Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Albendazole for Enhancing Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity against U-87 MG Glioma Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of SLNs
3.3. Evaluation of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
3.4. Zeta Potential
3.5. Morphological Characterization
3.6. Entrapment Efficiency of ASLNs
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release
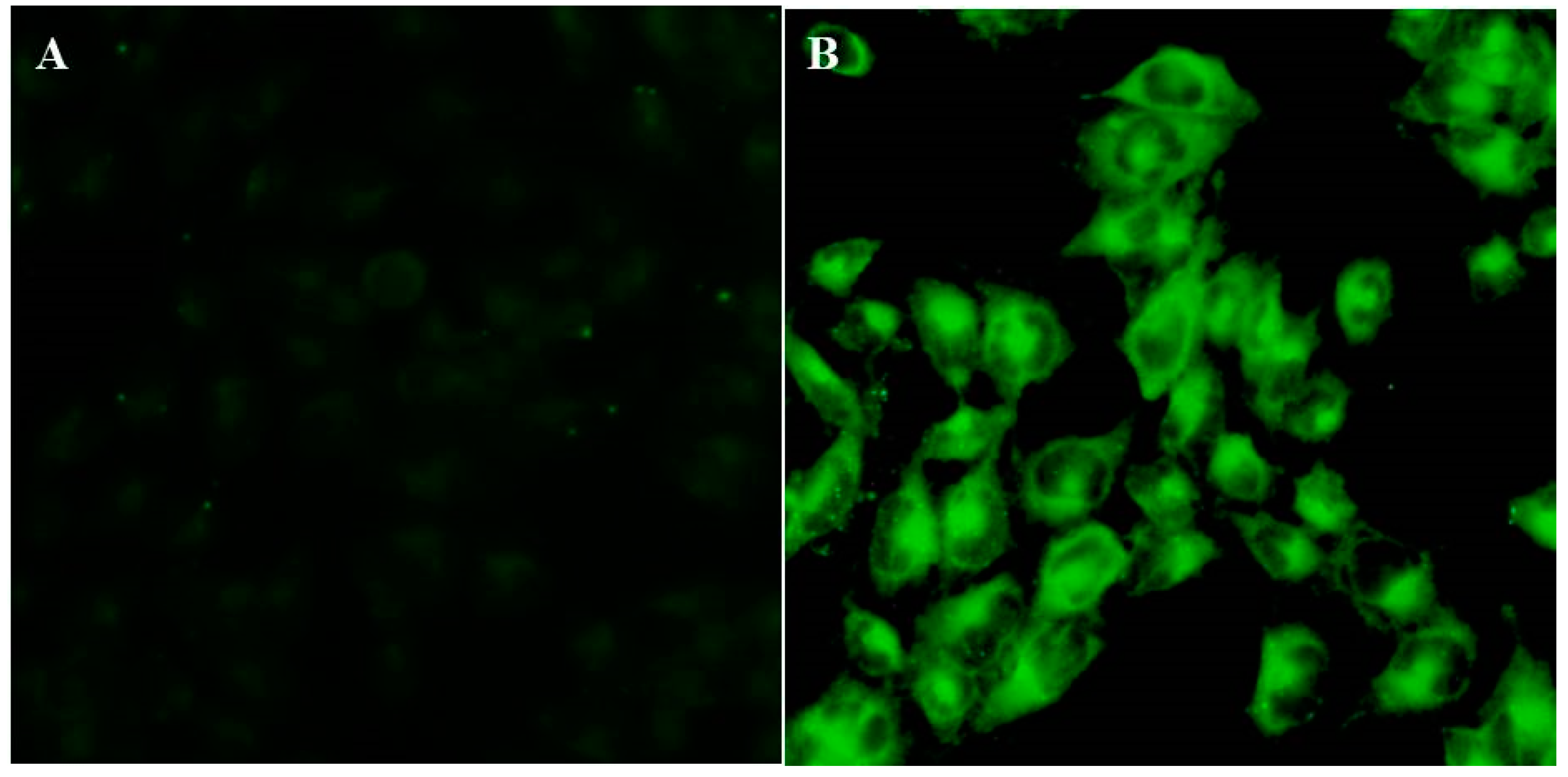
3.8. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
3.9. Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticles
3.10. Statistical Analyses of Data
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, M.C.; Marchetti, J.M. Development of albendazole sulfoxide-loaded eudragit microparticles: A potential strategy to improve the drug bioavailability. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholami, M.H.; Akhter, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Morris, D.L. Antitumor activity of albendazole against the human colorectal cancer cell line ht-29: In vitro and in a xenograft model of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 55, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourgholami, M.H.; Cai, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Badar, S.; Links, M.; Morris, D.L. Inhibition of cell proliferation, vascular endothelial growth factor and tumor growth by albendazole. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Gao, X.; Pei, D.; Gao, C. Anthelmintic drug albendazole arrests human gastric cancer cells at the mitotic phase and induces apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Sinniah, B.; Krishnan, U. Albendazole, an effective single dose, broad spectrum anthelmintic drug. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1983, 32, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, T.; Plakogiannis, F.M. Development and oral bioavailability assessment of a supersaturated self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (smedds) of albendazole. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, A.J.; Llabot, J.M.; Sanchez Bruni, S.; Allemandi, D.; Palma, S.D. Self-dispersible nanocrystals of albendazole produced by high pressure homogenization and spray-drying. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.-S.; Lee, S.-E.; Ng, C.L.; Cho, C.-W.; Park, J.-S. Determination of preparation parameters for albendazole-loaded nanoparticles using chitosan and tripolyphosphate. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensel, P.E.; Gamboa, G.U.; Fabbri, J.; Ceballos, L.; Bruni, S.S.; Alvarez, L.I.; Allemandi, D.; Benoit, J.P.; Palma, S.D.; Elissondo, M.C. Cystic echinococcosis therapy: Albendazole-loaded lipid nanocapsules enhance the oral bioavailability and efficacy in experimentally infected mice. Acta Trop. 2015, 152, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjali, K.; Ujwala, S.; Bharkad, G.P.; Kavita, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles of albendazole for treatment of Toxocara canis infection: In-vivo efficacy studies. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.-Asia 2017, 7, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.S.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, T.H.; Jang, W.S.; Tunsirikongkon, A.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Enhancing the in vitro anticancer activity of albendazole incorporated into chitosan-coated plga nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M. Cancer nanotechnology: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marslin, G.; Revina, A.M.; Khandelwal, V.K.M.; Balakumar, K.; Prakash, J.; Franklin, G.; Sheeba, C.J. Delivery as nanoparticles reduces imatinib mesylate-induced cardiotoxicity and improves anticancer activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Patel, N.; Shah, M.K.; Khatri, P.; Vora, N. Recent advances in lipid-based vesicles and particulate carriers for topical and transdermal application. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rajala, A.; Rajala, R.V. Lipid nanoparticles for ocular gene delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, G.N.; Wong, M.Y.; Ling, L.U.; Shaikh, I.M.; Tan, K.B.; Chaudhury, A.; Tan, B.J. Lipid-based nanoparticulate systems for the delivery of anti-cancer drug cocktails: Implications on pharmacokinetics and drug toxicities. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, P.K.; Mishra, S.; Bajpai, M.; Mishra, A. Enhanced oral bioavailability of efavirenz by solid lipid nanoparticles: In vitro drug release and pharmacokinetics studies. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 363404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, S.; Raghavan, C.V.; Marslin, G.; Rahman, H.; Selvaraj, D.; Balakumar, K.; Franklin, G. Quillaja saponin: A prospective emulsifier for the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.K.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Preparation, in vitro evaluation and statistical optimization of carvedilol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for lymphatic absorption via oral administration. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: Structure. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, T. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of anticancer agents to tumor angiogenic vessels. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanam, V.; Marslin, G.; Krishnamoorthy, B.; Chellan, V.; Siram, K.; Natarajan, T.; Bhaskar, B.; Franklin, G. Poly (varepsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles of carboplatin: Preparation, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation in u-87 mg cell lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banna, G.L.; Collova, E.; Gebbia, V.; Lipari, H.; Giuffrida, P.; Cavallaro, S.; Condorelli, R.; Buscarino, C.; Tralongo, P.; Ferrau, F. Anticancer oral therapy: Emerging related issues. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010, 36, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Wang, A.; Chu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mu, H.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, Y. Intranasal delivery of rotigotine to the brain with lactoferrin-modified peg-plga nanoparticles for parkinson’s disease treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6547–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, P.; Pandey, B.; Lakhera, P.C.; Singh, K.P. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro release study of albendazole-encapsulated nanosize liposomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, A.R.; Scott, M.J.; Kennedy, N.I.; Jones, M.N. Effect of grafted polyethylene glycol (peg) on the size, encapsulation efficiency and permeability of vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2000, 1463, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwunze, M.O.; McEwan, D. The characterization of the sol-gel encapsulated curcumin as a possible sensor for small biologically important molecules. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 53, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garanti, T.; Stasik, A.; Burrow, A.J.; Alhnan, M.A.; Wan, K.-W. Anti-glioma activity and the mechanism of cellular uptake of asiatic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 500, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi, N.; Dobakhti, F.; Haniloo, A. Albendazole and praziquantel chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro release study. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Sample of the compound is not available from the authors. |






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marslin, G.; Siram, K.; Liu, X.; Khandelwal, V.K.M.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Franklin, G. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Albendazole for Enhancing Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity against U-87 MG Glioma Cell Lines. Molecules 2017, 22, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112040
Marslin G, Siram K, Liu X, Khandelwal VKM, Shen X, Wang X, Franklin G. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Albendazole for Enhancing Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity against U-87 MG Glioma Cell Lines. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112040
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarslin, Gregory, Karthik Siram, Xiang Liu, Vinoth Kumar Megraj Khandelwal, Xiaolei Shen, Xiang Wang, and Gregory Franklin. 2017. "Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Albendazole for Enhancing Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity against U-87 MG Glioma Cell Lines" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112040
APA StyleMarslin, G., Siram, K., Liu, X., Khandelwal, V. K. M., Shen, X., Wang, X., & Franklin, G. (2017). Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Albendazole for Enhancing Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity against U-87 MG Glioma Cell Lines. Molecules, 22(11), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112040




