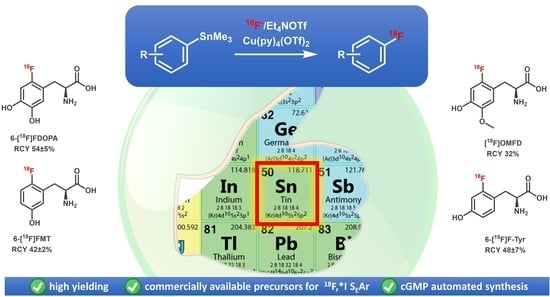
A Practical Method for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Aromatic Amino Acids from Nucleophilic [18F]Fluoride and Stannyl Precursors for Electrophilic Radiohalogenation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zarrad, F.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Krapf, P.; Zischler, J.; Neumaier, B. A Practical Method for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Aromatic Amino Acids from Nucleophilic [18F]Fluoride and Stannyl Precursors for Electrophilic Radiohalogenation. Molecules 2017, 22, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122231
Zarrad F, Zlatopolskiy BD, Krapf P, Zischler J, Neumaier B. A Practical Method for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Aromatic Amino Acids from Nucleophilic [18F]Fluoride and Stannyl Precursors for Electrophilic Radiohalogenation. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122231
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarrad, Fadi, Boris D. Zlatopolskiy, Philipp Krapf, Johannes Zischler, and Bernd Neumaier. 2017. "A Practical Method for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Aromatic Amino Acids from Nucleophilic [18F]Fluoride and Stannyl Precursors for Electrophilic Radiohalogenation" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122231
APA StyleZarrad, F., Zlatopolskiy, B. D., Krapf, P., Zischler, J., & Neumaier, B. (2017). A Practical Method for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Aromatic Amino Acids from Nucleophilic [18F]Fluoride and Stannyl Precursors for Electrophilic Radiohalogenation. Molecules, 22(12), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122231