Na/K Pump and Beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lung Cancer
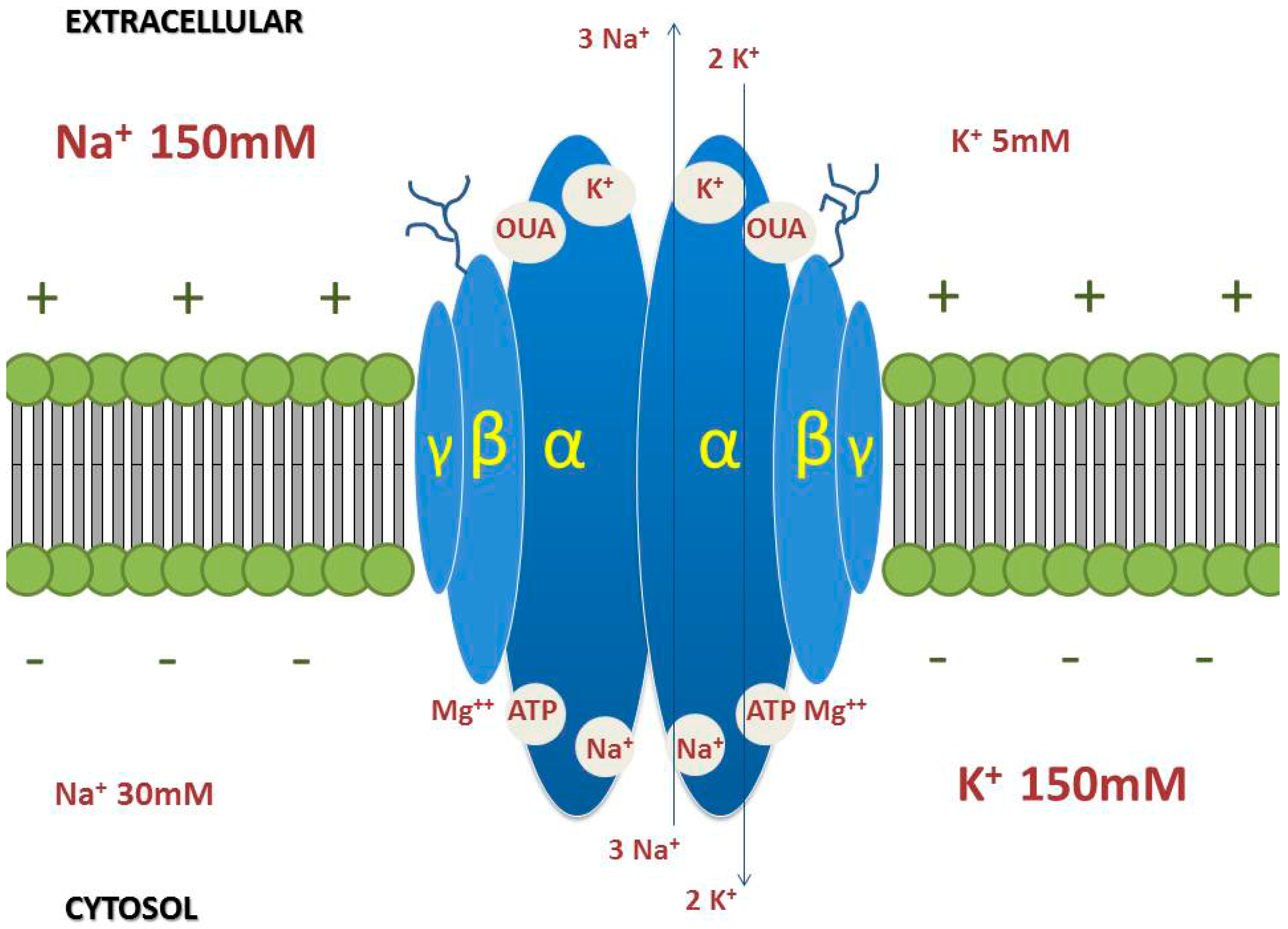
3. Na/K-ATPase
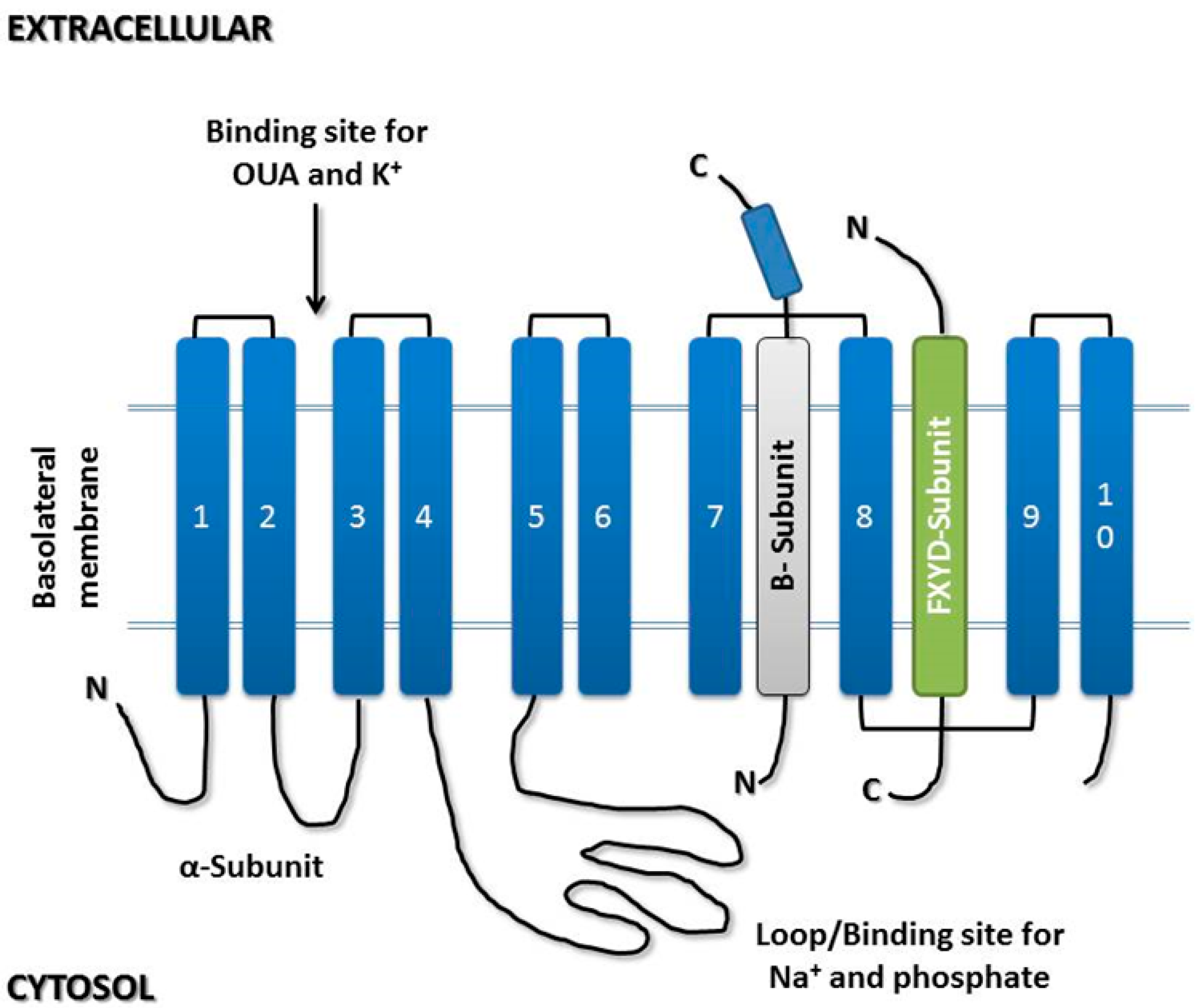
3.1. α-Subunit
3.2. β-Subunit
3.3. γ-Subunit
4. Na/K-ATPase: Expression in Cancer and Potential of Cardiotonic Steroids
5. Cardiotonic Steroids
5.1. Cardenolides
5.2. Bufadienolides
6. Role of Na/K-ATPase in the Lung
Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenkvist, B.; Bengtsson, E.; Dahlqvist, B.; Eriksson, O.; Jarkrans, T.; Nordin, B. Cardiac glycosides and breast cancer, revisited. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 306, 484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karasneh, R.A.; Murray, L.J.; Cardwell, C.R. Cardiac glycosides and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haux, J.; Klepp, O.; Spigset, O.; Tretli, S. Digitoxin medication and cancer; case control and internal dose-response studies. BMC Cancer 2001, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dela Cruz, C.S.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M. Lung cancer: Needs assessment, treatment and therapies. Br. J. Nurs. 2013, 22, S15, S16, S18, S20–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didkowska, J.; Wojciechowska, U.; Manczuk, M.; Lobaszewski, J. Lung cancer epidemiology: Contemporary and future challenges worldwide. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, S.S.; Bray, F.; Vizcaino, A.P.; Parkin, D.M. International lung cancer trends by histologic type: Male:female differences diminishing and adenocarcinoma rates rising. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, I.; Ishikawa, S.; Sohara, Y. Genes associated with succeptibility to lung adenocarcinoma among never smokers suggest the mechanism of disease. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 5229–5240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, I.; Ishikawa, S.; Ando, W.; Sohara, Y. Lung Adenocarcinoma in Never Smokers: Problems of Primary Prevention from Aspects of Susceptible Genes and Carcinogens. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 6207–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebben, J.D.; You, M. Brain metastasis in lung cancer: Building a molecular and systems-level understanding to improve outcomes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 78, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Suda, K.; Wiens, J.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, M.; Mohamad, O.; Yu, S.P. Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase induces hybrid cell death and enhanced sensitivity to chemotherapy in human glioblastoma cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtivelman, E.; Hensing, T.; Simon, G.R.; Dennis, P.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Bueno, R.; Salgia, R. Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1392–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, L.; Cappuzzo, F. Targeting MET in NSCLC: Looking for a needle in a haystack. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.H. Biochemistry of Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 511–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, M.; Gregersen, J.L.; Yatime, L.; Nissen, P.; Fedosova, N.U. Structures and characterization of digoxin- and bufalin-bound Na+,K+-ATPase compared with the ouabain-bound complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintas, L.E.; Pierre, S.V.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, Z.J. Alterations of Na+/K+-ATPase function in caveolin-1 knockout cardiac fibroblasts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skou, J.C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1957, 23, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skou, J.C. The identification of the sodium pump. Biosci. Rep. 2004, 24, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, P.L. Structure, function and regulation of Na,K-ATPase in the kidney. Kidney Int. 1986, 29, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Avila, J.; Cozar-Castellano, I.; Brownleader, M.D.; Trevan, M.; Francis, M.J.; Lamb, J.F.; Martin-Vasallo, P. Na+,K+-ATPase isozyme diversity; comparative biochemistry and physiological implications of novel functional interactions. Biosci. Rep. 2000, 20, 51–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, S.A.; Palmer, L.G.; Moon, S.Y.; Peralta Soler, A.; Apodaca, G.L.; Harper, J.F.; Zheng, Y.