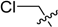Abstract
We designed and synthesized 26 prototype compounds and studied their anti-inflammatory activity and underlying molecular mechanisms. The inhibitory effects of the compounds on the production of nitric oxide (NO), cytokines, inflammatory-related proteins, and mRNAs in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages were determined by the Griess assay, Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Western blot analysis, and Reverse transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), respectively. Our results indicated that treatment with A2, A6 and B7 significantly inhibited the secretion of NO and inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 cells without demonstrable cytotoxicity. It was also found that A2, A6 and B7 strongly suppressed the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase enzyme COX-2, and prevented nuclear translocation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) p65 by inhibiting the degradation of p50 and IκBα. Furthermore, the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells was significantly inhibited by A2, A6 and B7. These findings suggest that A2, A6 and B7 may operate as an effective anti-inflammatory agent through inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in macrophages. Moreover, rat paw swelling experiments showed that these compounds possess anti-inflammatory activity in vivo, with compound A6 exhibiting similar activities to the reference drug Indomethacin.
1. Introduction
Activated macrophages play crucial roles in the initiation and maintenance of inflammation. Following activation by inflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), macrophages secrete a number of potent bioactive inflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandins (PGs), leukotrienes (LTs), and cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), that contribute to the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Of note, as an important inflammatory mediator, the paradoxical role of NO in the pathogenesis of inflammation generally depends upon concentration [11]. Appropriate levels of NO produced by inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in response to inflammatory stimuli such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-1β, and LPS assist in mounting an effective defense against pathogens [12]. However, sustained overproduction of NO by iNOS is believed to be detrimental to the host and is associated with the pathogenesis of a variety of inflammatory disorders [13]. Therefore, pharmacological interference with NO production is appreciated as a promising strategy of therapeutic intervention in inflammatory diseases [14]. Conversely, while the major role of housekeeping cyclooxygenase enzyme COX-1 is to regulate the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway [15], the inducible cyclooxygenase COX-2 is responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins [16,17], which makes COX-2 a selected target of anti-inflammatory drugs. Starting from the clinical use of aspirin, diclofenac, and indomethacin as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [18,19], the development of COXIBs [20,21,22] has provided some relief to patients suffering from a wide spectrum of inflammatory diseases. However, the cardiovascular side effects associated with the use of COXIBs is a limiting factor that has subdued the medicinal applications of this class of anti-inflammatory drugs [23,24,25,26,27,28], and hence, the search for new anti-inflammatory chemical entities continues.
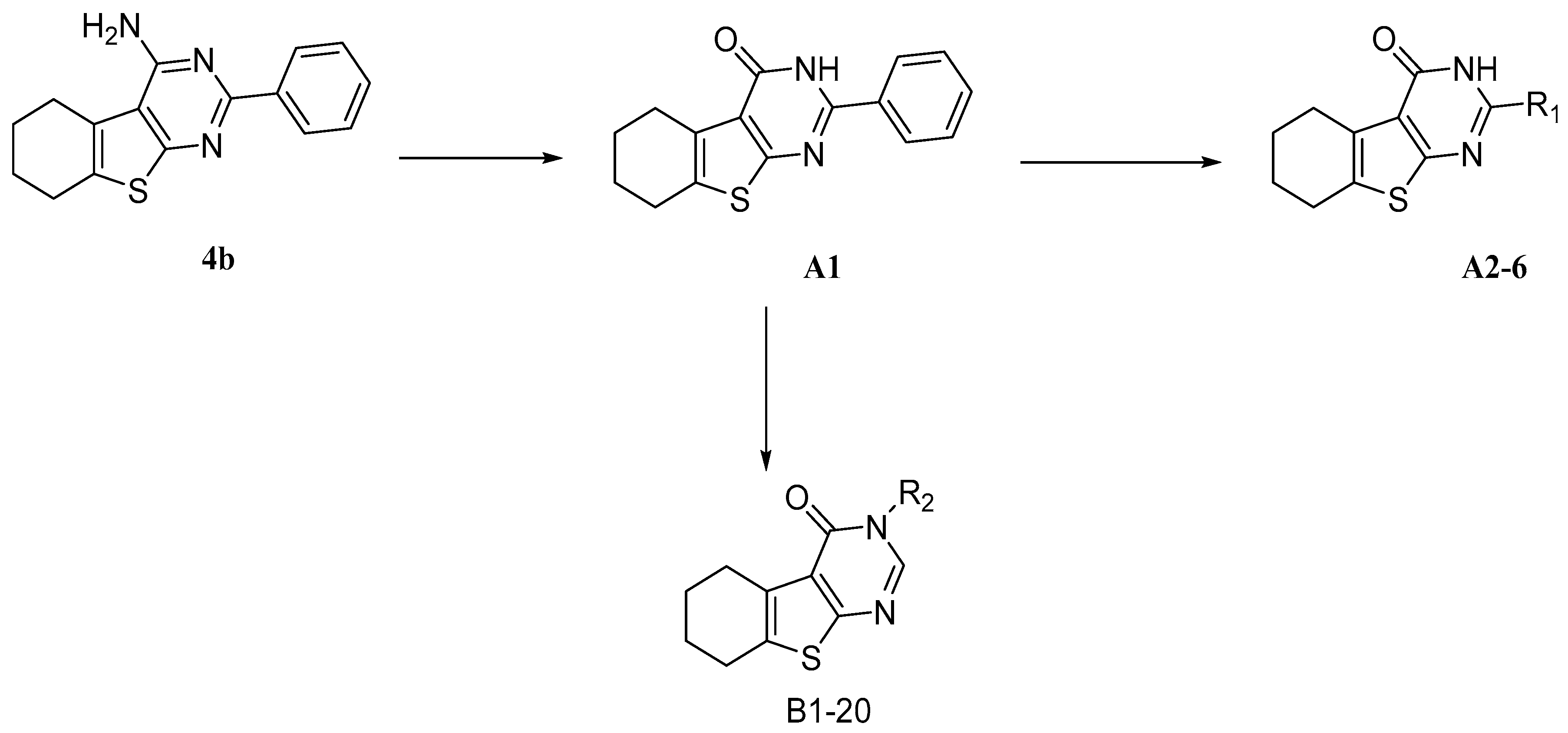
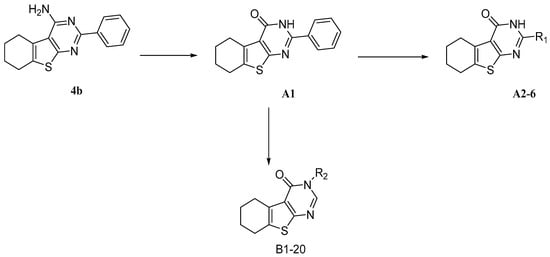
Previously, during the study of tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine series of fibroblast growth factor FGFR1 inhibitors, we were intrigued by the findings that compounds such as 4b (Scheme 1) inhibited the production of TNF-α and IL-6 [29]. In the literature, it is known that compounds with a similar thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold has been reported as anti-inflammatory agents [30,31]. In addition, as a bioisostere of quinazoline, thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine has been used extensively for a pharmacophore and synthesis of compounds with diverse biological activities, including anti-tumor [32,33,34,35,36,37,38], anti-microbial [33,39], anti-viral [40,41,42], anti-diabetic [43], anti-anxiolytic [44], and antioxidant [45] activities. We therefore set out to explore the potential anti-inflammatory activity of 4b, the tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine compound; however, the activity of 4b has room for improvement, so we attempted to change the amino into carbonyl to obtain the compound A1, possessing hydrogen bond receptor to improve the binding between compounds and inflammatory cytokine. According to preliminary anti-inflammation activity screening, A1 is superior to 4b (51.64% and 49.83% for anti-IL-6, as well as 50.70% 48.23% for anti-TNF-alpha). Furthermore, we performed further structural modifications to A1 at 2 and 3 positions, respectively, to get compounds with better anti-inflammatory activity and to study the underlying molecular mechanisms of this novel class of compounds.
Scheme 1.
Design of tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
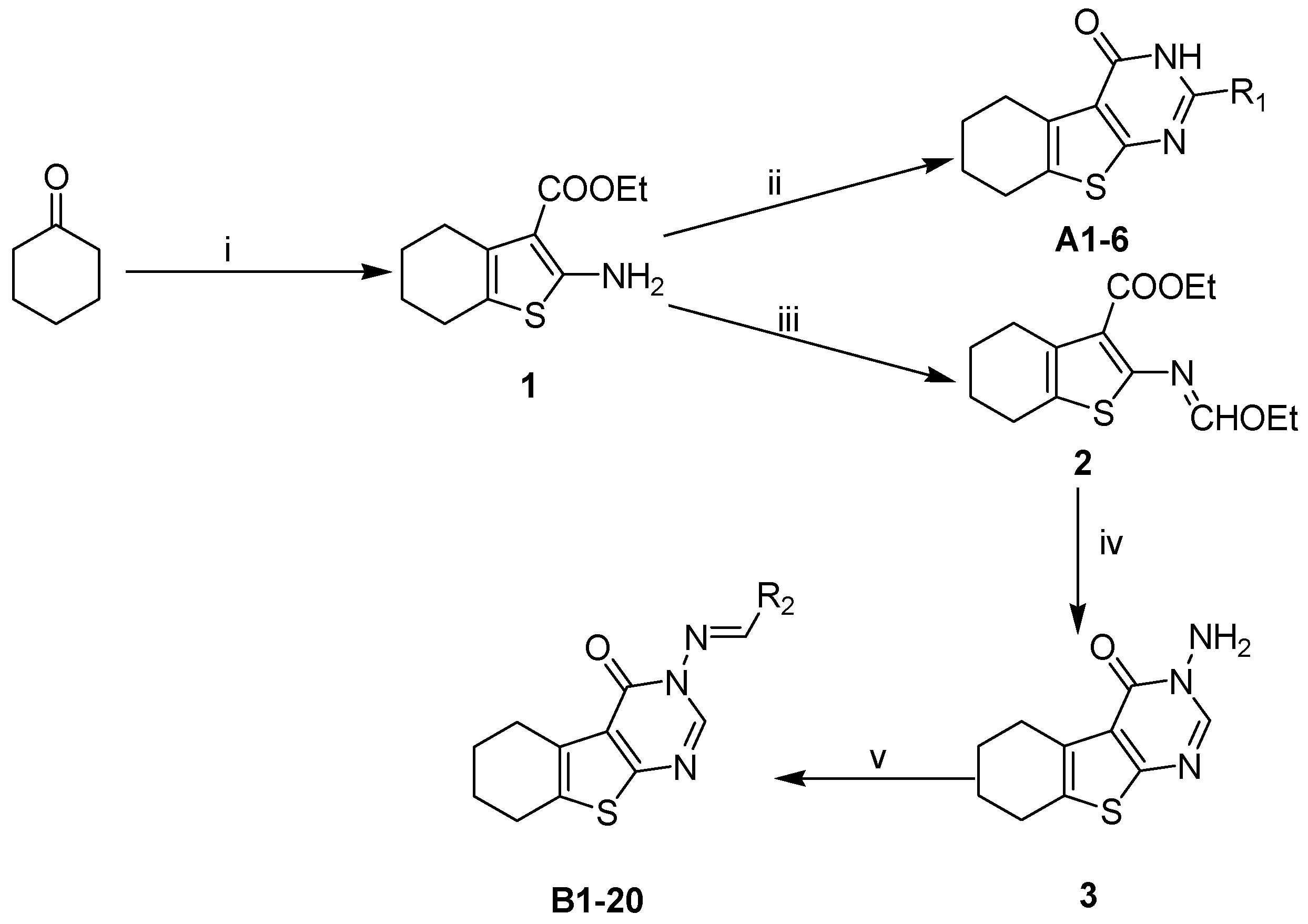
Based on the structure of template 4b, we envisaged that it would be interesting to explore the optimal interaction between the phenyl substituent and its biological target, as well as to exploit any potential hydrogen bonding that could result from the amino group on the pyrimidine ring. Thus, we attempted to introduce a carbonyl in place of the amino group, and to modify the 2-, and 3-positions of the tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine system. The construction of the desired template that features a fused tricyclic heterocycle began from the condensation of cyclohexanone and ethyl cyanoacetate in the presence of elemental sulfur (Scheme 2). The key intermediate 1 has functionalities at the 2- and 3-positions of the tetrahydrobenzothiophene ring that allow formation of the pyrimidine ring with different substituents. In one route, reaction of intermediate 1 with aryl or alkyl nitrile generated compounds A1–6 in good yields (Table 1). Alternatively, reaction of 1 with triethyl orthoformate in reflux acetic anhydride provided intermediate 2, which upon treatment with hydrazine hydrate readily cyclized to give compound 3. The exocyclic amine in 3 was then further functionalized to provide a variety of hydrazine imines, B1–20 (Table 2), using selected aldehydes.
