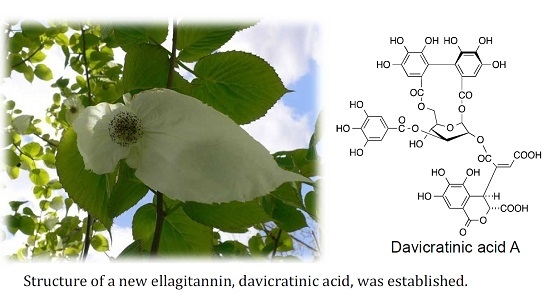
Ellagitannins of Davidia involucrata. I. Structure of Davicratinic Acid A and Effects of Davidia Tannins on Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Elucidation of the Structure of the New Ellagitannin
2.2. Biological Effects of Davidia Tannins
2.2.1. Antibacterial Effects
2.2.2. Cytotoxic Effects
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Materials
3.3. Isolation of Davicratinic Acid A (5)
3.4. Antibacterial Assay
3.5. Assay for Cytotoxic Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melchior, H.E.; Werdermann, E. A. Engler’s Syllabus der Pflanzenfamilien, 12th ed.; Grbrüder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 1964; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.J.; Ouyang, M.A.; Wang, S.B. Two new phenolic water-soluble constituents from branch bark of Davidia involucrata. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.W.; Ouyang, M.A.; Gao, B. Three new ring-A modified ursane triterpenes from Davidia involucrata. Molecules 2014, 19, 4897–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.W.; Ouyang, M.A.; Chen, Q.J.; Wu, Z.J. Five new taraxerene-type triterpenes from the branch barks of Davidia involucrata. Molecules 2014, 19, 17619–17631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, E.A.; Gupta, R.K.; Haslam, E. The metabolism of gallic acid and hexahydroxydiphenic acid in plants 3. Esters of (R)-hexahydroxydiphenic and (S)-hexahydroxydiphenic acid and dehydrohexahydroxydiphenic acid with d-glucopyranose (1C4 and related conformations). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1982, 11, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T. Systematics and health effects of chemically distinct tannins in medicinal plants. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2012–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H. Ellagitannins renewed the concept of tannins. In Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins; Quideu, S., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2009; Chapter 1; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirohama, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H.; Saitoh, H.; Nakao, Y.; Kawada, M.; Khalid, K.; Koshino, H.; et al. Inhibition of protein SUMOylation by davidiin, an ellagitannin from Davidia involucrata. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, K.; Shiota, S.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroda, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Antimicrobial activity of oleanolic acid from Salvia officinalis and related compounds on vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, T.; Kusuda, M.; Inada, K.; Ogawa, T.O.; Shiota, S.; Tsuchiya, T.; Yoshida, T. Effects of tannins and related polyphenols on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerdunbayaer; Orabi, M.A.; Aoyama, H.; Kuroda, T.; Hatano, T. Structures of two new flavonoids and effects of licorice phenolics on vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus species. Molecules 2014, 19, 3883–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerdunbayaer; Orabi, M.A.; Aoyama, H.; Kuroda, T.; Hatano, T. Structures of new phenolics isolated from licorice, and the effectiveness of licorice phenolics on vancomycin-resistant Enterococci. Molecules 2014, 19, 13027–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Miyake, M.; Nishitani, E.; Mori, K.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T.; Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Kozuka, M.; Mukainaka, T.; et al. Anti-tumor promoting activity of polyphenols from Cowania mexicana and Coleogyne ramosissima. Cancer Lett. 1999, 143, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, S.; Suganuma, M.; Imayoshi, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Fujiki, H. New TNF-alpha releasing inhibitors, geraniin and corilagin, in leaves of Acer nikoense, Megusurino-ki. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, T.; Mori, K.; Hayatsu, H. Inhibitory effect of tannins on direct-acting mutagens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 3755–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Chow, S.C.; Li, C.H.; Xiao, Z.; Feng, R.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y. A potential antitumor ellagitannin, davidiin, inhibited hepatocellular tumor growth by targeting EZH2. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orabi, M.A.; Taniguchi, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kishino, K.; Sakagami, H.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable tannins of tamaricaceous plants. III. Hellinoyl- and macrocyclic-type ellagitannins from Tamarix nilotica. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orabi, M.A.; Taniguchi, S.; Sakagami, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable tannins of tamaricaceous plants. V. Structures of monomeric-trimeric tannins and cytotoxicity of macrocyclic-type tannins isolated from Tamarix nilotica (1). J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orabi, M.A.; Taniguchi, S.; Sakagami, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable Tannins of Tamaricaceous Plants. 7.1 Structures and Cytotoxic Properties of Oligomeric Ellagitannins from Leaves of Tamarix nilotica and Cultured Tissues of Tamarix tetrandra. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, T.; Hattori, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Shingu, T.; Okuda, T. Gallotannins having a 1,5-anhydro-d-glucitol core and some ellagitannins from Acer species. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1902–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ashida, M.; Yazaki, K. Tannins of Casuarina and Stachyurus Species, Part 1. Structure of Pedunculagin, Casuarictin, Strictinin, Casuarinin, Casuariin, and Stachyurin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1983, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XCV. Isolation and characterization of helioscopinins and helioscopins, four new hydrolysable tannins from Euphorbia helioscopia L. (1). