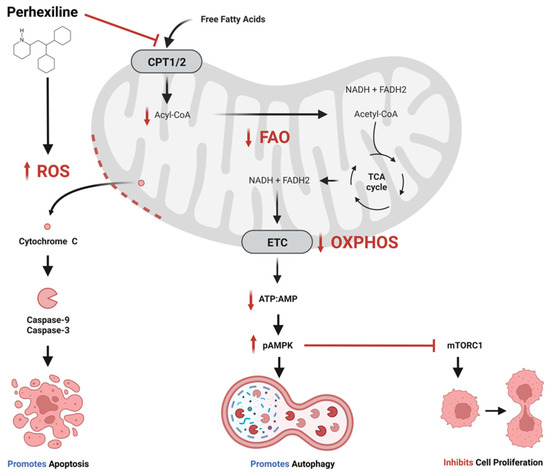
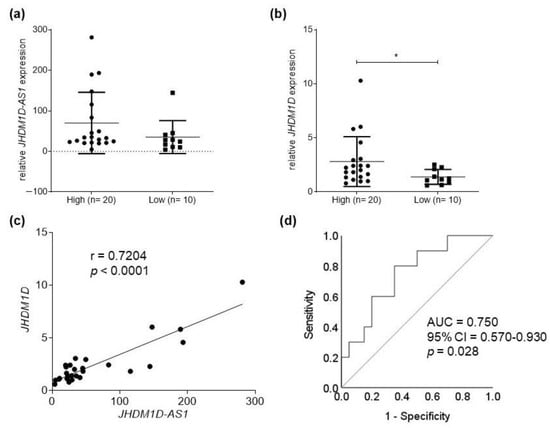
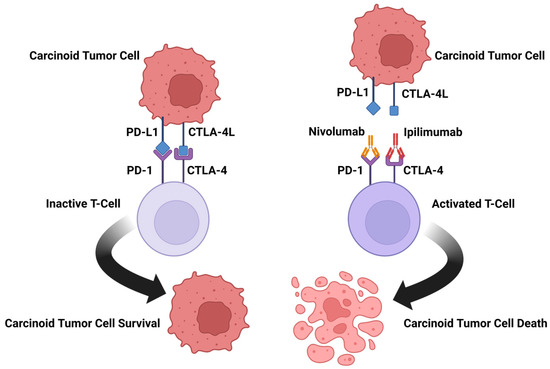
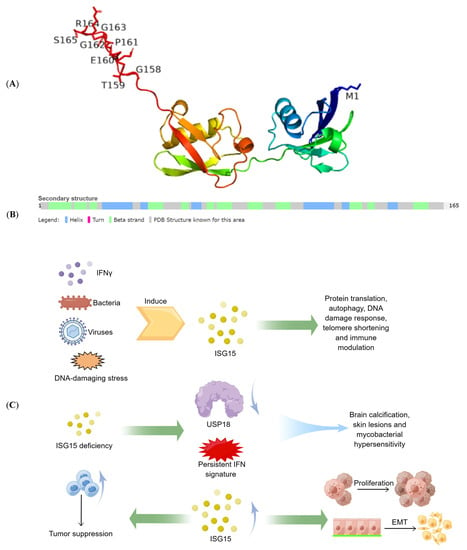
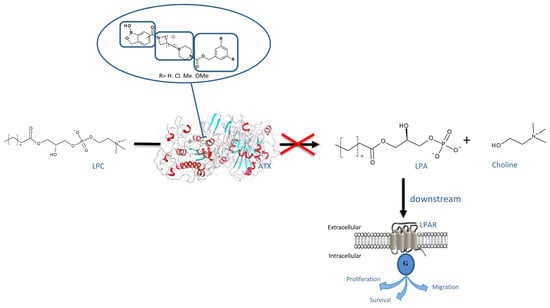
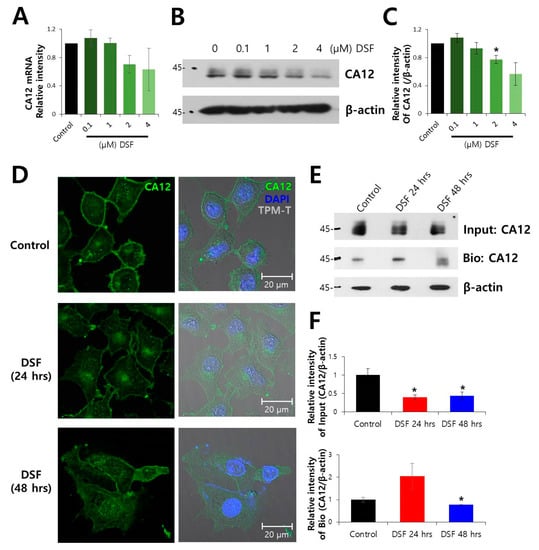
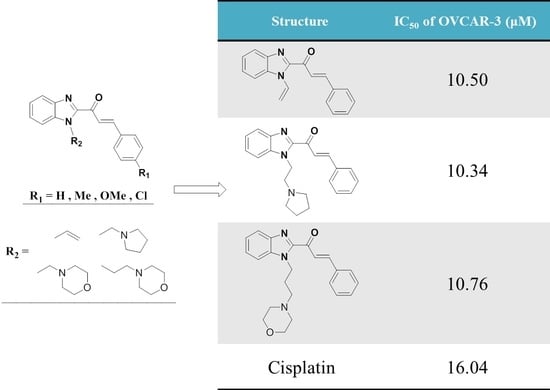
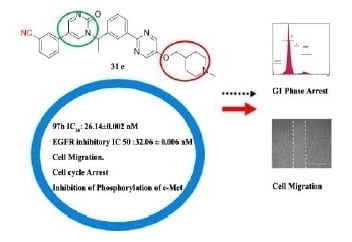