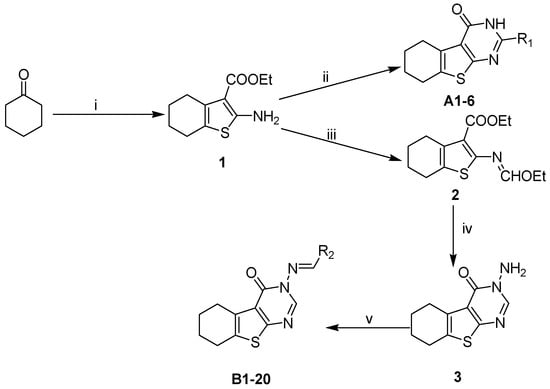
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of target compounds. Conditions: (i) S, Et2NH, EtOH, NCCH2COOEt; (ii) R1CN, HCl, dioxane, EtOH; (iii) Ac2O, CH(OEt)3; (iv) NH2NH2·H2O; and (v) R2CHO, EtOH, AcOH.

Table 1.
Chemical Structures of Target Compounds A1–6.

Table 2.
Chemical Structures of Target Compounds B1–20.
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
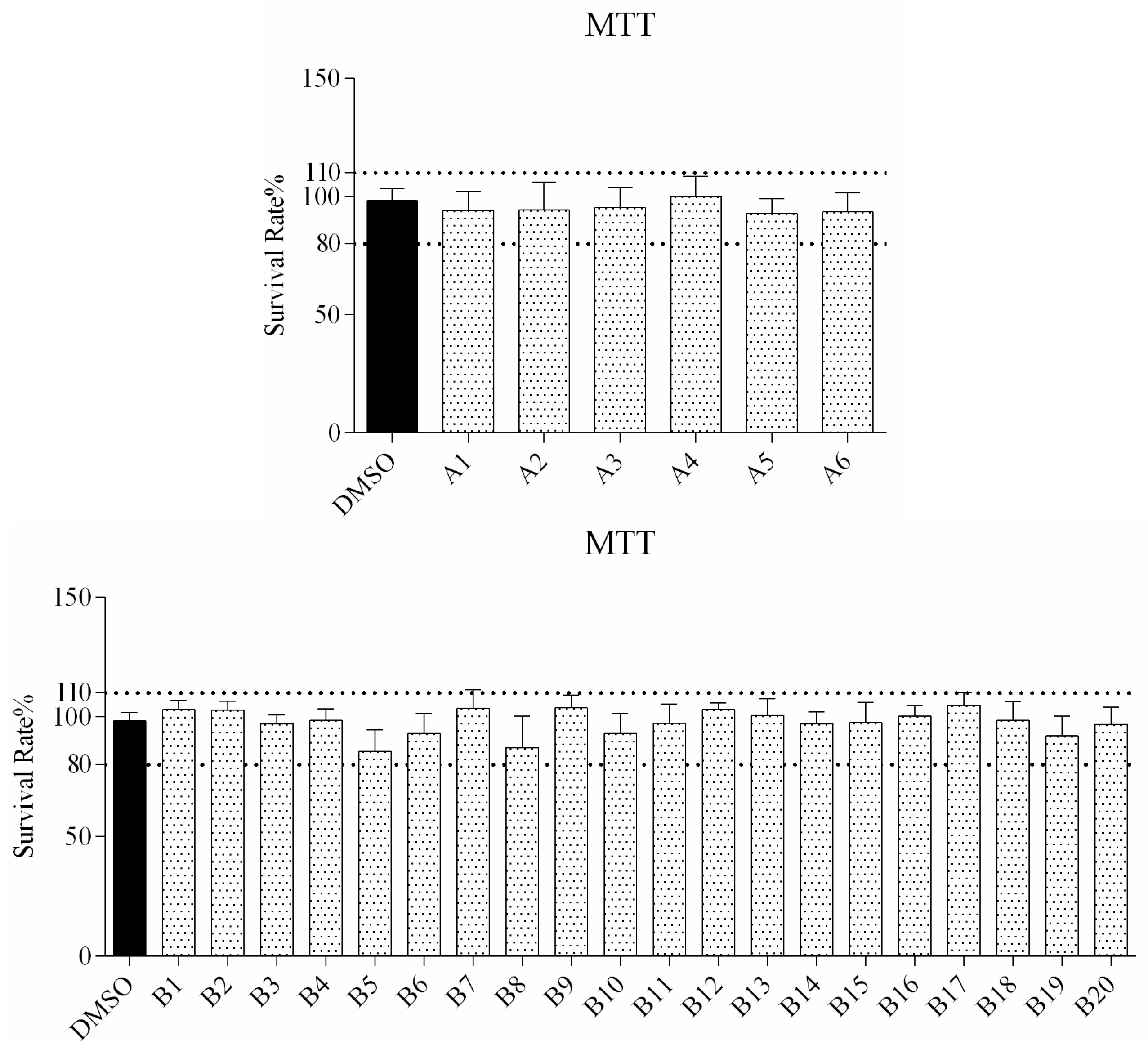
The cytotoxicity of all compounds was evaluated in RAW264.7 cells by MTT assay after 72 h of treatment. As observed from the cell viability data in Figure 1, the survival rate of all compound treated cells is higher than 80%, indicating that a concentration of up to 160 μM was not associated with any significant change in overall cell viability.
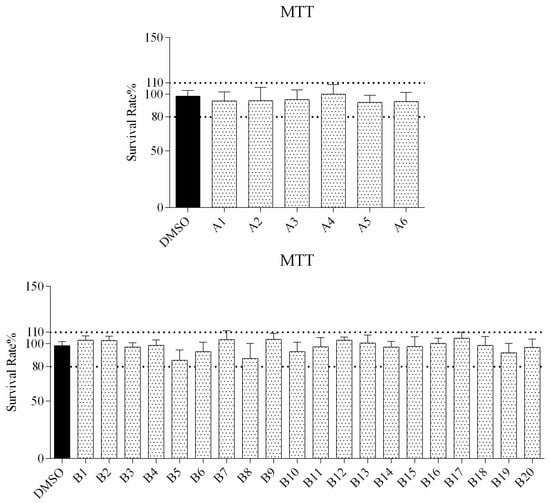
Figure 1.
In vitro survival rate of RAW264.7 cells treated with compound A1–6 and B1–20 at 160 μM.
2.2.2. Effects of Compound Treatment on Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion
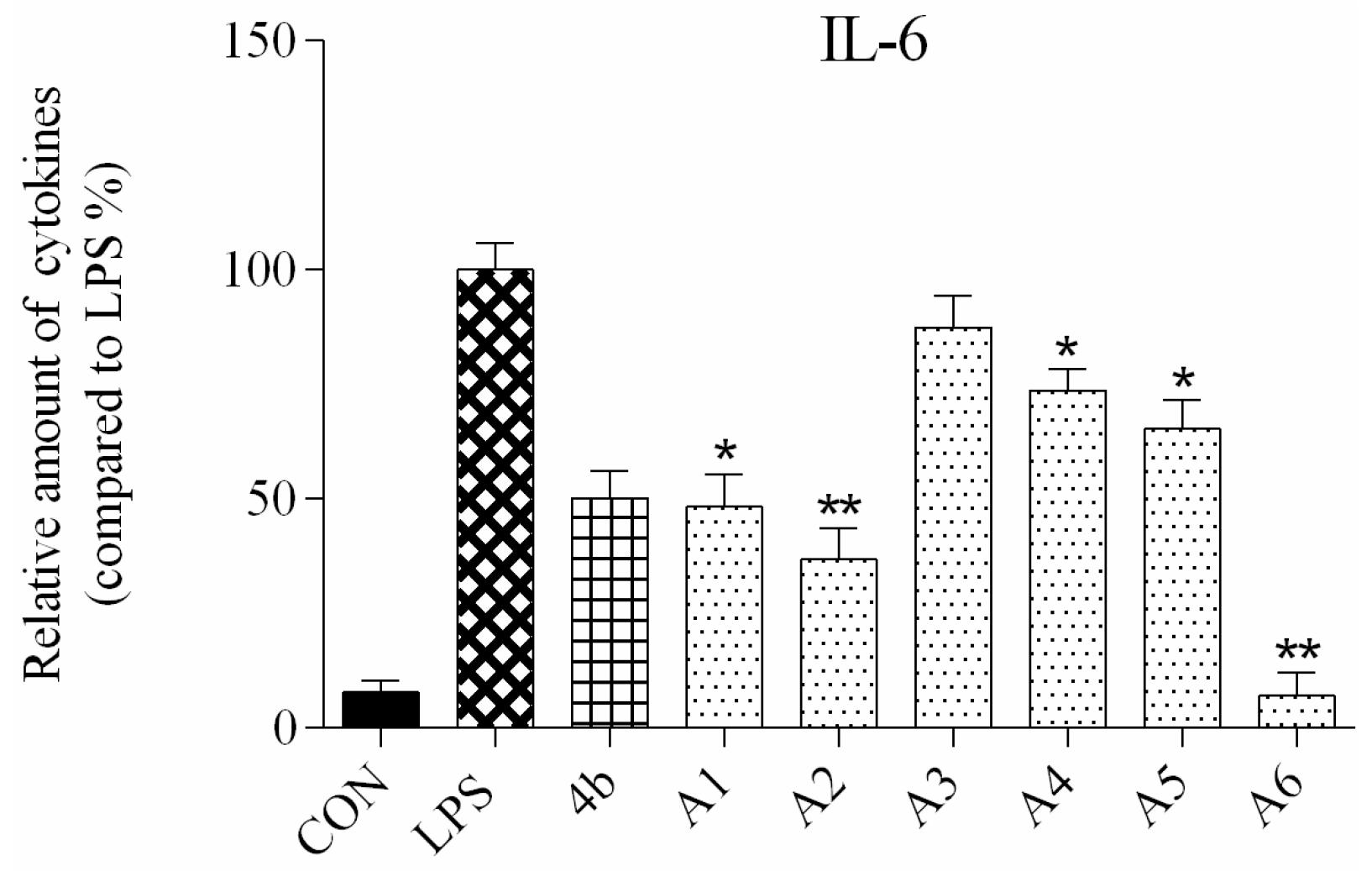
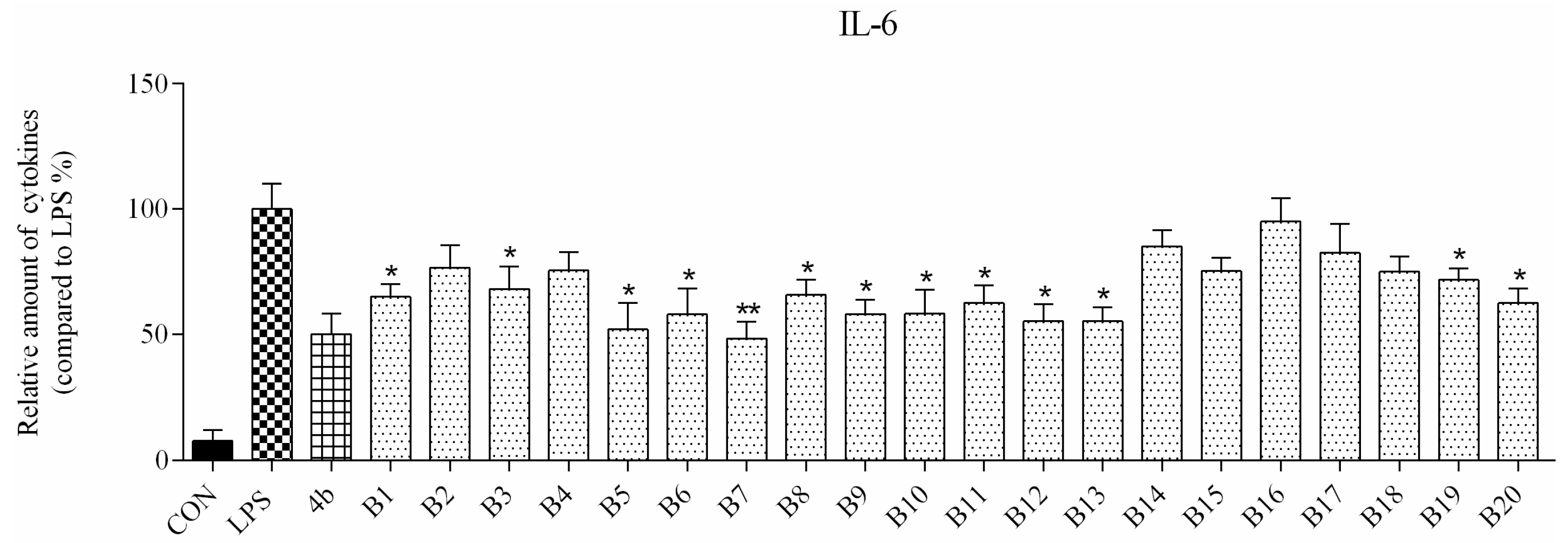
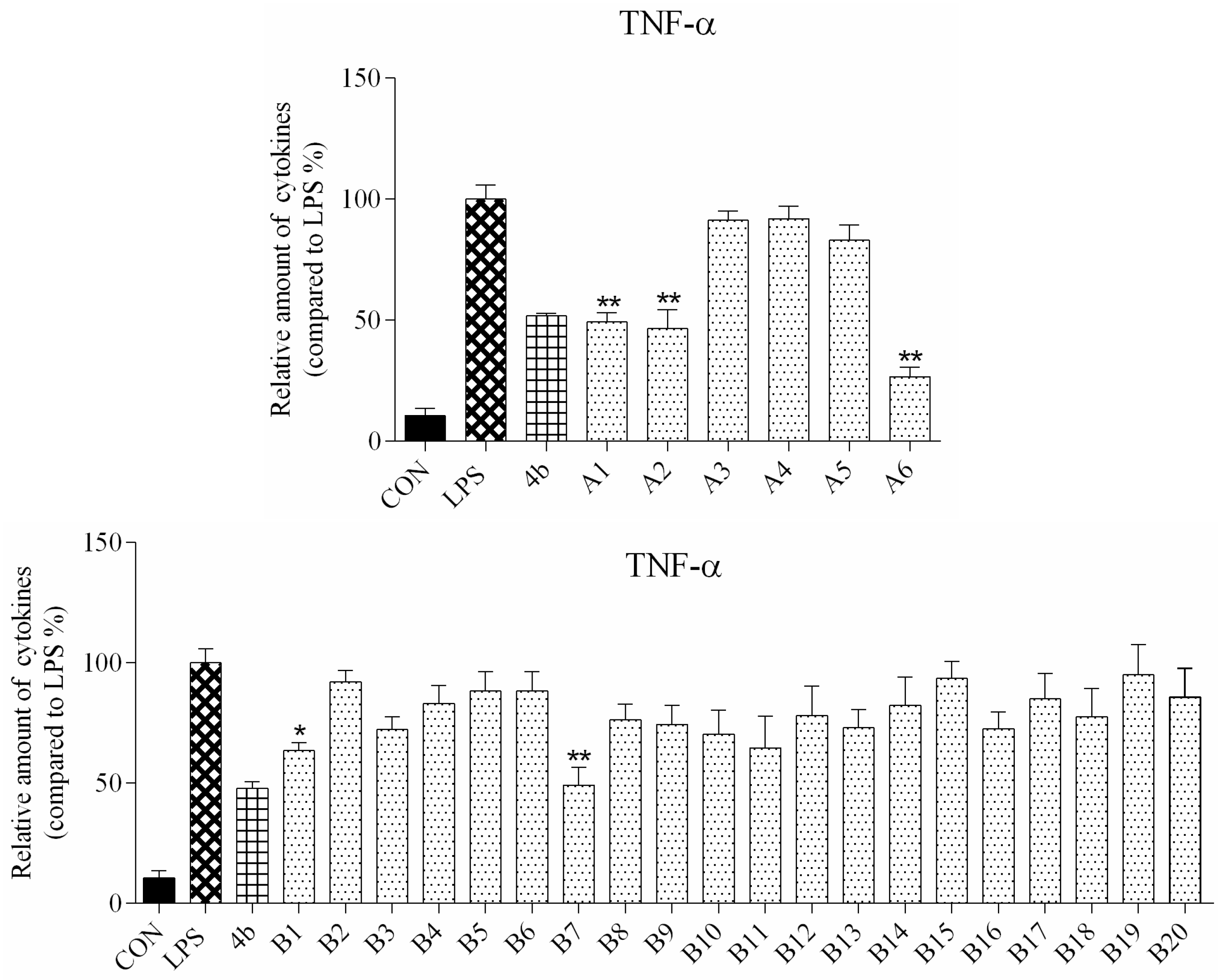
ELISA was used to evaluate secretion of the cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in macrophages following compound treatment. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, the secretion of inflammatory cytokines was significantly inhibited by most of the compounds at 10 μM concentration. Notably, compounds A2, A6, and B7 most strongly suppressed secretion of TNF-α and IL-6, and were selected for further characterization.

