 0 | 3.70 |
| 8i | 95.967 | 1.0 | 0 | 3.22 |
| 8j | 95.967 | 0.7 | 0 | 4.02 |
| DDO-6101 | 73.277 | 2.9 | 0 | <0.005 |
| GA | 120.323 | 3.6 | 1 | <0.005 |
| Group | Dose (mg/kg) | Body Weight (g) | Weight of Tumor (g) | Inhibitory Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Dose | After-Dose | ||||
| control | 0 | 20.95 ± 1.22 | 29.25 ± 3.37 | 1.36 ± 0.20 | 0.0 |
| 8g | 5 | 20.80 ± 1.53 | 28.53 ± 2.81 | 0.94 ± 0.24 a | 30.88 |
| 8g | 10 | 21.40 ± 1.81 | 28.08 ± 2.66 | 0.65 ± 0.17 b | 52.21 |
| 8g | 20 | 20.67 ± 1.30 | 27.73 ± 2.78 | 0.40 ± 0.14 b | 71.32 |
| DDO-6101 | 20 | 21.13 ± 1.22 | 27.69 ± 1.90 | 0.89 ± 0.18 b | 34.56 |
| 5-FU | 20 | 20.25 ± 1.27 | 24.43 ± 2.62 | 0.48 ± 0.17 b | 64.71 |
| Group | Dose (mg/kg) | Body Weight (g) | Weight of Tumor (g) | Inhibitory Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Dose | After-Dose | ||||
| control | 0 | 20.86 ± 1.18 | 28.55 ± 2.97 | 1.40 ± 0.22 | 0.0 |
| 8g | 50 | 20.67 ± 1.20 | 27.73 ± 2.78 | 0.47 ± 0.12 a | 66.43 |
| DDO-6101 | 50 | 21.13 ± 1.02 | 26.69 ± 1.90 | 1.10 ± 0.25 b | 21.43 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; You, Q.; Zhang, X. ‘Click Chemistry’ Synthesis of Novel Natural Product-Like Caged Xanthones Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Moiety with Improved Druglike Properties as Orally Active Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111834
Li X, Wu Y, Wang Y, You Q, Zhang X. ‘Click Chemistry’ Synthesis of Novel Natural Product-Like Caged Xanthones Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Moiety with Improved Druglike Properties as Orally Active Antitumor Agents. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Yue Wu, Yanyan Wang, Qidong You, and Xiaojin Zhang. 2017. "‘Click Chemistry’ Synthesis of Novel Natural Product-Like Caged Xanthones Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Moiety with Improved Druglike Properties as Orally Active Antitumor Agents" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111834
APA StyleLi, X., Wu, Y., Wang, Y., You, Q., & Zhang, X. (2017). ‘Click Chemistry’ Synthesis of Novel Natural Product-Like Caged Xanthones Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Moiety with Improved Druglike Properties as Orally Active Antitumor Agents. Molecules, 22(11), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111834