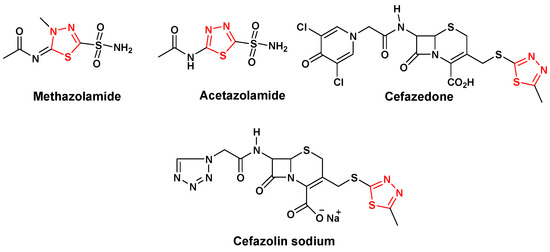
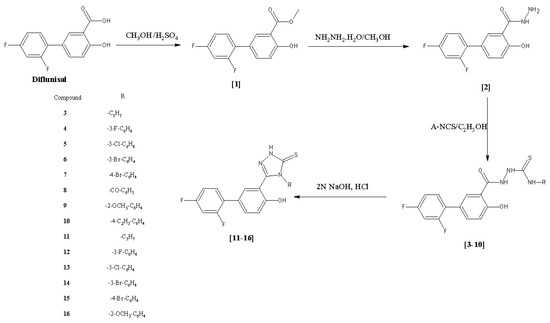
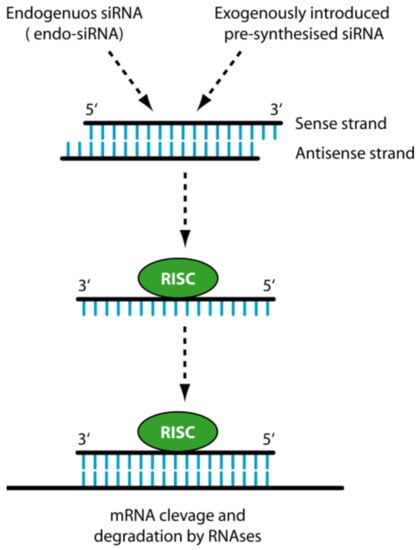
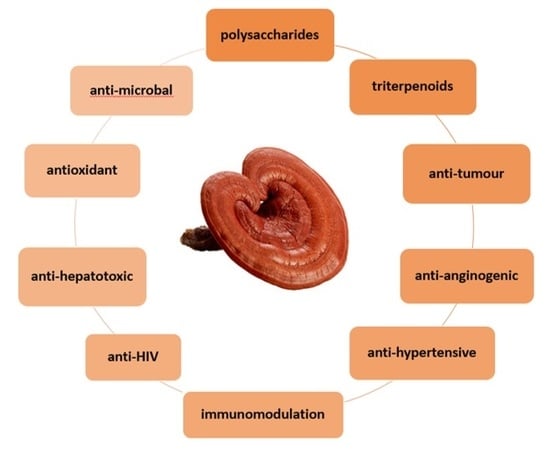
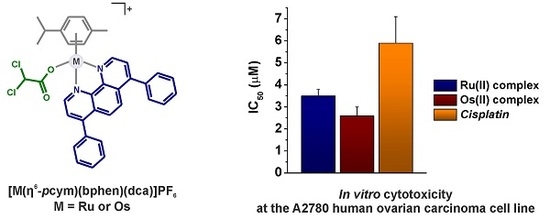
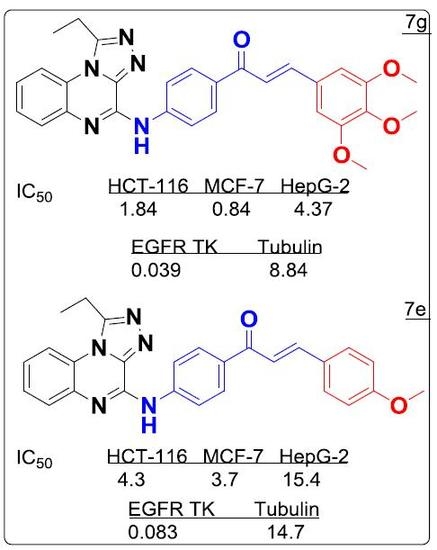
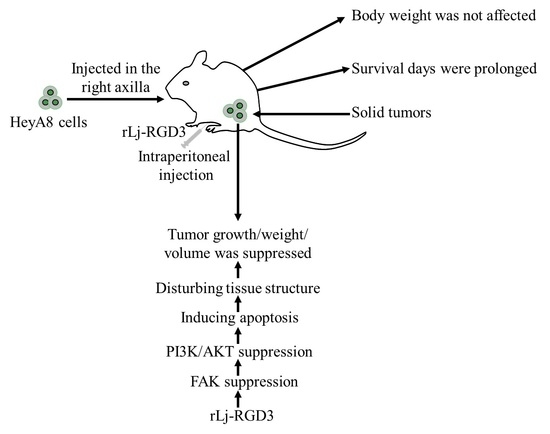