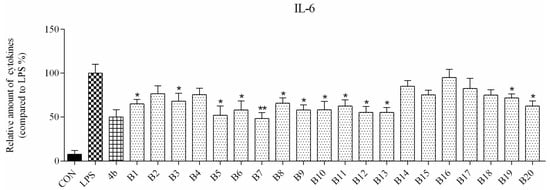
Figure 2.
Relative levels of cytokine IL-6 in macrophages after treatment with compounds A1–6 and B1–20 at 10 μM concentration as compared to LPS group and indomethacin group (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).
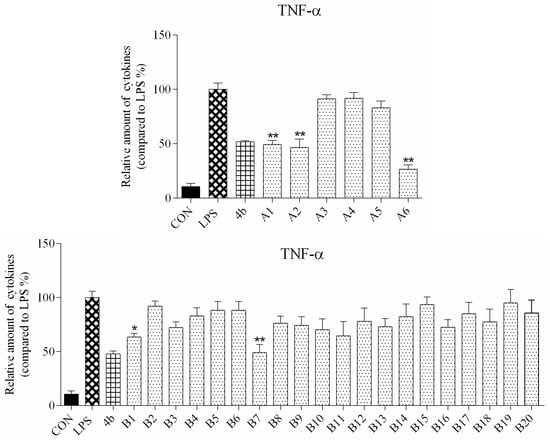
Figure 3.
Relative levels of cytokine TNF-α in macrophages after treatment with compounds A1–6 and B1–20 at 10 μM concentration as compared to LPS group and indomethacin group (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).
2.2.3. Preliminary Structure Activity Relationship (SAR)
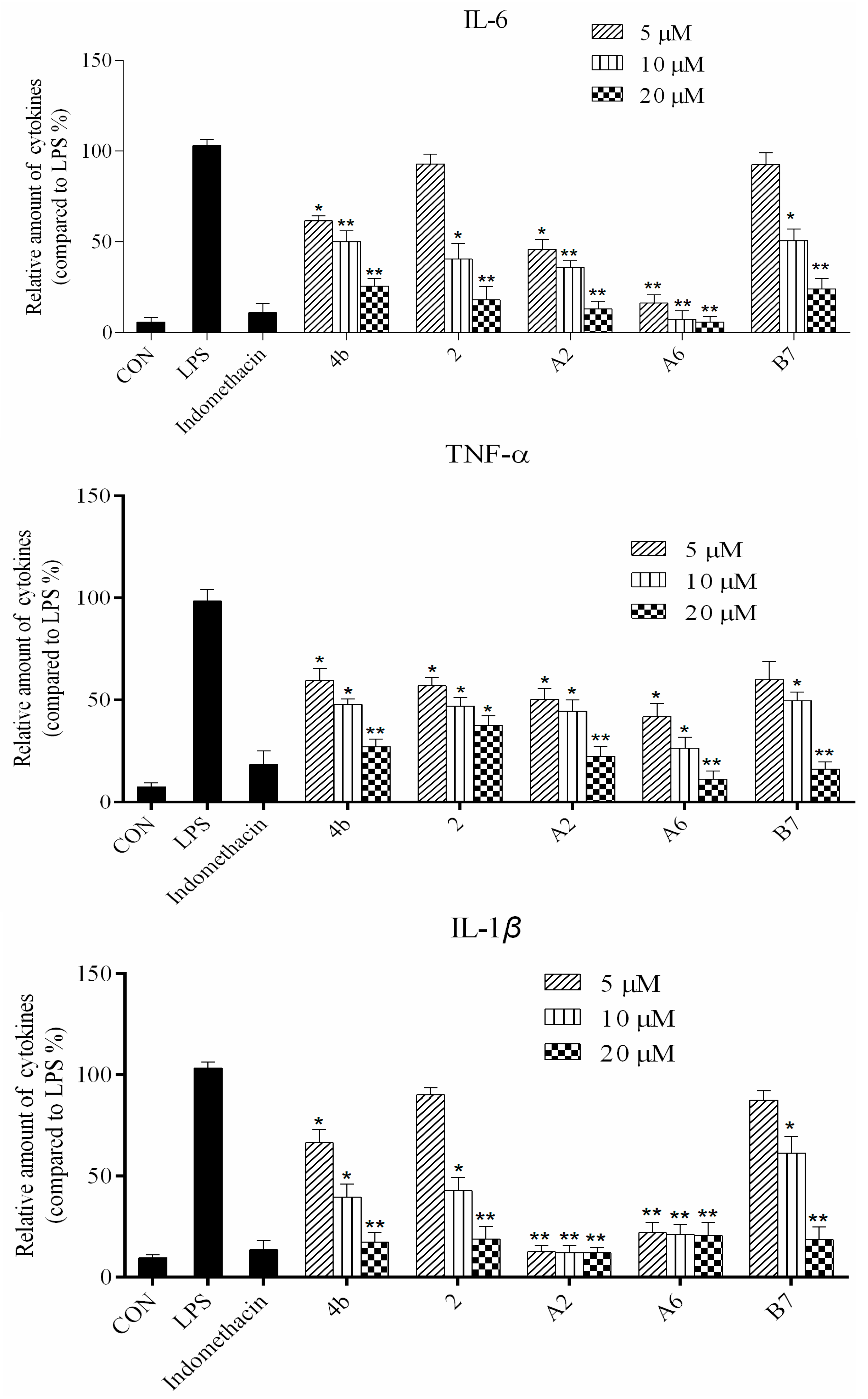
As shown in Figure 2, all compounds had significantly low cytotoxicity. As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, most of the tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives were found to exhibit comparable anti-IL-6 and anti-TNF-alpha activity with 4b, especially A2, A6, and B7, which showed great anti-inflammation activity. Replacing with chloromethyl group and pyridine at 2 position obtained better activity than 4b and other substitutes; the two groups, as electron donating groups, can improve the anti-inflammation activity. Moreover, replacing with naphthyl group at 3 position obtained the better activity for compound B7; naphthyl group can offer multi-π–π conjugated system, which contributes to binding with inflammatory cytokine obtain better inhibitory effection.
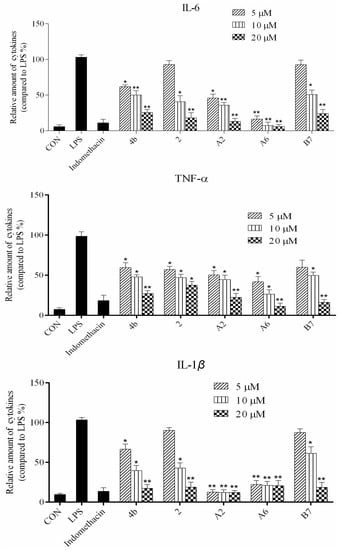
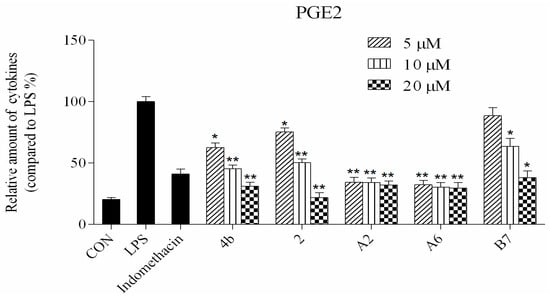
Figure 4.
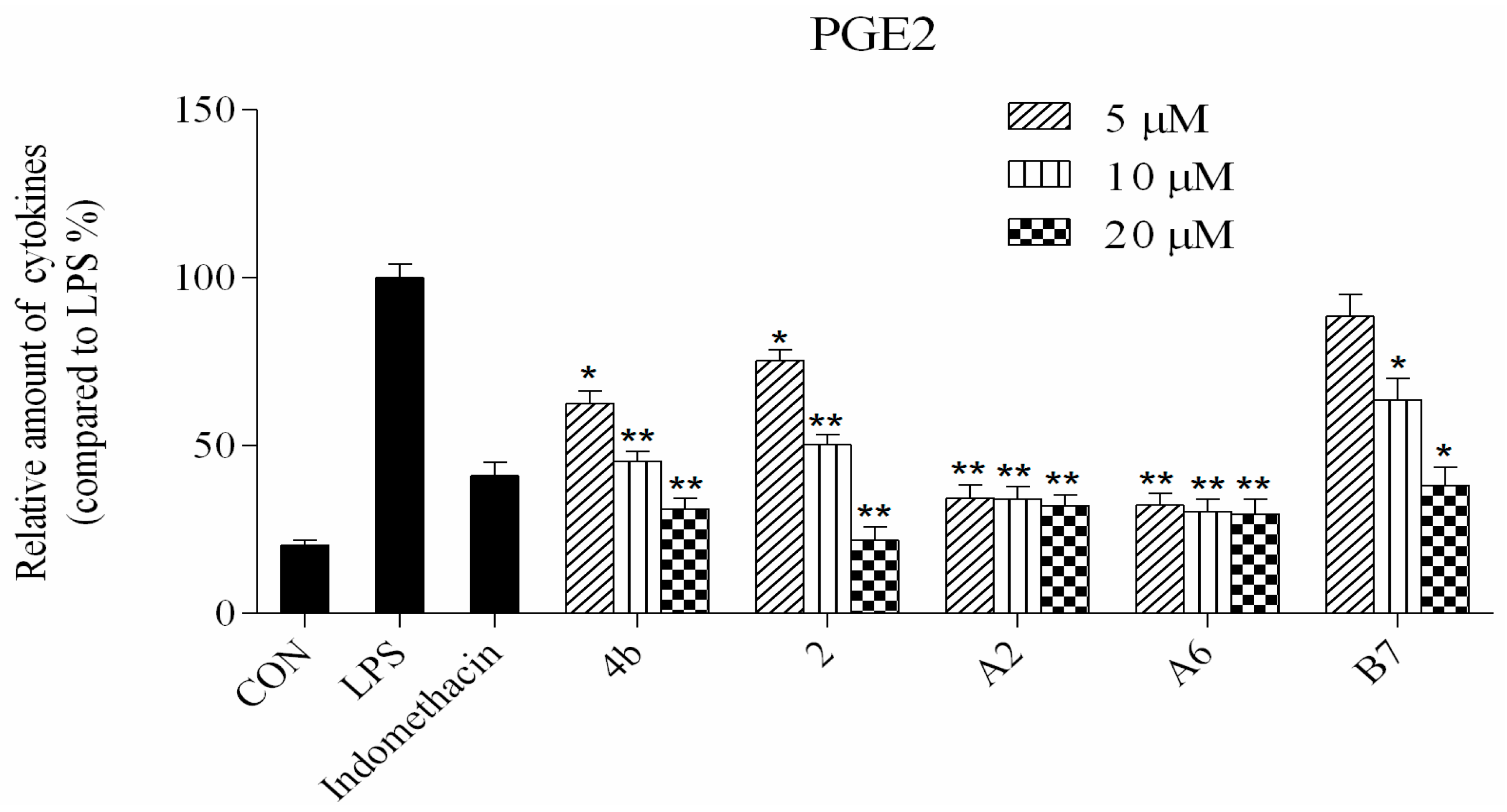
Compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7 reduced the production of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, and PGE2 at concentrations of 5 μM, 10 μM, and 20 μM (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).