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Na,K-ATPase activity is required for formation of tight junctions, desmosomes, and induction of polarity in epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3717–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, S.L.; Gopalakrishnapillai, A.; Barwe, S.P. Ion dependence of Na-K-ATPase-mediated epithelial cell adhesion and migration. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C437–C441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Cai, T. Na+-K+-ATPase-mediated signal transduction: From protein interaction to cellular function. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, G. Na,K-ATPase subunit heterogeneity as a mechanism for tissue-specific ion regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geering, K. Functional roles of Na,K-ATPase subunits. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Dufrasne, F.; Kiss, R. Na+/K+-ATPase and cancer. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2012, 1, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fambrough, D.M.; Lemas, M.V.; Hamrick, M.; Emerick, M.; Renaud, K.J.; Inman, E.M.; Hwang, B.; Takeyasu, K. Analysis of subunit assembly of the Na-K-ATPase. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C579–C589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lingrel, J.B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Roland, I.; van Quaquebeke, E.; Nilsson, B.; Mathieu, A.; van Vynckt, F.; Darro, F.; Blanco, G.; Facchini, V.; Kiss, R. The alpha1 subunit of the sodium pump could represent a novel target to combat non-small cell lung cancers. J. Pathol. 2007, 212, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seligson, D.B.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Eeva, M.; Tze, S.; Ball, W., Jr.; Horvath, S.; deKernion, J.B.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Na,K-adenosine triphosphatase alpha1-subunit predicts survival of renal clear cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, F.; Mijatovic, T.; Kondo, Y.; Sauvage, S.; Roland, I.; Debeir, O.; Krstic, D.; Vasic, V.; Gailly, P.; Kondo, S.; et al. Targeting the alpha 1 subunit of the sodium pump to combat glioblastoma cells. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, V.; Pirker, C.; Martin de Lassalle, E.; Vernier, M.; Mijatovic, T.; DeNeve, N.; Gaussin, J.F.; Dehoux, M.; Lefranc, F.; Berger, W.; et al. The sodium pump alpha1 sub-unit: A disease progression-related target for metastatic melanoma treatment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 3960–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; O’Doherty, G.A. Modulators of Na/K-ATPase: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. Na+, K+-ATPase: Functions in the nervous system and involvement in neurologic disease. Neurology 2011, 76, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geering, K. The functional role of beta subunits in oligomeric P-type ATPases. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2001, 33, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, W.F.; Barbosa, L.A.; Liu, L.; de Araujo, W.M.; de-Freitas-Junior, J.C.; Fortunato-Miranda, N.; Fontes, C.F.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. Ouabain-induced alterations of the apical junctional complex involve alpha1 and beta1 Na,K-ATPase downregulation and ERK1/2 activation independent of caveolae in colorectal cancer cells. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Cartwright, C.; Efuet, E.; Hamilton, S.R.; Wistuba, I.I.; Menter, D.; Addington, C.; Shureiqi, I.; Newman, R.A. Cellular location and expression of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha subunits affect the anti-proliferative activity of oleandrin. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.K.; Peleg, Y.; Cirri, E.; Belogus, T.; Lifshitz, Y.; Voelker, D.R.; Apell, H.J.; Garty, H.; Karlish, S.J. FXYD proteins stabilize Na,K-ATPase: Amplification of specific phosphatidylserine-protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9699–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, V.F.; Veiga-Lopes, F.E.; Barrabin, H.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Fontes, C.F. The gamma subunit of Na+, K+-ATPase: Role on ATPase activity and regulatory phosphorylation by PKA. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Kiss, R. Cardiotonic steroids-mediated Na+/K+-ATPase targeting could circumvent various chemoresistance pathways. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, S.A.; Palmer, L.G.; Quan, K.; Harper, J.F.; Ball, W.J., Jr.; Bander, N.H.; Peralta Soler, A.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit is required for epithelial polarization, suppression of invasion, and cell motility. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, H. Na/K-ATPase, endogenous digitalis like compounds and cancer development—A hypothesis. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederich, M.; Muller, F.; Cerella, C. Cardiac glycosides: From molecular targets to immunogenic cell death. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 125, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espineda, C.; Seligson, D.B.; James Ball, W., Jr.; Rao, J.; Palotie, A.; Horvath, S.; Huang, Y.; Shi, T.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Analysis of the Na,K-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit expression profiles of bladder cancer using tissue microarrays. Cancer 2003, 97, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.L.; Schuster, D.P. Positron emission tomography with (18F)fluorodeoxyglucose to evaluate neutrophil kinetics during acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. 2004, 286, L834–L840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.G.; de Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; da Silva, C.I.; de Souza e Souza, K.F.; Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Silva, A.R.; de Amorim, L.M.; Freire, A.S.; Santelli, R.E.; Diniz, L.P.; Gomes, F.C.; et al. Na/K-ATPase as a target for anticancer drugs: Studies with perillyl alcohol. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, W.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides and their mechanisms of action. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2007, 7, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, W.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: Their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C509–C536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akera, T.; Ng, Y.C. Digitalis sensitivity of Na+,K(+)-ATPase, myocytes and the heart. Life Sci. 1991, 48, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Kennedy, D.J. Regulation of Cardiac Remodeling by Cardiac Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase Isoforms. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S. Plant-derived cardiac glycosides: Role in heart ailments and cancer management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, C.D.; Mawji, I.A.; Anyiwe, K.; Williams, M.A.; Wang, X.; Venugopal, A.L.; Gronda, M.; Hurren, R.; Cheng, S.; Serra, S.; et al. Inhibition of the sodium potassium adenosine triphosphatase pump sensitizes cancer cells to anoikis and prevents distant tumor formation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Ingrassia, L.; Facchini, V.; Kiss, R. Na+/K+-ATPase alpha subunits as new targets in anticancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Target 2008, 12, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, A.; Lifshitz, Y.; Bab-Dinitz, E.; Kapri-Pardes, E.; Goldshleger, R.; Tal, D.M.; Karlish, S.J. Selectivity of digitalis glycosides for isoforms of human Na,K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19582–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, H.; Shinoda, T.; Cornelius, F.; Toyoshima, C. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase) with bound potassium and ouabain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13742–13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Involvement of the M7/M8 extracellular loop of the sodium pump alpha subunit in ion transport. Structural and functional homology to P-loops of ion channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16158–16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Koh, X.; Hua, F.; Li, G.; Larrick, J.W.; Bian, J.S. Cardioprotection induced by Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase activation involves extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wang, F.M.; Gao, M.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Hu, W.L.; Xu, R.C. Targeting the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase alpha1 subunit of hepatoma HepG2 cell line to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arresting. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyoshi, H.; Abdelhady, S.; Segerstrom, L.; Sveinbjornsson, B.; Nuriya, M.; Lundgren, T.K.; Desfrere, L.; Miyakawa, A.; Yasui, M.; Kogner, P.; et al. Quiescence and gamma H2AX in neuroblastoma are regulated by ouabain/Na,K-ATPase. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Menter, D.G.; Cartwright, C.; Chan, D.; Dixon, S.; Suraokar, M.; Mendoza, G.; Llansa, N.; Newman, R.A. Oleandrin-mediated inhibition of human tumor cell proliferation: Importance of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunits as drug targets. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Shen, J.J.; Li, D.D.; Jiang, X.J.; Si, S.Y.; Shao, R.G.; Wang, Z. Cardiac glycosides induce autophagy in human non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulation of dual signaling pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B. 2012, 44, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, R.A.; Yang, P.; Pawlus, A.D.; Block, K.I. Cardiac glycosides as novel cancer therapeutic agents. Mol. Interv. 2008, 8, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadi Kayali, M.A.J.; Laber, D.A.; Miller, D.; Kloecker, G.H. Phase II trial of second-line erlotinib and digoxin for nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Open Access J. Clin Trials 2011, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, H.A.; Stueckle, T.A.; Wang, H.Y.; O'Doherty, G.A.; Lowry, D.T.; Sargent, L.M.; Wang, L.; Dinu, C.Z.; Rojanasakul, Y. Digitoxin and a synthetic monosaccharide analog inhibit cell viability in lung cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, C.P.; Medarde, M.; Feliciano, A.S. A Short Review on Cardiotonic Steroids and Their Aminoguanidine Analogues. Molecules 2000, 5, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatovic, T.; Florence, L.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Van Vynckt, F.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. UNBS1450: A new hemi-synthetic cardenolide with promising anti-cancer activity. Drug Dev. Res. 2007, 68, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Lai, F.; Banerjee, M.; Duan, Q.; Li, Z.; Si, S.; Xie, Z. Expression of mutant alpha1 Na/K-ATPase defective in conformational transition attenuates Src-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5803–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Bi, L.L.; Li, X.; Miao, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.W. Anticancer effects of bufalin on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells: Roles of apoptosis and autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R.; Gong, X. Bufalin induces the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in glioma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, Y.B.L.; Katz, A.; Miklos, W.; Cimmino, A.; Tal, D.M.; Ainbinder, E.; Zehl, M.; Urban, E.; Evidente, A.; Kopp, B.; et al. Hellebrin and its aglycone form hellebrigenin display similar in vitro growth inhibitory effects