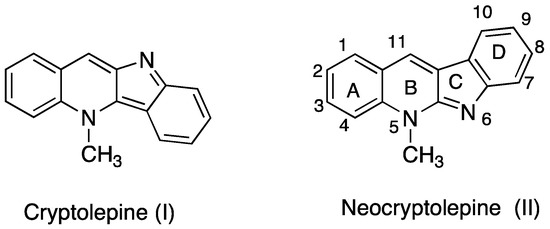
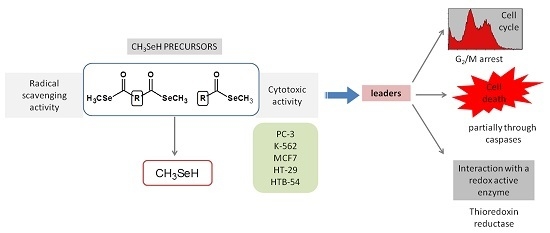
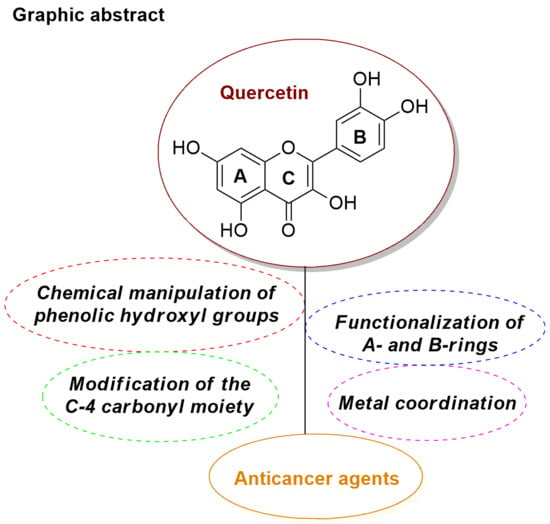
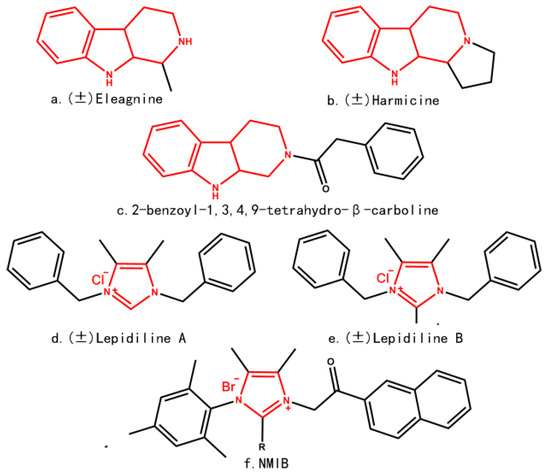
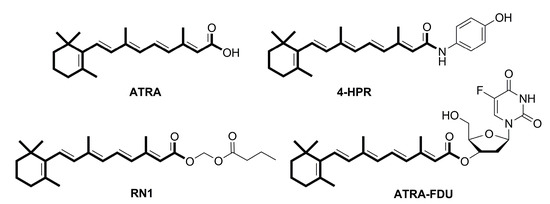
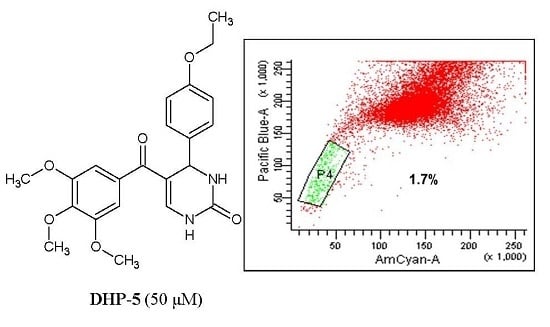
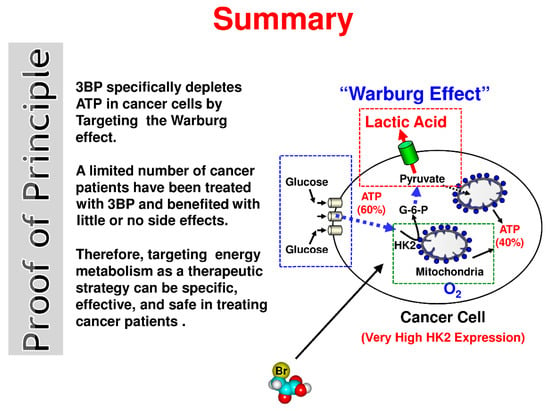
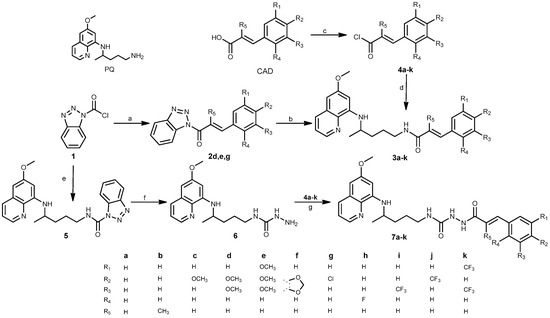