2.2.4. Dose Response Effects of Compound A2, A6, B7 on Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion
ELISA was used to evaluate cytokine TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and PGE2 secretion in macrophages following treatment with compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7. As shown in Figure 4, the secretion of four inflammatory cytokines was significantly inhibited by compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7 in a dose-dependent manner. Notably, treatment with A2 and A6 strongly suppressed cytokine secretion more significantly than compounds 4b, 2, and B7. Moreover, compound A6 inhibited the production of four inflammatory cytokines with similar activity to the positive control indomethacin at 10 μM.
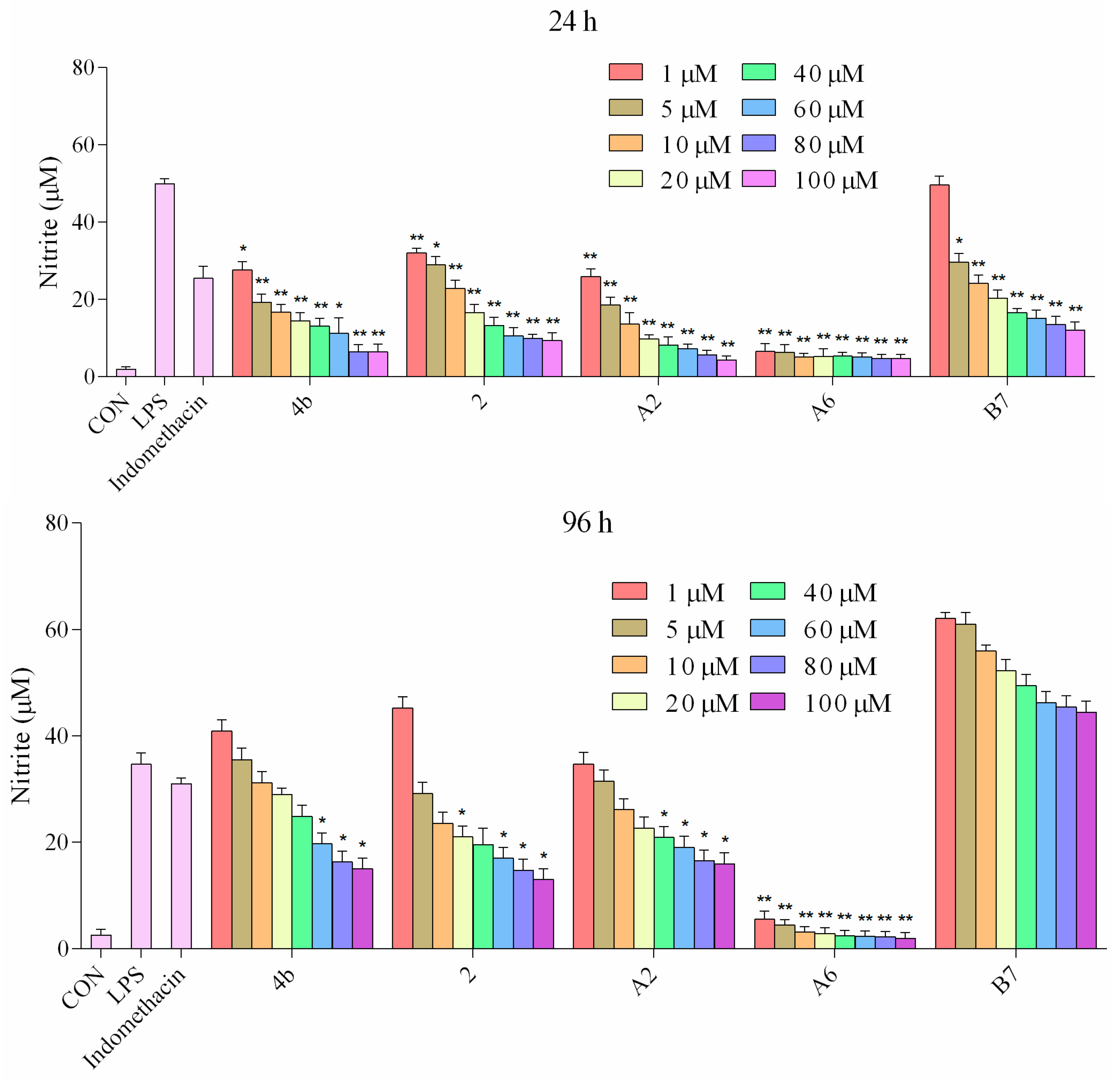
2.2.5. Inhibitory Effects of Compounds A2, A6, B7 on NO Production
It has been well established that NO production is correlated with various inflammatory diseases. We investigated the suppressive effects of compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7 on NO levels in macrophages stimulated with LPS. The supernatant was treated with a range of concentrations (1–100 μM) of compounds for 1 h followed by stimulation with LPS for 24 h and 96 h, and NO production was measured using Griess reagent. It was found that compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7 dramatically inhibited the release of NO in a dose-dependent manner following LPS stimulation (Figure 5). The effects at 24 h were more significant compared to 96 h. In particular, compound A6 displayed higher inhibitory activity when compared with the positive control indomethacin at 1 μM.
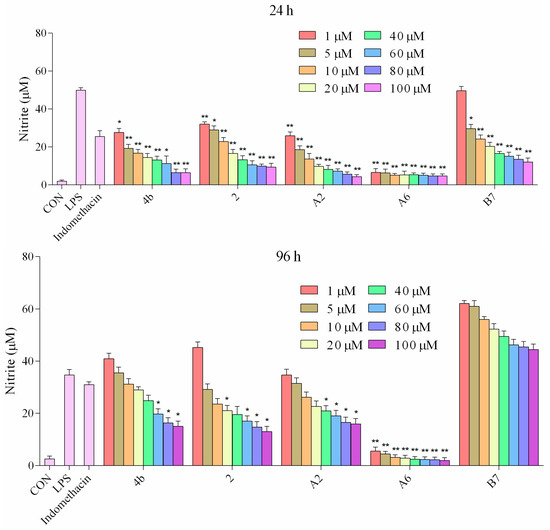
Figure 5.
Production of NO in macrophages following treatment with different concentrations of 4b, 2, A2, A6, B7, and 1 μM indomethacin for 24 and 96 h (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).
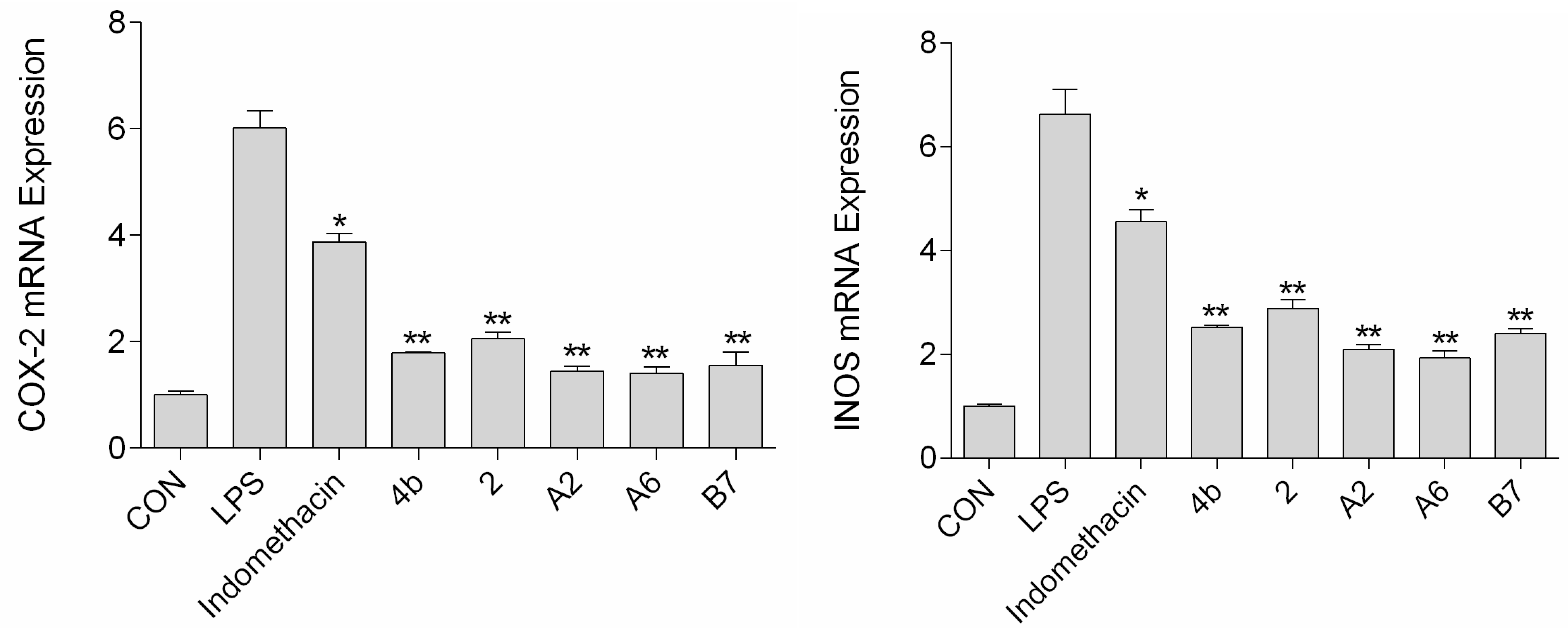
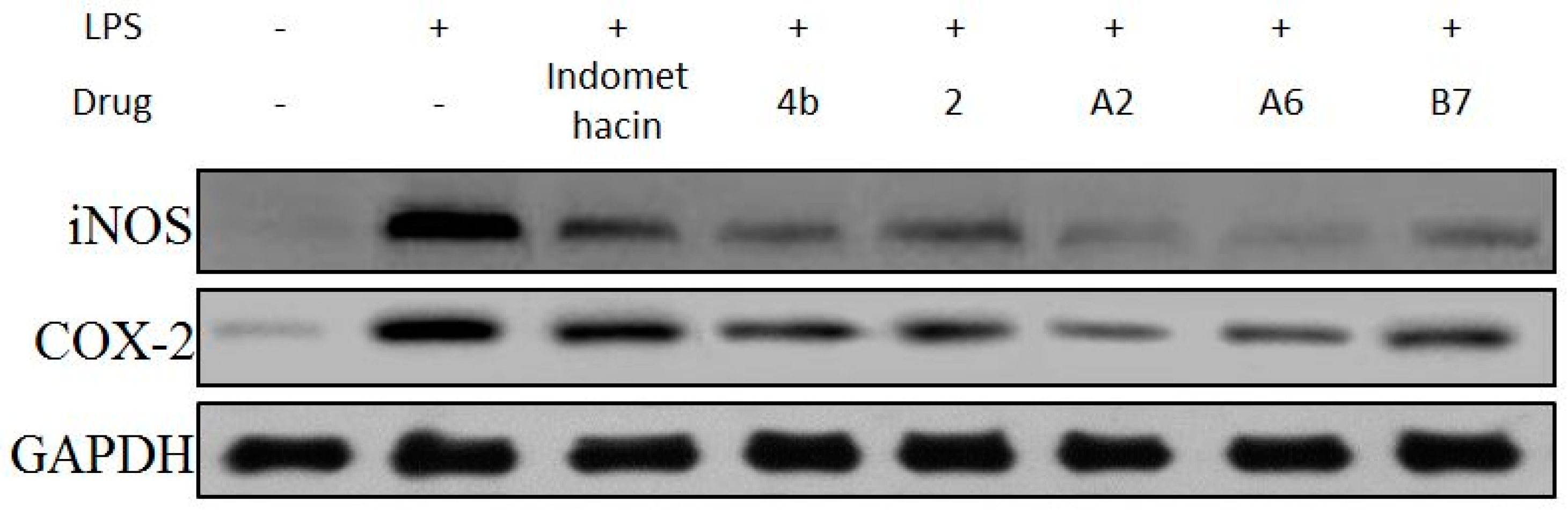
2.2.6. Effects of Compounds A2, A6, B7 on iNOS and COX-2 Expression Levels
The effects of compound A2, A6, and B7 treatment on mRNA and protein expression of iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 cells were investigated by RT-PCR analysis and Western blotting. As shown in Figure 6, treatment with A2, A6, and B7 markedly reduced iNOS and COX-2 mRNA levels, with higher inhibitory effects compared to indomethacin. Moreover, as shown in Figure 7, compounds A2, A6, and B7 significantly decreased the protein levels of iNOS and COX-2.
