Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance
Abstract
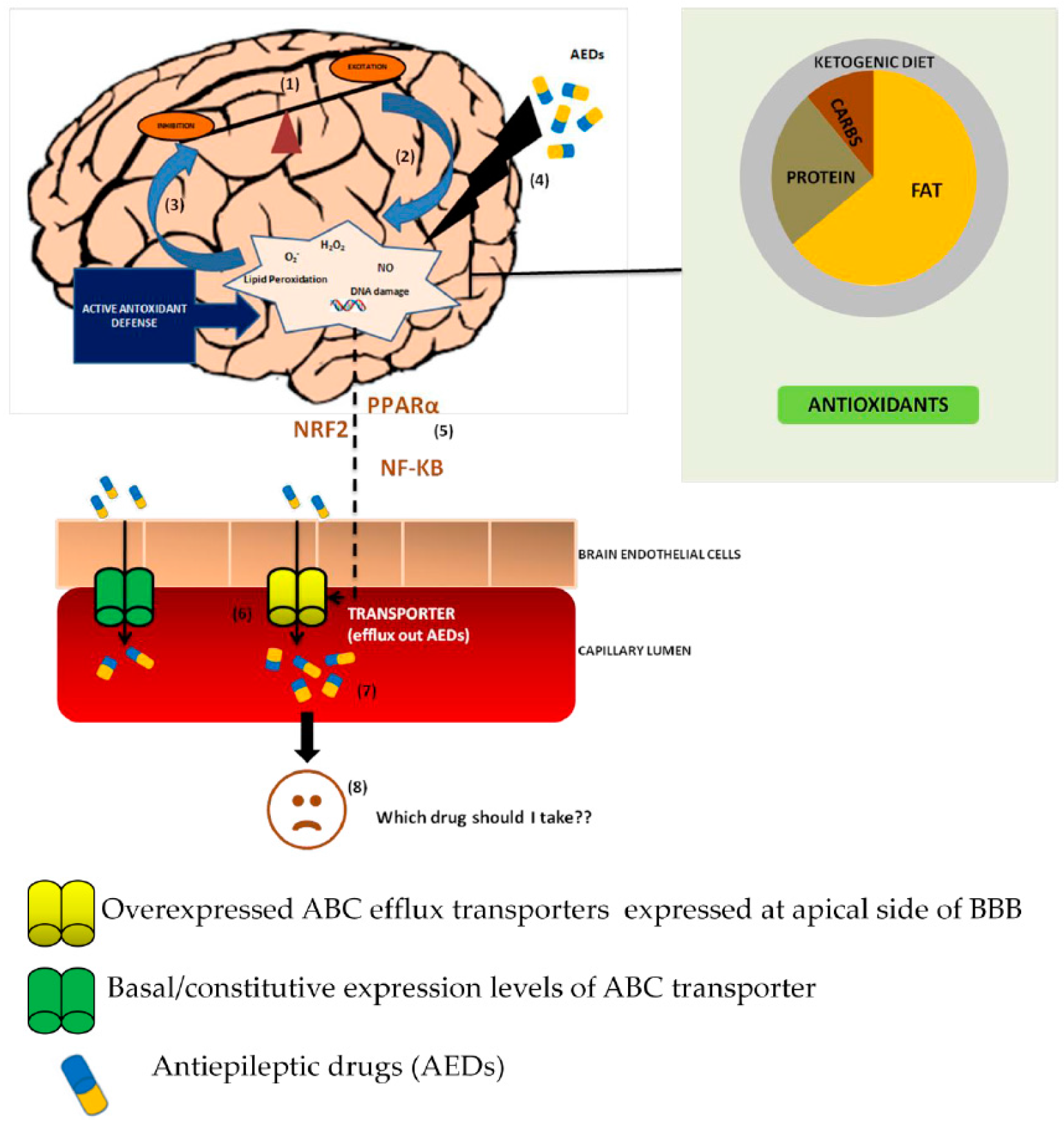
:1. Introduction
2. Contribution of Epilepsy to Oxidative Stress
2.1. Patient-Study
2.2. In Vivo Studies
3. Antiepileptic Drugs and Oxidative Stress
3.1. In Vivo Studies
3.2. In Vitro Studies
4. Oxidative Stress Regulates ABC Transporters
5. Role of Ketogenic Diet and Antioxidants in Pharmacoresistance
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, J.; Pickard, N.; Whitfield, A.; Hakin, N. A population-based study of the prevalence, clinical characteristics and effect of ethnicity in epilepsy. Seizure 2000, 9, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Johnson, M.R. Intrinsic Severity as a Determinant of Antiepileptic Drug Refractoriness. Epilepsy Curr. 2008, 8, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, S.; Beck, H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pharmacoresistance in epilepsy. Brain 2006, 129, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.M. Mechanisms of antiepileptic drug resistance. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2003, 16, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loscher, W.; Potschka, H. Drug resistance in brain diseases and the role of drug efflux transporters. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Potschka, H. Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 22–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareš, J.; Stopka, P.; Nohejlová, K.; Rokyta, R. Oxidative stress induced by epileptic seizure and its attenuation by melatonin. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62 (Suppl. 1), S67–S74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Menon, B.; Ramalingam, K.; Kumar, R.V. Oxidative stress in patients with epilepsy is independent of antiepileptic drugs. Seizure 2012, 21, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.; González, M.E.; Lorigados, L.; Morales, L.; Riverón, G.; Bauzá, J.Y. Oxidative stress markers in surgically treated patients with refractory epilepsy. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumià, J.; Marmol, F.; Sanchez, J.; Giménez-Crouseilles, J.; Carreño, M.; Bargalló, N.; Boget, T.; Pintor, L.; Setoain, X.; Donaire, A. Oxidative stress markers in the neocortex of drug-resistant epilepsy patients submitted to epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 107, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, A.J.; Baudry, M. Oxygen free radicals in rat limbic structures after kainate-induced seizures. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.P.; Ho, Y.S.; Patel, M. Mitochondrial superoxide production in kainate-induced hippocampal damage. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Li, Q.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Crapo, J.; Liang, L.P. Activation of NADPH oxidase and extracellular superoxide production in seizure-induced hippocampal damage. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantseva, M.V.; Perez Velazquez, J.L.; Tsoraklidis, G.; Mendonca, A.J.; Adamchik, Y.; Mills, L.R.; Carlen, P.L.; Burnham, M.W. Oxidative stress is involved in seizure-induced neurodegeneration in the kindling model of epilepsy. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.M.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Souza, F.C.F.; Viana, G.S.B.; Fonteles, M.M.F. Oxidative stress in the hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in Wistar rats. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, D.F.; Camara, A.K.S. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in excitable cells: Modulators of mitochondrial and cell function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 1373–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, W.S.; Kudin, A.P.; Vielhaber, S.; Blumcke, I.; Zuschratter, W.; Schramm, J.; Beck, H.; Elger, C.E. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in the epileptic focus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoffner, J.M.; Lott, M.T.; Lezza, A.M.; Seibel, P.; Ballinger, S.W.; Wallace, D.C. Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fiber disease (MERRF) is associated with a mitochondrial DNA tRNA(Lys) mutation. Cell 1990, 61, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.P.; Waldbaum, S.; Rowley, S.; Huang, T.T.; Day, B.J.; Patel, M. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and epilepsy in SOD2 deficient mice: Attenuation by a lipophilic metalloporphyrin. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmore, L.J.; Triggs, W.J. Effect of phenytoin and corticosteroids on seizures and lipid peroxidation in experimental posttraumatic epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 60, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahle, C.; Dasgupta, A. Decreased total antioxidant capacity and elevated lipid hydroperoxide concentrations in sera of epileptic patients receiving phenytoin. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Wu, H.M.; Kao, S.H.; Wei, Y.H. Phenytoin-mediated oxidative stress in serum of female epileptics: A possible pathogenesis in the fetal hydantoin syndrome. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1997, 16, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeta, K.H.; Mehla, J.; Gupta, Y.K. Curcumin is protective against phenytoin-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rats. Brain Res. 2009, 1301, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Zlabek, V.; Velisek, J.; Grabic, R.; Machova, J.; Randak, T. Modulation of antioxidant defence system in brain of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after chronic carbamazepine treatment. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, A.; Cengiz, M.; Seven, M.; Ulutin, T. Changes in the Antioxidant System in Epileptic Children Receiving Antiepileptic Drugs: Two-Year and superoxide dismutase activities decreased in patients receiving. J. Child Neurol. 2001, 16, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michoulas, A.; Tong, V.; Teng, X.W.; Chang, T.K.; Abbott, F.S.; Farrell, K. Oxidative stress in children receiving valproic acid. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, S.A.; Abdellah, M.M. Trace elements and electrolytes homeostasis and their relation to antioxidant enzyme activity in brain hyperexcitability of epileptic patients. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 96, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ren, R.N.; Chen, X.M.; Ye, L.Y. An experimental study on hepatotoxicity of topiramate in young rats. Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2007, 9, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kubera, M.; Budziszewska, B.; Jaworska-Feil, L.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Leskiewicz, M.; Tetich, M.; Maes, M.; Kenis, G.; Marciniak, A.; Czuczwar, S.J.; et al. Effect of topiramate on the kainate-induced status epilepticus, lipid peroxidation and immunoreactivity of rats. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.A.; Almeida, J.P.C.; Freitas, R.M.; Nascimento, V.S.; Aguiar, L.M.; Júnior, H.V.; Fonseca, F.N.; Viana, G.S.; Sousa, F.C.; Fonteles, M.M.; et al. Effects of levetiracetam in lipid peroxidation level, nitrite-nitrate formation and antioxidant enzymatic activity in mice brain after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 27, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Hiramatsu, M.; Willmore, L.J. Zonisamide reduces the increase in 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine levels formed during iron-induced epileptogenesis in the brains of rats. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.A.G.; Medina, W.S.G.; Martins, N.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.C.; Curti, C.; Santos, A.C. Involvement of oxidative stress in the hepatotoxicity induced by aromatic antiepileptic drugs. Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, A.; Cardile, V. An In Vitro Study of New Antiepileptic Drugs and Astrocytes. Epilepsia 2003, 44 (Suppl. 10), 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.D.A.; Linhares, M.I.; Chaves Filho, A.J.M.; Rios, E.R.V.; Lima, C.N.D.C.; Venancio, E.T.; de Souza, A.G.; de Lima, K.A.; de Sousa, F.C.F.; Gaspar, D.M.; et al. Antioxidant properties of antiepileptic drugs levetiracetam and clonazepam in mice brain after in vitro-induced oxidative stress. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 10, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Stettner, M.; Dehmel, T.; Mausberg, A.K.; Köhne, A.; Rose, C.R.; Kieseier, B.C. Levetiracetam exhibits protective properties on rat Schwann cells in vitro. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2011, 16, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanuma, M.; Miyazaki, I.; Diaz-Corrales, F.J.; Kimoto, N.; Kikkawa, Y.; Takeshima, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Murata, M. Neuroprotective effects of zonisamide target astrocyte. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziroǧlu, M.; Yürekli, V.A. Effects of antiepileptic drugs on antioxidant and oxidant molecular pathways: Focus on trace elements. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 33, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishler, D.M.; Weinberg, K.I.; Hinton, D.R.; Barbaro, N.; Annett, G.M.; Raffel, C. MDR1 gene expression in brain of patients with medically intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 1995, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ong, W.Y.; Lee, T. Induction of P-glycoprotein expression in astrocytes following intracerebroventricular kainate injections. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 126, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.M.; Heffernan, J.; Squier, M.V. Over-expression of P-glycoprotein in malformations of cortical development. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 3437–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.M.; Lin, W.R.; Squier, M.V.; Thom, M. Multidrug-resistance protein 1 in focal cortical dysplasia. Lancet 2001, 357, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, U.; Potschka, H.; Löscher, W. Lack of effects of prolonged treatment with phenobarbital or phenytoin on the expression of P-glycoprotein in various rat brain regions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 451, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, S.M.; Desai, S.Y.; Marroni, M.; Cucullo, L.; Goodrich, K.; Bingaman, W.; Mayberg, M.R.; Bengez, L.; Janigro, D. Overexpression of multiple drug resistance genes in endothelial cells from patients with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potschka, H.; Volk, H.; Löscher, W. Pharmacoresistance and expression of multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein in kindled rats. Neuroreport 2004, 15, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, K.; Gastens, A.M.; Volk, H.A.; Löscher, W. Expression of the multidrug transporter MRP2 in the blood-brain barrier after pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 69, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, E.A.; Redeker, S.; Aronica, E.; Edelbroek, P.M.; Gorter, J.A. Expression of multidrug transporters MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP shortly after status epilepticus, during the latent period, and in chronic epileptic rats. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronica, E.; Gorter, J.A.; Redeker, S.; Van Vliet, E.A.; Ramkema, M.; Scheffer, G.L.; Scheper, R.J.; van der Valk, P.; Leenstra, S.; Baayen, J.C.; et al. Localization of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) in microvessel endothelium of human control and epileptic brain. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D.; Löscher, W. Drug resistance in epilepsy: Putative neurobiologic and clinical mechanisms. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Ishihara, H.; Langmann, T.; Schmitz, G.; Stieger, B.; Wieser, H.G.; Yonekawa, Y.; Frei, K. Distribution and functional activity of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated proteins in human brain microvascular endothelial cells in hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 68, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Kwan, P.; Zuo, Z.; Baum, L. The transport of antiepileptic drugs by P-glycoprotein. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J. Interaction of Antiepileptic Drugs with Human P-Glycoprotein in Vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, J.; Cho, Y.-J.; Heo, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, B.I.; et al. A nonsynonymous variation in MRP2/ABCC2 is associated with neurological adverse drug reactions of carbamazepine in patients with epilepsy. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2010, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potschka, H.; Fedrowitz, M.; Löscher, W. P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein are involved in the regulation of extracellular levels of the major antiepileptic drug carbamazepine in the brain. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3557–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sills, G.J.; Kwan, P.; Butler, E.; de Lange, E.C.M.; van der Berg, D.J.; Brodie, M.J. P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of antiepileptic drugs: Preliminary studies in mdr1a knockout mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2002, 3, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambeck, B.; Jürgens, U.H.; May, T.W.; Wolfgang Pannek, H.; Behne, F.; Ebner, A.; Behne, F.; Ebner, A.; Gorji, A.; Straub, H.; Speckmann, E.J.; Pohlmann-Eden, B.; et al. Comparison of brain extracellular fluid, brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, and serum concentrations of antiepileptic drugs measured intraoperatively in patients with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, C.L.; Mealey, K.L. Assessment of antiepileptic drugs as substrates for canine P-glycoprotein. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 68, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Luna-Tortós, C.; Römermann, K.; Fedrowitz, M. Do ATP-binding cassette transporters cause pharmacoresistance in epilepsy? Problems and approaches in determining which antiepileptic drugs are affected. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2808–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radisch, S.; Dickens, D.; Lang, T.; Bonnett, L.; Arlanov, R.; Johnson, M.R.; Schwab, M.; Marson, A.G.; Pirmohamed, M. A comprehensive functional and clinical analysis of ABCC2 and its impact on treatment response to carbamazepine. Pharmacogenom. J. 2014, 14, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Tortós, C.; Fedrowitz, M.; Löscher, W. Evaluation of transport of common antiepileptic drugs by human multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRP1, 2 and 5) that are overexpressed in pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, A.; Pirmohamed, M.; Tettey, J.N.; Morgan, P.; Chadwick, D.; Kevin Park, B. Carbamazepine is not a substrate for P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerveny, L.; Pavek, P.; Malakova, J.; Staud, F.; Fendrich, Z. Lack of interactions between breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) and selected antiepileptic agents. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zuo, Z.; Kwan, P.; Baum, L. In vitro transport profile of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine acetate, and their active metabolites by human P-glycoprotein. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrend, L.; Henderson, G.; Zwacka, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Signalling Molecular Mechanisms of Signalling transformation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Q.; Yu, N.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.D. Nuclear factor-kappa B activity regulates brain expression of P-glycoprotein in the kainic acid-induced seizure rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 670613. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, J.M.; Dieter, M.Z.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Slitt, A.L.; Guo, G.; Tanaka, Y.; Scheffer, G.L.; Chan, J.Y.; Manautou, J.E.; Chen, Y.; et al. Oxidative and electrophilic stress induces multidrug resistance-associated protein transporters via the nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2 transcriptional pathway. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Campos, C.R.; Peart, J.C.; Smith, L.K.; Boni, J.L.; Cannon, R.E.; Miller, D.S. Nrf2 Upregulates ATP Binding Cassette Transporter Expression and Activity at the Blood-Brain and Blood-Spinal Cord Barriers. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8585–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronaldson, P.T.; Bendayan, R. HIV-1 viral envelope glycoprotein gp120 produces oxidative stress and regulates the functional expression of multidrug resistance protein-1 (Mrp1) in glial cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B.; Block, M.L.; Hong, J.-S.; Miller, D.S. Diesel exhaust particles induce oxidative stress, proinflammatory signaling, and P-glycoprotein up-regulation at the blood-brain barrier. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Hyperammonemia enhances the function and expression of P-glycoprotein and Mrp2 at the blood-brain barrier through NF-κB. J. Neurochem. 2015, 131, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Sun, B.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, C.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shu, N.; Zhao, K. Acute liver failure impairs function and expression of breast cancer-resistant protein (BCRP) at rat blood-brain barrier partly via ammonia-ROS-ERK1/2 activation. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebacher, N.A.; Richardson, D.R.; Jansson, P.J. Glucose modulation induces reactive oxygen species and increases P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance to chemotherapeutics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2557–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Shen, G.; Yerramilli, U.R.; Lin, W.; Xu, C.; Nair, S.; Kong, A.N.T. In vivo pharmacokinetics, activation of MAPK signaling and induction of phase II/III drug metabolizing enzymes/transporters by cancer chemopreventive compound BHA in the mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorter, J.A.; Potschka, H. Limbic seizures induce P-glycoprotein in rodent brain: Functional implications for pharmacoresistance. J. Neurosci. 2012, 22, 5833–5839. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Pekcec, A.; Toellner, K.; Miller, D.S.; Potschka, H. Seizure-induced up-regulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier through glutamate and cyclooxygenase-2 signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, V.; Teng, S.; Piquette-Miller, M. Regulation of drug transporters during infection and inflammation. Mol. Interv. 2007, 7, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wedel-Parlow, M.; Wölte, P.; Galla, H.J. Regulation of major efflux transporters under inflammatory conditions at the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-S.; Lin, K.-L. Ketogenic diet: An early option for epilepsy treatment, instead of a last choice only. Biomed. J. 2013, 36, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bough, K.J.; Rho, J.M. Anticonvulsant mechanisms of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalouf, M.; Rho, J.M.; Mattson, M.P. The neuroprotective properties of calorie restriction, the ketogenic diet, and ketone bodies. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 59, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasior, M.; Rogawski, M.A.; Hartman, A.L. Neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects of the ketogenic diet. Behav. Pharmacol. 2006, 17, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, E.G.; Chaffe, H.; Schwartz, R.H.; Lawson, M.S.; Edwards, N.; Fitzsimmons, G.; Whitney, A.; Cross, J.H. The ketogenic diet for the treatment of childhood epilepsy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Rho, J.M. The ketogenic diet as a treatment paradigm for diverse neurological disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Cunnane, S.C. Breath acetone is a reliable indicator of ketosis in adults consuming ketogenic meals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turkdogan, D.; Toplan, S.; Karakoc, Y. Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidative Enzyme Activities in Childhood Epilepsy. J. Child Neurol. 2002, 17, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi, M.R.; Shams, S.; Nouri, M.; Mohseni, M.; Shabanian, R.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Chegini, N.; Khodadad, A.; Safaralizadeh, R. A probable causative factor for an old problem: Selenium and glutathione peroxidase appear to play important roles in epilepsy pathogenesis. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudha, K.; Rao, A.V.; Rao, A. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in epilepsy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 303, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael-Titus, A.T.; Priestley, J.V. Omega-3 fatty acids and traumatic neurological injury: From neuroprotection to neuroplasticity? Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, N.; Vallée, L.; Lecointe, C.; Bouchaert, E.; Staels, B.; Bordet, R.; Auvin, S. Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α agonist, exerts anticonvulsive properties. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 94394–94398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.M.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Dieter, M.Z.; Tanaka, Y.; Peters, J.M.; Manautou, J.E.; Klaassen, C. Nrf2- and PPARα-mediated regulation of hepatic Mrp transporters after exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorodecanoic acid. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, T.; Wolters, H.; Bloks, V.W.; Havinga, R.; Jansen, P.L.M.; Staels, B.; Kuipers, F. Induction of hepatic ABC transporter expression is part of the PPARα-mediated fasting response in the mouse. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaeri, S.; Emamghoreishi, M. Acute and chronic effects of N-acetylcysteine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizure and neuromuscular coordination in mice. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 40, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DU, P.; Tang, H.-Y.; Li, X.; Lin, H.-J.; Peng, W.-F.; Ma, Y.; Fan, W.; Wang, X. Anticonvulsive and antioxidant effects of curcumin on pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 1975–1979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yokozawa, T.; Satoh, A.; Cho, E.J. Ginsenoside-Rd attenuates oxidative damage related to aging in senescence-accelerated mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M. Altered CYP expression and function in response to dietary factors: Potential roles in disease pathogenesis. Curr. Drug Metab. 2006, 7, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.Y.L.; Chui, W.K.; Chan, A. Drug interactions between chemotherapeutic regimens and antiepileptics. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 1385–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.C.; Lin, S.P.; Hou, Y.C. A new herb-drug interaction of Polygonum cuspidatum, a resveratrol-rich nutraceutical, with carbamazepine in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grewal, G.K.; Kukal, S.; Kanojia, N.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S.; Kukreti, R. Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance. Molecules 2017, 22, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365
Grewal GK, Kukal S, Kanojia N, Saso L, Kukreti S, Kukreti R. Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrewal, Gurpreet Kaur, Samiksha Kukal, Neha Kanojia, Luciano Saso, Shrikant Kukreti, and Ritushree Kukreti. 2017. "Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance" Molecules 22, no. 3: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365
APA StyleGrewal, G. K., Kukal, S., Kanojia, N., Saso, L., Kukreti, S., & Kukreti, R. (2017). Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance. Molecules, 22(3), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365