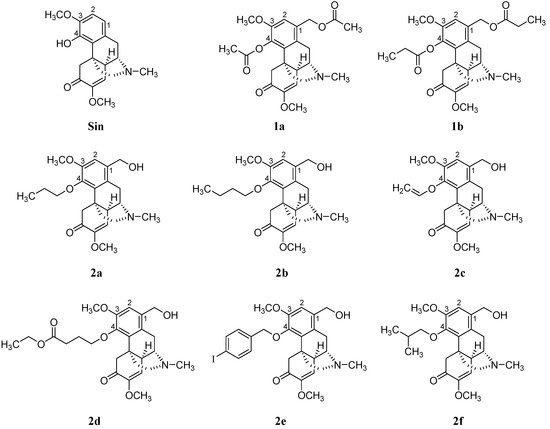
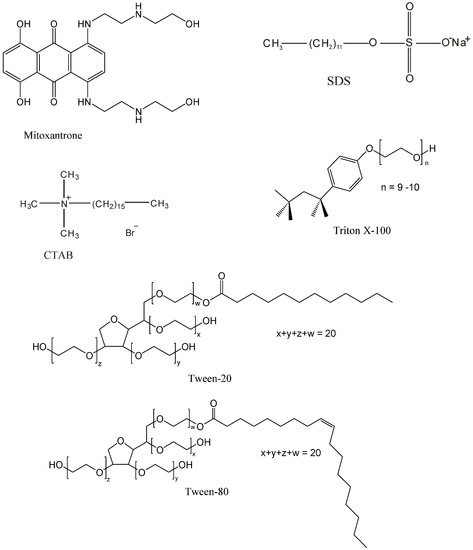
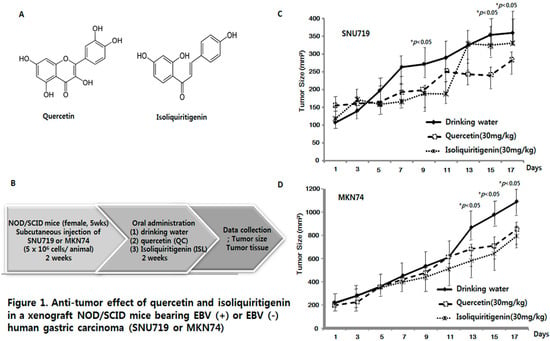
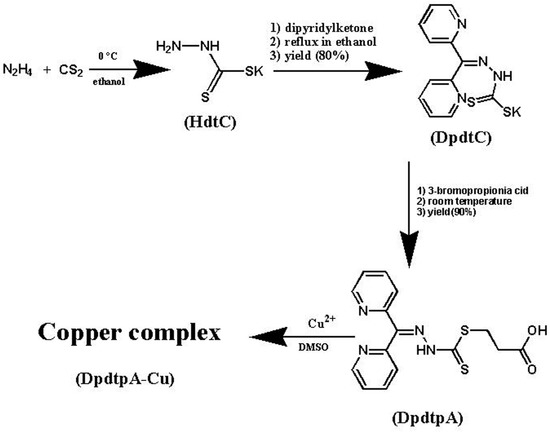
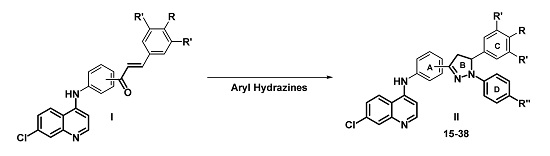
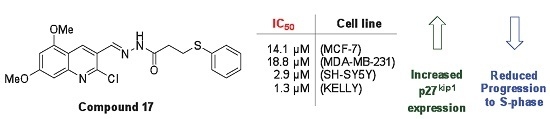
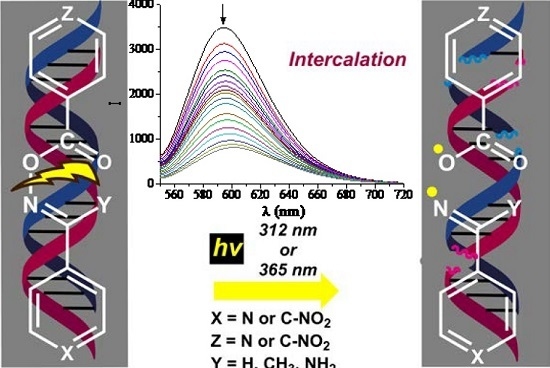