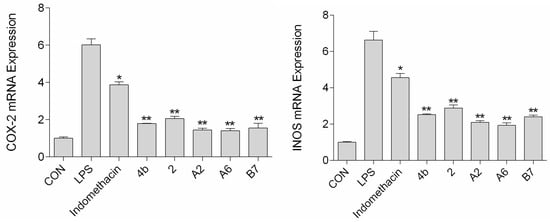
Figure 6.
The expression of COX-2 and iNOS mRNA after treatment with 10 μM compound 4b, 2, A2, A6, B7, or indomethacin (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).
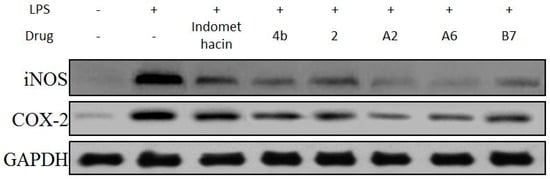
Figure 7.
Immunoblotting of cellular proteins COX-2 and iNOS expression in RAW264.7 cells treated with 10 μM compounds 4b, 2, A2, A6, B7, or indomethacin. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
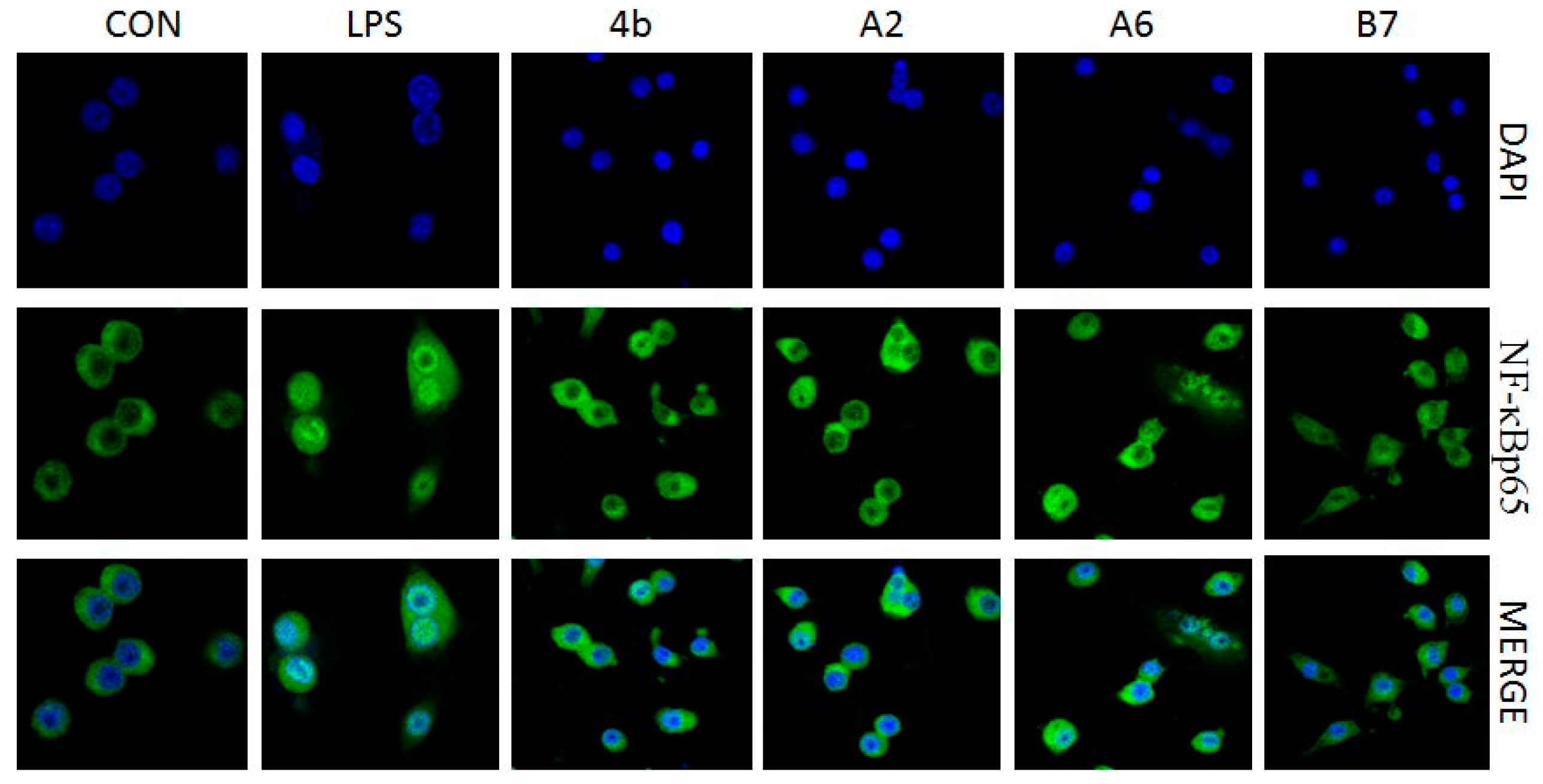
2.2.7. Effects of Compounds A2, A6, B7 on Cellular NF-κB p65 Translocation
Transcription factor NF-κB signaling is pivotal in the induction of inflammatory responses. A key event involves IκB (inhibitors of NF-kB) phosphorylation and degradation that leads to the release of NF-κB p65 subunit from the cytoplasm, followed by translocation to the nucleus, where it binds to target promoters, and activates transcription of inflammatory genes including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12, and COX-2. The effects of compound A2, A6, B7 on NF-κB p65 subunit nuclear translocation was determined in an immunofluorescence assay. As shown in Figure 8, LPS induction increased NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation (green dots in blue nucleus), while, in A2, A6, and B7 pretreated macrophages, LPS-induced nuclear p65 decreased, suggesting that A2, A6, and B7 inhibited p65 translocation from cytoplasm to nuclei. The results suggest that the anti-inflammatory activity of compounds A2, A6, and B7 may be associated with inhibitory effects on NF-κB activation.
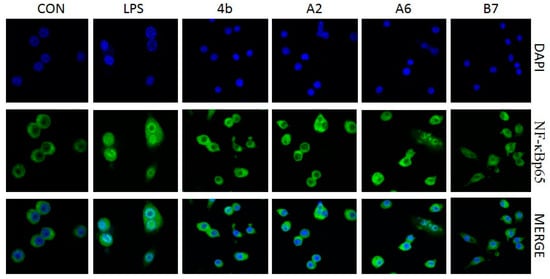
Figure 8.
Immunofluorescence of NF-κB p65 in RAW264.7 cells exposed to LPS (100 ng/mL) with or without compound 4b, A2, A6, and B7 (10 μM).
2.2.8. Effects of Compounds A2, A6, B7 on MAPKs Phosphorylation in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
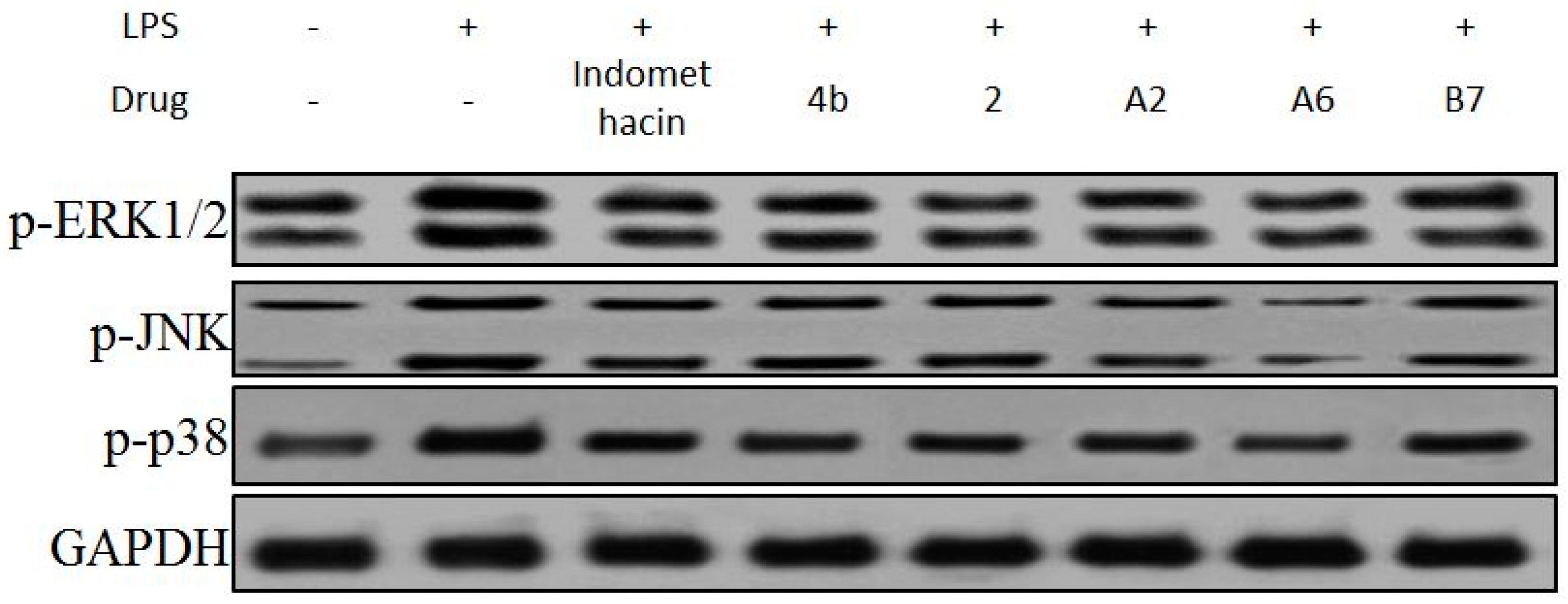
In mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, ERK1/2, p38, and JNK protein kinases are essential regulators of the inflammatory response [46]. The effects of compound A2, A6, B7 on the activation of MAPKs were determined by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies for the corresponding phosphorylated forms. As displayed in Figure 9, compound A2, A6, and B7 treatment markedly inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK compared to indomethacin treatment, with compound A6 exhibiting the most significant inhibitory effect.
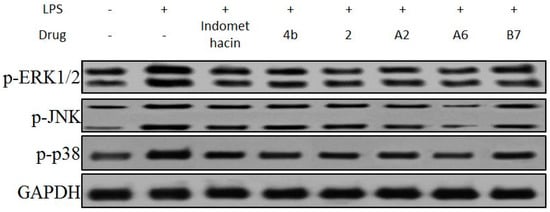
Figure 9.