in cancer cells and binding profiles to the alpha subunits of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Gabrielli, N.M.; Vadasz, I. Novel concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L665–L681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawedia, J.D.; Yang, F.; Sartor, M.A.; Gozal, D.; Czyzyk-Krzeska, M.; Menon, A.G. Hypoxia and hypoxia mimetics decrease aquaporin 5 (AQP5) expression through both hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and proteasome-mediated pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, X.X.; Li, H.L.; Li, R.Q. Endogenous acetylcholine increases alveolar epithelial fluid transport via activation of alveolar epithelial Na,K-ATPase in mice. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 217, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morty, R.E.; Eickelberg, O.; Seeger, W. Alveolar fluid clearance in acute lung injury: What have we learned from animal models and clinical studies? Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Burth, P.; Silva, A.R.; de Moraes, I.M.; de Jesus Oliveira, F.M.; Santelli, R.E.; Freire, A.S.; Bozza, P.T.; Younes-Ibrahim, M.; de Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; et al. Oleic acid inhibits lung Na/K-ATPase in mice and induces injury with lipid body formation in leukocytes and eicosanoid production. J. Inflamm. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Burth, P.; Silva, A.R.; de Moraes, I.M.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Santelli, R.E.; Freire, A.S.; Younes-Ibrahim, M.; de Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; de Castro-Faria, M.V. Na/K-ATPase assay in the intact mice lung subjected to perfusion. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Silva, A.R.; Burth, P.; Castro-Faria, M.V.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Role of Oleic Acid-Triggered Lung Injury and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 260465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Burth, P.; Silva, A.R.; de Moraes, I.M.; Oliveira, F.M.; Santelli, R.E.; Freire, A.S.; de Lima, G.S.; da Silva, E.D.; da Silva, C.I.; et al. Murine lung injury caused by Leptospira interrogans glycolipoprotein, a specific Na/K-ATPase inhibitor. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Medeiros-de-Moraes, I.M.; Oliveira, F.M.; Burth, P.; Bozza, P.; Castro Faria, M.V.; Silva, A.R.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C. Omega-9 Oleic Acid Induces Fatty Acid Oxidation and Decreases Organ Dysfunction and Mortality in Experimental Sepsis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimas, K.; Papadopoulou, N.; Baskakis, C.; Prousis, K.C.; Tsakos, M.; Alkahtani, S.; Honisch, S.; Lang, F.; Calogeropoulou, T.; Alevizopoulos, K.; et al. Steroidal cardiac Na+/K+ ATPase inhibitors exhibit strong anti-cancer potential in vitro and in prostate and lung cancer xenografts in vivo. Anti-Cancer Agent Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziff, O.J.; Kotecha, D. Digoxin: The good and the bad. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iisalo, E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1977, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durlacher, C.T.; Chow, K.; Chen, X.W.; He, Z.X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Zhou, S.F. Targeting Na(+)/K(+) -translocating adenosine triphosphatase in cancer treatment. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys. 2015, 42, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, P.; Owens, T.A.; David, J.M.; Petrelli, N.J.; Christensen, B.C.; Lakshmikuttyamma, A.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Epigenetic silencing of Na,K-ATPase beta 1 subunit gene ATP1B1 by methylation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, L.; Tidow, H.; Clausen, M.J.; Nissen, P. Na(+),K (+)-ATPase as a docking station: Protein-protein complexes of the Na(+),K (+)-ATPase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiner-Bobis, G. The Na(+), K(+)-ATPase: More than just a sodium pump. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaustein, M.P. Endogenous ouabain: Role in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 1748–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Askari, A. Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase as a signal transducer. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khundmiri, S.J.; Salyer, S.A.; Farmer, B.; Qipshidze-Kelm, N.; Murray, R.D.; Clark, B.J.; Xie, Z.; Pressley, T.A.; Lederer, E.D. Structural determinants for the ouabain-stimulated increase in Na-K ATPase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Haas, M.; Liang, M.; Cai, T.; Tian, J.; Li, S.; Xie, Z. Ouabain assembles signaling cascades through the caveolar Na+/K+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17250–17259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Tian, J.; Liu, L.; Pierre, S.; Liu, J.; Shapiro, J.; Xie, Z.J. Identification of a pool of non-pumping Na/K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10585–10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Quaquebeke, E.; Simon, G.; Andre, A.; Dewelle, J.; El Yazidi, M.; Bruyneel, F.; Tuti, J.; Nacoulma, O.; Guissou, P.; Decaestecker, C.; et al. Identification of a novel cardenolide (2′′-oxovoruscharin) from Calotropis procera and the hemisynthesis of novel derivatives displaying potent in vitro antitumor activities and high in vivo tolerance: Structure-activity relationship analyses. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.I.; Plaza, A.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Mahalel, U.A.; Springuel, I.V.; Oleszek, W.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Cardenolide glycosides from Pergularia tomentosa and their proapoptotic activity in Kaposi’s sarcoma cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Op De Beeck, A.; van Quaquebeke, E.; Dewelle, J.; Darro, F.; de Launoit, Y.; Kiss, R. The cardenolide UNBS1450 is able to deactivate nuclear factor kappaB-mediated cytoprotective effects in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Jungwirth, U.; Heffeter, P.; Hoda, M.A.; Dornetshuber, R.; Kiss, R.; Berger, W. The Na+/K+-ATPase is the Achilles heel of multi-drug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 282, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Mathieu, V.; Gaussin, J.F.; De Neve, N.; Ribaucour, F.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Dumont, P.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. Cardenolide-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization demonstrates therapeutic benefits in experimental human non-small cell lung cancers. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Xie, J. The Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction as a target for new drug development. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Cai, T.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Haas, M.; Maksimova, E.; Huang, X.Y.; Xie, Z.J. Binding of Src to Na+/K+-ATPase forms a functional signaling complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakawa-Naito, A.; Uhlen, P.; Lal, M.; Aizman, O.; Mikoshiba, K.; Brismar, H.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A. Cell signaling microdomain with Na,K-ATPase and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor generates calcium oscillations. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50355–50361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Malmersjo, S.; Li, J.; Ando, H.; Aizman, O.; Uhlen, P.; Mikoshiba, K.; Aperia, A. Distinct role of the N-terminal tail of the Na,K-ATPase catalytic subunit as a signal transducer. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21954–21962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houede, N.; Pourquier, P. Targeting the genetic alterations of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: Its potential use in the treatment of bladder cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 145, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, K.; Kometiani, P.; Xie, Z.; Askari, A. Role of protein kinase C in the signal pathways that link Na+/K+-ATPase to ERK1/2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42050–42056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, K.; Liu, L.; Tian, J.; Kometiani, P.; Xie, Z.; Askari, A. Positive inotropic effect of ouabain on isolated heart is accompanied by activation of signal pathways that link Na+/K+-ATPase to ERK1/2. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 41, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Cai, T.; Tian, J.; Ivanov, A.V.; Giovannucci, D.R.; Xie, Z. Na/K-ATPase tethers phospholipase C and IP3 receptor into a calcium-regulatory complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 4034–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesher, M.; Shpolansky, U.; Rosen, H.; Lichtstein, D. The digitalis-like steroid hormones: New mechanisms of action and biological significance. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 2093–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Pierre, S.V.; Askari, A. Association of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway with digitalis-induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C1489–C1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, K.M.; Swarts, H.G.; Fedosova, N.U.; Russel, F.G.; Koenderink, J.B. Na,K-ATPase activity modulates Src activation: A role for ATP/ADP ratio. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Cai, T.; Tian, J.; Qu, W.; Xie, Z.J. Functional characterization of Src-interacting Na/K-ATPase using RNA interference assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19709–19719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eva, A.; Kirch, U.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Signaling pathways involving the sodium pump stimulate NO production in endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeino, M.; Brenk, R.; Gruber, L.; Zehl, M.; Urban, E.; Kopp, B.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of cardiotonic steroids in sensitive and multidrug-resistant leukemia cells and the link with Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 150, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, H. The “Lower Threshold” phenomenon in tumor cells toward endogenous digitalis-like compounds: Responsible for tumorigenesis? J. Carcinog. 2012, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerella, C.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Assembling the puzzle of anti-cancer mechanisms triggered by cardiac glycosides. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Raju, U.; Milas, L.; Molkentine, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, P.; Cohen, L.; Meng, Z.; Liao, Z. Huachansu, containing cardiac glycosides, enhances radiosensitivity of human lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, E.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Pongrakhananon, V. Ouabain downregulates Mcl-1 and sensitizes lung cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C263–C272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Dan, C.; Jinjun, B.; Su, F.; Wei, C.; Ri, Z.; Lin, M.; Zi-chun, H. Novel role of Na+,K+-ATPase ligands in regulating cytokines mRNA stability by HuR signalosome and the underlying pathophysiologic relevance. RNA Dis. 2015, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Yim, H.Y.; He, N.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, E.; Song, M.; et al. Cardiac glycosides display selective efficacy for STK11 mutant lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, T.C.; Wang, W.; Song, X. Temozolomide-perillyl alcohol conjugate induced reactive oxygen species accumulation contributes to its cytotoxicity against non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, R.; Han, N.; Xia, M.; Ye, C.; Hao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Saiki, I.; Yin, J. TXA9, a cardiac glycoside from Streptocaulon juventas, exerts a potent anti-tumor activity against human non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Steroids 2015, 94, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauf, P.K.; Alqahtani, T.; Flues, K.; Meller, J.; Adragna, N.C. Interaction between Na-K-ATPase and Bcl-2 proteins BclXL and Bak. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, C51–C60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, X.; Fan, X.X.; He, J.X.; Huang, J.; Xiao, D.K.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zheng, S.Y.; Xu, J.H.; Yao, X.J.; et al. Compound Library Screening Identified Cardiac Glycoside Digitoxin as an Effective Growth Inhibitor of Gefitinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Downregulation of alpha-Tubulin and Inhibition of Microtubule Formation. Molecules 2016, 21, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongrakhananon, V.; Stueckle, T.A.; Wang, H.Y.; O'Doherty, G.A.; Dinu, C.Z.; Chanvorachote, P.; Rojanasakul, Y. Monosaccharide digitoxin derivative sensitize human non-small cell lung cancer cells to anoikis through Mcl-1 proteasomal degradation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Levine, B. Autosis and autophagic cell death: The dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shoji-Kawata, S.; Sumpter, R.M., Jr.; Wei, Y.; Ginet, V.; Zhang, L.; Posner, B.; Tran, K.A.; Green, D.R.; Xavier, R.J.; et al. Autosis is a Na+,K+-ATPase-regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy-inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia-ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20364–20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenti, A.; Grumati, P.; Cusinato, F.; Orso, G.; Bonaldo, P.; Trevisi, L. Cardiac glycoside ouabain induces autophagic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells via a JNK-dependent decrease of Bcl-2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, R.; Shao, R.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z. Src mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation and autophagic cell death induced by cardiac glycosides in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, E26–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aperia, A. New roles for an old enzyme: Na,K-ATPase emerges as an interesting drug target. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, F.; Xu, Z.; Burth, P.; Mathieu, V.; Revelant, G.; de Castro Faria, M.V.; Noyon, C.; Garcia, D.G.; Dufour, D.; Bruyere, C.; et al. 4-Bromo-2-(piperidin-1-yl)thiazol-5-yl-phenyl methanone (12b) inhibits Na+/K(+)-ATPase and Ras oncogene activity in cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocafull, M.A.; Thomas, L.E.; del Castillo, J.R. The second sodium pump: From the function to the gene. Pflugers Arch. 2012, 463, 755–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felippe Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.; Ribeiro Silva, A.; Ignácio da Silva, C.; Caire Castro-Faria-Neto, H.; Burth, P. Na/K Pump and Beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy. Molecules 2017, 22, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040578
Felippe Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque C, Ribeiro Silva A, Ignácio da Silva C, Caire Castro-Faria-Neto H, Burth P. Na/K Pump and Beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy. Molecules. 2017; 22(4):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040578
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelippe Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, Cassiano, Adriana Ribeiro Silva, Camila Ignácio da Silva, Hugo Caire Castro-Faria-Neto, and Patrícia Burth. 2017. "Na/K Pump and Beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy" Molecules 22, no. 4: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040578
APA StyleFelippe Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C., Ribeiro Silva, A., Ignácio da Silva, C., Caire Castro-Faria-Neto, H., & Burth, P. (2017). Na/K Pump and Beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a Modulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy. Molecules, 22(4), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040578