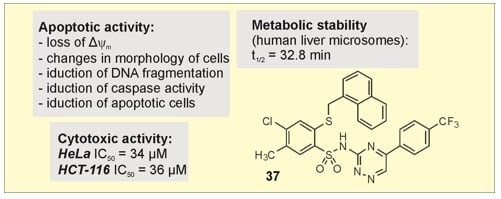
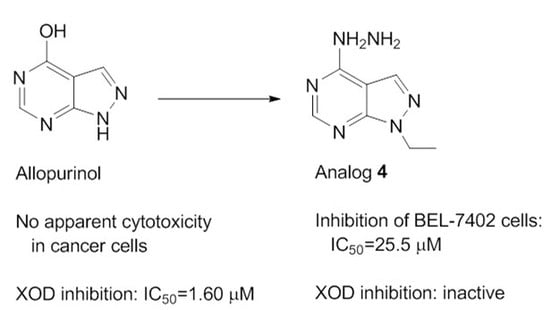
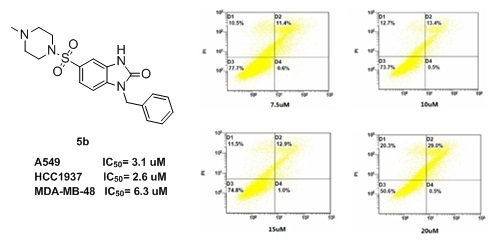
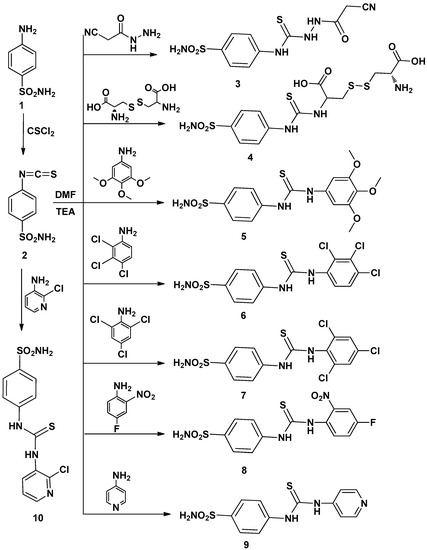
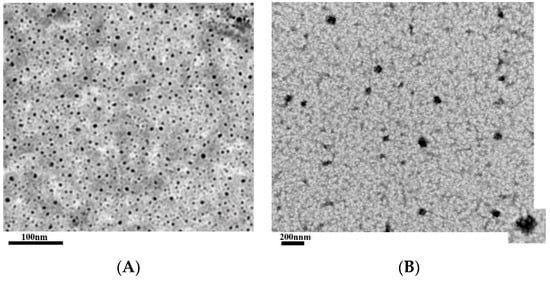
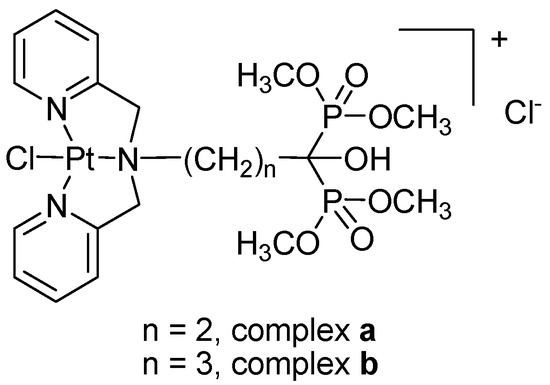
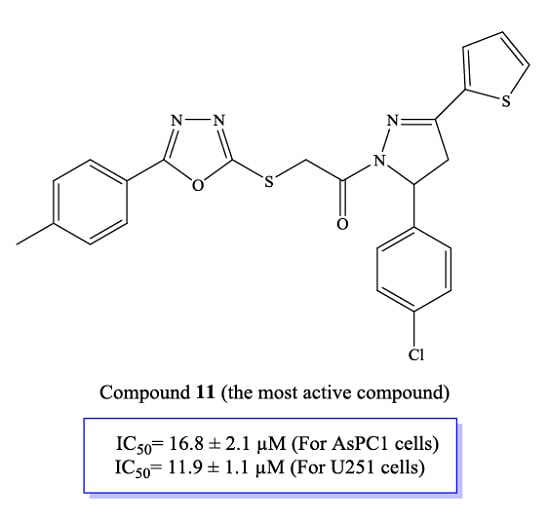
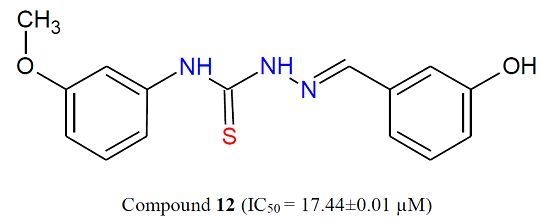