Immunoblotting of p-ERK1/2, p-p38, and p-JNK of MAPK signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells treated with 10 μM compound 4b, 2, A2, A6, and B7, or indomethacin. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
2.2.9. Effects of Compounds A2, A6, B7 Treatment on NF-κB Activation in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
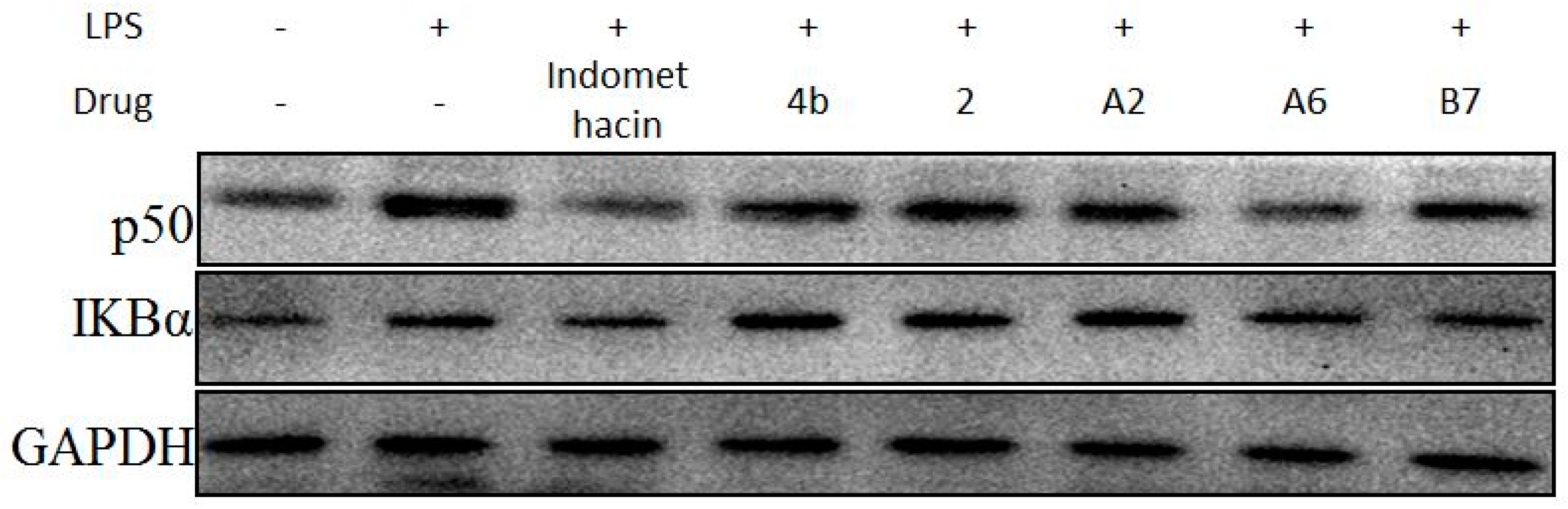
Due to the importance of NF-κB activation in the regulation of the inflammatory response, the effects of compound A2, A6, and B7 treatment on LPS-induced changes in the levels of p50 and IκBα were determined (Figure 10). The results showed that, similar to indomethacin, treatment with A2, A6, and B7 effectively blocked LPS-induced activation of NF-κB in macrophages, with A6 exhibiting the most significant inhibitory effect.
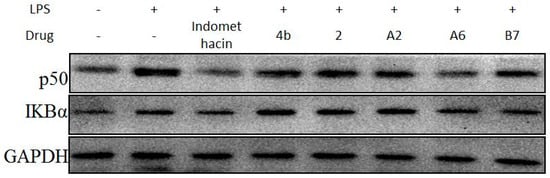
Figure 10.
Immunoblotting of p50 and IKBα of NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells treated with 10 μM compound 4b, 2, A2, A6, B7, or indomethacin. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
2.2.10. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of A2, A6, and B7 in Carrageenan-Induced Rat Paw Edema
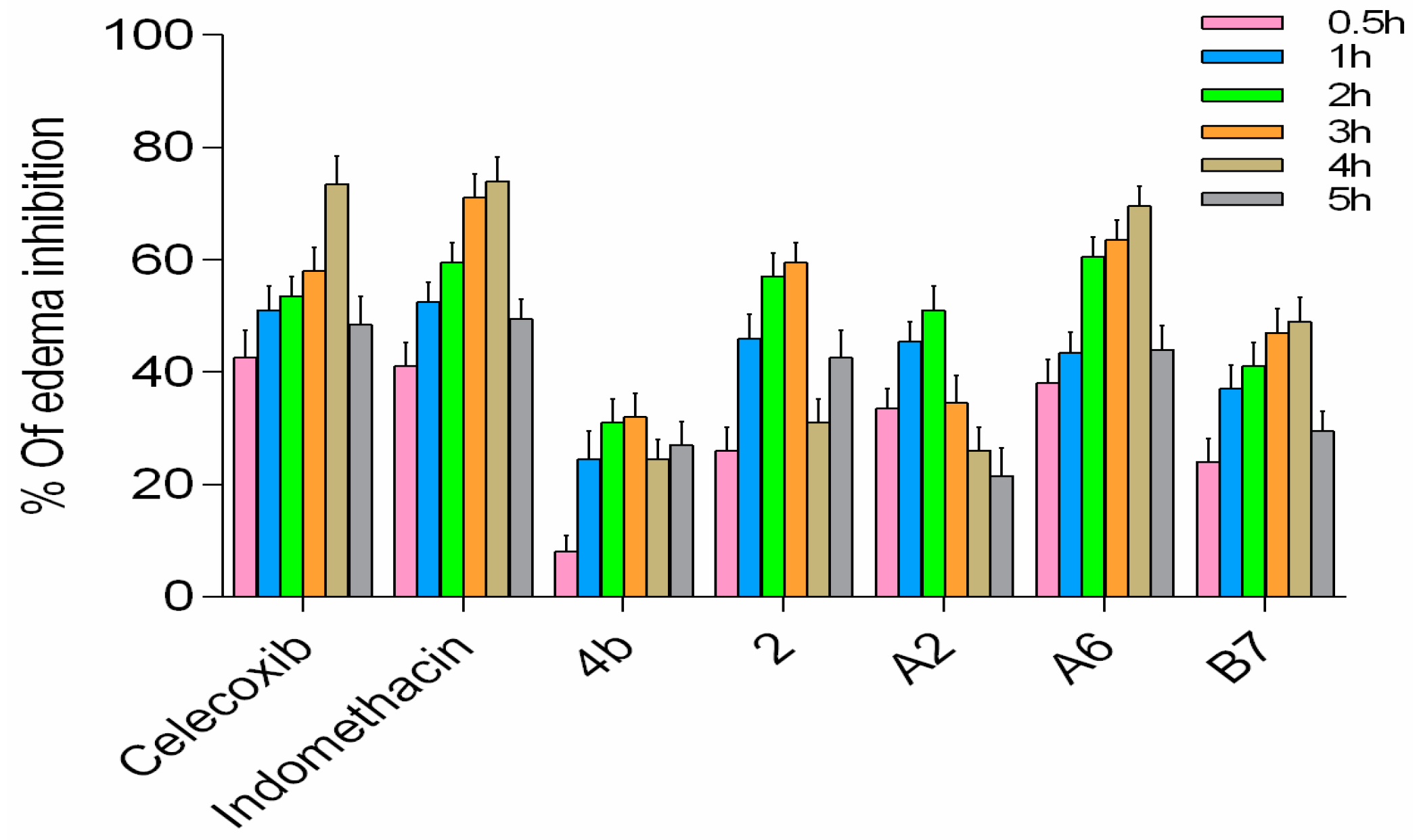
In the rat paw edema model, both the compound group and positive control group showed reduction of carrageenan-induced rat paw edema at varying levels (Figure 11). Compounds A2, A6, and B7 displayed improved activity compared to 4b, with A6 exhibiting the highest in vivo activity among the three new analogs, comparable to celecoxib and indomethacin. Based on all results, A6 can serve as a lead compound for further studies.
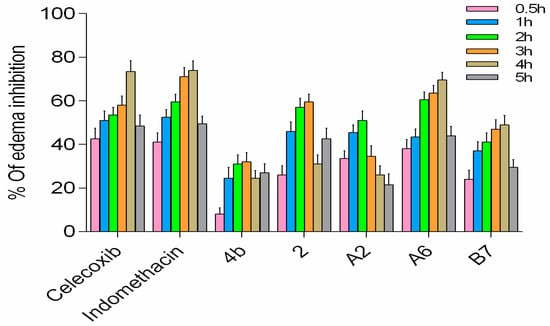
Figure 11.
In vivo anti-inflammatory activity of A2, A6, and B7 against carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
Melting points were determined in SGWX-4 microscopic melting point meter and are uncorrected. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker 600 MHz NMR spectrometer, using CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 as solvents. Chemical shifts are expressed in ppm with TMS as internal reference. J values are provided in hertz. Mass spectra were recorded on Bruker micrOTOF QII mass spectrometer. Reactions were monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) on glass plates coated with silica gel GF-254. Column chromatography was performed with 200–300 mesh silica gel.
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1
To a round bottom flask, 3.2 g sulfur was added, along with 11 mL cyanoacetic acid ethyl ester, 10 mL cyclohexanone, and 20 mL ethanol at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for 10 min, then 8 mL diethylamine was added and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction mixture was suction-filtered and the cake was rinsed with water:ethanol = 1:1 three times, and the filtrate was dried to afford a light yellow solid.
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of A1–6
One gram of intermediate 1 and 2 molar equivalents of an appropriately substituted nitrile were dissolved in 15 mL dioxane, and the mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 10 min, then 20 mL hydrochloric acid was added. The reaction continued for 6 h, and was cooled to ambient temperature, poured into ice water, and adjusted to slightly basic using ammonia. The precipitate was suction-filtered to afford the crude product. Silica gel column chromatography using 3:1 petroleum ether:ethyl acetate as eluent yielded compounds A1–6.
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2 and 3
One gram of intermediate 1 and 0.1 g of acetic anhydride were dissolved in triethoxymethane, and the reaction was refluxed for 6 h. The reaction was cooled to ambient temperature and concentrated under vacuum to give a red semi-solid. Recrystallization of the crude product using ethanol/n-hexane afforded intermediate 2. Intermediate 2 was added to hydrazine hydrate in a molar ratio of 1:1.5, and the neat reaction was refluxed overnight, and monitored by TLC until completion. TLC analysis was performed using 1:1 petroleum ether:ethyl acetate, and the retention factor of target materials are 0.4–0.6. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum, and the crude product was recrystallized using 1:1 ethanol/n-hexane to afford Intermediates 3.
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of B1–20
To a round bottom flask, 1.12 g of intermediate 3 was added, along with 6 mL anhydrous ethanol, and appropriately substituted aldehyde. The reaction was warmed to 50 °C and 2 mL acetic acid was added. The reaction was refluxed for 6 h, and then the response process was monitored by TLC analysis using 1:2 petroleum ether:ethyl acetate, and the retention factor of target compounds are 0.3–0.5. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and was filtered. The product was purified by crystallization with ethanol to afford compounds B1–20.
2-Phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A1). Yield 79%; m.p. 210–212 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.40 (d, J = C-NMR 7.8 Hz, 2H, 2’,6’-Ph-H), 7.44 (dt, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 6.0 Hz, 3H, 3’,4’,5’-Ph-H), 5.34 (s, 1H, -NH), 2.95 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.83 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.96 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.37, 158.69, 145.76, 137.40, 134.71, 131.18, 129.18, 127.05, 113.52, 25.73, 25.28, 22.57, 22.51; ESI-MS m/z: 283.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C16H14N2OS: 282.4.
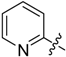
2-(Pyridin-2-yl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A2). Yield 80%; m.p. 201–203 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.82 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H, Pyridin-H), 8.50 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Pyridin-H), 7.84 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Pyridin-H), 7.43 (m, 1H, Pyridin-H), 5.85 (s, 1H, -NH), 2.98 (t, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.85 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.95 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.58, 158.08, 149.00, 148.72, 148.21, 137.61, 134.92, 132.26, 126.06, 123.40, 121.90, 25.77, 25.51, 23.11, 22.38. ESI-MS m/z: 284.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C15H13N3OS: 283.4.
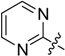
2-(Pyrimidin-2-yl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A3). Yield 82%; m.p. 220–221°C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.78 (s, 1H, -NH), 8.96 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, 4’,6’-Pyrimidin-H), 7.47 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H, 5-Pyrimidin-H), 3.09 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.84 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.95 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 167.76, 162.90, 158.24, 158.08, 156.48, 136.88, 125.73, 121.00, 116.32, 26.22, 25.78, 22.65, 22.61; ESI-MS m/z: 285.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C14H12N4OS: 284.3.
2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A4). Yield 64%; m.p. > 250 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.21 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.28 (s, 1H, -NH), 7.98 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, 2’,6’-Ph-H), 6.86 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, 3’,5’-Ph-H), 2.88 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.71 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.77 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ163.34, 158.67, 157.96, 145.73, 137.40, 130.72, 127.54, 127.33, 116.47, 114.64, 26.07, 25.69, 22.71, 22.68; ESI-MS m/z: 298.9 [M + 1]+, calculated for C16H14N2O2S: 298.3.
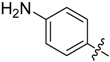
2-(4-Aminophenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A5). Yield 66%; m.p. > 250 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.03 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, 2’,6’-Ph-H), 6.82(s, 1H, -NH), 6.59 (m, 4H, 3’,5’-Ph-H + NH2), 2.88 (t, 2H, J = 6.0 Hz, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.71 (t, 2H, J = 6.0 Hz, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.80 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ166.64, 158.77, 157.96, 150.71, 131.40, 130.02, 129.17, 127.04, 125.03, 113.42, 112.84, 26.23, 25.78, 22.65, 22.61; ESI-MS m/z: 298.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C16H15N3OS: 297.4.
2-(Chloromethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (A6). Yield 79%; m.p. 234–236 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 4.51 (s, 2H, 2-CH2Cl), 2.84 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.72 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.75 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.26, 158.53, 152.16, 133.74, 131.14, 121.86, 42.86, 25.44, 24.75, 22.66, 21.94. ESI-MS m/z: 254.8 [M + 1]+, calculated for C11H11ClN2OS: 254.7.