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, R.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and Related Compounds. LXXXVII: Isolation and Characterization of Four New Hydrolyzable Tannins from the Leaves of Mallotus repandus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Uebayashi, H.; Ito, H.; Shiota, S.; Tsuchiya, T.; Yoshida, T. Phenolic constituents of Cassia seeds and antibacterial effect of some naphthalenes and anthraquinones on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, W.M.; Jin, K.T.; Ramli, R.; Khaithir, T.M.N.; Wiart, C. Antibacterial effects of ellagitannins from Acalypha wilkesiana var. macafeana hort.: Surface morphology analysis with environmental scanning with electron microscopy and synergy with antibiotics. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caturla, N.; Vera-Samper, E.; Villalain, J.; Mateo, C.R.; Micol, V. The relationship between the antioxidant and the antibacterial properties of galloylated catechins and the structure of phospholipid model membranes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kishi, N.; Koshiura, R.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T. Relationship between the structures and the antitumor activities of tannins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakagami, H.; Jiang, Y.; Kusama, K.; Atsumi, T.; Ueha, T.; Toguchi, M.; Iwakura, I.; Satoh, K.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; et al. Cytotoxic activity of hydrolyzable tannins against human oral tumor cell lines—A possible mechanism. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Chien, C.H.; Kanegae, H.; Kawase, M. Selective toxicity and type of cell death induced by various natural and synthetic compounds in oral squamous cell carcinoma. In Vivo 2007, 21, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, S.; Nogaki, R.; Bao, L.M.; Kuroda, T.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T. Furosonin, a Novel Hydrolyzable Tannin from Geranium thunbergii. Heterocycles 2012, 86, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Kantoh, K.; Ono, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Sakagami, H.; Wakabayashi, H. Hormetic and anti-radiation effects of tropolone-related compounds. In Vivo 2010, 24, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamura, S.; Nishiyama, E.; Yamazaki, T.; Otsuka, N.; Taniguchi, S.; Ogawa, W.; Hatano, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kuroda, T. Action mechanism of 6,6′-dihydroxythiobinupharidine from Nuphar japonicum, which showed anti-MRSA and anti-VRE activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, C.; Uesawa, Y.; Ishii-Nozawa, R.; Ishihara, M.; Kagaya, H.; Kanamoto, T.; Terakubo, S.; Nakashima, H.; Takao, K.; Sugita, Y.; et al. Quantitative structure-cytotoxicity relationship of 3-styrylchromones. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Matsuno, S.; Sakagami, H.; Okada, Y.; Shirataki, Y. Search of new cytotoxic crude materials against human oral squamous cell carcinoma using 1H-NMR-based metabolomics. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 4117–4120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and Related Compounds. C.: Reaction of Dehydrohexahydroxydiphenic Acid Esters with Bases, and Its Application to the Structure Determination of Pomegranate Tannins, Granatins A and B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Sample of the compound 5 is available from the authors.



| Compounds | MIC (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | VRE | |||
| S. aureus | E. faecium | E. faecalis | ||
| OM481 | OM584 | FN-1 | NCTC12201 | |
| 1 | 64 | 64 | >128 | 16 |
| 2 | 128 | 128 | >128 | 128 |
| 4 | 64 | 64 | >128 | 64 |
| Linezolid | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Compounds | CC50 ± SD (µM) b,c | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Tumor Cells | Human Normal Oral Cells | |||||||
| Ca9-22 | HSC-2 | HSC-3 | HSC-4 | HGF | HPLF | HPC | TS d | |
| 1 | 140 ± 8.7 | 112.3 ± 11.2 | 99.6 ± 8.6 | 152.7 ± 13.6 | 254.7 ± 16.3 | 309.0 ± 12.8 | 256 ± 28.8 | 2.2 |
| 4 | 97.3 ± 9.0 | 111.0 ± 3.5 | 114.7 ±14.5 | 95.3 ± 22.3 | 128.7 ± 3.8 | 155.0 ± 11.4 | 131.0 ± 1.7 | 1.3 |
| Resveratrol | 106 ± 6.0 | 71.0 ± 0.6 | 67.7 ±1.3 | 46.2 ± 6.9 | 215.0 ± 29.7 | 198.3 ± 22.3 | 214.0 ± 12.1 | 2.9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimozu, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Esumi, A.; Aoyama, H.; Kuroda, T.; Sakagami, H.; Hatano, T. Ellagitannins of Davidia involucrata. I. Structure of Davicratinic Acid A and Effects of Davidia Tannins on Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Molecules 2017, 22, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030470
Shimozu Y, Kimura Y, Esumi A, Aoyama H, Kuroda T, Sakagami H, Hatano T. Ellagitannins of Davidia involucrata. I. Structure of Davicratinic Acid A and Effects of Davidia Tannins on Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030470
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimozu, Yuuki, Yuriko Kimura, Akari Esumi, Hiroe Aoyama, Teruo Kuroda, Hiroshi Sakagami, and Tsutomu Hatano. 2017. "Ellagitannins of Davidia involucrata. I. Structure of Davicratinic Acid A and Effects of Davidia Tannins on Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas" Molecules 22, no. 3: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030470
APA StyleShimozu, Y., Kimura, Y., Esumi, A., Aoyama, H., Kuroda, T., Sakagami, H., & Hatano, T. (2017). Ellagitannins of Davidia involucrata. I. Structure of Davicratinic Acid A and Effects of Davidia Tannins on Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Molecules, 22(3), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030470