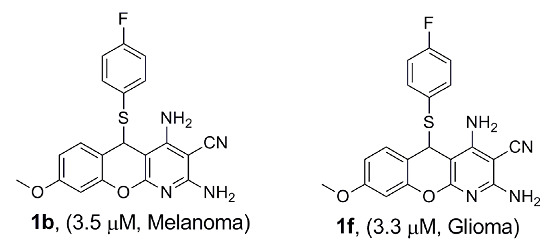
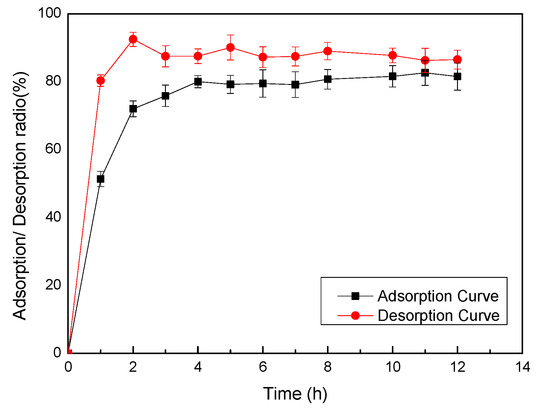
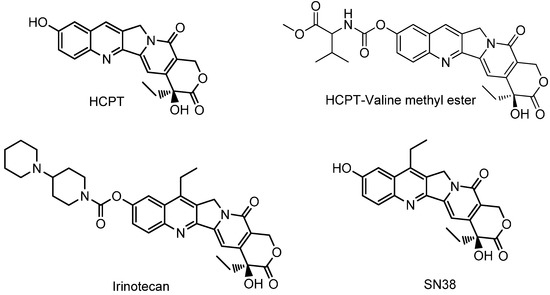
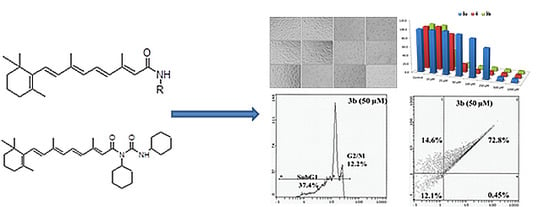
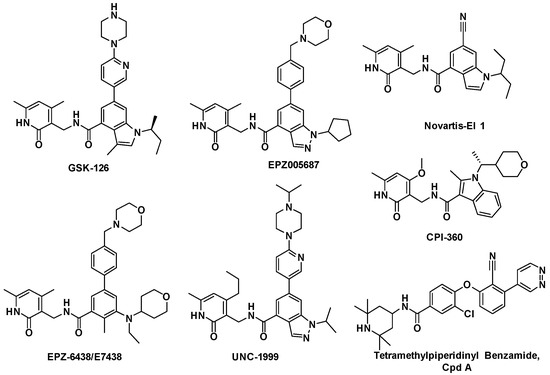
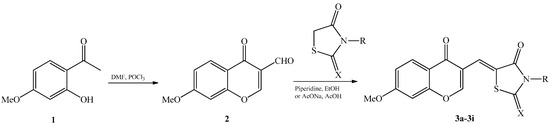
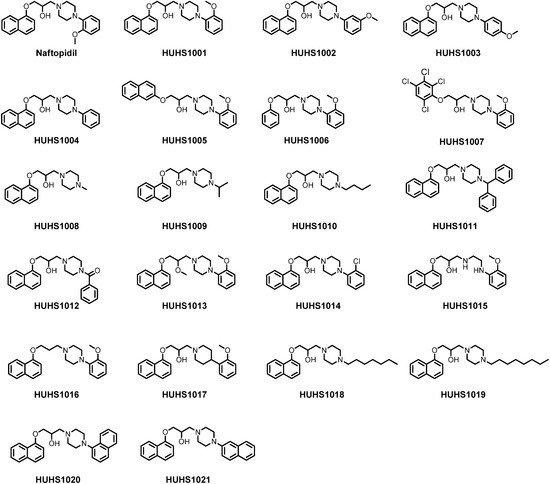