(E)-3-(Benzylideneamino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B1). Yield 83%; m.p. 216–218 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.67 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.19 (s, 1H, 2-pyrimidin-H), 7.89 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.36 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.09 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.04 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.77 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.39, 160.58, 159.15, 156.69, 147.36, 134.57, 134.13, 132.30, 127.01, 123.49, 120.07, 119.99, 115.23, 25.87, 25.46, 23.00, 22.40. ESI-MS m/z: 310.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H15N3OS: 309.4.
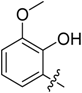
(E)-3-((2-Methoxybenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B2). Yield 80%; m.p. 169–171 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.69 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.19 (s, 1H, 2-pyrimidin-H), 8.09 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.48 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.04 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.88 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.49, 160.62, 159.65, 156.09, 144.89, 134.65, 134.03, 132.30, 127.19, 123.49, 121.39, 120.99, 111.40, 55.77, 25.87, 25.46, 23.00, 22.40; ESI-MS m/z: 340.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C18H17N3O2S: 339.4.
(E)-3-((2,3-Dimethoxybenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B3). Yield 78%; m.p. 226–228 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.66 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.19 (s, 1H, 2-pyrimidin-H), 7.68 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.14 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.07 (dd, J1 = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.94 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.91 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.06 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.31, 160.60, 156.09, 153.04, 150.47, 144.98, 134.72, 132.36, 126.85, 124.44, 123.50, 118.43, 116.12, 62.34, 56.10, 25.92, 25.48, 23.01, 22.40. ESI-MS m/z: 370.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C19H19N3O3S: 369.4.
(E)-3-((2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B4). Yield 82%; m.p. 197–199 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.43 (s, 1H, -OH), 9.42 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.13 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.05 (m, 2H, Ph-H), 6.94 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.94 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.03 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.31, 160.60, 156.09, 153.04, 150.47, 144.98, 134.72, 132.36, 126.85, 124.44, 123.50, 118.43, 116.12, 62.34, 25.92, 25.48, 23.01, 22.40. ESI-MS m/z: 356.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C18H17N3O3S: 355.4.
(E)-3-((2-Nitrobenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B5). Yield 69%; m.p. 225–227 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.17 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.24 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 8.15 (m, 2H, Ph-H), 7.77 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.71 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 3.04 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.81 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.49, 159.73, 156.43, 148.86, 145.36, 133.95, 132.55, 132.51, 132.12, 129.62, 128.83, 125.05, 123.52, 25.83, 25.48, 22.97, 22.35. ESI-MS m/z: 355.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H14N4O3S: 354.4.
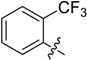
(E)-3-((2-(Trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B6). Yield 76%; m.p. 239–241°C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.17 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.24 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 8.15 (m, 2H, Ph-H), 7.77 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.71 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 3.04 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.81 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.36, 159.26, 156.51, 145.56, 135.08, 132.56, 132.29, 131.57, 131.48, 127.90, 126.18, 124.86, 123.51, 25.91, 25.47, 22.98, 22.34; ESI-MS m/z: 378.1 [M + 1]+, C18H14F3N3OS: 377.4.
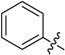
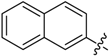
(E)-3-((Naphthalen-2-ylmethylene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B7). Yield 81%; m.p. > 250 °C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.71 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.28 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 8.15 (s, 1H, Naphthaline-H), 8.09 (dd, J1 = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H, Naphthaline-H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Naphthaline-H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Naphthaline-H), 7.60–7.53 (m, 2H, Naphthaline-H), 3.06 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.93 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.85, 160.54, 156.61, 145.43, 135.45, 134.96, 133.10, 132.27, 130.86, 129.02, 128.14, 126.99, 123.48, 122.88, 25.87, 25.47, 22.99, 22.40. ESI-MS m/z: 360.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C21H17N3OS: 359.4.
(E)-3-(((1-Methyl-1H-indol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B8). Yield 78%; m.p. 247–249 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.25 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.35 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Benzazole-H), 8.24 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.48 (s, 1H, Benzazole-H), 7.36 (dd, J1 = 4.8 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 2H, Benzazole-H), 7.31 (m, 1H, Benzazole-H), 3.82 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.87 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.44, 160.72, 156.36, 144.89, 138.23, 136.33, 134.33, 132.12, 125.39, 123.84, 123.50, 123.14, 122.27, 110.58, 109.87, 33.57, 25.87, 25.46, 23.02, 22.43; ESI-MS m/z: 363.3 [M + 1]+, calculated for C20H18N4OS: 362.4.
(E)-3-((Furan-2-ylmethylene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B9). Yield 78%; m.p. > 250 ° C. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.52 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.24 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H, Furan-H), 7.05 (m, 1H, Furan-H), 6.59 (dd, J1 = 3.6 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H, Furan-H), 3.03 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.95 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.47, 156.81, 151.58, 148.36, 146.74, 145.52, 135.10, 132.27, 123.38, 118.76, 112.64, 25.84, 25.47, 22.97, 22.38. ESI-MS m/z: 300.1 [M + 1]+, calculated for C15H13N3O2S:299.4.
3-((E)-((E)-3-(Furan-2-yl)allylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B10). Yield 81%; m.p. 218–220 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.18 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.13 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.52 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H, Furan-H), 6.94 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H, CH=CH), 6.88 (dd, J1 = 15.6 Hz, J2 = 9.0 Hz, 1H, CH=CH), 6.59 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H, Furan-H), 6.49 (dd, J1 = 3.6 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H, Furan-H), 3.03 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.51, 160.54, 156.45, 151.73, 145.10, 144.88, 134.90, 132.27, 131.82, 123.42, 122.52, 113.95, 112.56, 25.86, 25.47, 22.99, 22.40; ESI-MS m/z: 326.1 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H15N3O2S: 325.4.
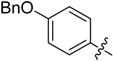
(E)-3-((4-(Benzyloxy)benzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B11). Yield 71%; m.p. > 250 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.32 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.18 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.79 (dd, J1 = 19.2 Hz, J2 = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 7.47 (m, 5H, Ph-H), 7.04 (dd, J1 = 12.6 Hz, J2 = 9.0 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 5.13 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 2H, -CH2-), 3.04 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.95 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.26, 162.32, 156.40, 146.16, 145.07, 136.38, 134.80, 130.71, 130.28, 128.84, 128.38, 127.64, 125.87, 123.45, 115.41,115.28, 70.32, 25.86, 25.47, 22.99, 22.40. ESI-MS m/z: 416.3 [M + 1]+, calculated for C24H21N3O2S: 415.5.
(E)-3-((4-(Dimethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B12). Yield 83%; m.p. 209–211 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.99 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.16 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.72 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 6.71 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 3.07 (s, 6H, N-CH3), 3.05–3.03 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.90 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.14, 160.70, 156.27, 153.33, 146.16, 144.70, 134.45, 132.18, 130.78, 123.46, 119.98, 111.64, 111.46, 40.23, 25.87, 25.48, 23.03, 22.43. ESI-MS m/z: 353.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C19H20N4OS: 352.4.
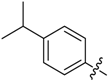
(E)-3-((4-Isopropylbenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B13). Yield 79%; m.p. 214–216 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.46 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.21 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 3.04 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.98 (td, J1 = 13.8 Hz, J2 = 7.2 Hz, 1H, CH), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.93 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.28 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 6H, CH3); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.29, 160.56, 156.49, 153.94, 145.28, 134.82, 132.25, 130.77, 128.94, 127.20, 123.46, 34.44, 25.86, 25.46, 23.86, 22.98, 22.39; ESI-MS m/z: 352.3 [M + 1]+, calculated for C20H21N3OS:351.4.
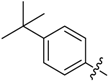
(E)-3-((4-(Tert-butyl)benzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B14). Yield 85%; m.p. 230–232 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.47 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.21 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 3.05 (m, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (m, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.94 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.36 (s, 9H, CH3); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.18, 160.02, 156.53, 156.19, 145.33, 134.85, 132.27, 130.41, 128.67, 126.07, 123.49, 112.29, 35.28, 31.28, 25.88, 25.48, 23.00, 22.40; ESI-MS m/z: 366.3 [M + 1]+, calculated for C21H23N3OS: 365.4.
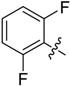
(E)-3-((2,6-Difluorobenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B15). Yield 78%; m.p. 218–220 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.96 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.23 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.78 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.22 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.13 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.94 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.39, 156.71, 155.13, 145.68, 135.28, 132.44, 123.45, 113.01, 112.85, 111.48, 25.87, 25.48, 22.97, 22.36; ESI-MS m/z: 346.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H13F2N3OS: 345.4.
(E)-3-((2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B16). Yield 76%; m.p. 226–228 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.99 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.22 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.39 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.13 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.06 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.92 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.25, 160.51, 159.29, 156.66, 145.81, 135.05, 32.88, 132.46, 129.48, 125.43, 123.53, 116.26, 116.11, 25.91, 25.46, 22.97, 22.34; ESI-MS m/z: 362.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H13ClFN3OS: 361.8.
(E)-3-((2-Bromo-6-fluorobenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B17). Yield 71%; m.p. 207–209 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.96 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.22 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.31 (m, 1H, Ph-H), 7.17 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.79 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.90 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.25, 160.51, 159.29, 156.66, 145.81, 135.05, 32.88, 132.46, 129.48, 125.43, 123.53, 116.26, 116.11, 25.91, 25.46, 22.97, 22.34; ESI-MS m/z: 406.1, 408.1 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H13BrFN3OS: 406.2.
(E)-3-((2,5-Dibromobenzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B18). Yield 75%; m.p. 199–201 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.13 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.26 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 8.25 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.51 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 7.46 (dd, J1 = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 2.4 Hz, 1H, Ph-H), 3.06 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.92 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.34, 159.81, 156.80, 145.83, 135.84, 135.25, 134.84, 134.52, 132.51, 130.88, 124.68, 123.47, 122.02, 25.94, 25.48, 22.97, 22.34; ESI-MS m/z: 468.0 [M + 1]+, calculated for C17H13Br2N3OS: 467.2.
(E)-4-(((4-Oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-3(4H)-yl)imino)methyl)phenyl acetate (B19). Yield 76%; m.p. 215–217 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.60 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.22 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.33 (s, 3H, COCH3), 1.91 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.07, 162.43, 156.67, 153.81, 145.49, 135.04, 132.30, 130.90, 130.00, 125.57,122.38, 25.88, 25.48, 22.99, 22.39, 21.32. ESI-MS m/z: 368.2 [M + 1]+, calculated for C19H17N3O3S: 367.4.
(E)-3-((4-(Allyloxy)benzylidene)amino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (B20). Yield 74%; m.p. 178–180 °C; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.32 (s, 1H, N=CH-Ph), 8.19 (s, 1H, 2-Pyrimidin-H), 7.80 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 6.99 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, Ph-H), 6.07 (m, 1H, CH2CH=CH2), 5.44 (dd, J1 = 17.4 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H, CH2CH=CH2), 5.33 (dd, J1 = 10.2 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H, CH2CH=CH2), 4.61 (m, 2H, CH2CH=CH2), 3.05 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 8-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 2.80 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, 5-Tetrahydrophenyl-H), 1.95 (m, 4H, 6,7-Tetrahydrophenyl-H); 13C-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.33, 162.18 160.63, 156.41, 145.08, 134.80, 132.71, 132.24, 130.69, 125.77, 123.47, 118.34, 115.27, 69.07, 25.87, 25.48, 23.01, 22.41. ESI-MS m/z: 365.1 [M + 1]+, calculated for C20H19N3O2S: 365.4.
3.2. Cell Viability Assay
RAW264.7 cells were plated at 5 × 103/well and cultured in complete RPMI-1640 medium containing 5% heat inactivated serum, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin, in incubator under 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 24 h. Compounds were dissolved in DMSO and diluted with 1640 medium to the desired concentrations. Cells and compound solutions were incubated for 72 h together, then 5 mg/mL fresh MTT solution was added to every hole and the cells were cultured for another 3 h in the CO2 incubator. One hundred milliliters of DMSO was used as blank control, and the optical density was recorded at 590 nm. Cell viability is usually expressed as the ratio of absorbance.
3.3. Determination of Cytokines
ELISA was prepared by adding 100 μL/well mixture, which contains 40 μL capture antibodies, 9 mL sterile water, and 1 mL coating buffer, and the plate was kept at 4 °C overnight. On the next day, the plate was washed with PBST three times, sealed for 1 h on table concentrator, and again washed with PBST three times. A mixture of 5% sample and 95% AD was added and the plate was incubated on table concentrator for 2 h. Then 40 μL detection antibody was mixed with 100 μL AD and was added to ELISA plate 100 μL/well and the ELISA plate was incubated on table concentrator for 1 h. The wells were washed with PBST three times and HRP was added at 100 μL/well, incubated on table concentrator for another 30 min. Finally, the wells were washed with PBST five times and TMP was added at 100 μL/well, kept in dark place until color changed to blue. Then, 2 M H2SO4 was added at 50 μL/well to stop the reaction and the OD value was measured at 450 nm.
