1
Inorganic Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 6 Traian Vuia Street, 020956 Bucharest, Romania
2
Organic Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 6 Traian Vuia Street, 020956 Bucharest, Romania
3
Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry “Petru Poni”, 41A Grigore Ghica Voda Alley, 700487 Iasi, Romania
4
Environmental and Food Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Victor Babeş”, 2nd Eftimie Murgu Sq., 300041 Timişoara, Romania
5
“Pius Brinzeu” Timișoara County Emergency Clinical Hospital, Oncogen Institute, 156 Liviu Rebreanu, 300723 Timişoara, Romania
6
Functional Sciences Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Victor Babeş”, 2 Eftimie Murgu Square, 300041 Timişoara, Romania
7
Pharmaceutical Botany and Cell Biology Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 6 Traian Vuia Street, 020956 Bucharest, Romania
8
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 6 Traian Vuia Street, 020956 Bucharest, Romania
9
Coordination Chemistry Department, Moldova State University, 60 Mateevici Street, 2009 Chisinau, Moldova
10
Inorganic Chemistry Department, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Bucharest, 23 Dumbrava Rosie Street, 020462 Bucharest, Romania
11
Pharmaceutical Physics Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 6 Traian Vuia Street, 020956 Bucharest, Romania
add
Show full affiliation list
Molecules 2017, 22(4), 650; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040650 - 19 Apr 2017
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 6475
Abstract
Hydrazone complexes of Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Ni(II) and Pt(II) with N-isonicotinoyl-N′-(3-metoxy-2 hydroxybenzaldehyde)-hydrazone (HL) were synthesized and characterized by different physico-chemical techniques including elemental and thermal analysis, magnetic susceptibility measurements, molar electric conductivity, as well as IR (infrared), 1
[...] Read more.
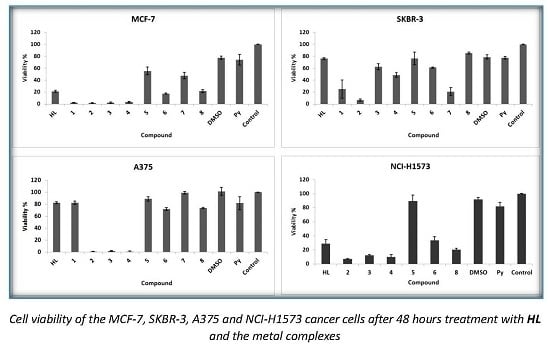
Hydrazone complexes of Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Ni(II) and Pt(II) with N-isonicotinoyl-N′-(3-metoxy-2 hydroxybenzaldehyde)-hydrazone (HL) were synthesized and characterized by different physico-chemical techniques including elemental and thermal analysis, magnetic susceptibility measurements, molar electric conductivity, as well as IR (infrared), 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR (hydrogen and carbon nuclear magnetic resonance, UV-Vis (ultraviolet-visible), FAB (fast atom bombardment), EPR (electron paramagnetic resonance), and mass spectroscopies. The crystal structure of ligand was determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Spectral data showed that hydrazone behaves as an ONO tridentate ligand through the azomethine nitrogen, phenolate and keto oxygen atoms. For the copper(II) complexes, metal–ligand bonding parameters were evaluated from the EPR spectra. These parameters indicate the presence of in-plane π bonding. In addition, the f values of complexes 1–4 indicate small distortion from planarity. The effect of these complexes on proliferation of human breast cancer (MCF-7 and SKBR-3), human melanoma (A375), lung adenocarcinoma cells (NCI-H1573) and their antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans strains were studied and compared with those of free ligand. The ligand and complexes 1–3 showed significant antimicrobial activity against the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans in comparison to the control drugs. The complexes 2–4 could be potential antitumor agents, leading to a significant improvement of the cytotoxic activity when compared with HL.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metal Based Drugs: Opportunities and Challenges)
▼
Show Figures