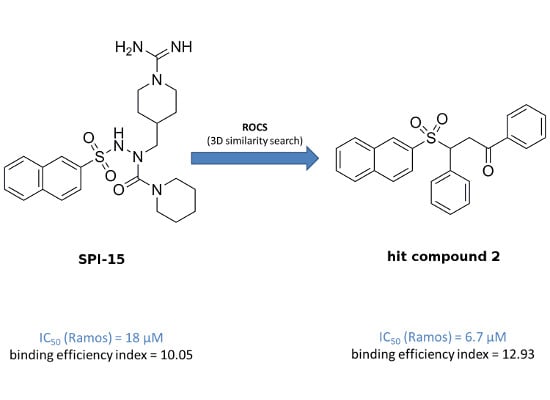
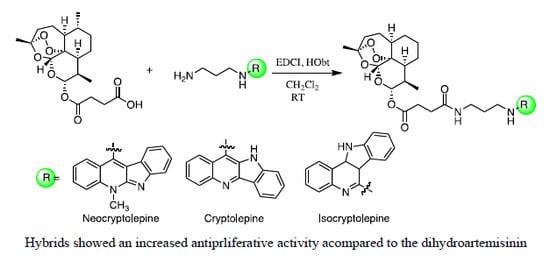
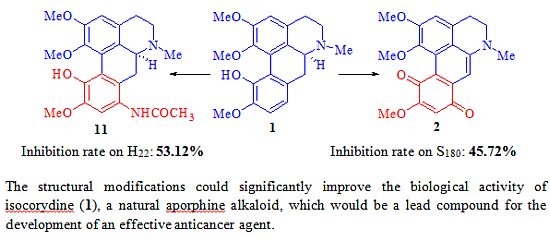
Efficient Pharmaceutical and Chemical Approaches for Anticancer Therapy: Design, Preliminary Evaluations, and Further Developments
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Medicinal Chemistry".