3.4. Measurement of NO Levels
Ten microliters of cell supernatant was added to 96-well ELISA plate; 100 μL Griess reagent was added and mixed well; and the plate was stewed at room temperature and kept in dark place for 10 min. Absorbance at 540 nm was measured and the content of NO was calculated using the following formula:
Content of NO =
3.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time RT-PCR)
Ten microliters of 2× Real time PCT Master Mix, 1 μL template, 2 μL primer mixer, and 7 μL 0.1% DEPC water were added in 0.2 mL PCR tube. The conditions of the RT-PCR were as follows: pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, degeneration at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing 40 cycles at 60 °C for 20 s or 72 °C for 40 s. The primer sequences were as follows:
- GAPDH (149 bp)
- (Sense primer) 5′ TATGTCGTGGAGTCTACTGGT 3′
- (Anti-sense primer) 5′ GAGTTGTCATATTTCTCGTGG 3′
- COX2 (74 bp)
- (Sense primer) 5′ TGAGCAACTATTCCAAACCAGC 3′
- (Anti-sense primer) 5′ GCACGTAGTCTTCGATCACTATC 3′
- INOS (127 bp)
- (Sense primer) 5′ GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA 3′
- (Anti-sense primer) 5′ GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC 3′
3.6. Cellular NF-κB p65 Translocation Assay
The assay was performed using a cellular NF-κB p-65 translocation kit (Beyotime Biotech, Nantong, China) following the manufacturer's instructions. The red and blue fluorescence of the P65 protein and nuclei were visualized simultaneously by fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) at an excitation wavelength of 350 nm for DAPI and 540 nm for Cy3.
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
The treated cells were collected and lysed. An amount of 40 μg of the whole cell lysate was separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate−polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electro-transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Each membrane was pre-incubated for 1 h at room temperature in Tris-buffered saline, pH 7.6, containing 0.05% Tween 20 and 5% non-fat milk. The nitrocellulose membrane was incubated with specific antibodies against p-JNK, IKBα p-p38, p50, p-ERK1/2, COX-2, iNOS, or GAPDH (Santa Cruz Biotech Co. Ltd. Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Immunoreactive bands were detected by incubating with secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase and visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
3.8. Animal Study
Rats, obtained from Laboratory Animal Center of Wenzhou Medical University (Wenzhou, China), were used to study the anti-inflammatory activity of compounds. All experimental procedures and protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Wenzhou Medical University and were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Forty-eight SD male rats (weighting 150 to 190 g) were divided into 6 groups, with 8 male rats (weighting 150 to 190 g) in each group. Compounds were dissolved in 0.5% aqueous CMC solution. Groups of rats were fed for 3 days in room temperature adaptability conditions. Intragastric administration of 1 mL dose of the compounds was applied at 10 mg/kg per day for three consecutive days. Edema was induced by subcutaneous injection of 1% sterilized carrageenan saline solution in a volume of 0.1 mL/rat at the right hind paws 1 h after the last dose. Rat paw volume was measured after carrageenan injection at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 h. Measurements were repeated three times and the average was used to assess the extent of paw swelling. The inhibition rate for rat paw swelling was calculated by the following formula:
where VR represents the volume of right foot for each group at each time point, and V0 represents the volume of the right foot at 0 h.
Inhibition rate (%) = [(VR − V0)control − (VR − V0)treat]/(VR − V0)control × 100%
3.9. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). T-test was used to analyze the differences between groups of data. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Pro (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). p Values less than 0.05 (p < 0.05) were considered statistically significant. p values less than 0.01 (p < 0.01) were considered notable statistically significant. All experiments were repeated at least three times.
4. Conclusions
Twenty-six tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives were synthesized. The anti-inflammatory effects of these compounds were evaluated in a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays, including the inhibition of NO, iNOS, and COX-2 production; pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion; and mRNA expression. In an effort to elucidate the potential mechanisms of anti-inflammatory activity, we also evaluated the phosphorylation of MAPK and the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated macrophages.
The results of the present study provided evidence that treatment with A2, A6, and B7 can inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators, including NO, inflammatory cytokines, iNOS, and COX-2, in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells without cytotoxicity. These effects can be attributed to the inhibition of NF-κB activation by the degradation of IκBα and p50 and the blockade of MAPK phosphorylation. Animal experimental findings suggest that the inhibition of carrageenan-induced rat paw edema by A6 is similar to indomethacin and celecoxib. Taken together, A6 is selected as a lead compound for further optimization and mechanistic studies.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373262), Public Technology Applied Research Projects of Science and Technology Development of Zhejiang Province (2016C37010), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY16B020010), Xinmiao Talent Project of Zhejiang Province (2016R413079), and The Opening Project of Zhejiang Provincial Top Key Discipline of Pharmaceutical Sciences (201710, 201715).
Author Contributions
Faqing Ye, Yuan Zhang and Lu Luo conceived and designed the experiments; Yuan Zhang, Lu Luo, Chao Han, Handeng Lv, Kaiqi Wu, Suwei Pan, Di Chen and Guoliang Shen performed the experiments; Faqing Ye, Yuan Zhang, Lu Luo, Chao Han, Handeng Lv, Kaiqi Wu, Suwei Pan, Di Chen and Guoliang Shen analyzed the data; Faqing Ye, Yuan Zhang contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Faqing Ye, Yuan Zhang, Lu Luo, Chao Han and Handeng Lv discussed the data and wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interests.
References
- Hua, L.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Cosenza, M.; Kim, M.O.; Huang, H.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Brosnan, C.F.; Lee, S.C. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in inducible nitric oxide synthase and TNFalpha expression in human fetal astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 126, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawate, S.; Shen, Q.; Fan, F.; Bhat, N.R. Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferongamma. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 77, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Feng, H.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Yu, L.; Deng, X. Valnemulin downregulates nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and cytokine production via inhibition of NF-kappaB and MAPK activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, K.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, H.J.; Jung, H.J.; Cho, Y.W.; Yun, K.; Lee, K.T. Inhibition of LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-kappa B inactivation in RAW264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the IKK and MAPK pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.J.; Hong, S.G.; Lee, J.W.; Jeong, W.S. Red ginseng marc oil inhibits iNOS and COX-2 via NF-kappaB and p38 pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Molecules 2012, 17, 13769–13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.; Chen, D.; Xiong, Y.; Lian, M.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. 6-Gingerol protects intestinal barrier from ischemia/reperfusion-induced damage via inhibition of p38 MAPK to NF-kappaB signalling. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhou, K.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; Lin, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T. Involvement of MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling in the activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in experimental colitis by chronic vagus nerve stimulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69424. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Cao, J.; Fang, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Ran, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, D.; et al. Geniposide suppresses LPS-induced nitric oxide, PGE2 and inflammatory cytokine by downregulating NF-kappaB, MAPK and AP-1 signaling pathways in macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Chen, Z. Emodin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting activation of the p38 MAPK-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, T.F. The disintegrin, trimucrin, suppresses LPS-induced activation of phagocytes primarily through blockade of NF-kappaB and MAPK activation. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. 2016, 389, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Jimenez, F.J.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Herrero, M.T.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Agundez, J.A. An Update on the Role of Nitric Oxide in the Neurodegenerative Processes of Parkinson's Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hsu, A.; Moore, P.K. Actions and interactions of nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulphide in the cardiovascular system and in inflammation—A tale of three gases! Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, A. Nitric Oxide Synthase and Cyclooxygenase Pathways: A Complex Interplay in Cellular Signaling. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2559–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.L.; Botting, R.M.; Hla, T. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: The biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 387–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler thrombosis. Vasc. Boil. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrono, C.; Baigent, C. Low-dose aspirin, coxibs, and other NSAIDS: A clinical mosaic emerges. Mol. Interv. 2009, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoutakis, V.A.; Carter, C.A.; Mickle, T.R.; Smith, V.H.; Arkin, C.R.; Alissandratos, J.; Petty, D.E. Review of diclofenac and evaluation of its place in therapy as a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agent. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1988, 22, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hisa, T.; Arai, J.; Saito, Y.; Yamamoto, F.; Mukai, T.; Ohshima, T.; Maeda, M.; Ohkubo, Y. Isomeric methoxy analogs of nimesulide for development of brain cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-targeted imaging agents: Synthesis, in vitro COX-2-inhibitory potency, and cellular transport properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6807–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consalvi, S.; Biava, M.; Poce, G. COX inhibitors: A patent review (2011–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, A.M.; Ali, H.I.; Almalki, W.H.; Azim, M.A.; Abourehab, M.A.; Abdelazeem, A.H. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Some Novel Pyrrolizine Derivatives as COX Inhibitors with Anti-Inflammatory/Analgesic Activities and Low Ulcerogenic Liability. Molecules 2016, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogne, J.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Pratico, D. Adverse cardiovascular effects of the coxibs. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W.B.; West, C.R.; Borer, J.S.; Gorelick, P.B.; Lavange, L.; Pan, S.X.; Weiner, E.; Verburg, K.M. Risk of cardiovascular events in patients receiving celecoxib: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 99, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueggemann, L.I.; Mackie, A.R.; Mani, B.K.; Cribbs, L.L.; Byron, K.L. Differential Effects of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors on Vascular Smooth Muscle Ion Channels May Account for Differences in Cardiovascular Risk Profiles. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 76, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, G.A. Cardiovascular pharmacology of nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and coxibs: Clinical considerations. Am J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 26d–32d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Wittes, J.; McMurray, J.; Co, A.S.C.S. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.A. The coxibs and traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A current perspective on cardiovascular risks. Can. J. Cardiol. 2007, 23, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Fu, W.; Xie, Z.; Ye, F. Synthesis and Evaluation of Biological and Antitumor Activities of Tetrahydrobenzothieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine Derivatives as Novel Inhibitors of FGFR1. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarsamy, V.; Meena, S.; Ramseshu, K.V.; Solomon, V.R.; Thirumurugan, K.; Dhanabal, K.; Murugan, M. Synthesis, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenic index and antibacterial activities of novel 2-methylthio-3-substituted-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo (b) thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, H.N.; El-Gazzar, A.R.; Nawwar, G.A. Synthesis, biological and medicinal significance of S-glycosido-thieno[2,3-d]-pyrimidines as new anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Peng, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Tong, L.; Qu, R.; Jiang, H.; Ding, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 6-alkenylamides substituted of 4-anilinothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines as irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.E.; Abdel Gawad, N.M.; George, R.F.; Akar, Y.A. Synthesis, antitumor and antibacterial activities of some novel tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozorov, K.; Zhao, J.Y.; Elmuradov, B.; Pataer, A.; Aisa, H.A. Recent developments regarding the use of thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one derivatives in medicinal chemistry, with a focus on their synthesis and anticancer properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 552–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeel, M.M.; Refaat, H.M.; Kassab, A.E.; Shahin, I.G.; Abdelghany, T.M. Synthesis, anticancer activity and effects on cell cycle profile and apoptosis of novel thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine and thieno[3,2-e]triazolo[4,3-c]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrova, A.; Wesselinova, D.; Tsenov, J.A.; Lubenov, L.A. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of some new thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-ones containing 1,2,4-triazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangjee, A.; Li, W.; Kisliuk, R.L.; Cody, V.; Pace, J.; Piraino, J.; Makin, J. Design, synthesis, and X-ray crystal structure of classical and nonclassical 2-amino-4-oxo-5-substituted-6-ethylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines as dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors and as potential antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4892–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Coumar, M.S.; Chu, C.Y.; Lin, W.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Chen, C.T.; Shiao, H.Y.; Rafi, S.; Wang, S.Y.; Hsu, H.; et al. Design and synthesis of tetrahydropyridothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold based epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors: The role of side chain chirality and Michael acceptor group for maximal potency. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7316–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewal, M.B.; Wani, A.S.; Vidaillac, C.; Oupicky, D.; Rybak, M.J.; Firestine, S.M. Thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidinedione derivatives as antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 51, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaoka, T.; Chung, S.; Caboni, P.; Rausch, J.W.; Wilson, J.A.; Taskent-Sezgin, H.; Beutler, J.A.; Tocco, G.; Le Grice, S.F. Exploiting drug–resistant enzymes as tools to identify thienopyrimidinone inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, H.N.; Hussein, H.A.; El-Gazzar, A.R. Synthesis of substituted thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dithiones and their S-glycoside analogues as potential antiviral and antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashad, A.E.; Ali, M.A. Synthesis and antiviral screening of some thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleosides. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2006, 25, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.F.; Peng, L.; Zhang, G.C.; Lan, X.B.; Li, C.F.; Chen, F.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Lin, Z.X.; Chen, L.; Dai, R.K.; et al. The highly potent and selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors bearing a thienopyrimidine scaffold effectively treat type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Yoshida, M.; Emoto, H.; Ishii, H.; Koga, K.; Tanaka, M. Effects of acute and chronic administration of MCI-225, a new selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor with 5-HT3 receptor blocking action, on extracellular noradrenaline levels in the hypothalamus of stressed rats. Jpn. J. Pharm. 2000, 83, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaiah, Y.; Harikrishna, N.; Nagaraju, K.; Venkata Rao, C. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of 1,3,4-oxadiazole tagged thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 58, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommes, D.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; van Deventer, S.J.H. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signal transduction pathways and novel anti-inflammatory targets. Gut 2003, 52, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).