Viewed by 931356Editors
Interests: development of new chemical and enzymatic methods for the treatment of life threatening diseases; anti-infective agent; glycosidase enzyme inhibitors; anti-viral agents; personalised medicines
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: dendrimer nanocarriers; biopolymers; clinical pharmaceutics; polymer nanoparticulates
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: heterocycles; medicinal chemistry; green chemistry; microwave-induced synthesis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: medicinal chemistry; organic synthesis; parasitic diseases; orphan drugs
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: medicinal chemistry; organic chemistry; anti-opportunistic agents; anti-parasitic agents; prodrugs
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
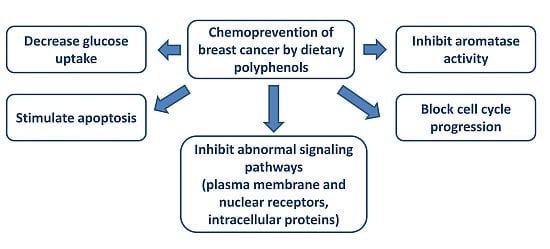
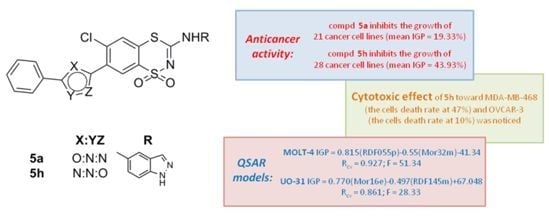
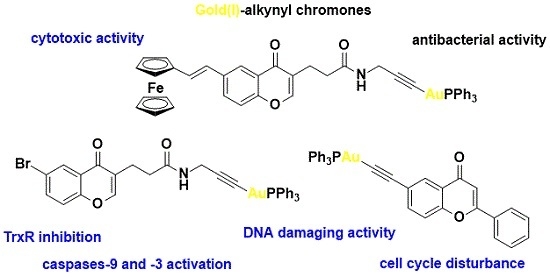
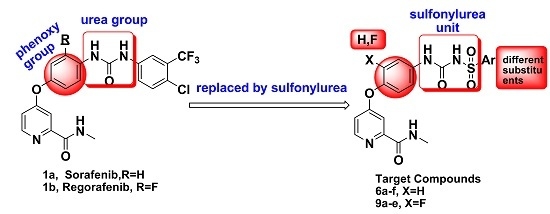
Developing novel cancer therapeutics is essential for treating cancer, a complex, multi-factorial disease that is dreaded worldwide. Although significant advances have been made in recent years in preventing and treating cancer, the mortality rate is still unacceptably high. Many of the current chemotherapeutics are limited by significant side effects, unpredictable efficacies or acquired resistances. Recent discoveries concerning the pathogenesis and biology of cancer have unraveled new, strategic cellular targets for drug intervention. This has allowed the rational development of novel cancer therapeutics. For this Special Issue, we invite the submission of manuscripts that focus on the design, synthesis, evaluation, and further development of investigational agents (including natural products) as potential cancer chemotherapeutics.
Prof. Dr. Helen Osborn
Dr. Mohammad Najlah
Collection Editors
Dr. Jean Jacques Vanden Eynde
Dr. Annie Mayence
Dr. Tien L. Huang
Former Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss francs).
Keywords
- anticancer activity
- anticancer agents
- antiproliferative effects
- antitumor activity
- apoptosis
- cancer cells
- chemotherapy
- cytotoxicity
- oncology
- tumor cells